系列文章
目录
2.14 startWindowManagerService
2.15 WindowManagerService.main
2.21 InputDispatcherThread::threadLoop
2.22 InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce
2.31 registerDeviceForEpollLocked
2.37 handleConfigurationChangedLocked
2.38 notifyInputDevicesChanged
2.39 QueuedInputListener::flush
2.40 NotifyConfigurationChangedArgs::notify
2.41 notifyConfigurationChanged
2.44 dispatchConfigurationChangedLocked
2.45 runCommandsLockedInterruptible
2.46 doNotifyConfigurationChangedInterruptible
2.47 notifyConfigurationChanged
2.48 notifyConfigurationChanged
4.14 startWindowManagerService
4.15 WindowManagerService.main
4.21 InputDispatcherThread::threadLoop
4.22 InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce
4.31 registerDeviceForEpollLocked
4.37 handleConfigurationChangedLocked
4.38 notifyInputDevicesChanged
4.39 QueuedInputListener::flush
4.40 NotifyConfigurationChangedArgs::notify
4.41 notifyConfigurationChanged
4.44 dispatchConfigurationChangedLocked
4.45 runCommandsLockedInterruptible
4.46 doNotifyConfigurationChangedInterruptible
4.47 notifyConfigurationChanged
4.48 notifyConfigurationChanged
5.4 InputDispatcherConfiguration
5.8 InputDeviceConfigurationFileType
1.简介
IMS启动的主要步骤:
1.首先,在systemserver启动中创建了java层的InputManagerService对象。
2.在framwork层的InputManagerService构造函数中,创建了NativeInputManager对象,由此通过jni进入native层。
3.在NativeInputManager对象中创建EventHub类对象,此对象通过epoil和notify监听/dev/input路径下是否有设备添加和删除事件
4.在NativeInputManager对象中创建InputManager类对象,InputManager类对象中创建了InputDispatcher和InputReader对象,并创建了分发线程和读取线程。
5.启动WMS对象,将IMS引用传入WMS中,这样WMS可以实时更新窗口信息到IMS中,IMS又保存着MWS实现的回调类,将用于派发消息到WMS。
6.先启动分发线程,分发线程无消息陷入休眠,然后启动读取线程。
7.因为是开机刚启动,因此要扫描/dev/input的所有设备节点,并读取设备并配置。每扫描完成一个设备,就生成对应的add事件,当设备全部扫描完成后,则生成扫描完成事件。此时是在在读取线程的mEventHub->getEvents函数中完成的。
8.处理设备add事件,即读取所有设备信息,生成对应的InputDevice对象,并配置好inputmapper。
9.处理设备完成扫描事件。唤醒分发线程,先通知java层监听设备变化的listener,然后派发消息到WMS,告诉系统设备已经完成配置。
1.1 类图
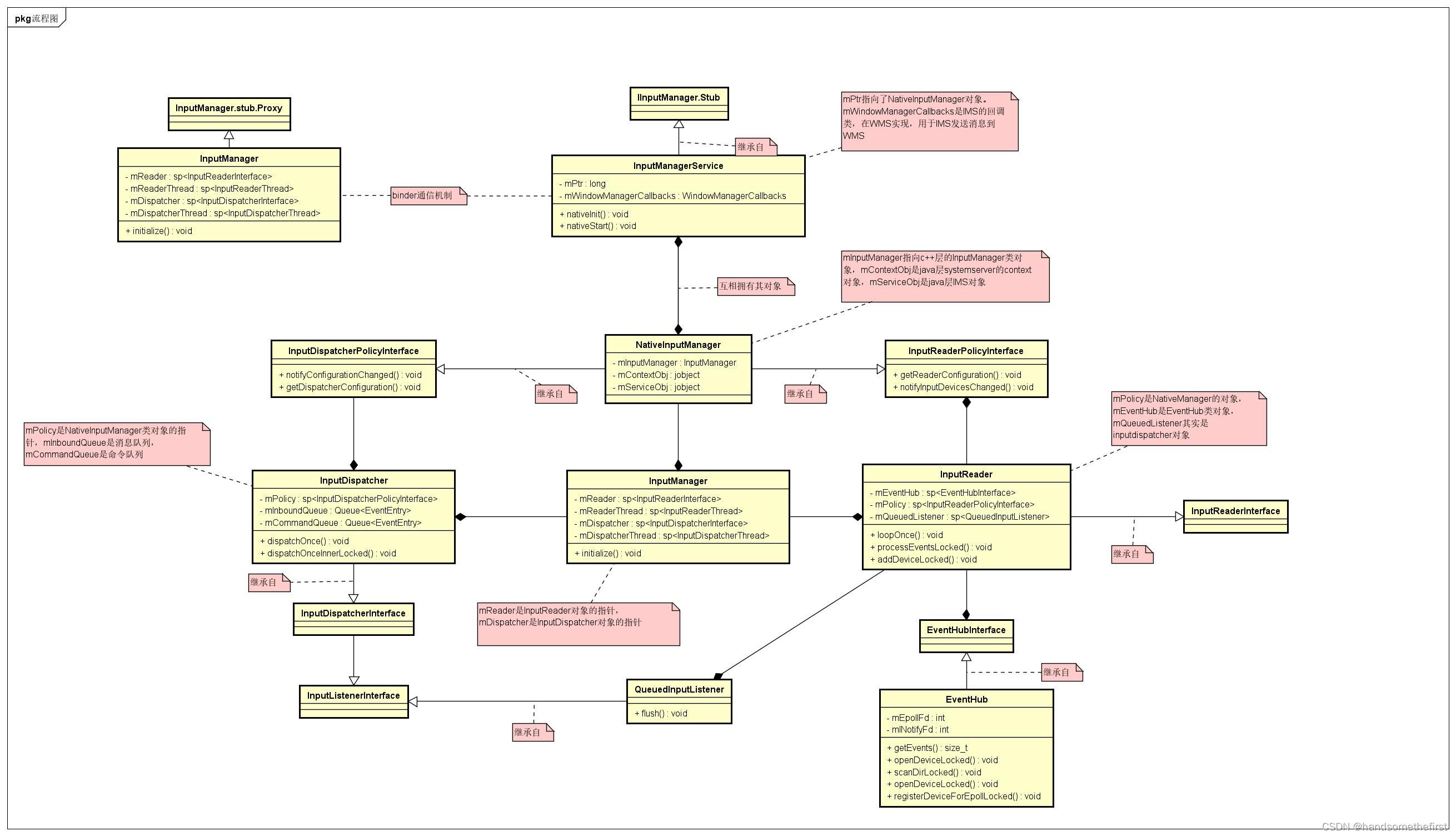
1.2 调用栈
因为在追随源码的过程,会非常痛苦,时而就会忘记追到那了,每每分析源码的时候都令人头疼。所以我们先来看一下调用栈。
main
{
2.1 SystemServer().run;
{
2.2 startOtherServices
{
2.3 startInputManagerService
{
2.4 new InputManagerService
{
2.5 nativeInit
{
2.6 new NativeInputManager
{
2.7 new EventHub
{
1.创建epoil和notify监听/dev/input路径下是否有设备添加和删除事件
}
2.8 new InputManager
{
2.9 new InputDispatcher
2.10 new InputReader
2.11 initialize
{
2.12 new InputReaderThread
2.13 new InputDispatcherThread
}
}
}
}
}
}
2.14 startWindowManagerService
{
2.15 WindowManagerService.main
}
2.16 startInputManager
{
2.17 mInputManager.start
{
2.18 nativeStart
{
2.19 mInputManager.start
{
2.20 mDispatcherThread->run//开启分发线程
{
2.21 threadLoop
{
2.22 dispatchOnce
{
2.23 dispatchOnceInnerLocked
分发线程休眠
}
}
}
2.24 mReaderThread->run//开启reader线程
{
2.25 threadLoop
{
2.26 loopOnce
{
2.27 mEventHub->getEvents
{
2.28 scanDevicesLocked//扫描/dev/input下的设备
{
2.29 scanDirLocked
{
2.30 openDeviceLocked//打开设备,获取设备的厂商信息和按键等配置文件加载到map中,并为设备配置class
{
2.31 registerDeviceForEpollLocked//打开设备后,将此设备添加到epoll中监听是否有事件
}
}
}
为每个设备生成对应的设备add事件
}
2.32 processEventsLocked
{
2.33 addDeviceLocked
{
2.34 createDeviceLocked//根据device结构体生成InputDevice类对象,然后根据各种class生成对应的mapper对象并配置maper对象的参数。如坐标映射等。
2.35 configure
}
2.36 removeDeviceLocked
2.37 handleConfigurationChangedLocked
}
2.38 notifyInputDevicesChanged //通知监听Input输入设备变化的listener
2.39 QueuedInputListener::flush
{
2.40 NotifyConfigurationChangedArgs::notify
{
2.41 InputDispatcher::notifyConfigurationChanged //唤醒2.23处的派发线程进行派发
{
2.42 dispatchOnce
{
2.43 dispatchOnceInnerLocked //生成ConfigurationChangedEntry事件,用于表示配置发生变化
{
2.44 dispatchConfigurationChangedLocked //生成一个command命令事件。为了告诉policy配置已发生变化。并将此命令放入命令队列中。
}
2.45 runCommandsLockedInterruptible
{
2.46 doNotifyConfigurationChangedInterruptible
{
2.47 notifyConfigurationChanged
