动态内存分配
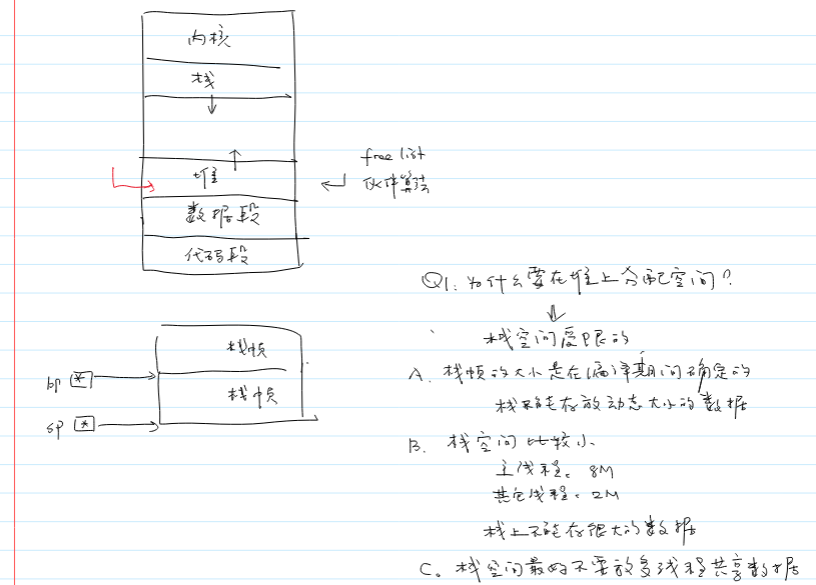
为什么要在堆上分配空间?
1.栈空间受限的比较小,栈帧的大小是在编译期间确定的
2.在c中栈无法存放动态大小的数据
3.栈空间最好不要存放多线程共享数据:栈空间独立性即每个线程都有自己的栈地址,栈空间是私有的
如何申请堆空间
malloc不对内存块进行清零,而calloc对内存块进行清零

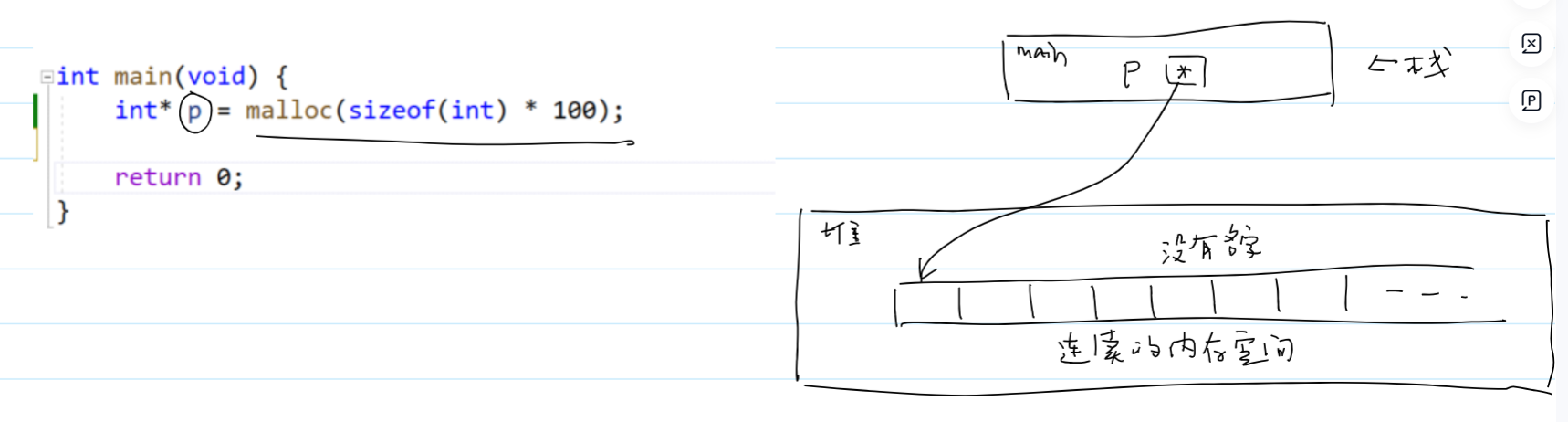
c中可以直接写int* p=malloc(sizeof(int)*100) ,
但c++中要自己将void*转化成int*---->int* p=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*100)

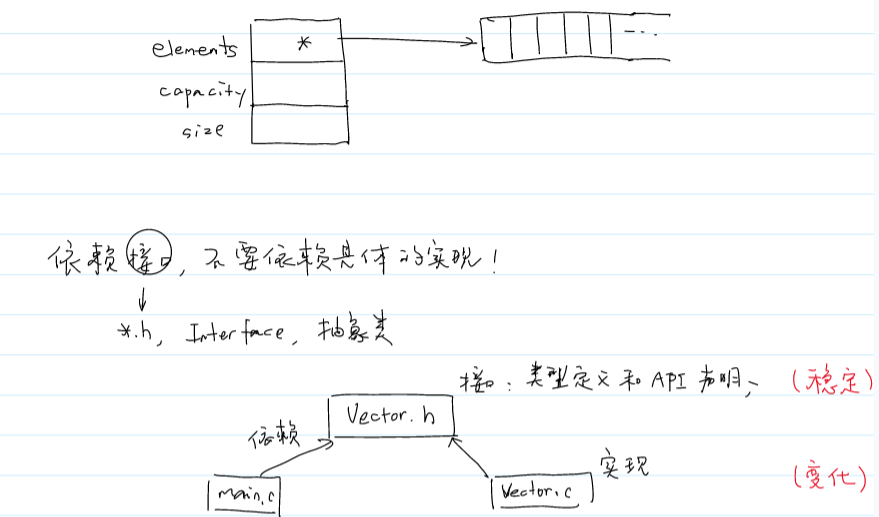
动态数组

为什么上图int arr1[n]会报错?
因为上面的内容是存在栈中的,应该在编译期间就确定大小,而int arr1[n]中的n是变的,在运行时确定大小,所以会报错
模型
realloc(和上两个一样,失败返回空指针)
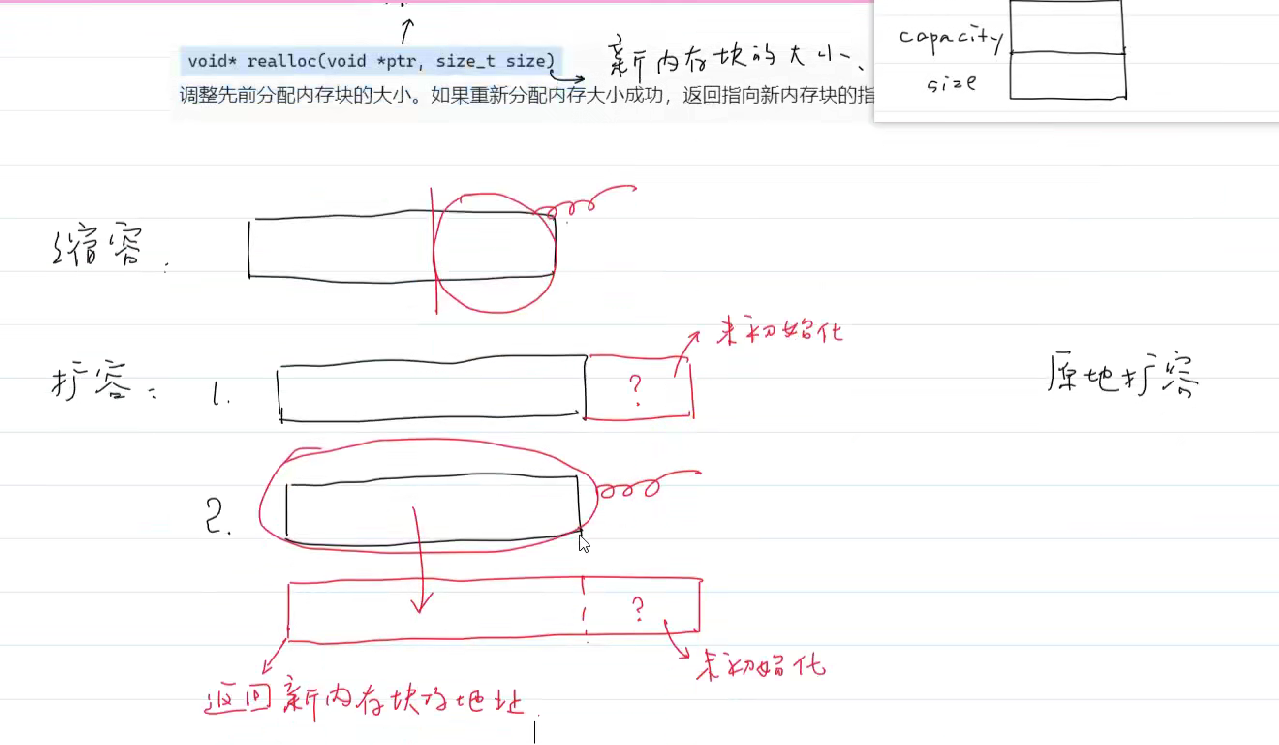
创建销毁动态数组 及添加元素
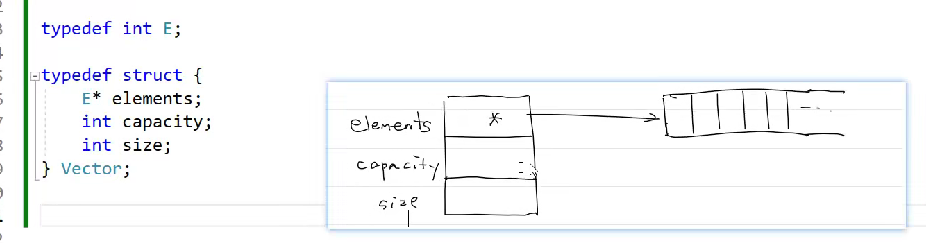
上图结构体和数组都是用malloc在堆中实现
