我解释说ToStringBuilder将十六进制格式的身份哈希码添加到其输出中。 在本文中,我将更深入地研究ToStringBuilder对以十六进制格式显示的身份哈希码的使用。 甚至那些不使用ToStringBuilder也可能会发现此信息很有用,因为Java的标准Object.toString()也使用有效表示其身份哈希码的十六进制表示形式。
我将从使用ToStringBuilder一个非常简单的Java示例开始。 本示例使用下面显示的三个Java类( Person.java , Employee.java和Main.java )。
人.java
package dustin.examples;
import org.apache.commons.lang.builder.ToStringBuilder;
/**
* A simple representation of a Person intended only to demonstrate Apache
* Commons ToStringBuilder.
*
* @author Dustin
*/
public class Person
{
/** Person's last name (surname). */
protected final String lastName;
/** Person's first name. */
protected final String firstName;
/**
* Parameterized constructor for obtaining an instance of Person.
*
* @param newLastName Last name of new Person instance.
* @param newFirstName First name of new Person instance.
*/
public Person(final String newLastName, final String newFirstName)
{
this.lastName = newLastName;
this.firstName = newFirstName;
}
/**
* Provide String representation of this Person instance.
* @return My String representation.
*/
@Override
public String toString()
{
final ToStringBuilder builder = new ToStringBuilder(this);
builder.append("First Name", this.firstName);
builder.append("Last Name", this.lastName);
return builder.toString();
}
}Employee.java
package dustin.examples;
import java.util.Objects;
import org.apache.commons.lang.builder.ToStringBuilder;
/**
* Simple class intended to demonstrate ToStringBuilder.
*
* @author Dustin
*/
public class Employee extends Person
{
/** Employee ID. */
private final String employeeId;
/**
* Parameterized constructor for obtaining an instance of Employee.
*
* @param newLastName Last name of the employee.
* @param newFirstName First name of the employee.
* @param newId Employee's employee ID.
*/
public Employee(
final String newLastName, final String newFirstName, final String newId)
{
super(newLastName, newFirstName);
this.employeeId = newId;
}
/**
* Provide String representation of me.
*
* @return My String representation.
*/
@Override
public String toString()
{
final ToStringBuilder builder = new ToStringBuilder(this);
builder.appendSuper(super.toString());
builder.append("Employee ID", this.employeeId);
return builder.toString();
}
/**
* Simple object equality comparison method.
*
* @param obj Object to be compared to me for equality.
* @return {@code true} if the provided object and I are considered equal.
*/
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj)
{
if (obj == null)
{
return false;
}
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
{
return false;
}
final Employee other = (Employee) obj;
if (!Objects.equals(this.employeeId, other.employeeId))
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
/**
* Hash code for this instance.
*
* @return My hash code.
*/
@Override
public int hashCode()
{
int hash = 3;
hash = 19 * hash + Objects.hashCode(this.employeeId);
return hash;
}
}Main.java(版本1)
package dustin.examples;
import static java.lang.System.out;
/**
* Simple class enabling demonstration of ToStringBuilder.
*
* @author Dustin
*/
public class Main
{
/**
* Main function for running Java examples with ToStringBuilder.
*
* @param args the command line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args)
{
final Person person = new Person("Washington", "Willow");
out.println(person);
final Employee employee = new Employee("Lazentroph", "Frank", "56");
out.println(employee);
}
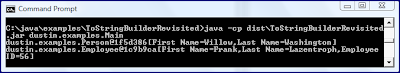
}上面的例子很简单,其输出如下所示:
上面描述的输出显示了为ToStringBuilder生成的两个实例的输出所打印的字符串。 Person类实例的字符串表示形式包括字符串“ 1f5d386”,而Employee类实例的字符串表示形式包括字符串“ 1c9b9ca”。 这些字符串是每个对象的身份哈希码的十六进制表示形式 。
字符串“ 1f5d386”和“ 1c9b9ca”看起来不像我们中的很多人习惯的整数哈希码,因为它们以十六进制表示。 Integer.toHexString(int)方法[自JDK 1.0.2起可用]是一种方便的方法,用于以十六进制格式打印整数,可用于转换“常规”哈希码以查看它们是否与ToStringBuilder生成的哈希码匹配。 我已经在Main类的新版本中的实例的哈希码上添加了对该方法的调用。
Main.java(版本2)
package dustin.examples;
import static java.lang.System.out;
/**
* Simple class enabling demonstration of ToStringBuilder.