{
2.48 notifyConfigurationChanged //此时通知配置变化到了java层的WMS
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}1.3 启动时序图
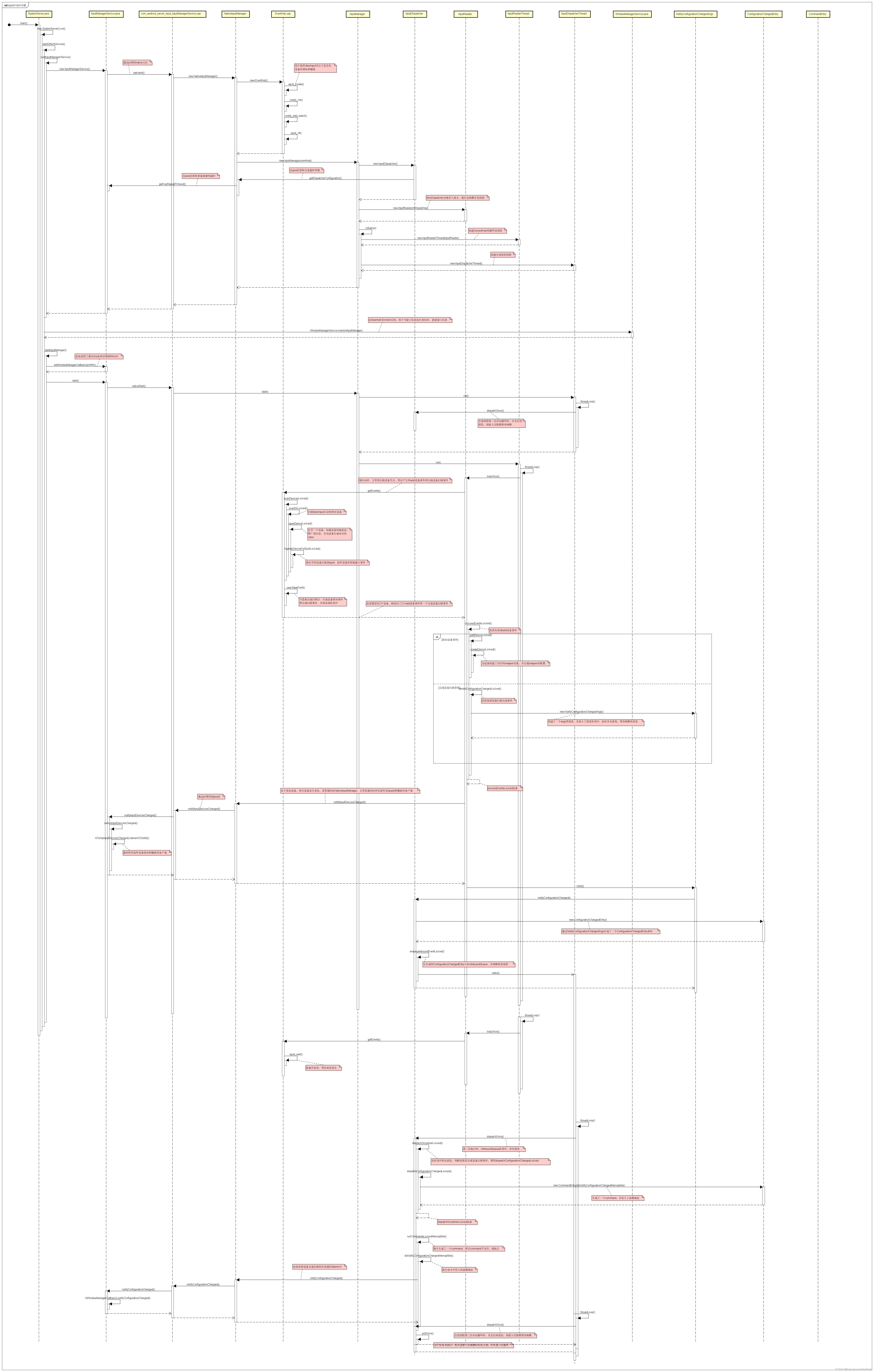
图片可保存到本地,放大观看。
1.4 相关文件主要路径
| 类 | 所在文件路径 |
| InputManagerService | frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/input/InputManagerService.java |
| SystemServer | frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/Systemserver.java |
| NativeInputManager | frameworks/base/services/core/jni/com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp |
| InputDispatcher | frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/InputDispatcher.cpp |
| InputManager | frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/InputManager.cpp |
| InputReader | frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/InputReader.cpp |
| EV_ABS等定义 | kernel/msm-4.14/include/uapi/linux/input-event-codes.h |
| InputPublisher类 | frameworks/native/libs/input/InputTransport.cpp |
| AxisInfo的信息 | frameworks/native/include/input/KeyLayoutMap.h |
| VIew | /frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ |
| abs轴信息 | prebuilts/gcc/linux-x86/host/x86_64-linux-glibc2.15-4.8/sysroot/usr/include/linux/input.h |
2 启动流程——部分源码分析
1.此处采用andorid9 代码进行分析。会删除部分不太重要的代码,方便读者读懂input的主要流程。
本人仍然认为要想真正的懂的一个模块,其实更需要诸位读者自行从源码一行行进行分析。本人会将全部代码分析内容放在第三节,感兴趣的读者或者正在分析源码的读者参考。
2.1 systemserver启动
从systemserver的main函数开始分析。
//frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SystemServer().run();
}//frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java
protected void run() {
startOtherServices();//启动其他服务,如IMS,WMS
}2.2 startOtherServices
//frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java
private void startOtherServices() {
......
startInputManagerService();
startWindowManagerService();
startInputManager();
......
}
2.3 startInputManagerService
//frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java
protected void startInputManagerService() {
mInputManager = new InputManagerService(mSystemContext);//new了一个InputManagerService类的对象,但此时并未调用其start方法。
}
2.4 InputManagerService
//frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/input/InputManagerService.java
public InputManagerService(Context context) {
this.mContext = context;//其实就是systemserver的context
this.mHandler = new InputManagerHandler(DisplayThread.get().getLooper());//使用display的looper创建了InputManagerHandler
mPtr = nativeInit(this, mContext, mHandler.getLooper().getQueue());//调用了nativeInit方法,
//传入参数为this=InputManagerService对象,
//mContext是systemserver的context,getQueue是display的looper的消息队列
//返回值:mPtr是nativeInit返回的值,是指向NativeInputManager的指针。
LocalServices.addService(InputManagerInternal.class, new LocalService());
}2.5 nativeInit
//frameworks/base/services/core/jni/com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp
static jlong nativeInit(JNIEnv* env, jclass /* clazz */,jobject serviceObj, jobject contextObj, jobject messageQueueObj) {
sp<MessageQueue> messageQueue = android_os_MessageQueue_getMessageQueue(env, messageQueueObj);//根据传入的java队列,获取native的消息队列
NativeInputManager* im = new NativeInputManager(contextObj, serviceObj,
messageQueue->getLooper());//创建了NativeInputManager类指针,
//传入参数:contextObj=systemserver的context,serviceObj=InputManagerService对象,looper是display的native的looper的消息队列
return reinterpret_cast<jlong>(im);//将NativeInputManager类指针用reinterpret_cast强制转化为jlong并返回
}2.6 NativeInputManager
//frameworks/base/services/core/jni/com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp
NativeInputManager::NativeInputManager(jobject contextObj,jobject serviceObj, const sp<Looper>& looper) :mLooper(looper), mInteractive(true) {
JNIEnv* env = jniEnv();
sp<EventHub> eventHub = new EventHub();//创建了EventHub类的对象,并用强指针指向它
