a “plugin” refers to a special class that’s listening for any public method call to another object.
We say any public method, but that’s not quite accurate. If the public method uses the final
keyword, or the class itself uses the final
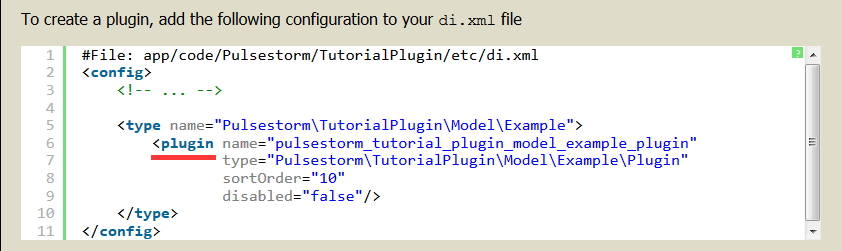
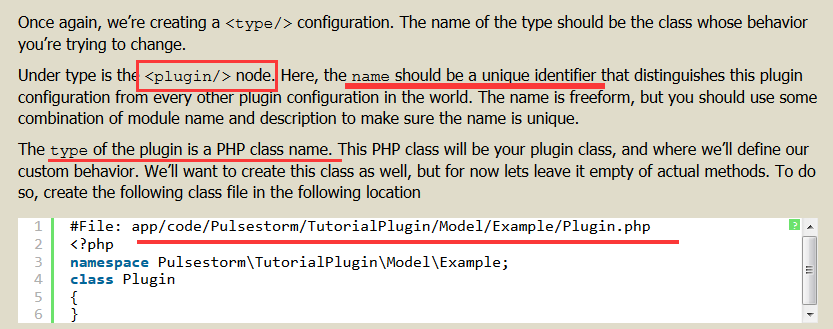
keyword, you won’t be able to use a plugin. 创建 plugin:
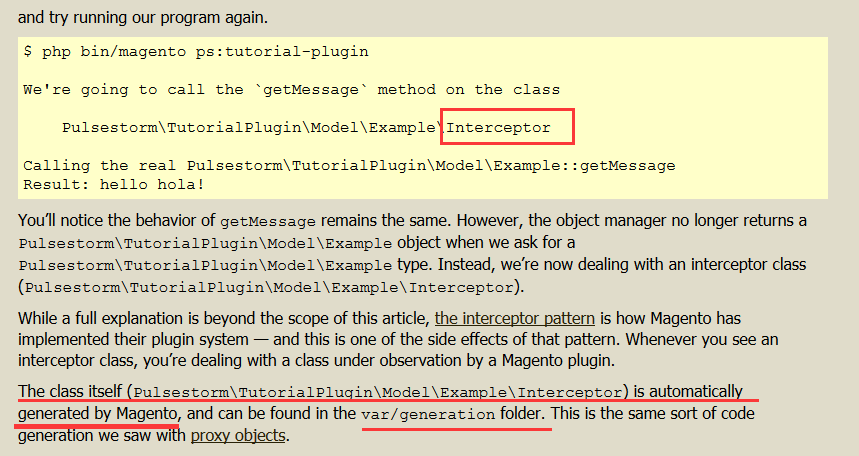
在 var/generation 下自定生成。将有和父类一样的行为。Plugins: After Methods:改变返回值
#File: app/code/Pulsestorm/TutorialPlugin/Model/Example/Plugin.php
<?php
namespace Pulsestorm\TutorialPlugin\Model\Example;
class Plugin
{
public function afterGetMessage($subject, $result)
{
echo "Calling " , __METHOD__,"\n";
return $result;
}
}驼峰命名,
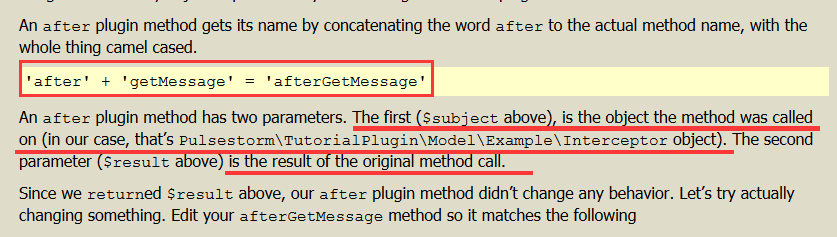
第一个参数,为 Interceptor.php
第二个参数 , $result 是原先方法访问的结果。Since we returned $result above, our after plugin method didn’t change any behavior.
