可执行规范是可以用作设计规范的测试。 通过启用公共语言(在DDD世界中,这也称为无处不在的语言 ),它们使技术和业务团队能够进入同一页面。 它们充当代码的未来维护者的文档。
在本文中,我们将看到一种编写自动测试的自以为是的方式,该方法也可以用作可执行规范。
让我们从一个例子开始。 假设我们正在为企业创建会计系统。 该系统将允许其用户将收入和支出记录到不同的帐户中。 在用户开始记录收入和支出之前,他们应该能够在系统中添加新帐户。 假设“添加新帐户”用例的规范如下所示–
场景1
给定帐户不存在 用户添加新帐户时 然后添加的帐户具有给定的名称 然后添加的帐户具有给定的初始余额 然后添加的帐户具有用户的ID
方案2
给定帐户不存在 当用户添加初始余额为负的新帐户时 然后添加新帐户失败
情况3
具有相同名称的给定帐户 用户添加新帐户时 然后添加新帐户失败
为了创建一个新帐户,用户需要在系统中输入一个帐户名和一个初始余额。 如果不存在具有给定名称的帐户并且给定的初始余额为正,则系统将创建该帐户。
我们将首先写下一个测试,该测试将捕获第一个场景的第一个“ Given-When-Then”部分。 这就是它的样子–
class AddNewAccountTest {
@Test
@DisplayName ( "Given account does not exist When user adds a new account Then added account has the given name" )
void accountAddedWithGivenName() {
} } @DisplayName批注是在JUnit 5中引入的。它为测试分配了易于理解的名称。 这是我们执行此测试时看到的标签,例如在像IntelliJ IDEA这样的IDE中。
现在,我们将创建一个类,负责添加帐户
class AddNewAccountService {
void addNewAccount(String accountName) {
} } 该类定义单个方法,该方法接受帐户名称并负责创建帐户,即将其保存到持久数据存储中。 由于我们决定将此类称为AddNewAccountService,因此我们还将测试重命名为AddNewAccountServiceTest以遵循JUnit世界中使用的命名约定。
现在,我们可以继续编写测试了–
class AddNewAccountServiceTest {
@Test
@DisplayName ( "Given account does not exist When user adds a new account Then added account has the given name" )
void accountAddedWithGivenName() {
AddNewAccountService accountService = new AddNewAccountService();
accountService.addNewAccount( "test account" );
// What to test?
} } 我们应该测试/验证什么以确保正确实施该方案? 如果再次阅读我们的规范,很显然,我们想创建一个用户指定名称的“帐户”,因此我们应该在此处进行测试。 为此,我们必须首先创建一个代表帐户的类-
@AllArgsConstructor class Account {
private String name; } Account类只有一个名为name的属性。 它将具有其他字段,例如用户ID和余额,但是我们目前尚未测试它们,因此我们不会立即将它们添加到类中。
现在,我们已经创建了Account类,我们如何保存它,更重要的是,我们如何测试所保存的帐户具有用户指定的名称? 有许多方法可以做到这一点,而我的首选方法是定义一个接口,该接口将封装此保存操作。 让我们继续创建它–
interface SaveAccountPort {
void saveAccount(Account account); } AddNewAccountService将通过构造函数注入注入该接口的实现–
@RequiredArgsConstructor class AddNewAccountService {
private final SaveAccountPort saveAccountPort;
void addNewAccount(String accountName) {
} } 为了进行测试,我们将在Mockito的帮助下创建一个模拟实现,这样我们就不必担心实际的实现细节了–
@ExtendWith (MockitoExtension. class ) class AddNewAccountServiceTest {
@Mock
private SaveAccountPort saveAccountPort;
@Test
@DisplayName ( "Given account does not exist When user adds a new account Then added account has the given name" )
void accountAddedWithGivenName() {
AddNewAccountService accountService = new AddNewAccountService(saveAccountPort);
accountService.addNewAccount( "test account" );
// What to test?
