Spark 源码分析之ShuffleMapTask处理
更多资源
- SPARK 源码分析技术分享(bilibilid视频汇总套装视频): https://www.bilibili.com/video/av37442139/
- github: https://github.com/opensourceteams/spark-scala-maven
- csdn(汇总视频在线看): https://blog.csdn.net/thinktothings/article/details/84726769
视频分享:
- Spark 源码分析之ShuffleMapTask处理原理分析图解 (bilibili视频): https://www.bilibili.com/video/av37442139/?p=22
- Spark 源码分析之ShuffleMapTask处理源码分析 (bilibili视频): https://www.bilibili.com/video/av37442139/?p=23
- Spark 源码分析之ShuffleMapTask处理原理分析图解 (youtube视频): https://youtu.be/datHorBipMc
- Spark 源码分析之ShuffleMapTask处理源码分析 (youtube视频): https://youtu.be/cRW_MZ0k5Lw
<iframe width="800" height="500" src="//player.bilibili.com/player.html?aid=37442139&cid=66008946&page=22" scrolling="no" border="0" frameborder="no" framespacing="0" allowfullscreen="true"> </iframe>
<iframe width="800" height="500" src="//player.bilibili.com/player.html?aid=37442139&cid=66008946&page=23" scrolling="no" border="0" frameborder="no" framespacing="0" allowfullscreen="true"> </iframe>
图解
输入数据
a b k l j
c a n m o
排序后的数据
((0,b),1)
((0,j),1)
((0,l),1)
((0,n),1)
---------
((1,a),2)
((1,c),1)
((1,k),1)
((1,m),1)
((1,o),1)
输出数据
(b,1)
(j,1)
(l,1)
(n,1)
---------
(a,2)
(c,1)
(k,1)
(m,1)
(o,1)
粗粒度执行器处理LaunchTask消息
- CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend的receive()方法收到任务调度器发送过来的启动任务的消息,并进行消息处理: LaunchTask()
- 该方法中调用 Executor.launchTask()方法
case LaunchTask(data) =>
if (executor == null) {
exitExecutor(1, "Received LaunchTask command but executor was null")
} else {
val taskDesc = ser.deserialize[TaskDescription](data.value)
logInfo("Got assigned task " + taskDesc.taskId)
executor.launchTask(this, taskId = taskDesc.taskId, attemptNumber = taskDesc.attemptNumber,
taskDesc.name, taskDesc.serializedTask)
}
- Executor.launchTask()方法
- 用线程池来启动Task,这样保证任务可以排队等候
- 当线程池中的任务被执行时调用 TaskRunner.run()方法
// Maintains the list of running tasks.
private val runningTasks = new ConcurrentHashMap[Long, TaskRunner
// Start worker thread pool
private val threadPool = ThreadUtils.newDaemonCachedThreadPool("Executor task launch worker")
def launchTask(
context: ExecutorBackend,
taskId: Long,
attemptNumber: Int,
taskName: String,
serializedTask: ByteBuffer): Unit = {
val tr = new TaskRunner(context, taskId = taskId, attemptNumber = attemptNumber, taskName,
serializedTask)
runningTasks.put(taskId, tr)
threadPool.execute(tr)
}
- TaskRunner.run() 方法
- 调用Task的实现类,进行任务处理
- 实现类(ShuffleMapTask或ResutlTask)处理任务完成后,发送任务状态为TaskState.FINISHED 的消息
override def run(): Unit = {
val taskMemoryManager = new TaskMemoryManager(env.memoryManager, taskId)
val deserializeStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis()
Thread.currentThread.setContextClassLoader(replClassLoader)
val ser = env.closureSerializer.newInstance()
logInfo(s"Running $taskName (TID $taskId)")
execBackend.statusUpdate(taskId, TaskState.RUNNING, EMPTY_BYTE_BUFFER)
var taskStart: Long = 0
startGCTime = computeTotalGcTime()
try {
val (taskFiles, taskJars, taskBytes) = Task.deserializeWithDependencies(serializedTask)
updateDependencies(taskFiles, taskJars)
task = ser.deserialize[Task[Any]](taskBytes, Thread.currentThread.getContextClassLoader)
task.setTaskMemoryManager(taskMemoryManager)
// If this task has been killed before we deserialized it, let's quit now. Otherwise,
// continue executing the task.
