单件模式:用来创建独一无二的,只能有一个实例的对象。将使用和构造分离。
线程池(threadpool)、缓存(cache)、对话框、处理器、注册表对象、日志对象、打印机驱动程序对象、显卡设备驱动程序对象。
单件模式确保一个类之哟一个实例,并提供一个全局访问点。
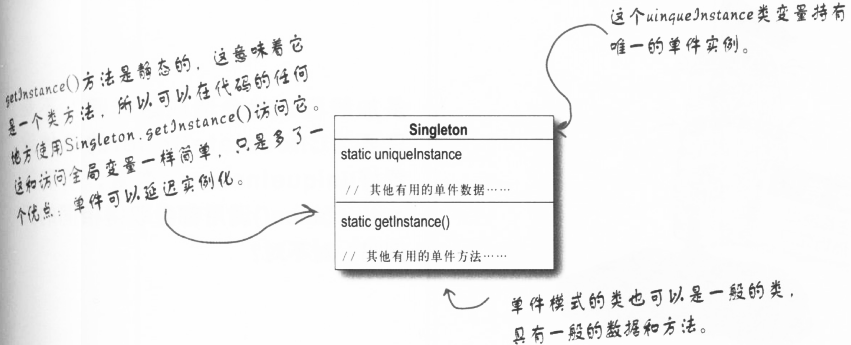
意图: 希望对象只有一个实例,单没有控制对象实例化的全局对象。还希望确保所有实体使用该对象相同的实例,无需将引用传给它们。
问题来了(多线程):
Double-Checked Locking 双重加锁模式
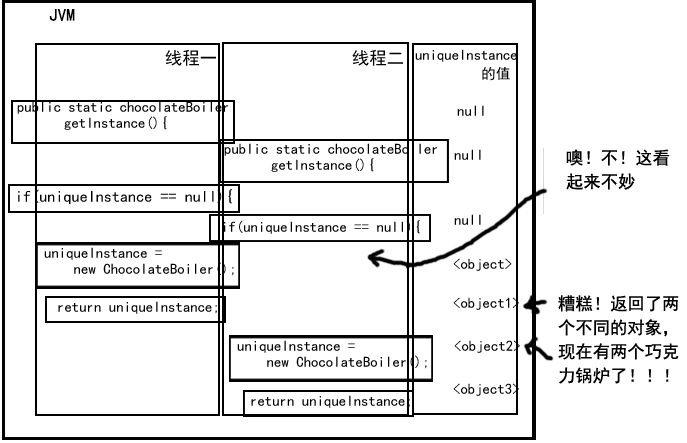
在C++中,可能会导致内存泄漏—-创建了两个对象,销毁时,只销毁了其中一个。
线程同步:
public class Singleton{
// 静态初始化器(static initializer)中创建单件,保证了线程安全。
private static Singleton uniqueInstance;
private Singleton(){}
public static synchronized Singleton getInstance(){
if(uniqueInstance == null)
uniqueInstance = new Singleton();
return uniqueInstance;
}
}但是每次执行都要先同步,判断对象是否存在,这样会严重影响性能。
public class Singleton{
private volatile static Singleton uniqueInstance;
private Singleton(){}
private static Singleton getInstance(){
if(uniqueInstance = null){
//synchronized (Singleton.class){
synchronized (this){
if (uniqueInstance = null)
uniqueInstance = new Singleton();
}
}
}
}当两个线程都运行到if(uniqueInstance = null)时候,都会执行下一句。等待同步。此句最多执行一次。(《Effective C++》、《More Effective C++》)
C++ Singleton design pattern
class S
{
public:
static S& getInstance()
{
static S instance; // Guaranteed to be destroyed.
// Instantiated on first use.
return instance;
}
private:
S() {}; // Constructor? (the {} brackets) are needed here.
// C++ 03
// ========
// Dont forget to declare these two. You want to make sure they
// are unacceptable otherwise you may accidentally get copies of
// your singleton appearing.
S(S const&); // Don't Implement
void operator=(S const&); // Don't implement
// C++ 11
// =======
// We can use the better technique of deleting the methods
// we don't want.
public:
S(S const&) = delete;
void operator=(S const&) = delete;
// Note: Scott Meyers mentions in his Effective Modern
// C++ book, that deleted functions should generally
// be public as it results in better error messages
// due to the compilers behavior to check accessibility
// before deleted status
};单例模式(C++):
class StringSingleton
{
public:
// Some accessor functions for the class, itself
std::string GetString() const {return mString; }
void SetString( const std::string & newString) { mString = newStr ; }
// The magic function, which allows access to the class from anywhere
// To get the value of the instance of the class, call:
// StringSingleton::Instance().GetString();
static StringSingleton &Instance()
{
// This line only runs once, thus creating the only instance in existence
static StringSingleton *instance = new StringSingleton;
// dereferencing the variable here, saves the caller from having to use
// the arrow operator, and removes temptation to try and delete the
// returned instance.
return *instance; // always returns the same instance
}
private:
// We need to make some given functions private to finish the definition of the singleton
StringSingleton(){} // default constructor available only to members or friends of this class
// Note that the next two functions are not given bodies, thus any attempt
// to call them implicitly will return as compiler errors. This prevents
// accidental copying of the only instance of the class.
StringSingleton(const StringSingleton &old); // disallow copy constructor
const StringSingleton &operator=(const StringSingleton &old); //disallow assignment operator
// Note that although this should be allowed,
// some compilers may not implement private destructors
// This prevents others from deleting our one single instance, which was otherwise created on the heap
~StringSingleton(){}
private: // private data for an instance of this class
std::string mString;
}互斥锁(C++)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/* Place holder for thread synchronization mutex */
class Mutex
{ /* placeholder for code to create, use, and free a mutex */
};
/* Place holder for thread synchronization lock */
class Lock
{ public:
Lock(Mutex& m) : mutex(m) { /* placeholder code to acquire the mutex */ }
~Lock() { /* placeholder code to release the mutex */ }
private:
Mutex & mutex;
};
class Singleton
{ public:
static Singleton* GetInstance();
int a;
~Singleton() { cout << "In Destructor" << endl; }
private:
Singleton(int _a) : a(_a) { cout << "In Constructor" << endl; }
static Mutex mutex;
// Not defined, to prevent copying
Singleton(const Singleton& );
Singleton& operator =(const Singleton& other);
};
Mutex Singleton::mutex;
Singleton* Singleton::GetInstance()
{
Lock lock(mutex);
cout << "Get Instance" << endl;
// Initialized during first access
static Singleton inst(1);
return &inst;
}
int main()
{
Singleton* singleton = Singleton::GetInstance();
cout << "The value of the singleton: " << singleton->a << endl;
return 0;
}





















 1601
1601

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








