A dataset can be written in two different formats: wide and long.
A wide format contains values that do not repeat in the first column.
A long format contains values that do repeat in the first column.
For example, consider the following two datasets that contain the exact same data expressed in different formats:
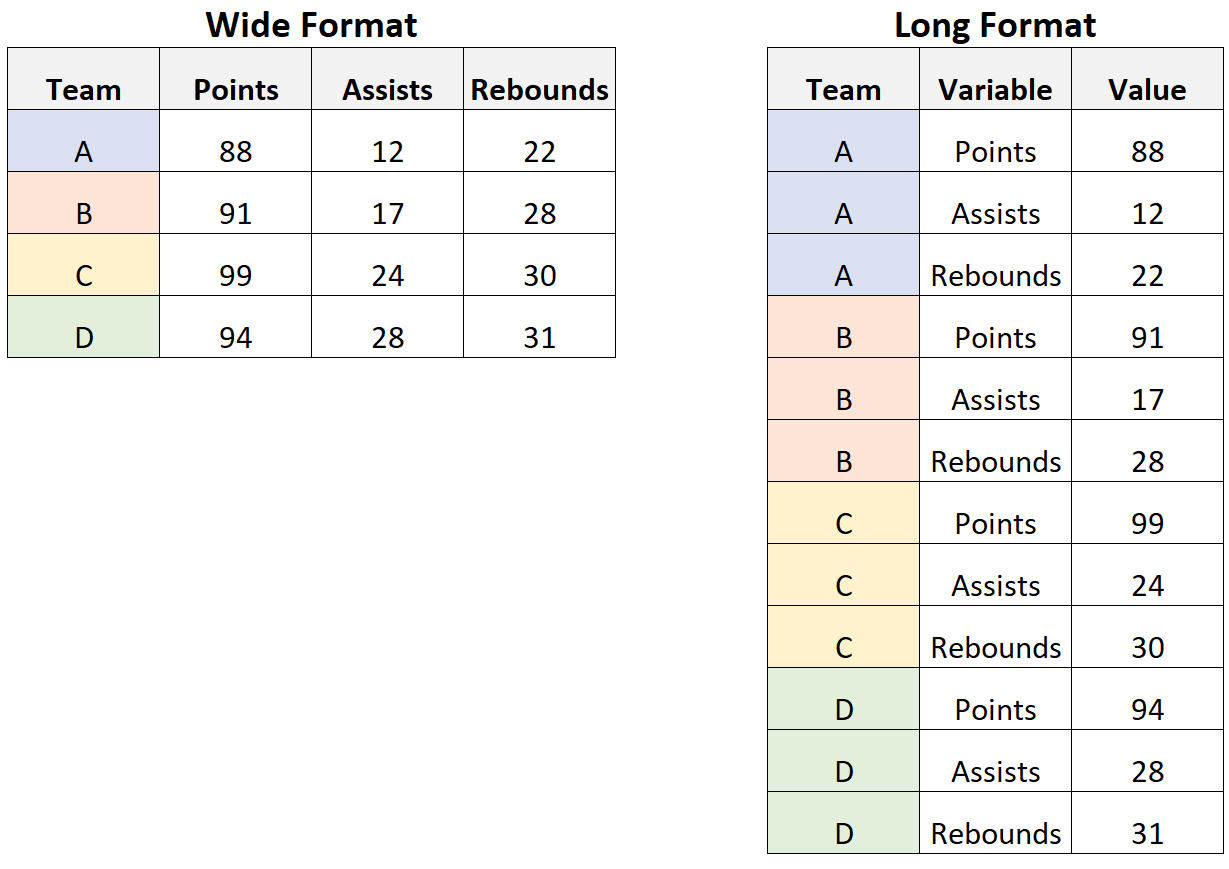
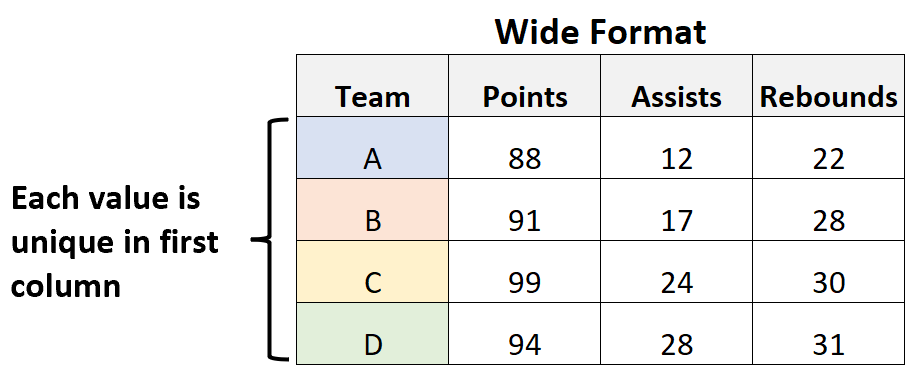
Notice that in the wide dataset, each value in the first column is unique.