if (killed) {
// Throw an exception rather than returning, because returning within a try{} block
// causes a NonLocalReturnControl exception to be thrown. The NonLocalReturnControl
// exception will be caught by the catch block, leading to an incorrect ExceptionFailure
// for the task.
throw new TaskKilledException
}
logDebug("Task " + taskId + "'s epoch is " + task.epoch)
env.mapOutputTracker.updateEpoch(task.epoch)
// Run the actual task and measure its runtime.
taskStart = System.currentTimeMillis()
var threwException = true
val (value, accumUpdates) = try {
val res = task.run(
taskAttemptId = taskId,
attemptNumber = attemptNumber,
metricsSystem = env.metricsSystem)
threwException = false
res
} finally {
val releasedLocks = env.blockManager.releaseAllLocksForTask(taskId)
val freedMemory = taskMemoryManager.cleanUpAllAllocatedMemory()
if (freedMemory > 0) {
val errMsg = s"Managed memory leak detected; size = $freedMemory bytes, TID = $taskId"
if (conf.getBoolean("spark.unsafe.exceptionOnMemoryLeak", false) && !threwException) {
throw new SparkException(errMsg)
} else {
logError(errMsg)
}
}
if (releasedLocks.nonEmpty) {
val errMsg =
s"${releasedLocks.size} block locks were not released by TID = $taskId:\n" +
releasedLocks.mkString("[", ", ", "]")
if (conf.getBoolean("spark.storage.exceptionOnPinLeak", false) && !threwException) {
throw new SparkException(errMsg)
} else {
logError(errMsg)
}
}
}
val taskFinish = System.currentTimeMillis()
// If the task has been killed, let's fail it.
if (task.killed) {
throw new TaskKilledException
}
val resultSer = env.serializer.newInstance()
val beforeSerialization = System.currentTimeMillis()
val valueBytes = resultSer.serialize(value)
val afterSerialization = System.currentTimeMillis()
for (m <- task.metrics) {
// Deserialization happens in two parts: first, we deserialize a Task object, which
// includes the Partition. Second, Task.run() deserializes the RDD and function to be run.
m.setExecutorDeserializeTime(
(taskStart - deserializeStartTime) + task.executorDeserializeTime)
// We need to subtract Task.run()'s deserialization time to avoid double-counting
m.setExecutorRunTime((taskFinish - taskStart) - task.executorDeserializeTime)
m.setJvmGCTime(computeTotalGcTime() - startGCTime)
m.setResultSerializationTime(afterSerialization - beforeSerialization)
m.updateAccumulators()
}
val directResult = new DirectTaskResult(valueBytes, accumUpdates, task.metrics.orNull)
val serializedDirectResult = ser.serialize(directResult)
val resultSize = serializedDirectResult.limit
// directSend = sending directly back to the driver
val serializedResult: ByteBuffer = {
if (maxResultSize > 0 && resultSize > maxResultSize) {
logWarning(s"Finished $taskName (TID $taskId). Result is larger than maxResultSize " +
s"(${Utils.bytesToString(resultSize)} > ${Utils.bytesToString(maxResultSize)}), " +
s"dropping it.")
ser.serialize(new IndirectTaskResult[Any](TaskResultBlockId(taskId), resultSize))
} else if (resultSize >= akkaFrameSize - AkkaUtils.reservedSizeBytes) {
val blockId = TaskResultBlockId(taskId)
env.blockManager.putBytes(
blockId, serializedDirectResult, StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK_SER)
logInfo(
s"Finished $taskName (TID $taskId). $resultSize bytes result sent via BlockManager)")
ser.serialize(new IndirectTaskResult[Any](blockId, resultSize))
} else {
logInfo(s"Finished $taskName (TID $taskId). $resultSize bytes result sent to driver")
serializedDirectResult
}
}
execBackend.statusUpdate(taskId, TaskState.FINISHED, serializedResult)
} catch {
case ffe: FetchFailedException =>
val reason = ffe.toTaskFailedReason
execBackend.statusUpdate(taskId, TaskState.FAILED, ser.serialize(reason))
case _: TaskKilledException | _: InterruptedException if task.killed =>
logInfo(s"Executor killed $taskName (TID $taskId)")
execBackend.statusUpdate(taskId, TaskState.KILLED, ser.serialize(TaskKilled))
case CausedBy(cDE: CommitDeniedException) =>
val reason = cDE.toTaskFailedReason
execBackend.statusUpdate(taskId, TaskState.FAILED, ser.serialize(reason))
case t: Throwable =>
// Attempt to exit cleanly by informing the driver of our failure.
