Spring Framework可以被使用在很多场合之中,考虑到目前大多数Java EE的项目是B/S结构的,所以这里的快速上手教程会以Spring MVC为切入点,用最简单的代码一步一步来实现一个图书列表的页面。
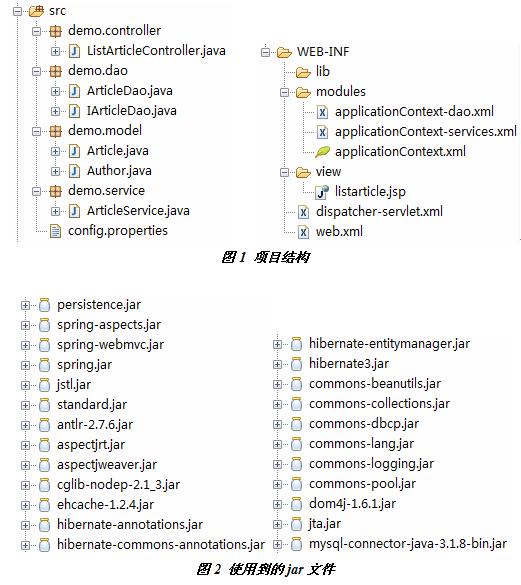
在正式动手之前需要做一些准备工作,先安装并设置好JDK 1.5和Tomcat 5,关于数据库及其访问方式可以根据个人习惯进行选择,教程中使用MySQL数据库和Hibernate(映射由Hibernate Annotation实现)。请将实际使用到的jar文件复制到WEB-INF/lib目录中,整个项目的结构见图1,教程中用到的jar文件见图2。
项目中的Bean定义分散在多个XML文件中,每完成一部分代码就给出相应的配置,最后再进行整合和部署。配置中使用default-autowire="byName"实现了Bean的自动织入,节省了很多个工作量,只需注意Bean及属性的命名即可。
Step 1.Business Objects & DAO
教程中的例子涉及到两个实体对象,代表文章的Article类和代表作者的Author类,分别对应了数据库中的article表和author表,一篇文章有一个作者,而一个作者可以有多篇文章。类的代码如下(省略getter和setter):
代码:Article.java
 package
demo.model;
package
demo.model;
 import
javax.persistence.
*
;
import
javax.persistence.
*
;
 @Entity
@Entity
 public
class
Article
...
{
public
class
Article
...
{ @Id
@Id @GeneratedValue
@GeneratedValue private Long id;
private Long id;
 private String title;
private String title;
 @ManyToOne
@ManyToOne private Author author;
private Author author;
 }
}
代码:Author.java
 package
demo.model;
package
demo.model;
 import
java.util.List;
import
java.util.List; import
javax.persistence.
*
;
import
javax.persistence.
*
;
 @Entity
@Entity
 public
class
Author
...
{
public
class
Author
...
{ @Id
@Id @GeneratedValue
@GeneratedValue private Long id;
private Long id;
 private String name;
private String name;
 @OneToMany
@OneToMany private List<Article> articles;
private List<Article> articles;
 }
}