mInputManager = new InputManager(eventHub, this, this);//创建了C++层的InputManager对象,并将EventHub类对象传入。
//参数分析:第二个this是NativeInputManager对象,第三个也是NativeInputManager对象,但代表的含义不同
//第一个this指,NativeInputManager继承自InputReaderPolicyInterface,
//第二个this指,NativeInputManager继承自InputDispatcherPolicyInterface
}2.7 EventHub
1.此处主要作用是:创建Epoll和iNotify对象,用于监听/dev/input节点下是否有设备增删。
当然,此时Epoll还未监听。因为并为调用epoll_wait函数,陷入等待事件发生。后续会调用。
简单介绍一下:
1.首先,要创建一个iNotify对象fd。此fd会监听/dev/input节点下时候有设备增删事件。
2.然后,将此iNotify对象添加到Epoll中监听,然后调用epoll_wait陷入等待状态,等待设备增删事件的发生。
3.当/dev/input节点下有设备增删的时候,epoll_wait会返回一个epoll_event的数组,此数组携带对应的iNotify对象fd和其他信息。
4.然后,iNotify对象就可以调用read读取其中的事件。
此处涉及知识点:Epoll和iNotify机制。请查看笔者另外一篇。
//frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/EventHub.cpp
EventHub::EventHub(void) :
mBuiltInKeyboardId(NO_BUILT_IN_KEYBOARD), mNextDeviceId(1), mControllerNumbers(),
mOpeningDevices(0), mClosingDevices(0),
mNeedToSendFinishedDeviceScan(false),
mNeedToReopenDevices(false), mNeedToScanDevices(true),
mPendingEventCount(0), mPendingEventIndex(0), mPendingINotify(false)
//参数分析:
//mBuiltInKeyboardId(NO_BUILT_IN_KEYBOARD),NO_BUILT_IN_KEYBOARD代表默认无内置键盘。
//mNextDeviceId,代表下一个设备id
//mOpeningDevices最近一次打开的设备,0代表最近无设备打开
//mClosingDevices,最近一次关闭的设备,0代表最近无设备关闭
//mNeedToSendFinishedDeviceScan,表示当设备扫描完成后,是否需要发送设备扫描完成的信号,默认为false
//mNeedToReopenDevices,表示是否需要重新打开设备
//mNeedToScanDevices,表示是否需要扫描设备,此处为是
//mPendingEventCount目前还未处理,正在等待处理的事件数量
//mPendingEventCount目前还未处理,马上要处理的下一个事件的索引。事件是由mPendingEventItems结构体数组存储。
//mPendingINotify,代表待定的通知
{
mEpollFd = epoll_create(EPOLL_SIZE_HINT);//创建epoll对象,mEpollFd为此对象的描述符
mINotifyFd = inotify_init();//创建inotify对象,mINotifyFd为此对象的描述符
int result = inotify_add_watch(mINotifyFd, DEVICE_PATH, IN_DELETE | IN_CREATE);//将一个用于监听输入设备节点的创建与删除的watch对象,
//添加到inotify对象中,此处DEVICE_PATH为"/dev/input",监听该目录下的设备节点创建与删除操作。
//当/dev/input/下的设备节点发生创建与删除操作时,都会将相应的事件信息写入到inotifyFd所描述的inotify对象中,
//此时可以通过read()函数从inotifyFd描述符中将事件信息读取出来。
struct epoll_event eventItem;//创建epoll_event结构体,此结构体
memset(&eventItem, 0, sizeof(eventItem));//初始值为0
eventItem.events = EPOLLIN;//可读,代表监听可读事件
eventItem.data.u32 = EPOLL_ID_INOTIFY;//EPOLL_ID_INOTIFY代表用于与设备无关的epoll通知的ID。此处为Epoll的通知id
result = epoll_ctl(mEpollFd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, mINotifyFd, &eventItem);//添加刚才监听目录下设备创建和删除的INotify到epoll实例,EPOLL_CTL_ADD表示增加事件
//epoll_ctl将事件监听添加到epoll对象中去。
//当/dev/input/下的设备节点发生创建与删除操作时,首先会将相应的事件信息写入到inotifyFd所描述的inotify对象中,又因为该inotifyFd被epoll监听可读,故直接生成eventItem事件
}2.8 InputManager
主要作用:
1.创建InputDispatcher对象,用于事件的分发。
2.创建InputReader对象,并将eventHub对象传递进去。用于事件的读取和加工。
3.在initialize函数中,创建了InputDispatcherThread线程和InputReaderThread线程。
//frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/InputManager.cpp
InputManager::InputManager(
const sp<EventHubInterface>& eventHub,
const sp<InputReaderPolicyInterface>& readerPolicy,
const sp<InputDispatcherPolicyInterface>& dispatcherPolicy) {
mDispatcher = new InputDispatcher(dispatcherPolicy);//创建InputDispatcher对象,传入的参数为NativeInputManager
mReader = new InputReader(eventHub, readerPolicy, mDispatcher);//创建InputReader对象,
//传入参数:
//eventHub=EventHub类对象,
//readerPolicy=NativeInputManager类对象,
//mDispatcher=InputDispatcher对象,此处作用简单说一下
//大致为当inputreader从eventHub中读取到数据后,对数据进行加工包装后,会添加到InputDispatcher的一个队列中,并唤醒他,然后执行分发。
initialize();//初始化
}2.9 InputDispatcher
//frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/InputDispatcher.cpp
InputDispatcher::InputDispatcher(const sp<InputDispatcherPolicyInterface>& policy) :
mPolicy(policy),
mPendingEvent(NULL), mLastDropReason(DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED),
mAppSwitchSawKeyDown(false), mAppSwitchDueTime(LONG_LONG_MAX),
mNextUnblockedEvent(NULL),
mDispatchEnabled(false), mDispatchFrozen(false), mInputFilterEnabled(false),