*
* @author Dustin
*/
public class Main
{
/**
* Main function for running Java examples with ToStringBuilder.
*
* @param args the command line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args)
{
final Person person = new Person("Washington", "Willow");
out.println(person);
out.println("\tHash Code (ten): " + person.hashCode());
out.println("\tHash Code (hex): " + Integer.toHexString(person.hashCode()));
final Employee employee = new Employee("Lazentroph", "Frank", "56");
out.println(employee);
out.println("\tHash Code (ten): " + employee.hashCode());
out.println("\tHash Code (hex): " + Integer.toHexString(employee.hashCode()));
}
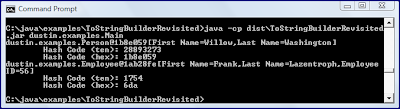
}执行以上操作会导致以下输出:
如输出所示, Person实例的哈希码的十六进制表示确实与该实例的ToStringBuilder生成的String中显示的匹配。 但是,不能对Employee实例说同样的话。 区别在于Person类不会覆盖hashCode()方法 ,因此默认情况下使用身份哈希码,而Employee类却覆盖其自己的hashCode() (因此与身份哈希码不同)。
Main的第三个版本使用System.identityHashCode(Object)输出身份哈希码[在我的博客文章Java的System.identityHashCode中进一步详细讨论]。
Main.java(版本3)
package dustin.examples;
import static java.lang.System.out;
/**
* Simple class enabling demonstration of ToStringBuilder.
*
* @author Dustin
*/
public class Main
{
/**
* Main function for running Java examples with ToStringBuilder.
*
* @param args the command line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args)
{
final Person person = new Person("Washington", "Willow");
out.println(person);
out.println("\tHash Code (ten): " + person.hashCode());
out.println("\tHash Code (hex): " + Integer.toHexString(person.hashCode()));
out.println("\t\tIdentity Hash (ten): " + System.identityHashCode(person));
out.println("\t\tIdentity Hash (hex): " + Integer.toHexString(System.identityHashCode(person)));
final Employee employee = new Employee("Lazentroph", "Frank", "56");
out.println(employee);
out.println("\tHash Code (ten): " + employee.hashCode());
out.println("\tHash Code (hex): " + Integer.toHexString(employee.hashCode()));
out.println("\t\tIdentity Hash (ten): " + System.identityHashCode(employee));
out.println("\t\tIdentity Hash (hex): " + Integer.toHexString(System.identityHashCode(employee)));
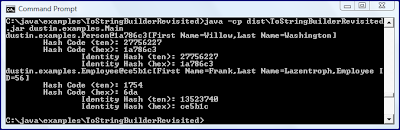
} 现在,我们可以将身份哈希码与ToStringBuilder生成的字符串进行比较。
最后一个示例明确地说明ToStringBuilder在其生成的输出中包括系统标识哈希码的十六进制表示。 如果要使用覆盖的哈希码而不是标识哈希码的十六进制表示形式,则可以使用ToStringStyle的实例(通常是StandardToStringStyle的实例),并且可以使用false参数调用方法setUseIdentityHashCode(boolean) 。 此实例ToStringStyle然后可以被传递到ToStringBuilder.setDefaultStyle(ToStringStyle)方法。
附带说明一下,上面显示的Employee类中的equals(Object)和hashCode()方法是由NetBeans 7.1自动生成的。 我很高兴地看到,该项目的Java源代码版本指定为JDK 1.7 ,这两种方法的自动生成利用了Objects类。
在本文中,我一直使用ToStringBuilder生成的输出来促进对身份哈希码的十六进制表示形式的讨论,但是我可以简单地将JDK自己内置的“默认” Object.toString()实现用于同一目的。 实际上,Javadoc甚至宣传了这一点:
Object类的toString方法返回一个字符串,该字符串包括该对象是其实例的类的名称,符号字符“ @”以及该对象的哈希码的无符号十六进制表示形式。 换句话说,此方法返回的字符串等于:
getClass().getName() + '@' + Integer.toHexString(hashCode())
我没有使用此示例开始的唯一原因是,我几乎总是在类中重写toString()方法 ,并且未获得此“默认”实现。 但是,当我使用ToStringBuilder实现重写的toString()方法时,确实看到了这些十六进制表示形式。 我可能会增加对Objects.toString()的使用,从而减少对ToStringBuilder使用。
我们中的许多人在日常的Java工作中都不会考虑十六进制表示形式或标识哈希码。 在此博客文章中,我以ToStringBuilder的输出为借口来更仔细地研究这两个概念。 在此过程中,我还简要介绍了Integer.toHexString(Object)方法,该方法对于以十六进制表示形式打印数字很有用。 了解Java对十六进制表示法的支持很重要,因为Java确实会出现在toString()输出 , 颜色标签 , 内存地址和其他地方。
参考: ToString: JCG合作伙伴提供 的身份哈希码的十六进制表示形式 实际事件启发博客中的达斯汀·马克思。
翻译自: https://www.javacodegeeks.com/2012/03/tostring-hexadecimal-representation-of.html







 本文探讨了Java中ToStringBuilder如何显示对象的身份哈希码的十六进制表示,以及如何通过Integer.toHexString()方法转换哈希码。作者通过示例展示了不同类的toString()方法如何处理哈希码,区分了覆盖hashCode()方法和使用System.identityHashCode()的情况。此外,还提到了Java内置的Object.toString()方法和Objects.toString()在输出哈希码中的作用。
本文探讨了Java中ToStringBuilder如何显示对象的身份哈希码的十六进制表示,以及如何通过Integer.toHexString()方法转换哈希码。作者通过示例展示了不同类的toString()方法如何处理哈希码,区分了覆盖hashCode()方法和使用System.identityHashCode()的情况。此外,还提到了Java内置的Object.toString()方法和Objects.toString()在输出哈希码中的作用。














 3757
3757

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