在MySQL中创建数据表的SQL语句如下,数据请自行添加(如果使用Hibernate,表可以根据映射自动生成,具体做法请参考Hibernate文档):
代码:数据库创建SQL
 CREATE
DATABASE
`articles`
DEFAULT
CHARACTER
SET
utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci;
CREATE
DATABASE
`articles`
DEFAULT
CHARACTER
SET
utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci; USE
articles;
USE
articles;
 CREATE
TABLE
`article` (
CREATE
TABLE
`article` ( `id`
bigint
(
20
)
NOT
NULL
auto_increment,
`id`
bigint
(
20
)
NOT
NULL
auto_increment, `title`
varchar
(
100
)
NOT
NULL
default
''
,
`title`
varchar
(
100
)
NOT
NULL
default
''
, `author_id`
bigint
(
20
)
NOT
NULL
default
'
0
'
,
`author_id`
bigint
(
20
)
NOT
NULL
default
'
0
'
, PRIMARY
KEY
(`id`)
PRIMARY
KEY
(`id`) ) ENGINE
=
MyISAM
DEFAULT
CHARSET
=
utf8;
) ENGINE
=
MyISAM
DEFAULT
CHARSET
=
utf8;
 CREATE
TABLE
`author` (
CREATE
TABLE
`author` ( `id`
bigint
(
20
)
NOT
NULL
auto_increment,
`id`
bigint
(
20
)
NOT
NULL
auto_increment, `name`
varchar
(
100
)
NOT
NULL
default
''
,
`name`
varchar
(
100
)
NOT
NULL
default
''
, PRIMARY
KEY
(`id`)
PRIMARY
KEY
(`id`) ) ENGINE
=
MyISAM
DEFAULT
CHARSET
=
utf8;
) ENGINE
=
MyISAM
DEFAULT
CHARSET
=
utf8;
考虑到可能会有多种DAO的实现,所以在DAO层先定义一个IArticleDao接口,随后可以自由选择具体的实现方式,此处结合Spring的HibernateDaoSupport使用Hibernate来进行实现:
代码:IArticleDao.java
 package
demo.dao;
package
demo.dao;
 import
java.util.List;
import
java.util.List;
 import
demo.model.Article;
import
demo.model.Article;

 public
interface
IArticleDao
...
{
public
interface
IArticleDao
...
{ public List<Article> loadAllArticles();
public List<Article> loadAllArticles(); }
}

代码:ArticleDao.java
 package
demo.dao;
package
demo.dao;
 import
java.util.List;
import
java.util.List; import
org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.support.HibernateDaoSupport;
import
org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.support.HibernateDaoSupport; import
demo.model.Article;
import
demo.model.Article;

 public
class
ArticleDao
extends
HibernateDaoSupport
implements
IArticleDao
...
{
public
class
ArticleDao
extends
HibernateDaoSupport
implements
IArticleDao
...
{
 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
 public List<Article> loadAllArticles() ...{
public List<Article> loadAllArticles() ...{ return (List<Article>)getHibernateTemplate().loadAll(Article.class);
return (List<Article>)getHibernateTemplate().loadAll(Article.class); }
}
 }
}

接下来对Hibernate进行相应的配置,如果使用了JDO或者iBatis,请参考Spring文档。applicationContext-dao.xml内容如下:
代码:applicationContext-dao.xml
 <?
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"
?>
<?
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"
?>
 <
beans
<
beans xmlns
="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns
="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
 xmlns:xsi
="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:xsi
="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
 xsi:schemaLocation
="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd"
xsi:schemaLocation
="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd"
 default-autowire
="byName"
>
default-autowire
="byName"
>
 <!--
DAO配置于此
-->
<!--
DAO配置于此
-->
 <
bean
id
="articleDao"
class
="demo.dao.ArticleDao"
/>
<
bean
id
="articleDao"
class
="demo.dao.ArticleDao"
/>

 <!--
数据源
-->
<!--
数据源
-->
 <!--
JNDI数据源
-->
<!--
JNDI数据源
-->
 <!--
<!--
 <bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jndi.JndiObjectFactoryBean">
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jndi.JndiObjectFactoryBean"> <property name="jndiName" value="${datasource.jndi.name}"/>
<property name="jndiName" value="${datasource.jndi.name}"/> </bean>
</bean> -->
-->

 <!--
JDBC数据源
-->
<!--
JDBC数据源
-->
 <
bean
id
="dataSource"
class
="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource"
destroy-method
="close"
>
<
bean
id
="dataSource"
class
="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource"
destroy-method
="close"
>
 <
property
name
="driverClassName"
value
="${datasource.jdbc.driverClassName}"
/>
<
property
name
="driverClassName"
value
="${datasource.jdbc.driverClassName}"
/>
 <
property
name
="url"
value
="${datasource.jdbc.url}"
/>
<
property
name
="url"
value
="${datasource.jdbc.url}"
/>
 <
property
name
="username"
value
="${datasource.jdbc.username}"
/>
<
property
name
="username"
value
="${datasource.jdbc.username}"
/>
 <
property
name
="password"
value
="${datasource.jdbc.password}"
/>
<
property
name
="password"
value
="${datasource.jdbc.password}"
/>
 </
bean
>
</
bean
>