mInputTargetWaitCause(INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_NONE)
//参数分析:
//mPolicy=NativeInputManager类对象
//mPendingEvent,含义为还未处理的事件,此处为NULL
//mLastDropReason,最近一次丢弃事件的原因,默认为DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED,表示不丢弃。
//mAppSwitchSawKeyDown,表示是否按下Home健,此处为flase
//mAppSwitchDueTime,代表,当用户按home健时,该操作事件最迟的分发时间。对于特殊按键 HOME, END_CALL, APP_SWITCH 增加了 0.5s 超时时间,超时之后会丢弃其他即将处理的按键事件。如果超时,则即 isAppSwitchDue 为 true 的情况,说明没有及时响应 HOME 键等操作,目的是优化 app 切换延迟,当切换超时,则抢占分发,丢弃其他所有即将要处理的事件
//mNextUnblockedEvent,下一个取消阻止的事件,含义为阻塞事件延迟优化。当用户打算将焦点转移到新应用程序时,会删除旧事件。直接到下一个事件。
//mDispatchEnabled,是否可以分发事件,此处为false,因为只是创建了对象,其工作线程还未启动。
//mDispatchFrozen,分发是否冻结,此处为false,如果为true则,不进行分发操作。InputDispatcher有三种状态,1.正常状态,2冻结状态,3.禁用状态。
//例如:当手机进入休眠状态时,InputDispatcher 会被禁用,而屏幕旋转过程中,InputDispatcher 会被暂时冻结
//mInputFilterEnabled,表示输入过滤是否使用,默认为false
//mInputTargetWaitCause,表示输入目标等待原因,即anr的原因,默认为无原因,anr代表应用无响应,可以理解为卡死
// 跟踪ANR超时。
//enum InputTargetWaitCause {
//INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_NONE,//anr无原因
//INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_SYSTEM_NOT_READY,//系统无响应
//INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_APPLICATION_NOT_READY,//应用无响应
//};
{
mLooper = new Looper(false);//创建了自己的looper对象
}2.10 InputReader
构造函数中保存了InputDispatcher对象,即listener,这里说明了inputreader线程加工好了消息后如何通知InputDispatcher线程去派发消息。
//frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/InputReader.cpp
InputReader::InputReader(const sp<EventHubInterface>& eventHub,
const sp<InputReaderPolicyInterface>& policy,
const sp<InputListenerInterface>& listener) :
mContext(this), mEventHub(eventHub), mPolicy(policy),
mGlobalMetaState(0), mGeneration(1),
mDisableVirtualKeysTimeout(LLONG_MIN), mNextTimeout(LLONG_MAX),
mConfigurationChangesToRefresh(0)
//参数分析:
//此处需要重点查看传入的参数listener,
//InputDispatcher继承自InputDispatcherInterface,InputDispatcherInterface继承自InputListenerInterface
//mContext=InputReader类对象
//mEventHub=传入的eventHub类对象
//mPolicy=传入的NativeInputManager类对象
//mGlobalMetaState,全局元状态,是int类型,不知道干啥的,后续瞅瞅
//mGeneration,用于表示设备更新的次数
//mDisableVirtualKeysTimeout,禁用虚拟键超时
//NextTimeout,下一次唤醒的时间
//mConfigurationChangesToRefres,当Configuration变化时,进行刷新,0代表无变化,1代表有变化,当为1时需要执行刷新的函数
{
mQueuedListener = new QueuedInputListener(listener);//创建输入监听对象,listener是传入的参数,是一个InputDispatcher类的对象,
}2.11 initialize
主要作用为:
1.创建了inputreader线程,此线程的作用是从eventHub中无休止的读取原始的事件,并进行加工,最终会得出三种事件类型,然后将事件会加入到InputDispatcher的一个队列中进行分发
2.创建了InputDispatcherThread线程,此线程主要进行事件的分发,其保存者wms的窗口信息,通过相关函数将事件准确的发送到指定窗口。
void InputManager::initialize() {
mReaderThread = new InputReaderThread(mReader);//创建了inputreader线程,传入了inputreader类对象,
//此线程的作用是从eventHub中无休止的读取原始的事件,并进行加工,最终会得出三种事件类型
//1.key事件,NotifyKeyArgs,
//2.Motion事件,NotifyMotionArgs,
//3.Switch事件,NotifySwitchArgs,
//然后会加入到InputDispatcher的一个队列中进行分发
mDispatcherThread = new InputDispatcherThread(mDispatcher);//创建了InputDispatcher线程,传入了InputDispatcher类对象
}2.12 InputReaderThread
InputReaderThread::InputReaderThread(const sp<InputReaderInterface>& reader) :
Thread(/*canCallJava*/ true), mReader(reader) {//给mReader赋了个值为inputreader类
//此线程会从eventHub中无休止的读取原始的事件,并进行加工
}2.13 InputDispatcherThread
InputDispatcherThread::InputDispatcherThread(const sp<InputDispatcherInterface>& dispatcher)
: Thread(/*canCallJava*/ true), mDispatcher(dispatcher) {}
//此线程会无休止地入队和分发输入事件2.14 startWindowManagerService
主要作用:
1.执行WMS的main方法,此时将mInputManager的引用传递到WMS中,因为当应用向WMS申请创建窗口是随时的,那么WMS就必须及时将窗口信息更新到IMS中,以便input消息能正确的发送给指定窗口。
protected void startWindowManagerService() {
mWm = WindowManagerService.main(mSystemContext, mInputManager,
mFactoryTestMode != FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL,
!mFirstBoot, mOnlyCore, new PhoneWindowManager());//调用WMS的main方法,把inputManager的引用放到WMS中,建立联系