} } 我们的测试设置现已完成。 现在,我们希望我们的测试方法(AddNewAccountService类的addNewAccount方法)调用SaveAccountPort的saveAccount方法,并将Account对象的名称设置为传递给该方法的对象。 让我们在测试中将其整理成句–
@ExtendWith (MockitoExtension. class ) class AddNewAccountServiceTest {
@Mock
private SaveAccountPort saveAccountPort;
@Captor
private ArgumentCaptor<Account> accountArgumentCaptor;
@Test
@DisplayName ( "Given account does not exist When user adds a new account Then added account has the given name" )
void accountAddedWithGivenName() {
AddNewAccountService accountService = new AddNewAccountService(saveAccountPort);
accountService.addNewAccount( "test account" );
BDDMockito.then(saveAccountPort).should().saveAccount(accountArgumentCaptor.capture());
BDDAssertions.then(accountArgumentCaptor.getValue().getName()).isEqualTo( "test account" );
} } 下面的行–
BDDMockito.then(saveAccountPort).should().saveAccount(accountArgumentCaptor.capture()); 验证一旦调用了被测试方法,即已调用SaveAccountPort的saveAccount方法。 我们还使用参数捕获器捕获传递到saveAccount方法的帐户参数。 下一行–
BDDAssertions.then(accountArgumentCaptor.getValue().getName()).isEqualTo( "test account" ); 然后验证捕获的帐户参数与测试中通过的名称相同。
为了使此测试通过,在我们的被测方法中需要的最少代码如下:
@RequiredArgsConstructor class AddNewAccountService {
private final SaveAccountPort saveAccountPort;
void addNewAccount(String accountName) {
saveAccountPort.saveAccount( new Account(accountName));
} } 这样,我们的测试开始通过!
让我们继续进行第一个方案的第二个“ Then”部分,它说–
然后添加的帐户具有给定的初始余额
让我们编写另一个测试来验证这一部分–
@Test @DisplayName ( "Given account does not exist When user adds a new account Then added account has the given initial balance" ) void accountAddedWithGivenInitialBalance() {
AddNewAccountService accountService = new AddNewAccountService(saveAccountPort);
accountService.addNewAccount( "test account" , "56.0" );
BDDMockito.then(saveAccountPort).should().saveAccount(accountArgumentCaptor.capture());
BDDAssertions.then(accountArgumentCaptor.getValue().getBalance())
.isEqualTo( new BigDecimal( "56.0" )); } 我们修改了addNewAccount方法以接受初始余额作为第二个参数。 我们还在帐户对象中添加了一个称为余额的新字段,该字段可以存储帐户余额–
@AllArgsConstructor @Getter class Account {
private String name;
private BigDecimal balance; } 由于我们更改了addNewAccount方法的签名,因此我们还必须修改我们的第一个测试–
@Test @DisplayName ( "Given account does not exist When user adds a new account Then added account has the given name" ) void accountAddedWithGivenName() {
AddNewAccountService accountService = new AddNewAccountService(saveAccountPort);
accountService.addNewAccount( "test account" , "1" );
BDDMockito.then(saveAccountPort).should().saveAccount(accountArgumentCaptor.capture());
BDDAssertions.then(accountArgumentCaptor.getValue().getName()).isEqualTo( "test account" ); } 如果我们现在运行新的测试,它将由于我们尚未实现的功能而失败。 现在就开始吧–
void addNewAccount(String accountName, String initialBalance) {
saveAccountPort.saveAccount( new Account(accountName, new BigDecimal(initialBalance))); } 我们的两个测试现在都应该通过。
由于我们已经进行了一些测试,现在该看看我们的实现,看看是否可以做得更好。 由于我们的AddNewAccountService非常简单,因此我们无需在此做任何事情。 对于我们的测试,我们可以消除测试设置代码中的重复项–两个测试都实例化AddNewAccountService的实例,并以相同的方式在其上调用addNewAccount方法。 是删除还是保留重复项取决于我们的测试编写方式-如果我们想使每个测试尽可能独立,那么就让它们保持原样。 但是,如果我们有通用的测试设置代码是可以的,那么我们可以按以下方式更改测试
@ExtendWith (MockitoExtension. class ) @DisplayName ( "Given account does not exist When user adds a new account" ) class AddNewAccountServiceTest {