 <!--
使用Annotation映射的sessionFactory
-->
<!--
使用Annotation映射的sessionFactory
-->
 <
bean
id
="sessionFactory"
class
="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.annotation.AnnotationSessionFactoryBean"
>
<
bean
id
="sessionFactory"
class
="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.annotation.AnnotationSessionFactoryBean"
>
 <
property
name
="dataSource"
ref
="dataSource"
/>
<
property
name
="dataSource"
ref
="dataSource"
/>
 <
property
name
="hibernateProperties"
>
<
property
name
="hibernateProperties"
>
 <
props
>
<
props
>
 <
prop
key
="hibernate.dialect"
>
${hibernate.dialect}
</
prop
>
<
prop
key
="hibernate.dialect"
>
${hibernate.dialect}
</
prop
>
 <
prop
key
="hibernate.show_sql"
>
${hibernate.show_sql}
</
prop
>
<
prop
key
="hibernate.show_sql"
>
${hibernate.show_sql}
</
prop
>
 <
prop
key
="hibernate.cache.use_query_cache"
>
${hibernate.cache.use_query_cache}
</
prop
>
<
prop
key
="hibernate.cache.use_query_cache"
>
${hibernate.cache.use_query_cache}
</
prop
>
 <
prop
key
="hibernate.cache.provider_class"
>
${hibernate.cache.provider_class}
</
prop
>
<
prop
key
="hibernate.cache.provider_class"
>
${hibernate.cache.provider_class}
</
prop
>
 </
props
>
</
props
>
 </
property
>
</
property
>
 <
property
name
="annotatedClasses"
>
<
property
name
="annotatedClasses"
>
 <
list
>
<
list
>
 <
value
>
demo.model.Article
</
value
>
<
value
>
demo.model.Article
</
value
>
 <
value
>
demo.model.Author
</
value
>
<
value
>
demo.model.Author
</
value
>
 </
list
>
</
list
>
 </
property
>
</
property
>
 </
bean
>
</
bean
>

 <!--
事务管理器,此处为Hibernate的事务管理器
-->
<!--
事务管理器,此处为Hibernate的事务管理器
-->
 <
bean
id
="transactionManager"
class
="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager"
/>
<
bean
id
="transactionManager"
class
="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager"
/>
 </
beans
>
</
beans
>

此处如果使用JNDI提供数据源,请根据注释进行调整。Spring的事务管理需要声明事务管理器,由于Hibernate、JDO、JDBC的事务管理器都不一样,所以将其与其他事务的配置分开存放。此外,配置中的一些参数使用了占位符(形如${}),这些内容将在Step 4中进行加载。
Step 2.Service
Service层只是调用DAO中的方法为控制器提供图书列表,Service最好能先给出接口,随后进行实现,但此处的功能比较简单,就直接进行实现了:
代码:ArticleService.java
 package
demo.service;
package
demo.service;
 import
java.util.List;
import
java.util.List; import
demo.dao.IArticleDao;
import
demo.dao.IArticleDao; import
demo.model.Article;
import
demo.model.Article;

 public
class
ArticleService
...
{
public
class
ArticleService
...
{ private IArticleDao articleDao;
private IArticleDao articleDao;

 public List<Article> loadAllArticles() ...{
public List<Article> loadAllArticles() ...{ return articleDao.loadAllArticles();
return articleDao.loadAllArticles(); }
}

 public void setArticleDao(IArticleDao articleDao) ...{
public void setArticleDao(IArticleDao articleDao) ...{ this.articleDao = articleDao;
this.articleDao = articleDao; }
} }
}

Spring通过setArticleDao方法为ArticleService注入DAO,也可以选择通过构造方法注入,2.5中还能用@Autowired进行注入。
applicationContext-services.xml内容如下:
代码:applicationContext-services.xml
 <?
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"
?>
<?
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"
?>
 <
beans
<
beans xmlns
="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns
="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
 xmlns:xsi
="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:xsi
="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
 xsi:schemaLocation
="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd"
xsi:schemaLocation
="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd"
 default-autowire
="byName"
>
default-autowire
="byName"
>
 <!--
Service配置于此
-->
<!--
Service配置于此
-->
 <
bean
id
="articleService"
class
="demo.service.ArticleService"
/>
<
bean
id
="articleService"
class
="demo.service.ArticleService"
/>
 </
beans
>
</
beans
>

