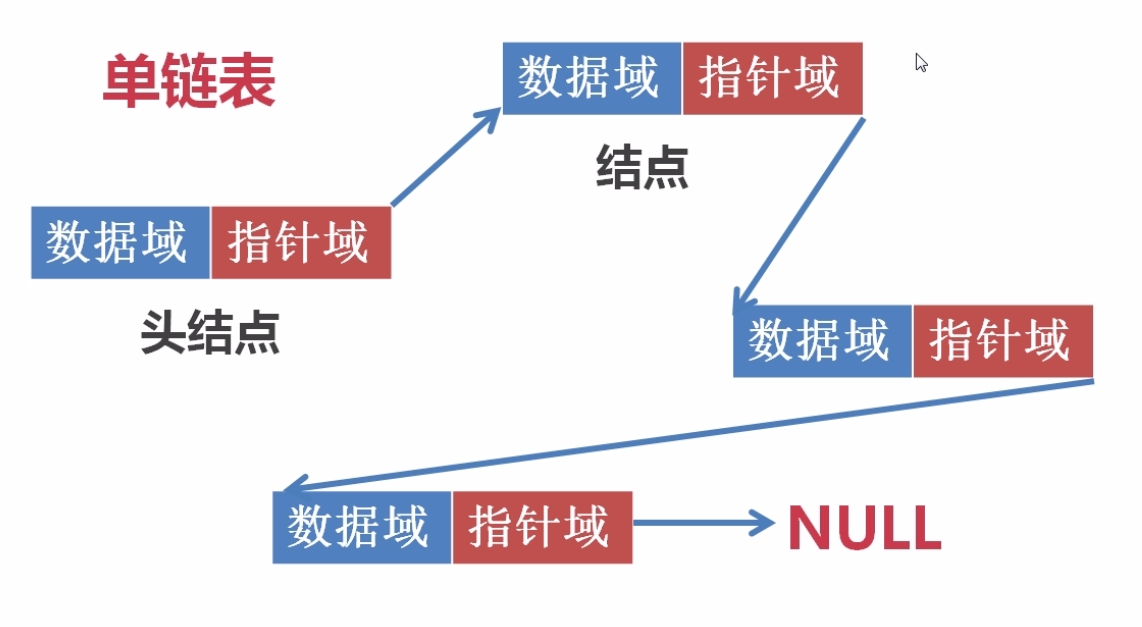
单链表是一种链式存取的数据结构,用一组地址任意的存储单元存储线性表中的数据元素,链表中的数据是以结点来表示的,每个结点的构成如图所示:数据域是存储数据的存储单元,指针域就是连接每个结点的地址数据。
单链表与顺序表相比:
1.顺序表可以方便的随机存取表中的任一结点,速度快;但是在表中插入删除一个数据时,为了保持其他数据的相对次序不变,平均需要移动一半的元素,效率很低;还有就是事先对表长估计无法确定,若是申请的表长过大,就会造成内存浪费,过小则还需要拷贝到一个更大的数组中,时间开销很大;
2,相反,链表则适用于插入删除频繁,表长估计不定的情形;
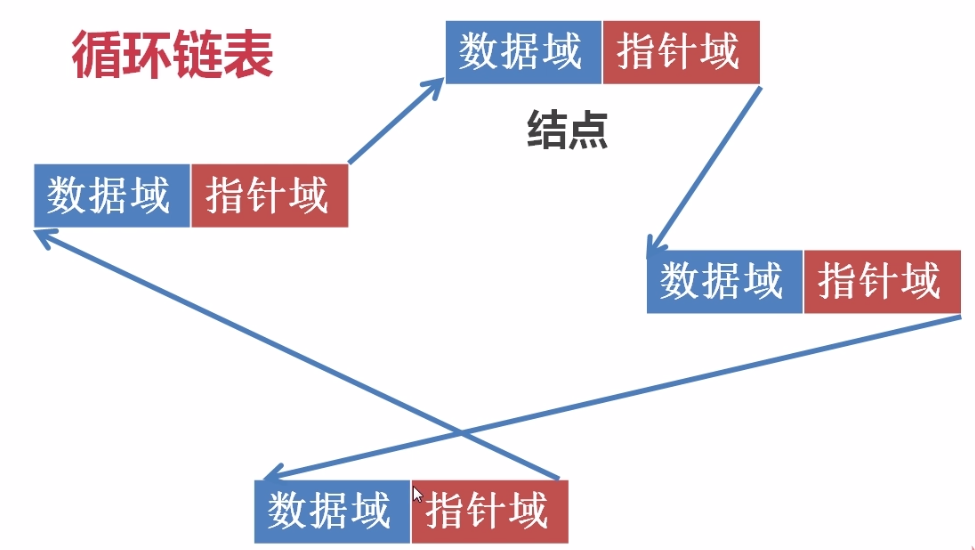
循环链表:是另一种形式的链式存贮结构,非常类似于单链表,它的特点是表中最后一个结点的指针域指向头结点,整个链表形成一个环。循环链表又分为单循环链表和多重循环链表。
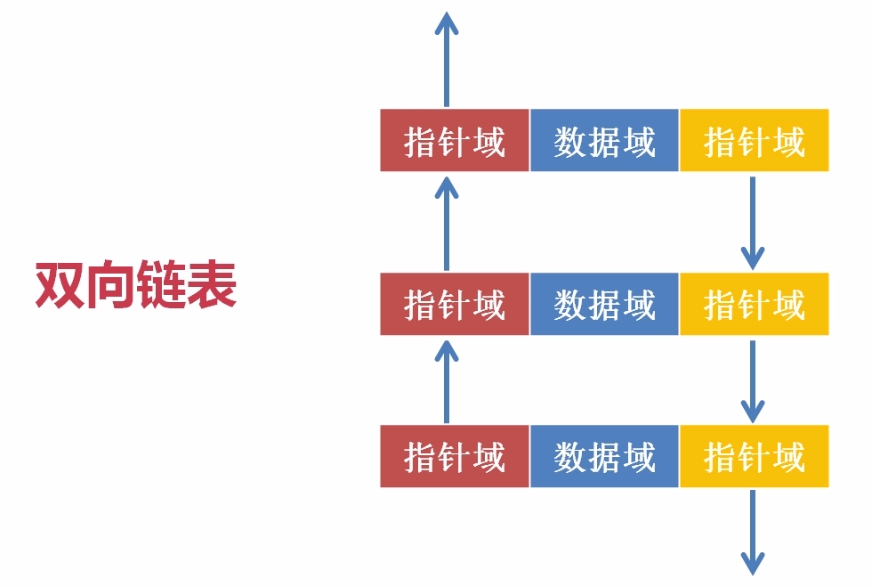
双向链表:也叫双链表,每个数据结点都有两个指针域,一个数据域;第一个指针域指向它的直接前驱,第二个指针域指向它的直接后继。可以看出来,从双链表的任意结点都可以很方便的访问它的前驱和后继结点。双向链表在插入操作时,需要考虑前后的方向的操作。
下面的例子主要是围绕单链表的实现,注释很详细,
一,链表的头文件List.h
#pragma once
#include "Node.h"
#ifndef LIST_H
#define LIST_H
class List
{
public:
List(int size);//构造函数,初始化线性表
~List();//析构函数,销毁线性表
void ClearList();//清空线性表
bool ListEmpty();//判断线性表是否为空
int ListLength();//获取线性表的长度
bool GetElem(int i, int *e);//获取指定元素
int LocateElem(int *e);//寻找第一个满足e的数据元素的位序
bool PriorElem(int *currentElem, int *preElem);//获取指定元素的前驱
bool NextElem(int *currentElem, int *nextElem);//获取指定元素的后继
void ListTraverse();//遍历整个线性表
bool ListInsert(int i, int *e);//在指定位置插入元素
bool ListDelete(int i, int *e);//删除指定位置的元素
/*************************************************************************/
//单链表
/*
public:
List();//构造函数,初始化线性表
~List();//析构函数,销毁线性表
void ClearList();//清空线性表
bool ListEmpty();//判断线性表是否为空
int ListLength();//获取线性表的长度
bool GetElem(int i, Node *pNode);//获取指定元素
int LocateElem(Node *pNode);//寻找第一个满足e的数据元素的位序
bool PriorElem(Node *pCurrentNode, Node *pPreNode);//获取指定元素的前驱
bool NextElem(Node *pCurrentNode, Node *pPreNode);//获取指定元素的后继
void ListTraverse();//遍历整个线性表
bool ListInsert(int i, Node *pNode);//在指定位置插入元素
bool ListDelete(int i, Node *pNode);//删除指定位置的元素
bool ListInsertHead(Node *pNode);//在头结点插入元素
bool ListInsertTail(Node *pNode);//在尾结点插入元素
private:
Node *m_pList;
int m_iLength;
*/
/*************************************************************************/
private:
int *m_pList;
int m_iSize;
int m_iLength;
};
#endif // !LIST_H
链表的cpp文件List.cpp
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "List.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//构造函数,初始化线性表
List::List(int size)
{
m_iSize = size;
m_pList = new int[m_iSize];
m_iLength = 0;
}
/**************************************/
//单链表中的构造函数
//List::List()
//{
// m_pList = new Node;//为结点申请一块内存
// m_pList->data = 0;//初始化单链表中的数据域
// m_pList->next = NULL;//初始化单链表中的指针域
// M_iLength = 0;
//}
/*************************************/
//析构函数,销毁线性表