private static final String ACCOUNT_NAME = "test account" ;
private static final String INITIAL_BALANCE = "56.0" ;
@Mock
private SaveAccountPort saveAccountPort;
@Captor
private ArgumentCaptor<Account> accountArgumentCaptor;
@BeforeEach
void setup() {
AddNewAccountService accountService = new AddNewAccountService(saveAccountPort);
accountService.addNewAccount(ACCOUNT_NAME, INITIAL_BALANCE);
}
@Test
@DisplayName ( "Then added account has the given name" )
void accountAddedWithGivenName() {
BDDMockito.then(saveAccountPort).should().saveAccount(accountArgumentCaptor.capture());
BDDAssertions.then(accountArgumentCaptor.getValue().getName()).isEqualTo(ACCOUNT_NAME);
}
@Test
@DisplayName ( "Then added account has the given initial balance" )
void accountAddedWithGivenInitialBalance() {
BDDMockito.then(saveAccountPort).should().saveAccount(accountArgumentCaptor.capture());
BDDAssertions.then(accountArgumentCaptor.getValue().getBalance())
.isEqualTo( new BigDecimal(INITIAL_BALANCE));
} } 请注意,我们还提取了@DisplayName的公共部分,并将其放在测试类的顶部。 如果我们不愿意这样做,我们也可以保持原样。
由于我们有多个通过的测试,因此从现在开始,每一次失败的测试通过,我们都会停一会儿,看看我们的实现,并尝试对其进行改进。 总而言之,我们的实施过程现在将包括以下步骤-
- 在确保现有测试持续通过的同时添加失败的测试
- 通过失败的测试
- 暂停片刻,然后尝试改善实施(代码和测试)
继续,我们现在需要使用创建的帐户存储用户ID。 按照我们的方法,我们将首先编写一个失败的测试以捕获此错误,然后添加使失败的测试通过的最少代码量。 一旦失败的测试开始通过,这就是实现的样子
@ExtendWith (MockitoExtension. class ) @DisplayName ( "Given account does not exist When user adds a new account" ) class AddNewAccountServiceTest {
private static final String ACCOUNT_NAME = "test account" ;
private static final String INITIAL_BALANCE = "56.0" ;
private static final String USER_ID = "some id" ;
private Account savedAccount;
@BeforeEach
void setup() {
AddNewAccountService accountService = new AddNewAccountService(saveAccountPort);
accountService.addNewAccount(ACCOUNT_NAME, INITIAL_BALANCE, USER_ID);
BDDMockito.then(saveAccountPort).should().saveAccount(accountArgumentCaptor.capture());
savedAccount = accountArgumentCaptor.getValue();
}
// Other tests.....
@Test
@DisplayName ( "Then added account has user's id" )
void accountAddedWithUsersId() {
BDDAssertions.then(accountArgumentCaptor.getValue().getUserId()).isEqualTo(USER_ID);
} } @RequiredArgsConstructor class AddNewAccountService {
private final SaveAccountPort saveAccountPort;
void addNewAccount(String accountName, String initialBalance, String userId) {
saveAccountPort.saveAccount( new Account(accountName, new BigDecimal(initialBalance), userId));
} } @AllArgsConstructor @Getter class Account {
private String name;
private BigDecimal balance;
private String userId; } 既然所有测试都通过了,那就是改进的时间了! 注意,addNewAccount方法已经接受了三个参数。 随着我们引入越来越多的帐户属性,其参数列表也将开始增加。 我们可以引入一个参数对象来避免这种情况
@RequiredArgsConstructor class AddNewAccountService {
private final SaveAccountPort saveAccountPort;
void addNewAccount(AddNewAccountCommand command) {
saveAccountPort.saveAccount(
new Account(
command.getAccountName(),
new BigDecimal(command.getInitialBalance()),
command.getUserId()
)
);
}
@Builder
@Getter
static class AddNewAccountCommand {
private final String userId;
private final String accountName;
private final String initialBalance;
} } @ExtendWith (MockitoExtension. class ) @DisplayName ( "Given account does not exist When user adds a new account" ) class AddNewAccountServiceTest {
// Fields.....