Let’s try actually changing something.
Edit your afterGetMessage method so
it matches the following#File: app/code/Pulsestorm/TutorialPlugin/Model/Example/Plugin.php
public function afterGetMessage($subject, $result)
{
return 'We are so tired of saying hello';
} You just used a plugin to change the value returned by the getMessage method.
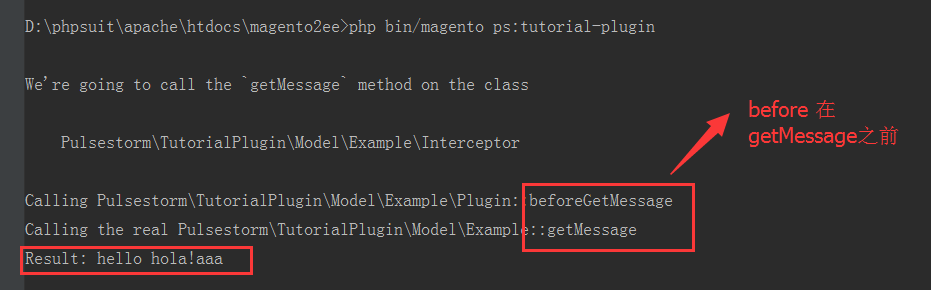
通过 plugin 改变返回结果。Plugins: Before Methods:改变参数
#File: app/code/Pulsestorm/TutorialPlugin/Model/Example/Plugin.php