Step 3.Controller & View
Spring MVC提供了多种实现控制器的方式,此处直接实现Controller接口,开发一个单一动作的简单控制器,从Service中取得图书列表,提供给视图进行呈现,ListArticleController内容如下:
代码:ListArticleController.java
 package
demo.controller;
package
demo.controller;
 import
java.util.List;
import
java.util.List;
 import
javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import
javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import
javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import
javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
 import
org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import
org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView; import
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.Controller;
import
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.Controller;
 import
demo.model.Article;
import
demo.model.Article; import
demo.service.ArticleService;
import
demo.service.ArticleService;

 public
class
ListArticleController
implements
Controller
...
{
public
class
ListArticleController
implements
Controller
...
{ private ArticleService articleService;
private ArticleService articleService;

 public ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception ...{
public ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception ...{ List<Article> articles = articleService.loadAllArticles();
List<Article> articles = articleService.loadAllArticles(); ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView();
ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView(); mav.addObject(articles);
mav.addObject(articles); return mav;
return mav; }
}

 public void setArticleService(ArticleService articleService) ...{
public void setArticleService(ArticleService articleService) ...{ this.articleService = articleService;
this.articleService = articleService; }
} }
}

ModelAndView中保存了要传递给视图的对象和具体要使用的视图文件,自2.0起, Spring MVC提供了Convention over Configuration的机制,大大简化了代码与配置。简单地说,名字以Controller结尾的控制器类都会被映射为相应的地址,ListArticleController对应/listarticle*,如果是MultiActionController则会被映射为一个目录;向ModelAndView添加对象时可以不用指定键(key),单一对象的键取决于类名,比如x.y.User的键是user,而某一类对象的Set、List或数组则稍有些复杂,取第一个对象的类名加上“List”作为它的键,比如这里的articles是一个存放Article对象的List,它的键就是articleList;具体的视图会根据请求自动在指定目录中寻找对应的视图文件,本例中就会寻找listarticle(后缀由配置文件决定)。关于Convention over Configuration还有些别的细节,请参考Spring文档的相关章节。
此处的视图比较简陋,只是一张表格,显示了图书的编号、书名和作者,使用JSTL的<c:forEach>标签来遍历列表,具体代码如下:
代码:listarticle.jsp

 <%
...
@ page pageEncoding="UTF-8"
%>
<%
...
@ page pageEncoding="UTF-8"
%>

 <%
...
@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core"
%>
<%
...
@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core"
%>

 <
html
>
<
html
>
 <
head
>
<
head
>
 <
title
>
Article List
</
title
>
<
title
>
Article List
</
title
>
 </
head
>
</
head
>
 <
body
>
<
body
>
 <
table
width
="80%"
cellspacing
="0"
cellpadding
="0"
border
="1"
>
<
table
width
="80%"
cellspacing
="0"
cellpadding
="0"
border
="1"
>
 <
thead
>
<
thead
>
 <
tr
align
="center"
>
<
tr
align
="center"
>
 <
td
width
="20%"
>
编号
</
td
><
td
width
="50%"
>
书名
</
td
><
td
width
="30%"
>
作者
</
td
>
<
td
width
="20%"
>
编号
</
td
><
td
width
="50%"
>
书名
</
td
><
td
width
="30%"
>
作者
</
td
>
 </
tr
>
</
tr
>
 </
thead
>
</
thead
>
 <
tbody
>
<
tbody
>
 <
c:forEach
items
="${articleList}"
var
="article"
>
<
c:forEach
items
="${articleList}"
var
="article"
>
 <
tr
>
<
tr
>
 <
td
align
="center"
>
${article.id}
</
td
>
<
td
align
="center"
>
${article.id}
</
td
>
 <
td
>
${article.title}
</
td
>
<
td
>
${article.title}
</
td
>
 <
td
>
${article.author.name}
</
td
>
<
td
>
${article.author.name}
</
td
>
 </
tr
>
</
tr
>
 </
c:forEach
>
</
c:forEach
>
 </
tbody
>
</
tbody
>
 </
table
>
</
table
>
 </
body
>
</
body
>
 </
html
>
</
html
>