//传入的参数mSystemContext=systemserver对象,mInputManager=InputManagerService对象,CarWindowManager对象。
ServiceManager.addService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE, mWm, /* allowIsolated= */ false,DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_CRITICAL | DUMP_FLAG_PROTO);//WMS添加进ServiceManager中,
ServiceManager.addService(Context.INPUT_SERVICE, mInputManager,/* allowIsolated= */ false, DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_CRITICAL);//IMS添加进ServiceManager中
}2.15 WindowManagerService.main
public static WindowManagerService main(final Context context, final InputManagerService im,
final boolean haveInputMethods, final boolean showBootMsgs, final boolean onlyCore,
WindowManagerPolicy policy) {
//接收参数分析:
//context=systemserver对象
//im = InputManagerService对象
//haveInputMethods应该是true
//policy接收一个PhoneWindowManager类对象
DisplayThread.getHandler().runWithScissors(() ->
sInstance = new WindowManagerService(context, im, haveInputMethods, showBootMsgs,
onlyCore, policy), 0);
return sInstance;
}2.16 startInputManager
1.IMS保存了InputMonitor对象,InputMonitor类是在WMS侧实现的IMS的回调类,此处说明了消息最终如何回调到WMS。
protected void startInputManager() {
mInputManager.setWindowManagerCallbacks(mWm.getInputMonitor());//设置回调,将WMS中的InputManagerCallback设置到inputManager中,
//这里说明了最终如何回调到WMS
mInputManager.start();//启动IMS
}
class InputMonitor implements InputManagerService.WindowManagerCallbacks
//继承自WindowManagerCallbacks,此回调类需要WMS是实现,主要是一些回调函数。此类的内部
//有一个内部类EventReceiverInputConsumer,用于接受IMS的消息。2.17 InputManager.start
public void start() {
nativeStart(mPtr);//mPtr是nativeInit返回的值,是指向NativeInputManager的指针。
}2.18 nativeStart
1.主要用于调用InputManager.start方法。
static void nativeStart(JNIEnv* env, jclass /* clazz */, jlong ptr) {
NativeInputManager* im = reinterpret_cast<NativeInputManager*>(ptr);//将ptr指针转化为NativeInputManager类指针
status_t result = im->getInputManager()->start();//调用了mInputManager.start()方法。
//而mInputManager是在NativeInputManager::NativeInputManager构造函数中,创建的指向inputManager对象的指针
}2.19 InputManager.start
1.DispatcherThread线程启动
2.ReaderThread线程启动
status_t InputManager::start() {
status_t result = mDispatcherThread->run("InputDispatcher", PRIORITY_URGENT_DISPLAY);//开启分发线程,
//PRIORITY_URGENT_DISPLAY重要显示线程的优先级,屏幕合成和获取输入事件使用这个级别
result = mReaderThread->run("InputReader", PRIORITY_URGENT_DISPLAY);//开启reader线程
return OK;
}2.20 mDispatcherThread->run
1.分发线程启动。
线程调用run方法后,会调用threadLoop方法,当其返回true并且没有调用requsetexit函数时,会一直循环的调用threadLoop函数
此处涉及Android侧的多线程篇,原理请查看本人的另一篇博客
2.21 InputDispatcherThread::threadLoop
bool InputDispatcherThread::threadLoop() {//线程调用run方法后,会调用threadLoop方法,
//当其返回true并且没有调用requsetexit函数时,会一直循环的调用threadLoop函数
mDispatcher->dispatchOnce();
return true;
}2.22 InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce
1.此时分发线程刚启动,消息和命令都没有,然后就陷入了无限等待inputreader线程唤醒状态。
//刚启动第一次循环时,分发线程执行的代码块
//本质上,第一次循环时,什么消息都没有,所以就是相当于任何函数都没执行,然后就陷入了无线等待唤醒
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce() {
nsecs_t nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MAX;//下一次唤醒该线程的时间,也可以说是下一次线程循环的执行时间点,默认最大值,即刚开始InputDispatcherThread线程无限等待
{
if (!haveCommandsLocked()) {//此时无命令。
//作用:检查inputdispatcher的缓存队列中是否有还未处理的命令
//只有无命令时才会执行dispatchOnceInnerLocked方法,进行事件的分发。
dispatchOnceInnerLocked(&nextWakeupTime);// 传入的nextWakeupTime决定了下次派发线程循环的执行时间点,
}
}
nsecs_t currentTime = now();//获取当前时间点
int timeoutMillis = toMillisecondTimeoutDelay(currentTime, nextWakeupTime);//下一次唤醒时间点-当前时间点=线程休眠时间
mLooper->pollOnce(timeoutMillis);//调用pollOnce使线程休眠,等待回调,唤醒或超时。
//Looper的pollOnce()的实质就是epoll_wait()。 因此派发线程的休眠在三种情况下可能被唤醒:
//1.调用Looper::wake()函数主动唤醒(有输入事件注入派发队列中时),
//2.到达nextWakeupTime的事件点时唤醒
//3.epoll_wait()监听的fd有epoll_event发生时唤醒(这种唤醒方式将在介绍ANR机制时讨论)。
}
bool InputDispatcher::haveCommandsLocked() const {//第一次线程循环执行,返回为false