<?php
namespace Pulsestorm\TutorialPlugin\Model\Example;
class Plugin
{
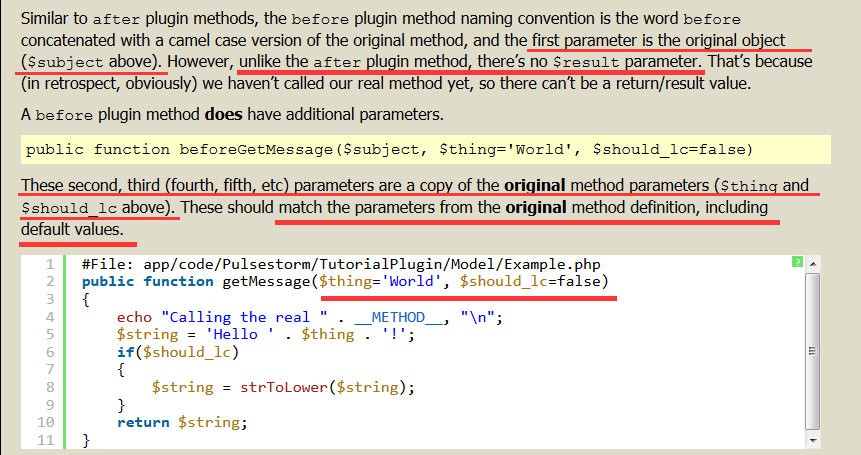
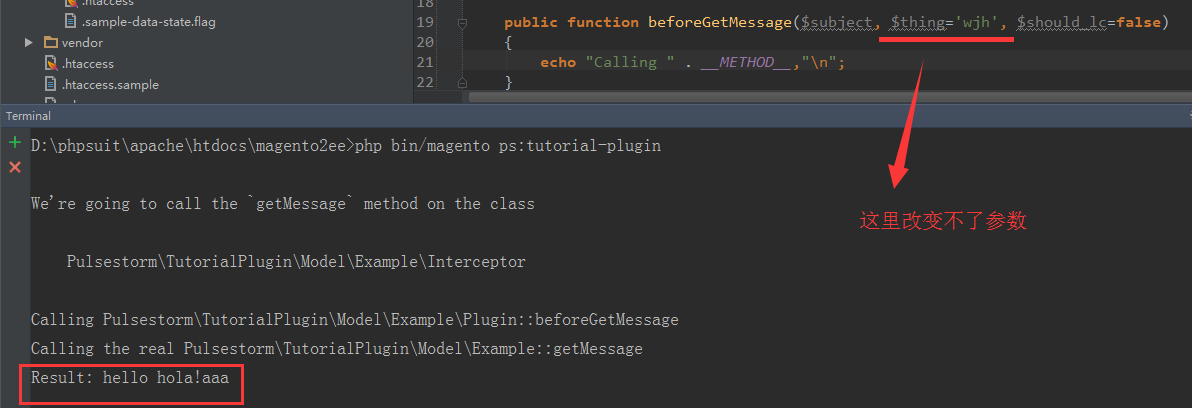
public function beforeGetMessage($subject, $thing='World', $should_lc=false)
{
echo "Calling " . __METHOD__,"\n";
}
}第一个参数: Interceptor.php
显而易见,没有$resutl 参数,
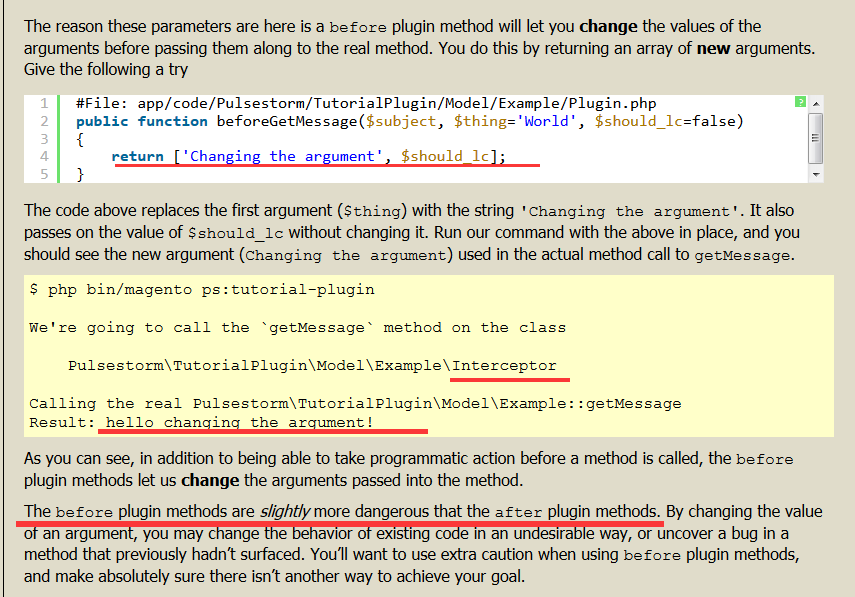
后面的参数匹配原先方法的参数,包括默认值 return 数组;
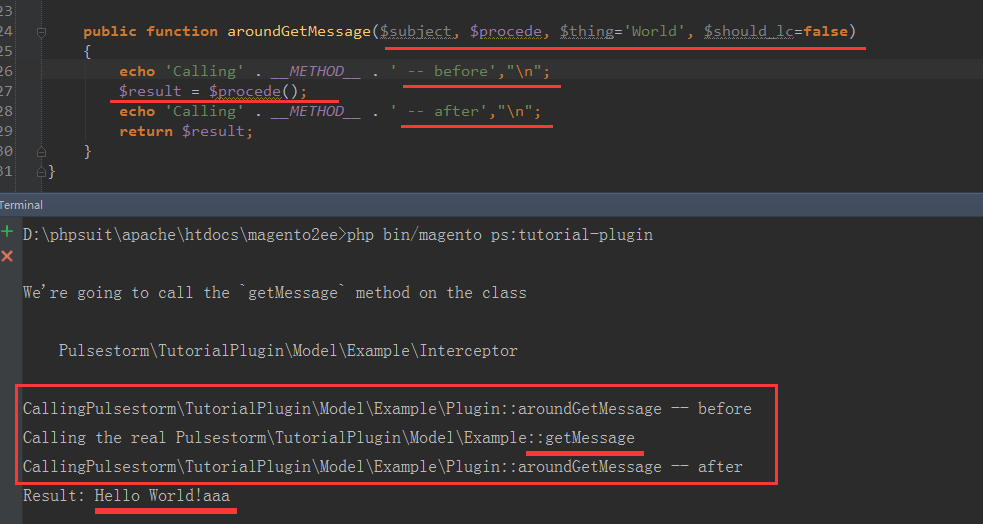
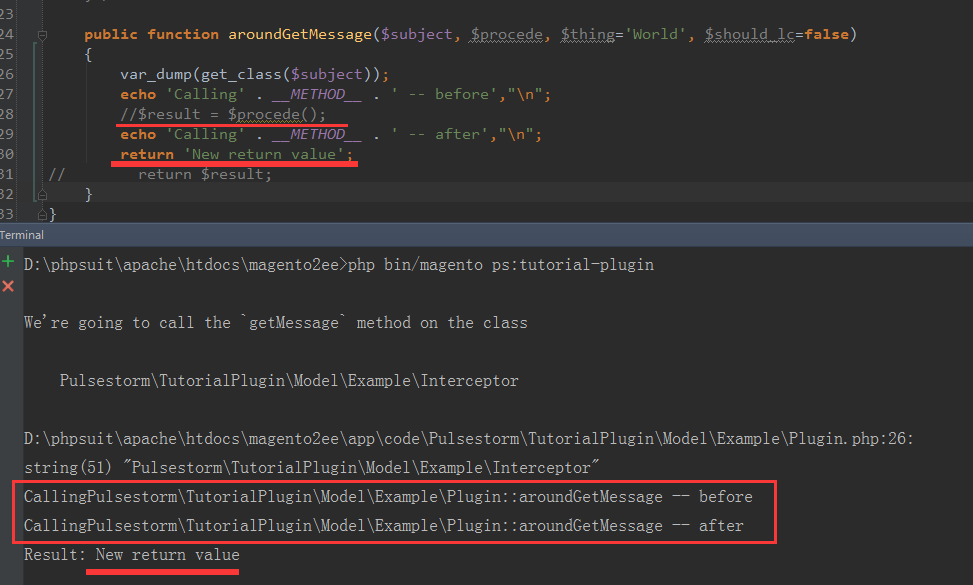
