1.概述
Linux进程间通信:IPC,即Interprocess Communication,就是两个或多个进程间进行数据传输。
Linux中有以下几种通信方法:
①管道
②命名管道
③信号量
④内存映射
⑤共享内存
⑥消息队列
以下均以伪代码来进行解释复习
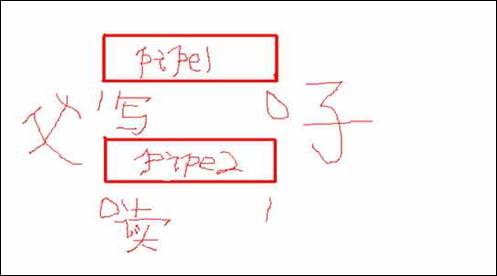
2.管道(pipe)
2.1聊天程序伪代码
| 1 | int pipe1_fd[2], pipe2_fd[2]; |
| 2 | char parent_buf[256], child_buf[256]; |
| 3 | |
| 4 | if(pipe(pipe1_fd)<0) |
| 5 | error; |
| 6 | if(pipe(pipe2_fd)<0) |
| 7 | error; |
| 8 | if(fork()==0) |
| 9 | {//child |
| 10 | close(pipe1_fd[1]);//对于子进程来说父亲的写是不用的 |
| 11 | close(pipe2_fd[0]);//对于子进程来说父亲的读是不用的 |
| 12 | while(1) |
| 13 | { |
| 14 | len = read(pipe1_fd[0], child_buf, 255);//读父亲写的数据,pipe1的读端 |
| 15 | printf("child_RECEIVE_father: %s/n", child_buf); |
| 16 | printf("childspeak: "); |
| 17 | fgets(child_buf, 256, stdin); |
| 18 | write(pipe2_fd[1], child_buf, strlen(child_buf));//从pipe2写入数据 |
| 19 | sleep(1); |
| 20 | } |
| 21 | close(pipe1_fd[0]);//子进程退出前关掉自己的写端、读端 |
| 22 | close(pipe2_fd[1]); |
| 23 | exit(); |
| 24 | } |
| 25 | else |
| 26 | { //parent |
| 27 | close(pipe1_fd[0]);//对于父进程来说子进程的读、写端是不用的 |
| 28 | close(pipe2_fd[1]); |
| 29 | while (1) |
| 30 | { |
| 31 | printf("fatherspeak: "); |
| 32 | fgets(parent_buf, 256, stdin); |
| 33 | if (strncmp(parent_buf,"quit", 4) == 0) |
| 34 | { |
| 35 | close(pipe1_fd[1]); |
| 36 | close(pipe2_fd[0]); |
| 37 | exit(0); |
| 38 | } |
| 39 | write(pipe1_fd[1],parent_buf,strlen(parent_buf));//父亲写数据,从pipe1 |
| 40 | sleep(1); |
| 41 | len = read(pipe2_fd[0],parent_buf,255);//父亲读数据,从pipe2 |
| 42 | parent_buf[len] = '/0'; |
| 43 | printf("father_RECEIVE_child: %s/n", parent_buf); |
| 44 | } |
| 45 | close(pipe1_fd[1]); |
| 46 | close(pipe2_fd[0]); |
| 47 | wait(&child_status); |
| 48 | exit(); |
| 49 | } |
2.2分析
①管道只能在有公共祖先的进程间使用。
②一个进程项管道中写的内容被管道另一端的进程读出。
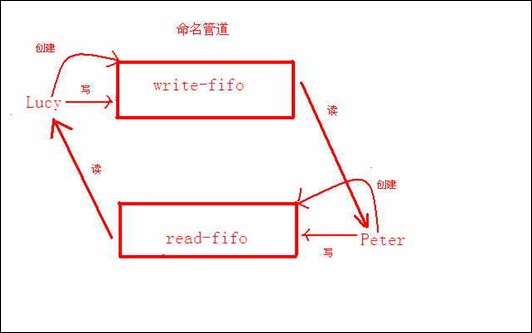
3.命名管道(FIFO)
3.1源代码
Lucy.c
| 1 | #include <sys/types.h> |
| 2 | #include <sys/stat.h> |
| 3 | #include <string.h> |
| 4 | #include <stdio.h> |
| 5 | #include <errno.h> |
| 6 | #include <fcntl.h> |
| 7 | #include <unistd.h> |
| 8 | //lucy.c |
| 9 | int main(void) |
| 10 | { |
| 11 | char write_fifo_name[] = "write-fifo";//lucy创建的命名管道 |
| 12 | char read_fifo_name[] = "read-fifo"; //是Peter创建的 |
| 13 | int write_fd, read_fd; |
| 14 | char buf[256]; |
| 15 | int len; |
| 16 | struct stat stat_buf; |
| 17 | |
| 18 | int ret = mkfifo(write_fifo_name, S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR);//创建函数 |
| 19 | if ( ret == -1) { |
| 20 | printf("Fail to create FIFO %s: %s", write_fifo_name, strerror(errno)); |
| 21 | exit(-1); |
| 22 | } |
| 23 | |
| 24 | write_fd = open(write_fifo_name, O_WRONLY); //lucy创建的命名管道,要用之前要打开 |
| 25 | if (write_fd == -1) { |
| 26 | printf("Fail to open FIFO %s: %s", write_fifo_name, strerror(errno)); |
| 27 | exit(-1); |
| 28 | } |
| 29 | |
| 30 | while ((read_fd = open(read_fifo_name, O_RDONLY)) == -1) {//等待Peter创建命名管道,(等Peter在线) |
| 31 | sleep(1); |
| 32 | } |
| 33 | while (1) { |
| 34 | printf("Lucy: "); |
| 35 | fgets(buf, 256, stdin); |
| 36 | buf[strlen(buf)-1] = '/0'; |
| 37 | if (strncmp(buf,"quit", 4) == 0) { |
| 38 | close(write_fd); |
| 39 | unlink(write_fifo_name); |
| 40 | close(read_fd); |
| 41 | exit(0); |
| 42 | } |
| 43 | write(write_fd, buf, strlen(buf));//lucy向 "write-fifo" 写信息 |
| 44 | len = read(read_fd, buf, 256); //只有读到东西才往下面走,否则一直等着读东西 |
| 45 | if ( len > 0) { |
| 46 | buf[len] = '/0'; |
| 47 | printf("Peter: %s/n", buf); |
| 48 | } |
| 49 | } |
| 50 | } |
Peter.c (略)
3.2分析
①命名管道创建之后,还需要打开。用open函数。
②一个FIFO被读模式打开,就一定要被其它进程以写模式打开,否则该进程一直阻塞。






















 884
884











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