//创建动态数组
Vector* vector_create(void){
Vector* v=malloc(sizeof(Vector));
if(v==MULL){
exit(1);
}
v->elements=malloc(sizeof(E)*8); //E* p=malloc(sizeof(E)*8);
if(v->elements==NULL){ //p==NULL
free(v);
exit(1);
} //v->elements=p;
v->capacity=8;
v->size=0;
}
//析构函数
void vector_destroy(Vector* v){
//释放是按声明的相反顺序释放,先申请v,在申请p(v->elements),所以先释放p
free(v->elements);
free(v);
}
void grow_capacity(Vector* v){
int new_capacity=v->capacity<1024 ? v->capacity<<1 : v->capacity+1024;
E* p=realloc(v->elements,new->capacity*sizeof(E));
if(p!=NULL){
exit(1);
}
v->elements=p;
v->capacity=new_capacity;
}
//往数组添加元素
void push_back(Vector* v,E val){
//判断是否需要扩容
if(v->size==v->capacity){
grow_capacity(v);
}
v->elements[v->size]==val;
v->size++;
}
//单元测试
int main(void){
Vector* v=vector_create();
for(int i=0;i<200;i++){
push_back(v,i);
}
vector_destory(v);
return 0;
}
free(释放内存空间)
垃圾回收器
减轻程序员负担
不确定因素--->stop the world--->不适合实时系统(必须在某个确定时间内完成某个业务)
没有垃圾回收器
c: free
c++: 析构函数,RALL,智能指针
Rust: 所有权机制(生命周期)
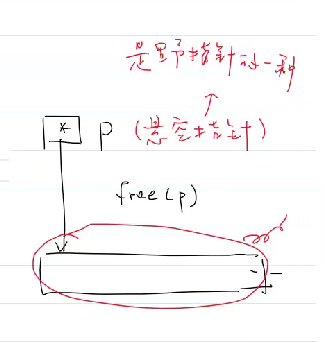
int main(void){
int* p=malloc(sizeof(int)*100); //malloc不会初始化,失败返回空指针
free(p); //不会改变p的值(存的地址),只是将p指向的内存空间释放,这时p是悬空指针
}
调用
free()释放内存后,原内存区域的数据不会被主动清除或重置,而是可能继续保留原有内容,直到被后续分配操作覆盖。这意味着从程序逻辑层面,访问已释放的内存属于“悬空指针”行为,可能导致不可预知的错误。
问题
1.double free
int main(void){