@BeforeEach
void setup() {
AddNewAccountService accountService = new AddNewAccountService(saveAccountPort);
AddNewAccountCommand command = AddNewAccountCommand.builder()
.accountName(ACCOUNT_NAME)
.initialBalance(INITIAL_BALANCE)
.userId(USER_ID)
.build();
accountService.addNewAccount(command);
BDDMockito.then(saveAccountPort).should().saveAccount(accountArgumentCaptor.capture());
savedAccount = accountArgumentCaptor.getValue();
}
// Remaining Tests..... } 如果现在在我的IDEA中运行测试,这就是我所看到的–
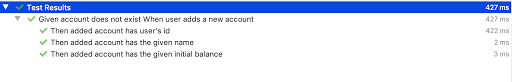
当我们尝试在此视图中阅读测试描述时,我们已经可以很好地了解“添加新帐户”用例及其工作方式。
好的,让我们继续进行用例的第二种情况,这是一个验证规则
给定帐户不存在
当用户添加初始余额为负的新帐户时
然后添加新帐户失败
让我们编写一个新的测试来尝试捕获这一点–
@ExtendWith (MockitoExtension. class ) @DisplayName ( "Given account does not exist When user adds a new account" ) class AddNewAccountServiceTest {
// Other tests
@Test
@DisplayName ( "Given account does not exist When user adds a new account with negative initial balance Then add new account fails" )
void addNewAccountFailsWithNegativeInitialBalance() {
AddNewAccountService accountService = new AddNewAccountService(saveAccountPort);
AddNewAccountCommand command = AddNewAccountCommand.builder().initialBalance( "-56.0" ).build(); AddNewAccountCommand command = AddNewAccountCommand.builder().initialBalance( ).build();
accountService.addNewAccount(command);
BDDMockito.then(saveAccountPort).shouldHaveNoInteractions();
} } 我们可以通过几种方法在服务中实施验证。 我们可以抛出一个异常详细说明验证失败,或者可以返回一个包含错误详细信息的错误对象。 在此示例中,如果验证失败,我们将抛出异常–
@Test @DisplayName ( "Given account does not exist When user adds a new account with negative initial balance Then add new account fails" ) void addNewAccountFailsWithNegativeInitialBalance() {
AddNewAccountService accountService = new AddNewAccountService(saveAccountPort);
AddNewAccountCommand command = AddNewAccountCommand.builder().initialBalance( "-56.0" ).build(); AddNewAccountCommand command = AddNewAccountCommand.builder().initialBalance( ).build();
assertThatExceptionOfType(IllegalArgumentException. class )
.isThrownBy(() -> accountService.addNewAccount(command));
BDDMockito.then(saveAccountPort).shouldHaveNoInteractions(); } 此测试验证以负余额调用addNewAccount方法时是否引发异常。 它还确保在这种情况下,我们的代码不会调用SaveAccountPort的任何方法。 在我们开始修改我们的服务以通过此测试之前,我们必须重构一下我们的测试设置代码。 这是因为在我们之前的重构中,我们将通用测试设置代码移到了一个方法中,该方法现在可以在每次测试之前运行–
@BeforeEach void setup() {
AddNewAccountService accountService = new AddNewAccountService(saveAccountPort);
AddNewAccountCommand command = AddNewAccountCommand.builder()
.accountName(ACCOUNT_NAME)
.initialBalance(INITIAL_BALANCE)
.userId(USER_ID)
.build();
accountService.addNewAccount(command);
BDDMockito.then(saveAccountPort).should().saveAccount(accountArgumentCaptor.capture());
savedAccount = accountArgumentCaptor.getValue(); } 现在,此设置代码与我们刚刚添加的新测试直接冲突–在每次测试之前,它将始终使用有效的命令对象调用addNewAccount方法,从而导致调用SaveAccountPort的saveAccount方法,从而导致新测试失败。
为了解决这个问题,我们将在测试类中创建一个嵌套类,在其中我们将移动现有的设置代码和通过测试–
@ExtendWith (MockitoExtension. class ) @DisplayName ( "Given account does not exist" ) class AddNewAccountServiceTest {
@Mock
private SaveAccountPort saveAccountPort;
