1 概述
在很多情况下,主线程创建并启动子线程,如果子线程中要进行大量的耗时运算,主线程往往将早于子线程结束,这时如果主线程想等待子线程执行完成后再结束,例如子线程处理一个数据,主线程要取到这个数据中的值,这个时候要用到join()方法。join()方法的作用是等待线程对象销毁。
2 学习join()前的铺垫
在介绍join方法前,先看一个实现。
public class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run(){
try{
int secondValue = (int) (Math.random() * 10000);
System.out.println(secondValue);
Thread.sleep(secondValue);
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class Run1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread t1 = new MyThread();
t1.start();
//Thread.sleep(?);
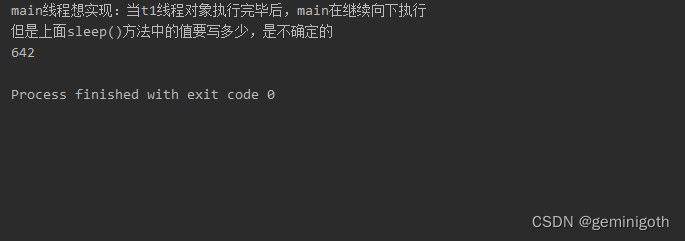
System.out.println("main线程想实现:当t1线程对象执行完毕后,main在继续向下执行");
System.out.println("但是上面sleep()方法中的值要写多少,是不确定的");
}
}
3 用join方法解决上面的问题
使用join方法可以解决上面的问题。
public class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run(){
try{
int secondValue = (int)(Math.random() * 10000);
System.out.println(secondValue);
Thread.sleep(secondValue);
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class Run1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
MyThread t1 = new MyThread();
t1.start();
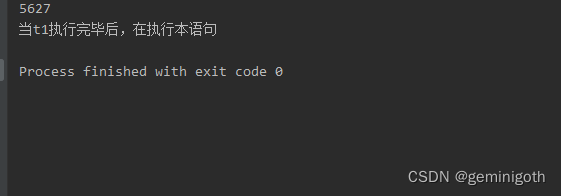
t1.join();
System.out.println("当t1执行完毕后,在执行本语句");
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
方法join的作用是使所属的线程对象x正常执行run方法中的任务,而使当前线程z进行无限期的阻塞,等待线程x销毁后再继续执行线程z后面的代码。也就是说,join方法具有串联执行的作用。另外,join也支持多个线程的等待,示例如下:
public class Test1 {
static int number1 = 0;
static int number2 = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t1 = new Thread() {
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
number1 = 1000;
};
};
Thread t2 = new Thread() {
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
number2 = 2000;
};
};
long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
t1.start();
t2.start();
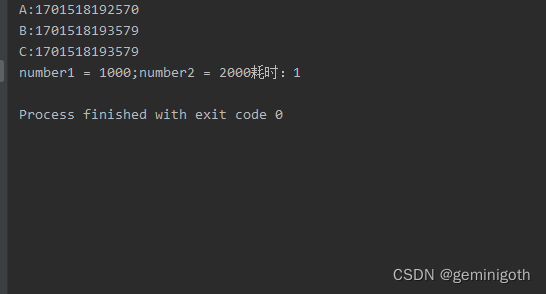
System.out.println("A:" + System.currentTimeMillis());
t1.join();
System.out.println("B:" + System.currentTimeMillis());
t2.join();
System.out.println("C:" + System.currentTimeMillis());
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("number1 = " + number1 + ";number2 = " + number2 + "耗时:" + (endTime - beginTime)/1000);
}
}
join方法具有是线程排队运行的效果,有些类似synchronzied同步的运行效果,但是它们的区别在于,join()在内部使用wait方法进行等待,会释放锁,而synchronzied关键字一直持有锁。
4 join和interrupt出现异常
在join方法运行过程中,如果当前线程对象被中断,则当前线程出现异常。
public class ThreadA extends Thread{
@Override
public void run(){
for (int i = 0; i < Integer.MAX_VALUE; i++) {
String s = new String();
Math.random();
}
}
}
public class ThreadB extends Thread{
@Override
public void run(){
try {