来改变传入的参数。Plugins: Around Methods

第一个参数是,Interceptor.php
第二个参数是 php 匿名函数
...
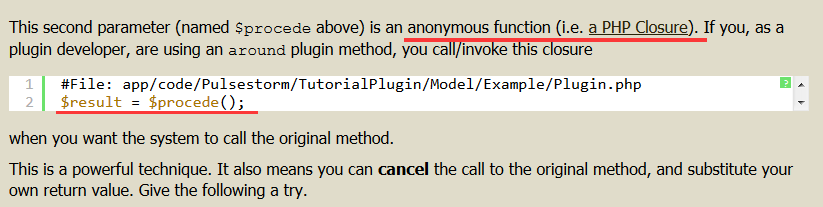
同时重写一个方法:
注意:
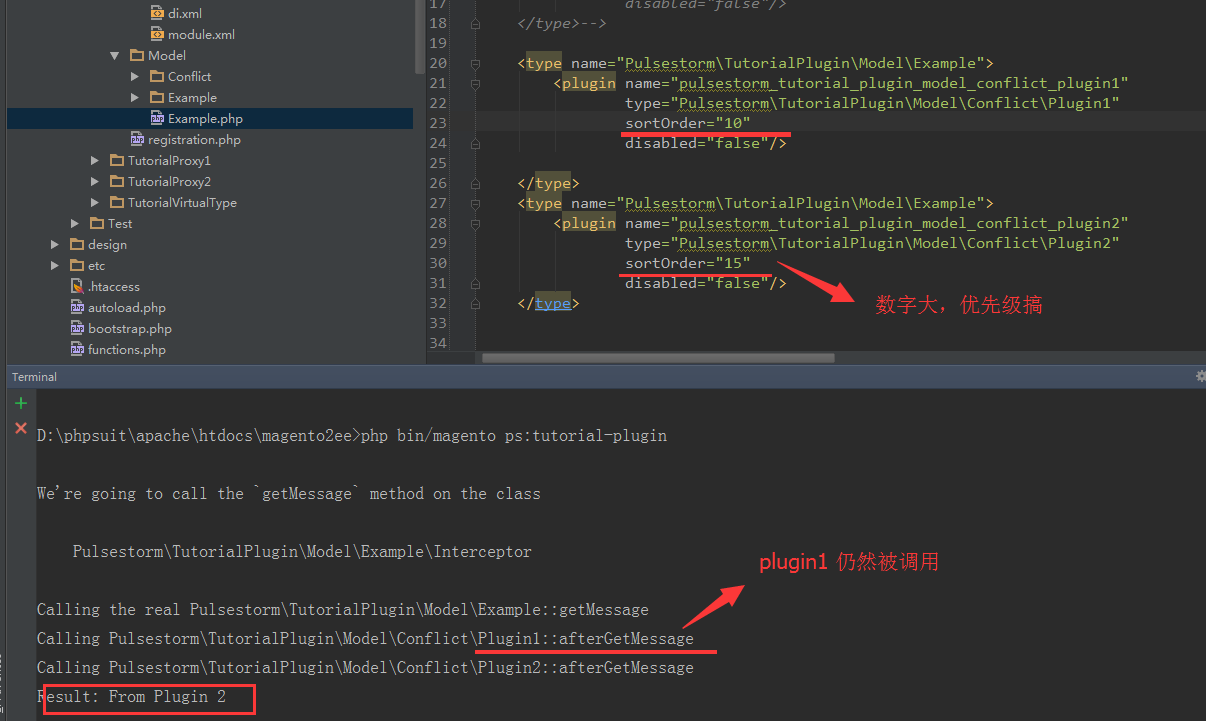
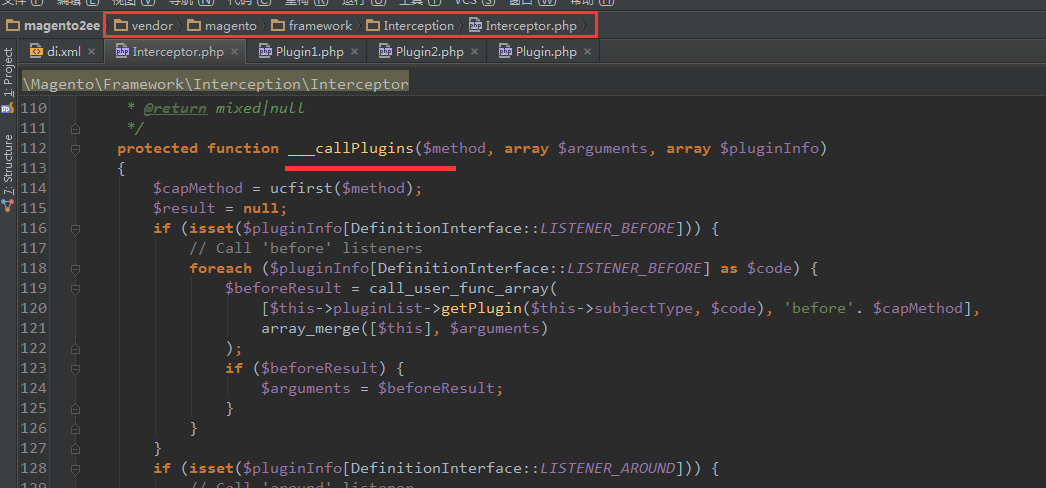
First, the interceptor class that makes this all possible is generated code, which means
if the class you’re observing with a plugin
changes — you’ll need to regenerate the interceptor.
如果需要观察plugin改变带来的变化,需要重新生成拦截器Next, with plugins (vs. rewrites) you lose the ability to change the behavior of a protected
method. Some will see this as a
con (less flexibility), and some will see
this a pro (respecting the protected access levels). It you need to change the behavior
of a protected method, class preferences or
argument replacement are more suitable tools.
如果 需要改变 protected 方法,class preference 或者 argument replacement是更好的选择。






















 2194
2194

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