// If anything goes wrong (or this was a fatal exception), we will delegate to
// the default uncaught exception handler, which will terminate the Executor.
logError(s"Exception in $taskName (TID $taskId)", t)
// SPARK-20904: Do not report failure to driver if if happened during shut down. Because
// libraries may set up shutdown hooks that race with running tasks during shutdown,
// spurious failures may occur and can result in improper accounting in the driver (e.g.
// the task failure would not be ignored if the shutdown happened because of premption,
// instead of an app issue).
if (!ShutdownHookManager.inShutdown()) {
val metrics: Option[TaskMetrics] = Option(task).flatMap { task =>
task.metrics.map { m =>
m.setExecutorRunTime(System.currentTimeMillis() - taskStart)
m.setJvmGCTime(computeTotalGcTime() - startGCTime)
m.updateAccumulators()
m
}
}
val serializedTaskEndReason = {
try {
ser.serialize(new ExceptionFailure(t, metrics))
} catch {
case _: NotSerializableException =>
// t is not serializable so just send the stacktrace
ser.serialize(new ExceptionFailure(t, metrics, false))
}
}
execBackend.statusUpdate(taskId, TaskState.FAILED, serializedTaskEndReason)
} else {
logInfo("Not reporting error to driver during JVM shutdown.")
}
// Don't forcibly exit unless the exception was inherently fatal, to avoid
// stopping other tasks unnecessarily.
if (Utils.isFatalError(t)) {
SparkUncaughtExceptionHandler.uncaughtException(t)
}
} finally {
runningTasks.remove(taskId)
}
}
}
- 先调用抽象类Task.run()方法,访方法中调用实现类的 runTask()方法
- 调用Task的实现类runTask()方法进行任务处理
val (value, accumUpdates) = try {
val res = task.run(
taskAttemptId = taskId,
attemptNumber = attemptNumber,
metricsSystem = env.metricsSystem)
threwException = false
res
}
ShuflleMapTask的处理进程
- ShuffleMapTask.runTask()方法
- 首先拿到参数
- 参数(rdd,dep) DAGScheduler对stage(ShhuffleMapStage)中引用的rdd和shuffleDep 进行了变量广播,所以这时可以直接取到,进行反序列化就可以用
- SuffileManager没有配参数,所以取SparkEnv中配置的默认org.apache.spark.shuffle.sort.SortShuffleManager
override def runTask(context: TaskContext): MapStatus = {
// Deserialize the RDD using the broadcast variable.
val deserializeStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis()
val ser = SparkEnv.get.closureSerializer.newInstance()
val (rdd, dep) = ser.deserialize[(RDD[_], ShuffleDependency[_, _, _])](
ByteBuffer.wrap(taskBinary.value), Thread.currentThread.getContextClassLoader)
_executorDeserializeTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - deserializeStartTime
metrics = Some(context.taskMetrics)
var writer: ShuffleWriter[Any, Any] = null
try {
val manager = SparkEnv.get.shuffleManager
writer = manager.getWriter[Any, Any](dep.shuffleHandle, partitionId, context)
writer.write(rdd.iterator(partition, context).asInstanceOf[Iterator[_ <: Product2[Any, Any]]])
writer.stop(success = true).get
} catch {
case e: Exception =>
try {
if (writer != null) {
writer.stop(success = false)
}
} catch {
case e: Exception =>
log.debug("Could not stop writer", e)
}
throw e
}
}
- DAGScheduller.scal 对stage中的数据进行序列化,保存到参数taskBinary中
// TODO: Maybe we can keep the taskBinary in Stage to avoid serializing it multiple times.
// Broadcasted binary for the task, used to dispatch tasks to executors. Note that we broadcast
// the serialized copy of the RDD and for each task we will deserialize it, which means each
// task gets a different copy of the RDD. This provides stronger isolation between tasks that
// might modify state of objects referenced in their closures. This is necessary in Hadoop
// where the JobConf/Configuration object is not thread-safe.
var taskBinary: Broadcast[Array[Byte]] = null
try {
// For ShuffleMapTask, serialize and broadcast (rdd, shuffleDep).