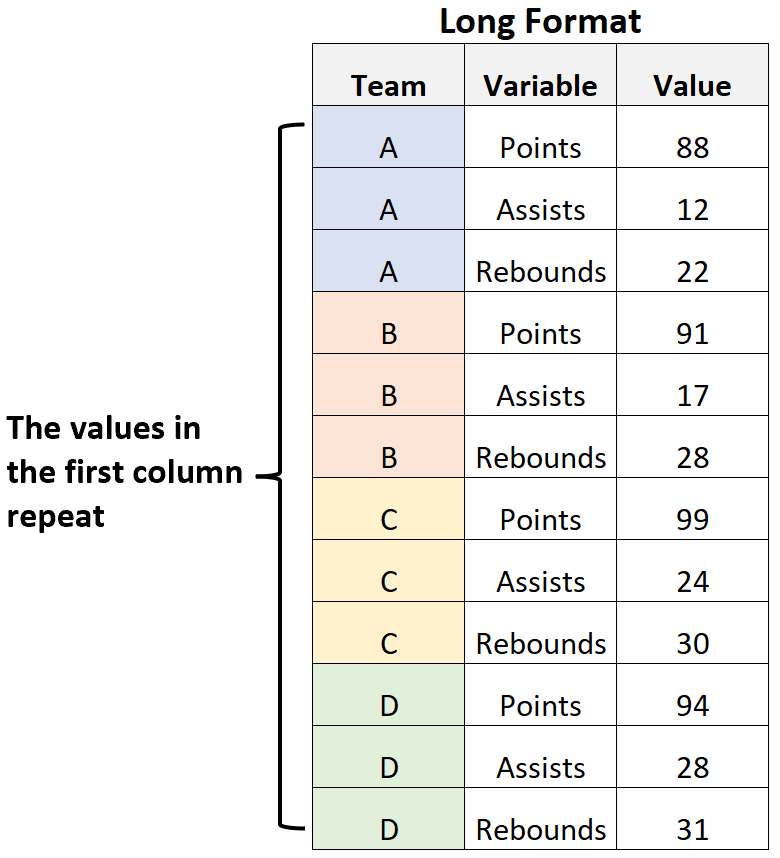
By contrast, in the long dataset the values in the first column repeat.
Both datasets contain the exact same information about the teams, but they’re simply expressed in different formats.
When to Use Wide vs. Long Data
Depending on what you want to do with your data, it may make more sense to have it in a wide or long format.
When to Use Wide Format
As a rule of thumb(根据经验), if you’re analyzing data then you typically will use a wide data format.
For example, if you want to find the average points, assists, and rebounds scored per team then it’s often easier to have the data in a wide format:
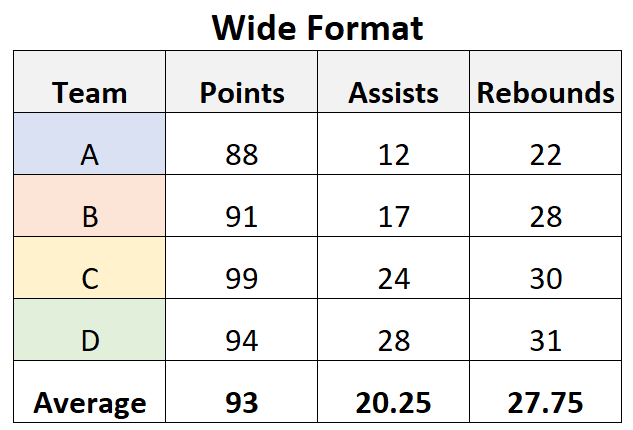
Most datasets that you encounter in the real world will also be recorded in a wide format because it’s easier for our brains to interpret.
For example, in the format above it’s easy to read the points, assists, and rebounds values for each team on the same row.
When to Use Long Format
As a rule of thumb, if you’re visualizing multiple variables in a plot using statistical software such as R you typically must convert your data to a long format in order for the software to create the plot.
Ref: https://www.statology.org/long-vs-wide-data/#:~:text=A%20dataset%20can%20be%20written,repeat%20in%20the%20first%20column.



























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