ThreadA a = new ThreadA();
a.start();
a.join();
System.out.println("线程B在run end时打印了");
}catch (InterruptedException e){
System.out.println("线程B在catch中打印了");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class ThreadC extends Thread{
private ThreadB threadB;
public ThreadC(ThreadB threadB) {
this.threadB = threadB;
}
@Override
public void run(){
threadB.interrupt();
}
}
public class Run1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
ThreadB b = new ThreadB();
b.start();
Thread.sleep(2000);
ThreadC c = new ThreadC(b);
c.start();
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
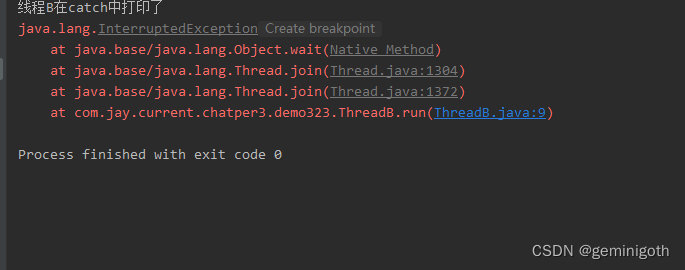
可见,如果方法join与interrupt彼此遇到,程序会出现异常,无论它们执行的顺序是怎样的。
5 join(long)的使用
join(long)中的参数用于设定最长的等待时间,当线程小于long时间销毁或long时间到达并重新获得了锁时,当前线程会继续向后运行。如果没有重新获得锁,线程会一直尝试,直到获得锁为止。
public class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run(){
try {
System.out.println("开始执行run方法时间:" + Utils.data(System.currentTimeMillis()));
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println("结束执行run方法时间:" + Utils.data(System.currentTimeMillis()));
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class Run1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
MyThread thread = new MyThread();
thread.start();
System.out.println("main方法开始执行时间:"+ Utils.data(System.currentTimeMillis()));
thread.join(1000);
System.out.println("main方法结束执行时间:" + Utils.data(System.currentTimeMillis()));
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
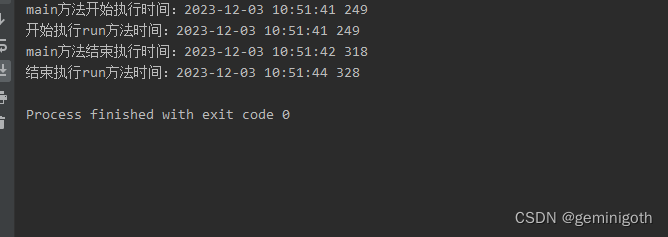
从运行结果看,run方法执行了3秒,main方法赞提暂停了1秒。
继续新建一个Run2.java运行类,把join(1000)改成8000毫秒
public class Run2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
MyThread thread = new MyThread();
thread.start();
System.out.println("main方法开始执行时间:"+ Utils.data(System.currentTimeMillis()));
thread.join(8000);
System.out.println("main方法结束执行时间:" + Utils.data(System.currentTimeMillis()));
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
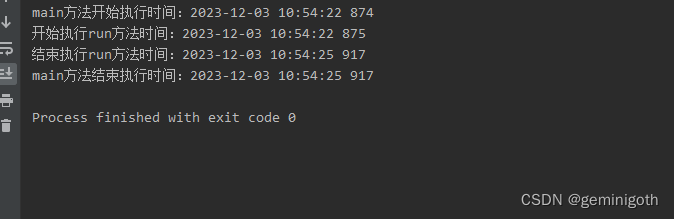
从运行结果看,run方法执行了3秒,main方法暂停了3秒 。根据以上案例可以分析出,join(long)方法和sleep(long)具有相似的功能,就是使当前线程暂停指定的时间。两者的区别是:join(long)暂停的时间是可变的,取决于线程是否销毁,而sleep(long)暂停的时间是固定的。








 本文介绍了Java中join()方法的使用,包括如何解决主线程等待子线程执行完毕的问题,join()方法的工作原理,以及它与sleep和synchronized的异同。同时讨论了join方法与interrupt的异常情况和join(long)的可变等待时间特性。
本文介绍了Java中join()方法的使用,包括如何解决主线程等待子线程执行完毕的问题,join()方法的工作原理,以及它与sleep和synchronized的异同。同时讨论了join方法与interrupt的异常情况和join(long)的可变等待时间特性。

















 377
377

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