为了使用Spring MVC,需要在web.xml中配置一个分派器,将一些特定格式的请求交给Spring MVC来处理(其实就是一个Servlet,这和Struts有些类似),如果它的名字是dispatcher,那么Spring默认会去寻找名为dispatcher-servlet.xml的配置文件,该文件内容如下:
代码:dispatcher-servlet.xml
 <?
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"
?>
<?
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"
?>
 <
beans
<
beans xmlns
="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns
="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
 xmlns:xsi
="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:xsi
="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
 xsi:schemaLocation
="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd"
xsi:schemaLocation
="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd"
 default-autowire
="byName"
>
default-autowire
="byName"
>
 <!--
SpringMVC相关Bean配置
-->
<!--
SpringMVC相关Bean配置
-->

 <!--
View Resolver
-->
<!--
View Resolver
-->
 <
bean
id
="viewResolver"
class
="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"
>
<
bean
id
="viewResolver"
class
="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"
>
 <
property
name
="viewClass"
value
="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.JstlView"
/>
<
property
name
="viewClass"
value
="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.JstlView"
/>
 <
property
name
="prefix"
value
="/WEB-INF/view/"
/>
<
property
name
="prefix"
value
="/WEB-INF/view/"
/>
 <
property
name
="suffix"
value
=".jsp"
/>
<
property
name
="suffix"
value
=".jsp"
/>
 </
bean
>
</
bean
>

 <
bean
id
="viewNameTranslator"
class
="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.DefaultRequestToViewNameTranslator"
/>
<
bean
id
="viewNameTranslator"
class
="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.DefaultRequestToViewNameTranslator"
/>
 <
bean
class
="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.ControllerClassNameHandlerMapping"
/>
<
bean
class
="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.ControllerClassNameHandlerMapping"
/>

 <!--
以下为Controller
-->
<!--
以下为Controller
-->
 <
bean
id
="listArticleController"
class
="demo.controller.ListArticleController"
/>
<
bean
id
="listArticleController"
class
="demo.controller.ListArticleController"
/>

 </
beans
>
</
beans
>

配置中的DefaultRequestToViewNameTranslator和ControllerClassNameHandlerMapping就是用来实现Convention over Configuration的,而名为viewResolver的Bean则指定了一些视图的信息。
Step 4.Configuration & Deployment
至此,大部分的工作已经完成了,接下来就是加载properties文件和配置事务属性,这些都放在applicationContext.xml中:
代码:applicationContext.xml
 <?
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"
?>
<?
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"
?>
 <
beans
<
beans xmlns
="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns
="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
 xmlns:xsi
="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:xsi
="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
 xmlns:aop
="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:aop
="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
 xmlns:tx
="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:tx
="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
 xsi:schemaLocation
="
xsi:schemaLocation
=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.0.xsd"
>
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.0.xsd"
>

 <
bean
id
="propertyConfigurer"
class
="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer"
>
<
bean
id
="propertyConfigurer"
class
="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer"
>
 <
property
name
="locations"
>
<
property
name
="locations"
>
 <
list
>
<
list
>
 <
value
>
classpath:config.properties
</
value
>
<
value
>
classpath:config.properties
</
value
>
 </
list
>
</
list
>
 </
property
>
</
property
>
 </
bean
>
</
bean
>

 <!--
事务
-->
<!--
事务
-->
 <
tx:advice
id
="txAdvice"
>
<
tx:advice
id
="txAdvice"
>
 <
tx:attributes
>
<
tx:attributes
>
 <
tx:method
name
="get*"
read-only
="true"
/>
<
tx:method
name
="get*"
read-only
="true"
/>
 <
tx:method
name
="find*"
read-only
="true"
/>
<
tx:method
name
="find*"
read-only
="true"
/>
 <
tx:method
name
="load*"
read-only
="true"
/>
<
tx:method
name
="load*"
read-only
="true"
/>
 <
tx:method
name
="*"
/>
<
tx:method
name
="*"
/>
 </
tx:attributes
>
</
tx:attributes
>
 </
tx:advice
>
</
tx:advice
>