private AddNewAccountService accountService;
@BeforeEach
void setUp() {
accountService = new AddNewAccountService(saveAccountPort);
}
@Nested
@DisplayName ( "When user adds a new account" )
class WhenUserAddsANewAccount {
private static final String ACCOUNT_NAME = "test account" ;
private static final String INITIAL_BALANCE = "56.0" ;
private static final String USER_ID = "some id" ;
private Account savedAccount;
@Captor
private ArgumentCaptor<Account> accountArgumentCaptor;
@BeforeEach
void setUp() {
AddNewAccountCommand command = AddNewAccountCommand.builder()
.accountName(ACCOUNT_NAME)
.initialBalance(INITIAL_BALANCE)
.userId(USER_ID)
.build();
accountService.addNewAccount(command);
BDDMockito.then(saveAccountPort).should().saveAccount(accountArgumentCaptor.capture());
savedAccount = accountArgumentCaptor.getValue();
}
@Test
@DisplayName ( "Then added account has the given name" )
void accountAddedWithGivenName() {
BDDAssertions.then(savedAccount.getName()).isEqualTo(ACCOUNT_NAME);
}
@Test
@DisplayName ( "Then added account has the given initial balance" )
void accountAddedWithGivenInitialBalance() {
BDDAssertions.then(savedAccount.getBalance()).isEqualTo( new BigDecimal(INITIAL_BALANCE));
}
@Test
@DisplayName ( "Then added account has user's id" )
void accountAddedWithUsersId() {
BDDAssertions.then(accountArgumentCaptor.getValue().getUserId()).isEqualTo(USER_ID);
}
}
@Test
@DisplayName ( "When user adds a new account with negative initial balance Then add new account fails" )
void addNewAccountFailsWithNegativeInitialBalance() {
AddNewAccountCommand command = AddNewAccountCommand.builder()
.initialBalance( "-56.0" )
.build();
assertThatExceptionOfType(IllegalArgumentException. class )
.isThrownBy(() -> accountService.addNewAccount(command));
BDDMockito.then(saveAccountPort).shouldHaveNoInteractions();
} } 这是我们采取的重构步骤–
- 我们创建了一个内部类,然后用JUnit 5的@Nested批注标记内部类。
- 我们破坏了最外面的测试类的@DisplayName标签,并将“当用户添加新帐户时”部分移到了新引入的内部类中。 我们这样做的原因是因为此内部类将包含一组测试,这些测试将验证/验证与有效帐户创建方案有关的行为。
- 我们将相关的设置代码和字段/常量移到了这个内部类中。
- 我们从新测试中删除了“给定帐户不存在”部分。 这是因为最外层测试类上的@DisplayName已经包含了此内容,因此这里再也没有包含它。
现在是在IntelliJ IDEA中运行测试时的样子,
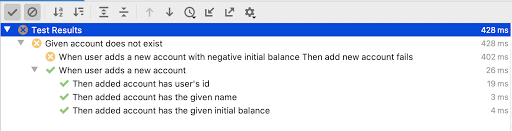
从屏幕截图中可以看到,我们的测试标签也按照我们在测试代码中创建的结构很好地进行了分组和缩进。 现在,让我们修改服务以使失败的测试通过–
void addNewAccount(AddNewAccountCommand command) {
BigDecimal initialBalance = new BigDecimal(command.getInitialBalance());
if (initialBalance.compareTo(BigDecimal.ZERO) < 0 ) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException( "Initial balance of an account cannot be negative" );
}
saveAccountPort.saveAccount(
new Account(
command.getAccountName(),
initialBalance,
command.getUserId()
)
); } 这样,我们所有的测试再次开始通过。 下一步是寻找可能的方法来改进现有的实现。 如果没有,那么我们将继续执行最终方案,这也是一个验证规则–
具有相同名称的给定帐户
用户添加新帐户时
然后添加新帐户失败
和往常一样,让我们编写一个测试来捕获这一点–
@Test @DisplayName ( "Given account with the same name exists When user adds a new account Then add new account fails" ) void addNewAccountFailsForDuplicateAccounts() {
AddNewAccountCommand command = AddNewAccountCommand.builder()
.accountName( "existing name" )