int* p=malloc(sizeof(int)*100);
free(p);
free(p); //double free
}
2.use after free
int main(void){
int* p=malloc(sizeof(int)*100);
free(p);
p[0]=10; //use after free
}
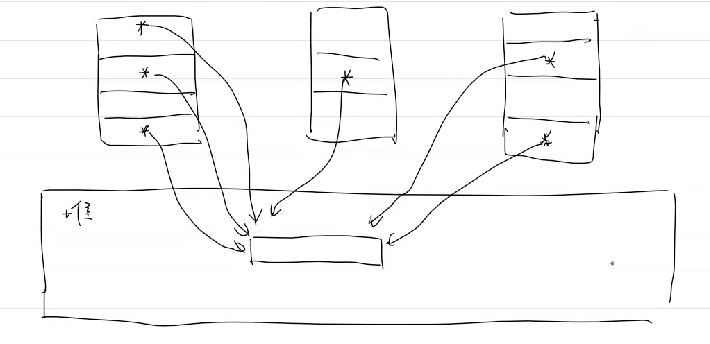
结论:当堆中空间不再使用时,应当有且仅有一次free(),这很难做到,如上图因为栈是每个线程都有,故栈中指针指向同一个堆中空间,巨容易发生冲突
动态分配的结构体(链表)
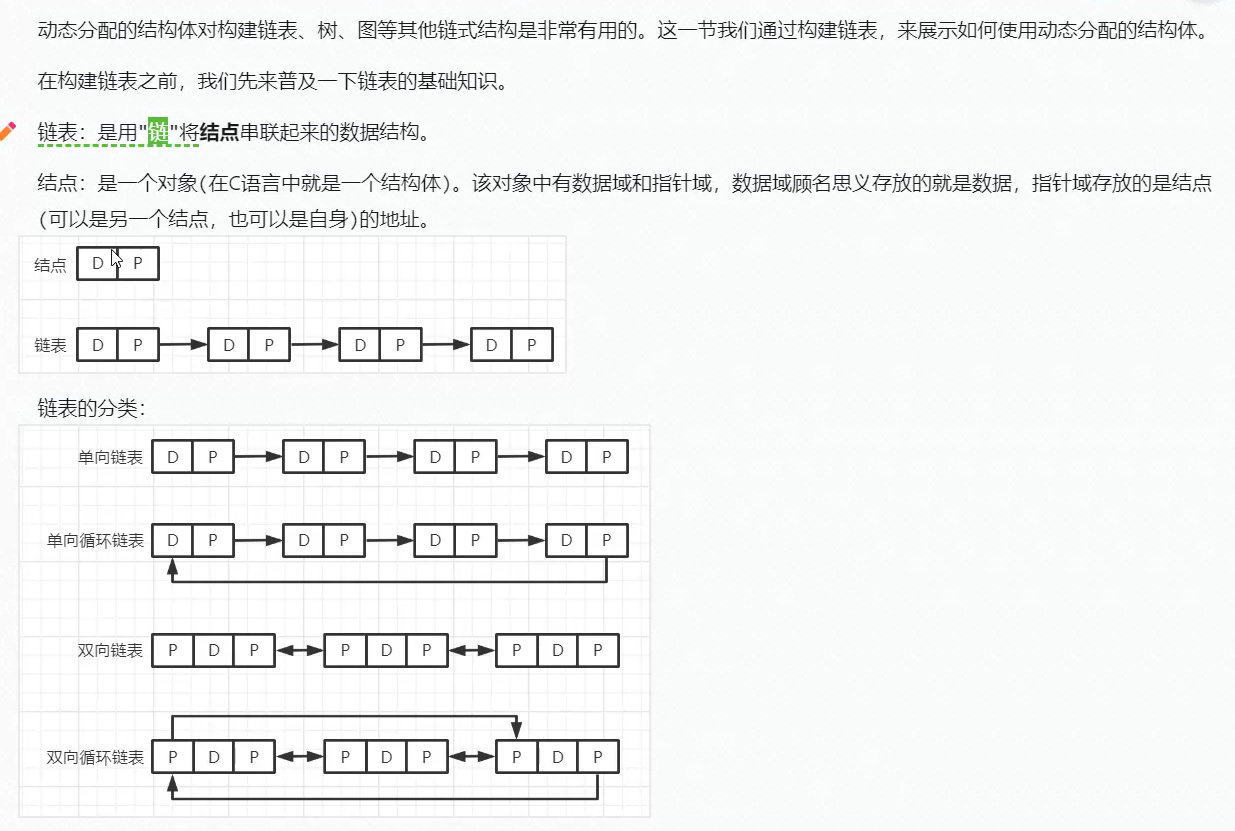
typedef struct node{
int data;
struct node* next;
} Node;
Node* addNode(Node* head,int data){
Node* s=malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(s==NULL){
exit(1);
} //注意申请堆空间记得判一下空 即不成功
s->next=head;
s->data=data;
head=s;
return head;
}
//不带头结点的头插法
int main(void){
Node* head = NULL;
head=addNode(head,1);