List::~List()
{
delete []m_pList;
m_pList = NULL;
}
/*************************************/
//单链表中的析构函数
//List::~List()
//{
// ClearList();//调用ClearList(),
// delete m_pList;//删除申请的内存
// m_pList = NULL;//将指针置为NULL
//}
/************************************/
//清空线性表
void List::ClearList()
{
m_iLength = 0;
}
/***********************************/
//清空单链表
//void List::ClearList()
//{
// Node *currentNode = m_pList->next;
// while (currentNode != NULL)
// {
// Node *temp = currentNode->next;//先找到当前结点的下一个结点的指针域
// delete currentNode;//然后删除当前结点
// currentNode = temp;//然后把下一个结点的指针置为当前结点,进行循环
// }
// m_pList->next = NULL;//跳出循环,把当前结点的指针置为NULL
//}
/**********************************/
//判断线性表是否为空,适用于单链表
bool List::ListEmpty()
{
if (m_iLength == 0)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
//获取线性表的长度,适用于单链表
int List::ListLength()
{
return m_iLength;
}
//获取指定元素
bool List::GetElem(int i, int * e)
{
if(i < 0 || i >= m_iSize)
{
return false;
}
*e = m_pList[i];
return true;
}
/*******************************************************************************/
//单链表中获取元素的函数
//bool List::GetElem(int i, Node *pNode)//该函数通过结点编号和结点地址(指针),获取该元素
//{
// if (i < 0 || i >= m_iLength)
// {
// return false;
// }
// Node *currentNode = m_pList;//把链表中的结点指针置为当前指针
// Node *currentNodeBefore = NULL;//并把当前结点指针的前一个结点的指针置为null
// for (int k = 0; k <= i; k++)//当前循环只为找到第i个结点
// {
// currentNodeBefore = currentNode;//把当前结点的指针指向
// currentNode = currentNode->next;
// }
// pNode->data = currentNode->data;
// return true;
//}
/*******************************************************************************/
//寻找第一个满足e的数据元素的位序
int List::LocateElem(int * e)
{
for (int i = 0; i < m_iLength; i++)
{
if (m_pList[i] == *e)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
/*******************************************************************************/
// 单链表中寻找第一个满足pNode结点的位序
//int List::LocateElem(Node *pNode)
//{
// Node *currentNode = m_pList;
// int count = 0;
// while (currentNode->next != NULL)
// {
// currentNode = currentNode->next;
// if (currentNode->data == pNode->data)
// {
// return count;
// }
// count++;
// }
// return -1;
//}
/*******************************************************************************/
//获取指定元素的前驱
bool List::PriorElem(int * currentElem, int * preElem)
{
int temp = LocateElem(currentElem);
if(temp == -1)
{
return false;
}
else
{
if (temp == 0)
{
return false;
}
else
{
*preElem = m_pList[temp - 1];
return true;
}
}
}