return !mCommandQueue.isEmpty();
}2.23 dispatchOnceInnerLocked
//刚开机启动后,第一次执行代码块为
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnceInnerLocked(nsecs_t* nextWakeupTime) {
nsecs_t currentTime = now();
if (!mDispatchEnabled) {//默认值为flase
resetKeyRepeatLocked();//将上一个事件指向的对象删除,并置空
}
//优化应用程序交换机的延迟。
//本质上,当按下应用程序切换键(HOME/ENDCALL)时,我们会开始短暂的超时。当它过期时,我们抢占分派并丢弃所有其他挂起的事件。
bool isAppSwitchDue = mAppSwitchDueTime <= currentTime;//mAppSwitchDueTime这个值是在EventEntry进入队列时设置的,默认值是最大值
//第一次循环时mAppSwitchDueTime值是LONG_LONG_MAX,所以isAppSwitchDue是false
//如果mAppSwitchDueTime小于当前时间,说明约定的最迟分发时间已经过去了,即没有即使响应home建等操作。
if (! mPendingEvent) {//如果没有待发送的事件,则从mInboundQueue队列中取出一个事件,进行分发
if (mInboundQueue.isEmpty()) {
//如果不需要生成重复按键事件,或还没有到达合适的时间点,
//则直接返回,派发线程再次沉睡
if (!mPendingEvent) {
return;
}
}
}
}2.24 mReaderThread->run
1.读取线程启动。
线程调用run方法后,会调用threadLoop方法,当其返回true并且没有调用requsetexit函数时,会一直循环的调用threadLoop函数
2.25 threadLoop
bool InputReaderThread::threadLoop() {//inputreader线程调用run方法后,会调用threadLoop方法,
//当其返回true并且没有调用requsetexit函数时,会一直循环的调用threadLoop函数
mReader->loopOnce();
return true;
}2.26 InputReader::loopOnce
//第一次启动时,执行的代码块
void InputReader::loopOnce() {
int32_t oldGeneration;
int32_t timeoutMillis;
bool inputDevicesChanged = false;
Vector<InputDeviceInfo> inputDevices;
{
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
oldGeneration = mGeneration;//值为1,在inputreader构造函数中mGeneration=1,
timeoutMillis = -1;
}
size_t count = mEventHub->getEvents(timeoutMillis, mEventBuffer, EVENT_BUFFER_SIZE);//通过EventHub的getEvents函数获取事件,
//并存放在mEventBuffer中。此时可以知道刚启动时,只是会生成所有已经扫描的设备的add类型的事件和一个完成设备扫描的事件
//参数分析:timeoutMillis=-1,代表啥意思不清楚,感觉如果数字为0代表立即执行
//mEventBuffer是一个存放从eventhub中读取的rawevent结构体类型的数组,源代码是:RawEvent mEventBuffer[EVENT_BUFFER_SIZE];
//EVENT_BUFFER_SIZE值是256,代表最大可以读取256个原始事件,RawEvent结构体如下
////从EventHub检索到的原始事件
//struct RawEvent {
//nsecs_t when;//时间
//int32_t deviceId;//事件发生的设备id
//int32_t type;//类型,例如按键事件等
//int32_t code;//扫描码,按键对应的扫描码
//int32_t value;//值,表示按键按下,或者抬起等
//};
{ // acquire lock
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
if (count) {//返回的事件数量大于,则调用processEventsLocked处理事件
processEventsLocked(mEventBuffer, count);
}
if (oldGeneration != mGeneration) {//此处是不等于的,因为当有add设备事件时processEventsLocked函数中调用addDeviceLocked,addDeviceLocked在完成设备配置后
//会调用bumpGenerationLocked函数,使得mGeneration+1,从而不相等
inputDevicesChanged = true;
getInputDevicesLocked(inputDevices);//获取所有的新的设备信息到inputDevices容器中
}
} // release lock
//
if (inputDevicesChanged) {//如果设备发生变化,生成一个通知设备事件的通知
mPolicy->notifyInputDevicesChanged(inputDevices);//此时mPolicy是NativeInputManager对象,所以此时调用到了NativeInputManager::notifyInputDevicesChanged
}
//发布事件。 一般此处只会处理加工后的原始输入事件,而此时开机启动只有设备添加和删除的事件,但是当设备完成扫描时会生成一个通知事件
//放入此队列。所以启动后,扫描完设备后,此容器只有一个扫描设备完成的通知事件
// mQueuedListener中。在循环的最后,通过调用flush()函数将所有事件交付给InputDispatcher
mQueuedListener->flush();
}2.27 mEventHub->getEvents
1.设备刚启动,扫描/dev/input下的所有输入设备,用Device类保存其信息,并生成DEVICE_ADDED类型的事件(设备增加类型事件)放入消息数组中
2.当完成所有设备扫描后,生成FINISHED_DEVICE_SCAN类型的事件,并通过event指针存放于buffer数组中。
3.返回存在设备增加事件和设备完成扫描事件的数组,让inputreader进行处理。
size_t EventHub::getEvents(int timeoutMillis, RawEvent* buffer, size_t bufferSize) {
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
struct input_event readBuffer[bufferSize];//bufferSize值为传入的256
RawEvent* event = buffer;//event指针指向传入的buffer首地址,每存入一个事件,event指针向后移动一个元素
size_t capacity = bufferSize;//capacity表示buffer中剩余端元素数量,capacity为0,表示buffer已满
bool awoken = false;
for (;;) {//死循环
nsecs_t now = systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC);//获取当前时间
if (mNeedToScanDevices) {//默认值为true,即第一次调用getevent时,会扫描/dev/input下的设备
mNeedToScanDevices = false;//设置为false,避免重复扫描设备
scanDevicesLocked();//执行扫描设备的函数。扫描/dev/input下的设备