 <
aop:config
proxy-target-class
="true"
>
<
aop:config
proxy-target-class
="true"
>
 <
aop:advisor
advice-ref
="txAdvice"
pointcut
="execution(* demo.service..*.*(..))"
/>
<
aop:advisor
advice-ref
="txAdvice"
pointcut
="execution(* demo.service..*.*(..))"
/>
 </
aop:config
>
</
aop:config
>
 </
beans
>
</
beans
>

pointcut属性确定了AOP拦截的方法,用的是AspectJ pointcut expression,此处对demo.service中每一个类的所有方法都进行了拦截,也就是它们都在事务中执行。
config.properties中保存了一些与数据库和Hibernate相关的配置信息,它们会代替XML中对应的占位符:
代码:config.properties
 # DataSource
# DataSource # JNDI datasource Eg. java:comp/env/jdbc/myds
# JNDI datasource Eg. java:comp/env/jdbc/myds datasource.jndi.name
=
datasource.jndi.name
=
 # JDBC datasource
# JDBC datasource datasource.jdbc.driverClassName
=
com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
datasource.jdbc.driverClassName
=
com.mysql.jdbc.Driver datasource.jdbc.url
=
jdbc:mysql://localhost/articles?useUnicode
=
true&characterEncoding
=
utf8
datasource.jdbc.url
=
jdbc:mysql://localhost/articles?useUnicode
=
true&characterEncoding
=
utf8 datasource.jdbc.username
=
root
datasource.jdbc.username
=
root datasource.jdbc.password
=
datasource.jdbc.password
=

 # Hibernate
# Hibernate hibernate.dialect
=
org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect
hibernate.dialect
=
org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect hibernate.show_sql
=
false
hibernate.show_sql
=
false hibernate.cache.use_query_cache
=
true
hibernate.cache.use_query_cache
=
true hibernate.cache.provider_class
=
org.hibernate.cache.EhCacheProvider
hibernate.cache.provider_class
=
org.hibernate.cache.EhCacheProvider
最后要看到的就是web.xml,每个Java EE的Web项目都会有这个配置文件,具体内容如下:
代码:web.xml
 <?
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"
?>
<?
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"
?>
 <
web-app
version
="2.4"
<
web-app
version
="2.4"
 xmlns
="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee"
xmlns
="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee"
 xmlns:xsi
="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:xsi
="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
 xsi:schemaLocation
="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee
xsi:schemaLocation
="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee  http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-app_2_4.xsd"
>
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-app_2_4.xsd"
>

 <!--
Spring ApplicationContext配置文件的路径可使用通配符,多个路径用,号分隔,此参数用于后面的Spring-Context loader
-->
<!--
Spring ApplicationContext配置文件的路径可使用通配符,多个路径用,号分隔,此参数用于后面的Spring-Context loader
-->
 <
context-param
>
<
context-param
>
 <
param-name
>
contextConfigLocation
</
param-name
>
<
param-name
>
contextConfigLocation
</
param-name
>
 <
param-value
>
/WEB-INF/modules/applicationContext*.xml
</
param-value
>
<
param-value
>
/WEB-INF/modules/applicationContext*.xml
</
param-value
>
 </
context-param
>
</
context-param
>

 <!--
SpringMVC 分派器及相关映射
-->
<!--
SpringMVC 分派器及相关映射
-->
 <
servlet
>
<
servlet
>
 <
servlet-name
>
dispatcher
</
servlet-name
>
<
servlet-name
>
dispatcher
</
servlet-name
>
 <
servlet-class
>
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
</
servlet-class
>
<
servlet-class
>
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
</
servlet-class
>
 <
load-on-startup
>
1
</
load-on-startup
>
<
load-on-startup
>
1
</
load-on-startup
>
 </
servlet
>
</
servlet
>

 <
servlet-mapping
>
<
servlet-mapping
>
 <
servlet-name
>
dispatcher
</
servlet-name
>
<
servlet-name
>
dispatcher
</
servlet-name
>
 <
url-pattern
>
*.html
</
url-pattern
>
<
url-pattern
>
*.html
</
url-pattern
>
 </
servlet-mapping
>
</
servlet-mapping
>