/*******************************************************************************/
//bool List::PriorElem(Node *pCurrentNode, Node *pPreNode)
//{
// Node *currentNode = m_pList;
// Node *tempNode = NULL;
// while (currentNode->next != NULL)
// {
// tempNode = currentNode;
// currentNode = currentNode->next;
// if (currentNode->data == pCurrentNode->data)
// {
// if (tempNode == m_pList)
// {
// return false;
// }
// pPreNode->data = tempNode->data;
// return true;
// }
// }
//}
/*******************************************************************************/
//获取指定元素的后继
bool List::NextElem(int * currentElem, int * nextElem)
{
int temp = LocateElem(currentElem);
if (temp == -1)
{
return false;
}
else
{
if (temp == m_iLength - 1)
{
return false;
}
else
{
*nextElem = m_pList[temp + 1];
return true;
}
}
}
/*******************************************************************************/
//bool List::NextElem(Node *pCurrentNode, Node *pNextNode)
//{
// Node *currentNode = m_pList;
//
// while (currentNode->next != NULL)
// {
// currentNode = currentNode->next;
// if (currentNode->data == pCurrentNode->data)
// {
// if (currentNode->next == NULL)
// return false;
// {
// return false;
// }
// pNextNode->data = currentNode->next->data;
// return true;
// }
// }
//}
/*******************************************************************************/
//遍历整个线性表
void List::ListTraverse()
{
for (int i = 0; i < m_iLength; i++)
{
cout << m_pList[i] << endl;
}
}
/*******************************************************************************/
// 遍历单链表
//void List::ListTraverse()
//{
// Node *currentNode = m_pList;
// while (currentNode->next != NULL)
// {
// currentNode = currentNode->next;
// currentNode->printNode();
//
// }
//}
/*******************************************************************************/
//在指定位置插入元素
bool List::ListInsert(int i, int * e)
{
if (i < 0 || i > m_iLength)
{
return false;
}
for (int k = m_iLength; k >= i; k--)
{
m_pList[k + 1] = m_pList[k];
}
m_pList[i] = *e;
m_iLength++;
return true;
}
/*******************************************************************************/
//在链表任意位置插入结点
//bool List::ListInsert(int i, Node *pNode)
//{
// if (i < 0 || i > m_iLength)
// {
// return false;
// }
// Node *currentNode = m_pList;//找到头结点并保存到currentNode
// for (int k = 0; k < i; k++)
// {
// currentNode = currentNode->next;
// }
// Node *newNode = new Node;
// if (newNode == NULL)
// {
// return false;
// }
// newNode->data = pNode->data;
// newNode->next = currentNode->next;
