你有没有考虑过,你的goroutines是如何被go的runtime系统调度的?是否尝试理解过为什么在程序中增加了并发,但并没有给它带来更好的性能?go执行跟踪程序可以帮助回答这些疑问,还有其他和其有关性能的问题,例如延迟、竞争和较低的并行效率。
该工具是Go 1.5版本加入的,通过度量go语言特定事件的运行时,例如:
-
创建,启动和终止goroutines
-
阻塞/非阻塞goroutines(syscalls, channels, locks)
-
网络 I/O
-
Syscalls
-
垃圾回收
Go 开箱就提供了一系列的性能监控 API 以及用于分析的工具, 可以快捷而有效地观察应用各个细节的 CPU 与内存使用概况, 包括生成一些可视化的数据(需要额外安装 Graphviz).
例子 gist 来自之前的 Trie 的实现, Ruby vs Go.
main 函数加上了下面几行:
| |
这里 os.Create("cpu_profile") 指定生成的数据文件, 然后 pprof.StartCPUProfile 看名字就知道是开始对 CPU 的使用进行监控. 有开始就有结束, 一般直接跟着 defer pprof.StopCPUProfile() 省的后面忘了. 编译执行一次以后会在目录下生成监控数据并记录到 cpu_profile. 接着就可以使用 pprof 来解读分析这些监控生成的数据.
When CPU profiling is enabled, the Go program stops about 100 times per second and records a sample consisting of the program counters on the currently executing goroutine’s stack.
CPU Profiling
| |
因为是在多核环境, 所以, 取样时间(Total samples) 占比大于 100% 也属于正常的. 交互操作模式提供了一大票的命令, 执行一下 help 就有相应的文档了. 比如输出报告到各种格式(pdf, png, gif), 方块越大个表示消耗越大.
又或者列出 CPU 占比最高的一些(默认十个)运行结点的 top 命令, 也可以加上需要的结点数比如 top15
| |
- flat: 是指该函数执行耗时, 程序总耗时 570ms,
main.NewNode的 200ms 占了 35.09% - sum: 当前函数与排在它上面的其他函数的 flat 占比总和, 比如
35.09% + 12.28% = 47.37% - cum: 是指该函数加上在该函数调用之前累计的总耗时, 这个看图片格式的话会更清晰一些.
可以看到, 这里最耗 CPU 时间的是 main.NewNode 这个操作.
除此外还有 list 命令可以根据匹配的参数列出指定的函数相关数据, 比如:
Memory Profiling
| |
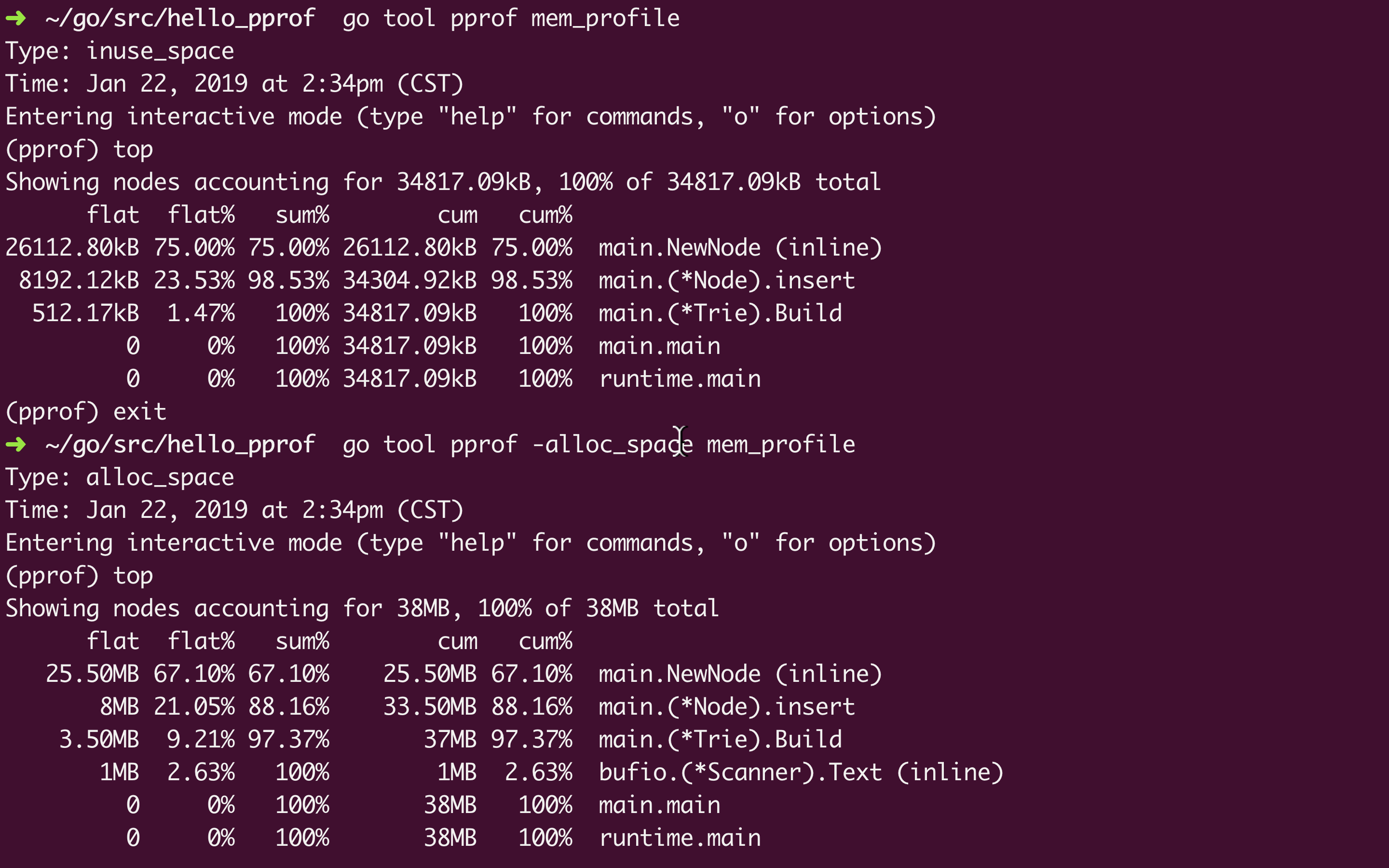
类似 CPU 的监控, 要监控内存的分配回收使用情况, 只要调用 pprof.WriteHeapProfile(memProfile)
然后是跟上面一样的生成图片:
Type: inuse_space 是监控内存的默认选项, 还可以选 -alloc_space, -inuse_objects, -alloc_objects
inuse_space 是正在使用的内存大小, alloc_space是从头到尾一共分配了的内存大小(包括已经回收了的), 后缀为 _objects 的是相应的对象数
net/http/pprof
对于 http 服务的监控有一些些的不同, 不过 Go 已经对 pprof 做了一些封装在 net/http/pprof
例子 gist 来自从 net/http 入门到 Gin 源码梳理
引入多一行 _ "net/http/pprof", 启用服务以后就可以在路径 /debug/pprof/ 看到相应的监控数据. 类似下面(已经很贴心的把各自的描述信息写在下边了):
用 wrk (brew install wrk) 模拟测试
wrk -c 200 -t 4 -d 3m http://localhost:8080/hello
还是没有前面的那些可视化图形 UI 直观, 不过可以通过 http://localhost:8080/debug/pprof/profile (其他几个指标也差不多, heap, alloc…)生成一个类似前面的 CPU profile 文件监控 30s 内的数据. 然后就可以用 go tool pprof来解读了.
| |

























 830
830

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