head=addNode(head,2);
head=addNode(head,3);
head=addNode(head,4); //4-->3-->2-->1
return 0;
}
//上述代码是错误的,因为head在main函数中,要想修改head的值要传递head地址而不是head值
typedef struct node{
int data;
struct node* next;
} Node;
Node* addNode(Node** phead,int data){
Node* s=malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(s==NULL){
exit(1);
} //注意申请堆空间记得判一下空 即不成功
s->next=*head;
s->data=data;
*phead=s;
return *phead;
}
//不带头结点的头插法
int main(void){
Node* head = NULL;
head=addNode(&head,1);
head=addNode(&head,2);
head=addNode(&head,3);
head=addNode(&head,4); //4-->3-->2-->1
return 0;
}
二级指针(指向指针的指针)
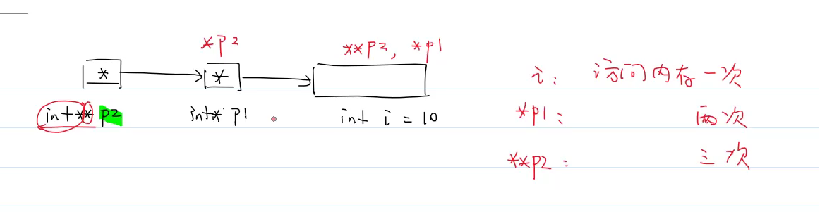
传一级指针还是传二级指针?