// currentNode->next = newNode;
// return true;
//}
/*******************************************************************************/
//删除指定位置的元素
bool List::ListDelete(int i, int * e)
{
if (i < 0 || i >= m_iLength)
{
return false;
}
*e = m_pList[i];
for (int k = i + 1; k < m_iLength; k++)
{
m_pList[k - 1] = m_pList[k];
}
m_iLength--;
return true;
}
/********************************************************************************/
//删除任意位置的结点
//bool List::ListDelete(int i, Node *pNode)
//{
// if (i < 0 || i >= m_iLength)
// {
// return false;
// }
// Node *currentNode = m_pList;
// Node *currentNodeBefore = NULL;
// for (int k = 0; k <= i; k++)
// {
// currentNodeBefore = currentNode;
// currentNode = currentNode->next;
// }
//
// currentNodeBefore->next = currentNode->next;
// pNode->data = currentNode->data;
// delete currentNode;
// currentNode = NULL;
// m_iLength--;
// return true;
//}
/********************************************************************************/
/********************************************************************************/
//在链表的头部插入结点
//bool List::ListInsertHead(Node *pNode)
//{
// Node *temp = m_pList->next;
// Node *newNode = new Node;//定义一个新的结点,从堆中申请内存
// if (newNode == NULL)
// {
// return false;
// }
// newNode->data = pNode->data;
// m_pList->next = newNode;//将新结点的指针域指向m_pList->next
// newNode->next = temp;
// m_iLength++;
// return true;
//}
/********************************************************************************/
/********************************************************************************/
//在链表的尾部插入结点
//bool List::ListInsertTail(Node *pNode)
//{
// Node *currentNode = m_pList;
// while (currentNode->next != NULL)
// {
// currentNode = currentNode->next;
// }
//
// Node *newNode = new Node;
// if (newNode == NULL)
// {
// return false;
// }
// newNode->data = pNode->data;
// newNode->next = NULL;
// currentNode->next = newNode;
// m_iLength++;
// return true;
//}
/*******************************************************************************/
结点的头文件Node.h和结点的cpp文件Node.cpp,可以自己补充想要实现的方法
下面是测试代码demo.cpp
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "List.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/***************************************************************************************/
/*
线性表--顺序表
3 5 7 2 9 1 8
前驱 后继
C语言类型的写法
BOOL InitList(List **list);//创建线性表
void DestroyList(List *list);//销毁线性表
void ClearList(List *list);//清空线性表
BOOL ListEmpty(List *list);//判断线性表是否为空