.build();
AddNewAccountService accountService = new AddNewAccountService(saveAccountPort);
assertThatExceptionOfType(IllegalArgumentException. class )
.isThrownBy(() -> accountService.addNewAccount(command));
BDDMockito.then(saveAccountPort).shouldHaveNoInteractions(); } 我们现在必须弄清的第一件事是如何找到现有帐户。 由于这将涉及查询我们的持久数据存储,因此我们将引入一个接口–
public interface FindAccountPort {
Account findAccountByName(String accountName); } 并将其注入我们的AddNewAccountService –
@RequiredArgsConstructor class AddNewAccountService {
private final SaveAccountPort saveAccountPort;
private final FindAccountPort findAccountPort;
// Rest of the code } 并修改我们的测试–
@Test @DisplayName ( "Given account with the same name exists When user adds a new account Then add new account fails" ) void addNewAccountFailsForDuplicateAccounts() {
String existingAccountName = "existing name" ;
AddNewAccountCommand command = AddNewAccountCommand.builder()
.initialBalance( "0" )
.accountName(existingAccountName)
.build();
given(findAccountPort.findAccountByName(existingAccountName)).willReturn(mock(Account. class ));
AddNewAccountService accountService = new AddNewAccountService(saveAccountPort,
findAccountPort);
assertThatExceptionOfType(IllegalArgumentException. class )
.isThrownBy(() -> accountService.addNewAccount(command));
BDDMockito.then(saveAccountPort).shouldHaveNoInteractions(); } 对AddNewAccountService的最后更改也将需要对现有测试进行更改,主要是在我们实例化该类的实例的位置。 但是,我们将做的改变不止于此–
@ExtendWith (MockitoExtension. class ) class AddNewAccountServiceTest {
@Mock
private SaveAccountPort saveAccountPort;
@Mock
private FindAccountPort findAccountPort;
@Nested
@DisplayName ( "Given account does not exist" )
class AccountDoesNotExist {
private AddNewAccountService accountService;
@BeforeEach
void setUp() {
accountService = new AddNewAccountService(saveAccountPort, findAccountPort);
}
@Nested
@DisplayName ( "When user adds a new account" )
class WhenUserAddsANewAccount {
private static final String ACCOUNT_NAME = "test account" ;
private static final String INITIAL_BALANCE = "56.0" ;
private static final String USER_ID = "some id" ;
private Account savedAccount;
@Captor
private ArgumentCaptor<Account> accountArgumentCaptor;
@BeforeEach
void setUp() {
AddNewAccountCommand command = AddNewAccountCommand.builder()
.accountName(ACCOUNT_NAME)
.initialBalance(INITIAL_BALANCE)
.userId(USER_ID)
.build();
accountService.addNewAccount(command);
BDDMockito.then(saveAccountPort).should().saveAccount(accountArgumentCaptor.capture());
savedAccount = accountArgumentCaptor.getValue();
}
@Test
@DisplayName ( "Then added account has the given name" )
void accountAddedWithGivenName() {
BDDAssertions.then(savedAccount.getName()).isEqualTo(ACCOUNT_NAME);
}
@Test
@DisplayName ( "Then added account has the given initial balance" )
void accountAddedWithGivenInitialBalance() {
BDDAssertions.then(savedAccount.getBalance()).isEqualTo( new BigDecimal(INITIAL_BALANCE));
}
@Test
@DisplayName ( "Then added account has user's id" )
void accountAddedWithUsersId() {