mNeedToSendFinishedDeviceScan = true;//mNeedToSendFinishedDeviceScan值为true,用于生成FINISHED_DEVICE_SCAN事件
}
while (mOpeningDevices != NULL) {
Device* device = mOpeningDevices;//此时mOpeningDevices值是刚打开过的device
mOpeningDevices = device->next;//device->next值为0,指向下一个设备
//生成DEVICE_ADDED类型的事件,并通过event指针存放于buffer数组中
event->when = now;
event->deviceId = device->id == mBuiltInKeyboardId ? 0 : device->id;//如果是内置键盘,则其id为0,如果不是则是device->id
event->type = DEVICE_ADDED;//类型
event += 1;//event的定义是RawEvent* event = buffer,event指针指向传入的buffer数组的首地址,即第0个元素,
//每存入一个事件,event指针向后移动一个元素
mNeedToSendFinishedDeviceScan = true;
if (--capacity == 0) {//buffer数组可容量-1
break;
}
}
if (mNeedToSendFinishedDeviceScan) {
mNeedToSendFinishedDeviceScan = false;
//生成FINISHED_DEVICE_SCAN类型的事件,并通过event指针存放于buffer数组中
event->when = now;
event->type = FINISHED_DEVICE_SCAN;
event += 1;
if (--capacity == 0) {
break;
}
}
bool deviceChanged = false;
/*如果存在未处理的事件,则从mPendingEventItems数组中取出事件
while (mPendingEventIndex < mPendingEventCount) {//此时刚开机启动。mPendingEventIndex和mPendingEventCount都为0
.......
}
*/
// 当event的指针不再指向buffer的首地址时,代表里面有数据,或者被唤醒时,立即退出循环
if (event != buffer || awoken) {//此时生成了两种事件,一个是扫描的所有打开设备的事件,还有一个是完成设备扫描报告的事件,故退出循环
break;
}
}
// 全部完成后,返回我们读取的事件数。
return event - buffer;
}2.28 scanDevicesLocked
void EventHub::scanDevicesLocked() {
status_t res = scanDirLocked(DEVICE_PATH);//调用scanDirLocked方法,DEVICE_PATH=/dev/input,返回0代表成功
if (mDevices.indexOfKey(VIRTUAL_KEYBOARD_ID) < 0) {//
//mDevices的定义是一个map容器,KeyedVector<int32_t, Device*> mDevices;mDevices中存放的是已经扫描完成的设备,即
//已经完成设备厂商信息的获取和注册进epoll监听的设备。VIRTUAL_KEYBOARD_ID的值等于-1
//此处如果从mDevice中没有找到虚拟键盘,则调用createVirtualKeyboardLocked方法创建虚拟键盘。
createVirtualKeyboardLocked();
}
}void EventHub::createVirtualKeyboardLocked() {
InputDeviceIdentifier identifier;//存储厂商信息的结构体
identifier.name = "Virtual";
identifier.uniqueId = "<virtual>";
assignDescriptorLocked(identifier);
Device* device = new Device(-1, VIRTUAL_KEYBOARD_ID, String8("<virtual>"), identifier);//创建了一个Device对象
device->classes = INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_KEYBOARD | INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_ALPHAKEY |
INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_DPAD | INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_VIRTUAL;//设置属性calss
loadKeyMapLocked(device);//加载kepMap,键盘映射表,保存到device->keyMap中。
addDeviceLocked(device);//添加设备到mDevices的map容器中
}2.29 scanDirLocked
1.循环打开/dev/input下的所有设备节点。
status_t EventHub::scanDirLocked(const char *dirname)
{
char devname[PATH_MAX];
char *filename;
DIR *dir;
struct dirent *de;
dir = opendir(dirname);
if(dir == NULL)
return -1;
strcpy(devname, dirname);
filename = devname + strlen(devname);
*filename++ = '/';
while((de = readdir(dir))) {//循环打开目录下的所有设备
if(de->d_name[0] == '.' &&
(de->d_name[1] == '\0' ||
(de->d_name[1] == '.' && de->d_name[2] == '\0')))
continue;
strcpy(filename, de->d_name);
openDeviceLocked(devname);//打开设备
}
closedir(dir);//关闭目录
return 0;
}
2.30 openDeviceLocked
主要作用为:
1.打开/dev/input/xxxx的设备,然后获取设备的驱动版本,设备产品,设备供应商,设备物理地址,设备标识符将信息保存到InputDeviceIdentifier类的identifier对象中,此对象主要用于存储设备厂商的所有信息。
2.假设此时有一个设备/dev/input/event0,根据其dentifier对象生成对应的Device类对象。然后加载设备的配置文件到device类对象的PropertyMap中。
配置文件主要有三类。
一.idc文件,主要用于触摸屏配置。
二.kl文件,主要用于键盘的扫描码和keycode的转化。
三.kcm文件,主要作用是将 Android按键代码与修饰符的组合映射到 Unicode。
3.从设备的fd中读取数据判断其设备类型为EV_KEY、EV_ABS、EV_REL、EV_SW、EV_LED、EV_FF类型。
一:EV_KEY,按键类型的事件。能够上报这类事件的设备有键盘、鼠标、手柄、手写板
等一切拥有按钮的设备(包括手机上的实体按键)。在Device结构体中,对应的事件
位掩码keyBitmask描述了设备可以产生的按键事件的集合。按键事件的全集包括字
符按键、方向键、控制键、鼠标键、游戏按键等。
二:EV_ABS,绝对坐标类型的事件。这类事件描述了在空间中的一个点,触控板、触
摸屏等使用绝对坐标的输入设备可以上报这类事件。事件位掩码absBitmask描述了
设备可以上报的事件的维度信息(ABS_X、ABS_Y、ABS_Z),以及是否支持多点
事件。
三:EV_REL,相对坐标类型的事件。这类事件描述了事件在空间中相对于上次事件
的偏移量。鼠标、轨迹球等基于游标指针的设备可以上报此类事件。事件位掩码
relBitmask描述了设备可以上报的事件的维度信息(REL_X、REL_Y、REL_Z)。