// For ResultTask, serialize and broadcast (rdd, func).
val taskBinaryBytes: Array[Byte] = stage match {
case stage: ShuffleMapStage =>
closureSerializer.serialize((stage.rdd, stage.shuffleDep): AnyRef).array()
case stage: ResultStage =>
closureSerializer.serialize((stage.rdd, stage.func): AnyRef).array()
}
taskBinary = sc.broadcast(taskBinaryBytes)
- taskBinary 序列化stage信息作为参数传输,由于是Broadcast 类型,所以在所有worker上会进行广播,这样就可以在执行task时,直接取
val tasks: Seq[Task[_]] = try {
stage match {
case stage: ShuffleMapStage =>
stage.pendingPartitions.clear()
partitionsToCompute.map { id =>
val locs = taskIdToLocations(id)
val part = stage.rdd.partitions(id)
stage.pendingPartitions += id
new ShuffleMapTask(stage.id, stage.latestInfo.attemptId,
taskBinary, part, locs, stage.internalAccumulators)
}
case stage: ResultStage =>
val job = stage.activeJob.get
partitionsToCompute.map { id =>
val p: Int = stage.partitions(id)
val part = stage.rdd.partitions(p)
val locs = taskIdToLocations(id)
new ResultTask(stage.id, stage.latestInfo.attemptId,
taskBinary, part, locs, id, stage.internalAccumulators)
}
}
- SuffileManager没有配参数,所以取SparkEnv中配置的默认org.apache.spark.shuffle.sort.SortShuffleManager
// Let the user specify short names for shuffle managers
val shortShuffleMgrNames = Map(
"hash" -> "org.apache.spark.shuffle.hash.HashShuffleManager",
"sort" -> "org.apache.spark.shuffle.sort.SortShuffleManager",
"tungsten-sort" -> "org.apache.spark.shuffle.sort.SortShuffleManager")
val shuffleMgrName = conf.get("spark.shuffle.manager", "sort")