你想修改哪个变量就传哪个变量的地址,如上例修改head的值就传head的地址(二级指针 )
函数指针
语法(how)
变量声明:int (*p) (int , int);
值 :foo , &foo
通过函数指针调用函数:p(a,b); (*p)(a,b);
int add(int a,int b){
return a+b;
}
int mul(int a,int b){
return a*b;
}
int main(void){
int (*p1) (int,int)=add; //声明指针变量并赋值,函数和数组相似,用函数名代替函数地址
int (*p2) (int , int)=&mul;
int m=p1(3,4); //调用也是,可以直接不解引用直接用指针变量名
int n=(*p2)(3,4);
return 0;
}
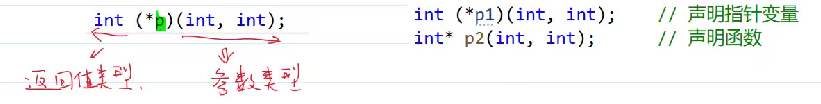 注意:int* p2(int,int)不是函数指针而是指针函数(返回值为int*的函数)
注意:int* p2(int,int)不是函数指针而是指针函数(返回值为int*的函数)
作用(why)
1.函数式编程(传递函数,返回函数),函数指针支持函数式编程
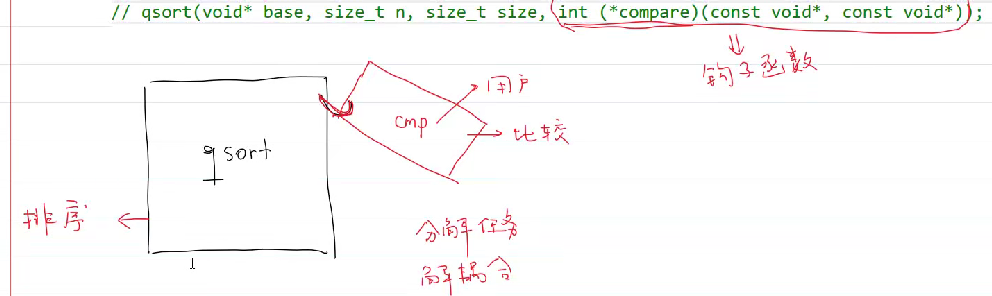
分解任务,解耦合
2.编写非常通用的函数(功能非常强大的函数)
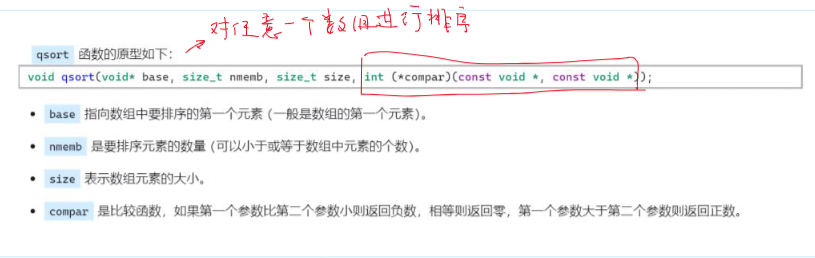
qsort (非常通用的排序函数)
 数组名作为参数传递会退化成指向它第一个元素的指针 !!!!!!!
数组名作为参数传递会退化成指向它第一个元素的指针 !!!!!!!
qsort底层原理是快速排序,比较规则是通过用户传递的函数指针cmp进行!!!!
qsort案例

typedef struct{
int id;
char name[20];
char gender;
int chinese;
int math;
int english
} Student
int cmp (const void* p1,const void* p2){
Student* s1=p1;
Student* s2=p2;
int total1=s1->chinese+s1->math+s1->english;
int total2=s2->chinese+s2->math+s2->english;
if(total1 != total2){
return total2 - total1;
}
if(s1->chinese != s2->chinese){
return total2 - total1;
}
if(s1->math != s2->math){
return total2 - total1;
}
return s1->id - s2->id;
}
void print_stu(Student* s){
printf("%d %s %c %d %d %d",s->id......);
}
int main(void){
Student students[5];
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
scanf("%d%s %c%d%d%d",
&students[i].id,
students[i].name,
&students[i].gender,
&students[i].chinese,
&students[i].math,
&students[i].english,);
}
qsort(students,5,sizeof(Student),cmp); //默认按从小到大排序
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
print_stu(&student[i]); //print_stu(student+i);
}
}





















 292
292

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