int ListLength(List *list);//获取线性表长度
BOOL GetElem(List *list, int i, Elem *e);//获取指定元素
int LocateElem(List *list, Elem *e);//寻找第一个满足e的数据元素的位序
BOOL PriorElem(List *list, Elem *currentElem, Elem *preElem);//获取指定元素的前驱
BOOL NextElem(List *list, Elem *currentElem, Elem *preElem);//获取指定元素的后继
BOOL ListInsert(List *list, int i, Elem *e);//在第i个位置插入元素
BOOL ListDelete(List *list, int i, Elem *e);//删除第i个位置的元素
void ListTraverse(List *list);//遍历线性表
*/
/********************************************************************************************/
int main(void)
{
//3 5 7 2 9 1 8
int e1 = 3;
int e2 = 5;
int e3 = 7;
int e4 = 2;
int e5 = 9;
int e6 = 1;
int e7 = 8;
int temp = 0;
List *list1 = new List(10);
cout << "length:" << list1->ListLength() << endl;
list1->ListInsert(0, &e1);
cout << "length:" << list1->ListLength() << endl;
list1->ListInsert(1, &e2);
cout << "length:" << list1->ListLength() << endl;
list1->ListInsert(2, &e3);
list1->ListInsert(3, &e4);
list1->ListInsert(4, &e5);
list1->ListInsert(5, &e6);
cout << "length:" << list1->ListLength() << endl;
list1->ListInsert(6, &e7);
list1->ListTraverse();
list1->PriorElem(&e4, &temp);
cout << "temp:" << temp << endl;
list1->NextElem(&e4, &temp);
cout << "temp:" << temp << endl;
list1->GetElem(0, &temp);
cout << "temp:" << temp << endl;
list1->LocateElem(&temp);
list1->ListDelete(0, &temp);
if (!list1->ListEmpty())
{
cout << "not empty " << endl;
}
list1->ClearList();
if (list1->ListEmpty())
{
cout << "empty " << endl;
}
list1->ListTraverse();
cout << "#" << temp << endl;
delete list1;
return 0;
/*******************************************************************************/
//单链表实现检测
/*Node node1;
node1.data = 3;
Node node2;
node2.data = 4;
Node node3;
node3.data = 5;
Node node4;
node4.data = 6;
Node node5;
node5.data = 7;
Node temp;
List *pList = new List();
pList->ListInsertHead(&node1);
pList->ListInsertHead(&node2);
pList->ListInsertHead(&node3);
pList->ListInsertHead(&node4);
pList->ListInsertTail(&node1);
pList->ListInsertTail(&node2);
pList->ListInsertTail(&node3);
pList->ListInsertTail(&node4);
pList->ListInsert(0,&node5);
pList->ListDelete(0, &temp);
pList->GetElem(0,&temp);
pList->PriorElem(&node4, &temp);
pList->NextElem(&node4, &temp);
pList->ListTraverse();
cout << "temp = " << temp.data << endl;
delete pList;
pList = NULL;*/
/*******************************************************************************/
}





















 1202
1202

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