val shuffleMgrClass = shortShuffleMgrNames.getOrElse(shuffleMgrName.toLowerCase, shuffleMgrName)
val shuffleManager = instantiateClass[ShuffleManager](shuffleMgrClass)
- RDD中的某个partition的迭代器作为参数,进行写入操作(最终的输出文件是ShuffleMapTask的输出)
writer.write(rdd.iterator(partition, context).asInstanceOf[Iterator[_ <: Product2[Any, Any]]])
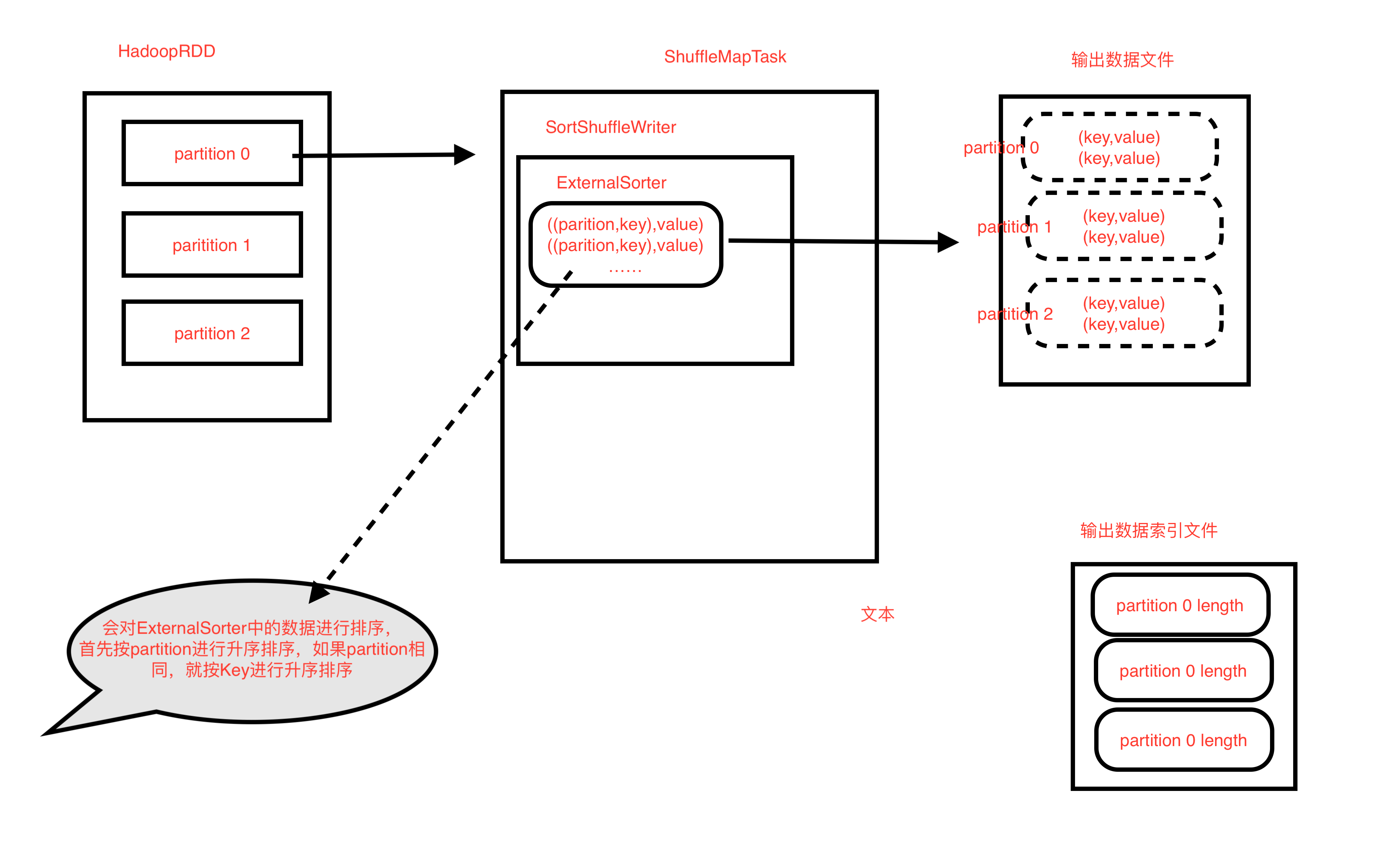
- SortShuffleManager.write()方法
- 首先判断依赖是否在map进行合并(mapSideCombine),reduceByKey算子写死为true
- 会实例化对象来存放数据(所以此时输出的数据是有序的)org.apache.spark.util.collection
- 实例ExternalSorter来进行排序
- 并把当前分区Iterator中的数据插入 ExternalSorter
- 写入输出文件val partitionLengths = sorter.writePartitionedFile(blockId, tmp)
/** Write a bunch of records to this task's output */
override def write(records: Iterator[Product2[K, V]]): Unit = {
sorter = if (dep.mapSideCombine) {
require(dep.aggregator.isDefined, "Map-side combine without Aggregator specified!")
new ExternalSorter[K, V, C](
context, dep.aggregator, Some(dep.partitioner), dep.keyOrdering, dep.serializer)
} else {
// In this case we pass neither an aggregator nor an ordering to the sorter, because we don't
// care whether the keys get sorted in each partition; that will be done on the reduce side
// if the operation being run is sortByKey.
new ExternalSorter[K, V, V](
context, aggregator = None, Some(dep.partitioner), ordering = None, dep.serializer)
}
sorter.insertAll(records)
// Don't bother including the time to open the merged output file in the shuffle write time,
// because it just opens a single file, so is typically too fast to measure accurately
// (see SPARK-3570).