BDDAssertions.then(accountArgumentCaptor.getValue().getUserId()).isEqualTo(USER_ID);
}
}
@Test
@DisplayName ( "When user adds a new account with negative initial balance Then add new account fails" )
void addNewAccountFailsWithNegativeInitialBalance() {
AddNewAccountCommand command = AddNewAccountCommand.builder()
.initialBalance( "-56.0" )
.build();
assertThatExceptionOfType(IllegalArgumentException. class )
.isThrownBy(() -> accountService.addNewAccount(command));
BDDMockito.then(saveAccountPort).shouldHaveNoInteractions();
}
}
@Test
@DisplayName ( "Given account with the same name exists When user adds a new account Then add new account fails" )
void addNewAccountFailsForDuplicateAccounts() {
String existingAccountName = "existing name" ;
AddNewAccountCommand command = AddNewAccountCommand.builder()
.initialBalance( "0" )
.accountName(existingAccountName)
.build();
given(findAccountPort.findAccountByName(existingAccountName)).willReturn(mock(Account. class ));
AddNewAccountService accountService = new AddNewAccountService(saveAccountPort,
findAccountPort);
assertThatExceptionOfType(IllegalArgumentException. class )
.isThrownBy(() -> accountService.addNewAccount(command));
BDDMockito.then(saveAccountPort).shouldHaveNoInteractions();
} } 这就是我们所做的–
- 我们创建了另一个内部类,将其标记为@Nested,然后将现有的通过测试移入其中。 这组测试测试在不存在具有给定名称的帐户时添加新帐户的行为。
- 我们已将测试设置代码移至新引入的内部类中,因为它们也与“不存在具有给定名称的帐户”的情况有关。
- 出于与上述相同的原因,我们还将@DisplayName注释从顶级测试类移至了新引入的内部类。
重构后,我们快速运行测试以查看一切是否按预期工作(测试失败,通过测试通过),然后继续修改我们的服务–
@RequiredArgsConstructor class AddNewAccountService {
private final SaveAccountPort saveAccountPort;
private final FindAccountPort findAccountPort;
void addNewAccount(AddNewAccountCommand command) {
BigDecimal initialBalance = new BigDecimal(command.getInitialBalance());
if (initialBalance.compareTo(BigDecimal.ZERO) < 0 ) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException( "Initial balance of an account cannot be negative" );
}
if (findAccountPort.findAccountByName(command.getAccountName()) != null ) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException( "An account with given name already exists" );
}
saveAccountPort.saveAccount(
new Account(
command.getAccountName(),
initialBalance,
command.getUserId()
)
);
}
@Builder
@Getter
static class AddNewAccountCommand {
private final String userId;
private final String accountName;
private final String initialBalance;
} } 我们所有的测试现在都是绿色的–
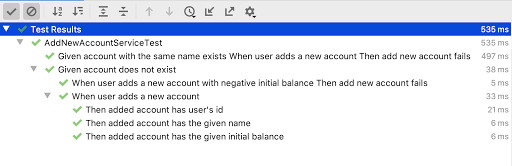
由于我们的用例实现现已完成,因此我们将最后一次查看实现,以查看是否可以改进任何东西。 如果没有,那么我们的用例实现现在就完成了!
总而言之,这就是我们在本文中所做的–
- 我们已经写下了要实现的用例
- 我们添加了一个失败的测试,并使用易于理解的名称进行标记
- 我们添加了使测试通过失败所需的最少代码量
- 一旦我们进行了一项以上的测试,在通过每项失败的测试之后,我们查看了实现并试图对其进行改进
- 在编写测试时,我们尝试以某种方式编写测试,以使用例规范反映在测试代码中。 为此,我们使用了–
- @DisplayName批注为我们的测试分配易于理解的名称
- @Nested用于按层次结构将相关测试分组,以反映我们的用例设置
- 使用了Mockito和AssertJ的BDD驱动的API来验证预期的行为
我们什么时候应该遵循这种编写自动化测试的风格? 该问题的答案与软件工程中的所有其他用法问题相同-取决于情况。 当我使用具有复杂业务/域规则的应用程序时,我个人更喜欢这种样式,该规则需要长期维护,为此需要与业务部门紧密合作,以及许多其他因素(例如,应用程序)架构,团队采用率等)。
与往常一样,完整的示例已提交给Github 。
直到下一次!





















 530
530

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








