策略模式(Strategy Pattern),定义了一系列算法,将每一种算法封装起来并可以相互替换使用,策略模式让算法独立于使用它的客户应用而独立变化。
策略模式属于行为型模式的一种。
说白了,策略模式就是将某一行为的不同实现方式使用接口与一组实现类的方式单独封装出来,然后使用聚合的方式应用于使用它的外部程序。
使用策略的外部程序直接面对的是策略的接口,并不关心策略是怎样实现的,这样也符合面向接口编程的设计原则,但是客户端程序需要知道各种具体策略并且了解各种具体
策略的功能。
接下来我们看例子:
某商场为迎接活动,特推出三种促销方式,其一,A类商品8折促销策略,其二,B类商品满1000减200促销策略,其三,C类商品200元以上部分打八折促销策略。接下来
我们使用策略模式来设计一下这个程序:
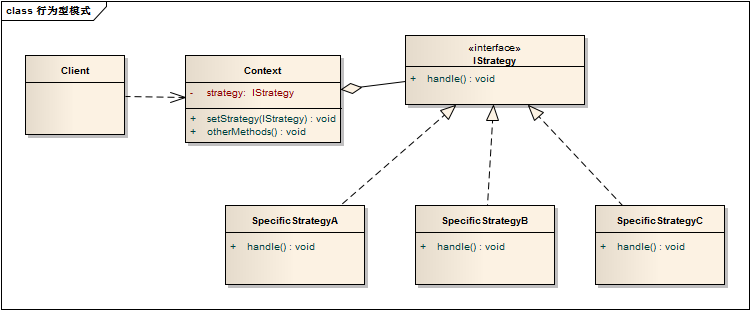
首先我们先参考一下策略模式的结构图
接下来很简单了,我们也没必要再设计这个商品促销程序的类图了,直接照着写代码就可以了:
策略类:
package com.demo.strategy;
/**
* 策略接口
*
* @author haicheng.cao
*
*/
public interface IStrategy {
/**
* 计算实际价格方法
*
* @param consumePrice
* 消费金额
* @return
*/
public double realPrice(double consumePrice);
}
package com.demo.strategy;
/**
* 打八折商品促销策略
*
* @author
*
*/
public class RebateStrategy implements IStrategy {
private final double rate;
/**
* 构造方法设置打折率
*/
public RebateStrategy() {
this.rate = 0.8;
}
/**
* 计算实际价格方法
*
* @param consumePrice
* 消费金额
* @return
*/
public double realPrice(double consumePrice) {
return consumePrice * this.rate;
}
}
package com.demo.strategy;
/**
* 满200,高于200部分打八折 商品促销策略
*
* @author
*
*/
public class PromotionalStrategy implements IStrategy {
/**
* 计算实际价格方法
*
* @param consumePrice
* 消费金额
* @return
*/
public double realPrice(double consumePrice) {
if (consumePrice > 200) {
return 200 + (consumePrice - 200) * 0.8;
} else {
return consumePrice;
}
}
}
package com.demo.strategy;
/**
* 满1000减200 商品促销策略
*
* @author
*
*/
public class ReduceStrategy implements IStrategy {
/**
* 计算实际价格方法
*
* @param consumePrice
* 消费金额
* @return
*/
public double realPrice(double consumePrice) {
if (consumePrice >= 1000) {
return consumePrice - 200;
} else {
return consumePrice;
}
}
}
package com.demo.context;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import com.demo.strategy.IStrategy;
/**
* 上下文环境
*
* @author
*
*/
public class Context {
// 当前策略
private IStrategy strategy;
// 设置当前策略
public void setStrategy(IStrategy strategy) {
this.strategy = strategy;
}
// 使用策略计算价格
public double cul(double consumePrice) {
// 使用具体商品促销策略获得实际消费金额
double realPrice = this.strategy.realPrice(consumePrice);
// 格式化保留小数点后1位,即:精确到角
BigDecimal bd = new BigDecimal(realPrice);
bd = bd.setScale(1, BigDecimal.ROUND_DOWN);
return bd.doubleValue();
}
}
客户端类:
package com.demo;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* 客户端应用程序
*
* @author
*
*/
public class Client {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建上下问环境对象实例
// Context context = new Context();
// 随机数对象
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
// 产生随机数的方式判断使用何种促销策略
int x = random.nextInt(3);
// 消费价格也是由随机数产生的(不能为0)
double consumePrice = 0;
while ((consumePrice = random.nextInt(2000)) == 0) {
}
double realPrice = consumePrice;
switch (x) {
case 0:
// 打八折商品
// context.setStrategy(new RebateStrategy());
realPrice = consumePrice * 0.8;
break;
case 1:
// 满200,高于200部分打八折 商品
// context.setStrategy(new PromotionalStrategy());
if (consumePrice > 200) {
realPrice = 200 + (consumePrice - 200) * 0.8;
}
break;
case 2:
// 满1000减200 商品
// context.setStrategy(new ReduceStrategy());
if (consumePrice >= 1000) {
realPrice = consumePrice - 200;
}
break;
}
System.out.print("【"
+ (x == 0 ? "打八折" : (x == 1 ? "高于200部分打八折"
: (x == 2 ? "满1000减200" : ""))) + "】商品:");
System.out.println("原价:" + consumePrice + " - 优惠后价格:" + realPrice);
}
}
}
接下来,我们去JDK中寻找一下策略模式的应用:
Comparator<T>类想必大家很熟悉了,Collections的sort方法就会传进去一个比较器,这里,Comparator类就是一个抽象策略角色,而Collections就是应用此策略的外部环境
角色,我们写一个简单的例子看一下他的使用:
package com.hirain.chc;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
public class SortDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
list.add(1);
list.add(100);
list.add(10);
Collections.sort(list);
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(list.get(i));
}
}
}
package com.hirain.chc;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class DescComparator implements Comparator<Integer>{
/**
* 返回正整数o2在前,返回负整数o1在前,返回0默认顺序。
* 后一个数小。
* 本方法实现的是逆序排列
*/
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
if (o1 > o2) {
return -1;
} else if (o1 == o2) {
return 0;
} else {
return 1;
}
}
}
package com.hirain.chc;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
public class SortDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
list.add(1);
list.add(100);
list.add(10);
Collections.sort(list);
Comparator<Integer> c = new DescComparator();
Collections.sort(list, c);
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(list.get(i));
}
}
}
本章完!























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