val output = shuffleBlockResolver.getDataFile(dep.shuffleId, mapId)
val tmp = Utils.tempFileWith(output)
try {
val blockId = ShuffleBlockId(dep.shuffleId, mapId, IndexShuffleBlockResolver.NOOP_REDUCE_ID)
val partitionLengths = sorter.writePartitionedFile(blockId, tmp)
shuffleBlockResolver.writeIndexFileAndCommit(dep.shuffleId, mapId, partitionLengths, tmp)
mapStatus = MapStatus(blockManager.shuffleServerId, partitionLengths)
} finally {
if (tmp.exists() && !tmp.delete()) {
logError(s"Error while deleting temp file ${tmp.getAbsolutePath}")
}
}
}
- ExternalSorter.insertAll
- 将分区中的数据插入PartitionedAppendOnlyMap对象map中
- reduceByKey()算子中 shouldCombine = true是写死的
- map中元素的数据格式为 ( (partition,key) ,value ) = ((分区编号,key),value)
- 默认在map端进行合并,所以此时对相同的Key,会执行reduceByKey()自定义的函数,也就是对相同的key的数据进行合并操作
- 如果当前分区的数据量太大,溢出部分数据到文件中
private var map = new PartitionedAppendOnlyMap[K, C]
def insertAll(records: Iterator[Product2[K, V]]): Unit = {
// TODO: stop combining if we find that the reduction factor isn't high
val shouldCombine = aggregator.isDefined
if (shouldCombine) {
// Combine values in-memory first using our AppendOnlyMap
val mergeValue = aggregator.get.mergeValue
val createCombiner = aggregator.get.createCombiner
var kv: Product2[K, V] = null
val update = (hadValue: Boolean, oldValue: C) => {
if (hadValue) mergeValue(oldValue, kv._2) else createCombiner(kv._2)
}
while (records.hasNext) {
addElementsRead()
kv = records.next()
map.changeValue((getPartition(kv._1), kv._1), update)
maybeSpillCollection(usingMap = true)
}
} else {
// Stick values into our buffer
while (records.hasNext) {
addElementsRead()
val kv = records.next()
buffer.insert(getPartition(kv._1), kv._1, kv._2.asInstanceOf[C])
maybeSpillCollection(usingMap = false)
}
}
}
- ExternalSorter.writePartitionedFile()
- 对 ExternalSorter中的数据进行排序,排序的规则为,(partition,key),先按partition进行升序排序,parition相等的再按key进行升序排序
- 每个任务单独建一个输出数据文件和索引文件(数据是先按parition升序排序,再按Key升序排序)
- 索引文件依次保存每个partition索引对应的文件长度
/**
* Write all the data added into this ExternalSorter into a file in the disk store. This is
* called by the SortShuffleWriter.
*
* @param blockId block ID to write to. The index file will be blockId.name + ".index".
* @return array of lengths, in bytes, of each partition of the file (used by map output tracker)
*/
def writePartitionedFile(
blockId: BlockId,
outputFile: File): Array[Long] = {
// Track location of each range in the output file
val lengths = new Array[Long](numPartitions)
if (spills.isEmpty) {
// Case where we only have in-memory data
val collection = if (aggregator.isDefined) map else buffer
val it = collection.destructiveSortedWritablePartitionedIterator(comparator)
while (it.hasNext) {
val writer = blockManager.getDiskWriter(blockId, outputFile, serInstance, fileBufferSize,
context.taskMetrics.shuffleWriteMetrics.get)
val partitionId = it.nextPartition()
while (it.hasNext && it.nextPartition() == partitionId) {
it.writeNext(writer)
}
writer.commitAndClose()
val segment = writer.fileSegment()
lengths(partitionId) = segment.length
}
} else {
// We must perform merge-sort; get an iterator by partition and write everything directly.
for ((id, elements) <- this.partitionedIterator) {
if (elements.hasNext) {
val writer = blockManager.getDiskWriter(blockId, outputFile, serInstance, fileBufferSize,
context.taskMetrics.shuffleWriteMetrics.get)
for (elem <- elements) {
writer.write(elem._1, elem._2)
}
writer.commitAndClose()
val segment = writer.fileSegment()
lengths(id) = segment.length
}
}
}
context.taskMetrics().incMemoryBytesSpilled(memoryBytesSpilled)
context.taskMetrics().incDiskBytesSpilled(diskBytesSpilled)
context.internalMetricsToAccumulators(
InternalAccumulator.PEAK_EXECUTION_MEMORY).add(peakMemoryUsedBytes)
lengths
}
- WritablePartitionedPairCollection.partitionKeyComparator.
- 排序规则
- 对 ExternalSorter中的数据进行排序,排序的规则为,(partition,key),先按partition进行升序排序,parition相等的再按key进行升序排序
/**
* A comparator for (Int, K) pairs that orders them both by their partition ID and a key ordering.
*/
def partitionKeyComparator[K](keyComparator: Comparator[K]): Comparator[(Int, K)] = {
new Comparator[(Int, K)] {
override def compare(a: (Int, K), b: (Int, K)): Int = {
val partitionDiff = a._1 - b._1
if (partitionDiff != 0) {
partitionDiff
} else {
keyComparator.compare(a._2, b._2)
}
}
}
}





















 350
350

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