 <
servlet-mapping
>
<
servlet-mapping
>
 <
servlet-name
>
dispatcher
</
servlet-name
>
<
servlet-name
>
dispatcher
</
servlet-name
>
 <
url-pattern
>
*.do
</
url-pattern
>
<
url-pattern
>
*.do
</
url-pattern
>
 </
servlet-mapping
>
</
servlet-mapping
>

 <!--
Spring ApplicationContext 载入
-->
<!--
Spring ApplicationContext 载入
-->
 <
listener
>
<
listener
>
 <
listener-class
>
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
</
listener-class
>
<
listener-class
>
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
</
listener-class
>
 </
listener
>
</
listener
>

 <!--
Spring 刷新Introspector防止内存泄露
-->
<!--
Spring 刷新Introspector防止内存泄露
-->
 <
listener
>
<
listener
>
 <
listener-class
>
org.springframework.web.util.IntrospectorCleanupListener
</
listener-class
>
<
listener-class
>
org.springframework.web.util.IntrospectorCleanupListener
</
listener-class
>
 </
listener
>
</
listener
>

 <!--
支持session scope的Spring bean
-->
<!--
支持session scope的Spring bean
-->
 <
listener
>
<
listener
>
 <
listener-class
>
org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextListener
</
listener-class
>
<
listener-class
>
org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextListener
</
listener-class
>
 </
listener
>
</
listener
>

 <!--
Character Encoding filter
-->
<!--
Character Encoding filter
-->
 <
filter
>
<
filter
>
 <
filter-name
>
setCharacterEncoding
</
filter-name
>
<
filter-name
>
setCharacterEncoding
</
filter-name
>
 <
filter-class
>
org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter
</
filter-class
>
<
filter-class
>
org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter
</
filter-class
>
 <
init-param
>
<
init-param
>
 <
param-name
>
encoding
</
param-name
>
<
param-name
>
encoding
</
param-name
>
 <
param-value
>
UTF-8
</
param-value
>
<
param-value
>
UTF-8
</
param-value
>
 </
init-param
>
</
init-param
>
 </
filter
>
</
filter
>

 <
filter-mapping
>
<
filter-mapping
>
 <
filter-name
>
setCharacterEncoding
</
filter-name
>
<
filter-name
>
setCharacterEncoding
</
filter-name
>
 <
url-pattern
>
/*
</
url-pattern
>
<
url-pattern
>
/*
</
url-pattern
>
 </
filter-mapping
>
</
filter-mapping
>

 <!--
Hibernate Open Session in View Filter
-->
<!--
Hibernate Open Session in View Filter
-->
 <
filter
>
<
filter
>
 <
filter-name
>
hibernateFilter
</
filter-name
>
<
filter-name
>
hibernateFilter
</
filter-name
>
 <
filter-class
>
org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.support.OpenSessionInViewFilter
</
filter-class
>
<
filter-class
>
org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.support.OpenSessionInViewFilter
</
filter-class
>
 </
filter
>
</
filter
>

 <
filter-mapping
>
<
filter-mapping
>
 <
filter-name
>
hibernateFilter
</
filter-name
>
<
filter-name
>
hibernateFilter
</
filter-name
>
 <
url-pattern
>
/*
</
url-pattern
>
<
url-pattern
>
/*
</
url-pattern
>
 </
filter-mapping
>
</
filter-mapping
>
 </
web-app
>
</
web-app
>

此处加载了Spring的配置文件,并对字符编码进行了处理,*.do和*.html的请求都转交给了Spring MVC的分派器。OpenSessionInViewFilter是用来解决Hibernate的OpenSessionInView问题的,如果没有使用Hibernate则无需配置此过滤器。
项目的部署和一般的Web项目没有任何区别,将项目打成War包或者直接将目录放到Tomcat的webapps中即可。假设目录的名字是SpringDemo,启动Tomcat后访问http://localhost:8080/SpringDemo/listarticle.html就能看到页面的效果了。






















 1966
1966

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