四:EV_SW,开关类型的事件。这类事件描述了若干固定状态之间的切换。手机上的静
音模式开关按钮、模式切换拨盘等设备可以上报此类事件。事件位掩码swBitmask表
示了设备可切换的状态列表。
五:EV_LED,光反馈类型事件。ledBitmask描述了设备是否支持光
六:EV_FF,力反馈类型,ffBitmask则描述了设备是否支持力反馈。
4.根据上诉大类型,生成更细分的类型——INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_xxx类型。如L按键事件可再通过有无X,y比特位,区分是键盘还是蓝牙手柄。
一:INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_KEYBOARD,可以上报鼠标按键以外的EV_KEY类型事件的设备都属于此类。如键盘、机身按钮(音量键、电源键等)。
二:INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_ALPHAKEY,可以上报字符按键的设备,例如键盘。此类 型的设备必定同时属于KEYBOARD。
三:INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_DPAD,可以上报方向键的设备。例如键盘、手机导航键
等。这类设备同时也属于KEYBOARD。
四:INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_GAMEPAD,可以上报游戏按键的设备,如游戏手柄。这类设备同时也属于KEYBOARD。
五:INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH,可以上报EV_ABS类型事件的设备都属于此类,如触摸屏和触控板。
六:INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH_MT,可以上报EV_ABS类型事件,并且其事件位掩码指示其支持多点事件的设备属于此类。例如多点触摸屏。这类设备同时也属于TOUCH类型。
七:INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_CURSOR,可以上报EV_REL类型的事件,并且可以上报BTN_MOUSE子类的EV_KEY事件的设备属于此类,例如鼠标和轨迹球。
八:INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_SWITCH,可以上报EV_SW类型事件的设备。
九:INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_JOYSTICK,属于GAMEPAD类型,并且属于TOUCH类型的设备。
十:INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_VIBRATOR,支持力反馈的设备。
十一:INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_VIRTUAL,虚拟设备。
十二:INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_EXTERNAL,外部设备,即非内建设备。如外接鼠标、键盘、游戏手柄等。
status_t EventHub::openDeviceLocked(const char *devicePath) {
char buffer[80];
int fd = open(devicePath, O_RDWR | O_CLOEXEC | O_NONBLOCK);//以读写,非阻塞,原子方式打开设备
//打开设备节点的文件描述符,用于获取设备信息以及读取原始输入事件
InputDeviceIdentifier identifier;//存储厂商的信息
//接下来的代码通过ioctl()函数从设备节点中获取输入设备的厂商信息
if(ioctl(fd, EVIOCGNAME(sizeof(buffer) - 1), &buffer) < 1) {//通过设备的fd,向驱动发送EVIOCGNAME指令,
//获取设备名称,写入buffer中
} else {
buffer[sizeof(buffer) - 1] = '\0';
identifier.name.setTo(buffer);//从buffer中取出名称信息,赋值给identifier的name属性
}
// 检查获取的设备名称是否在排除列表中下
for (size_t i = 0; i < mExcludedDevices.size(); i++) {// 检查获取的设备名称是否在排除列表中下,
//如果在mExcludedDevices列表中,则关闭此设备,并返回,mExcludedDevices列表在setExcludedDevices方法中赋值的,
//而setExcludedDevices方法是在inputreader构造函数中的refreshConfigurationLocked方法中调用的,
//同时mExcludedDevices最后是调用到java层ims中获取的。
const String8& item = mExcludedDevices.itemAt(i);
if (identifier.name == item) {
ALOGI("ignoring event id %s driver %s\n", devicePath, item.string());
close(fd);
return -1;
}
}
//获取设备驱动版本
int driverVersion;
if(ioctl(fd, EVIOCGVERSION, &driverVersion)) {//从驱动中获取的信息赋值给driverVersion
ALOGE("could not get driver version for %s, %s\n", devicePath, strerror(errno));
close(fd);
return -1;
}
//获取设备标识符
struct input_id inputId;
if(ioctl(fd, EVIOCGID, &inputId)) {//赋值给inputId
ALOGE("could not get device input id for %s, %s\n", devicePath, strerror(errno));
close(fd);
return -1;
}
identifier.bus = inputId.bustype;
identifier.product = inputId.product;//设备产品
identifier.vendor = inputId.vendor;//供应商
identifier.version = inputId.version;//版本
// 获取设备物理地址
if(ioctl(fd, EVIOCGPHYS(sizeof(buffer) - 1), &buffer) < 1) {//放于buffer中
//fprintf(stderr, "could not get location for %s, %s\n", devicePath, strerror(errno));
} else {
buffer[sizeof(buffer) - 1] = '\0';
identifier.location.setTo(buffer);//赋值给location
}
//获取设备唯一的id
if(ioctl(fd, EVIOCGUNIQ(sizeof(buffer) - 1), &buffer) < 1) {
//fprintf(stderr, "could not get idstring for %s, %s\n", devicePath, strerror(errno));
} else {
buffer[sizeof(buffer) - 1] = '\0';
identifier.uniqueId.setTo(buffer);//赋值给uniqueId
}
assignDescriptorLocked(identifier);//将identifier信息填充到fd,分配唯一标识设备的设备描述符,主要作用是填写identifier.nonce字段。
// 分配device,device对象获取fd的所有权
int32_t deviceId = mNextDeviceId++;//mNextDeviceId初始值为1,故deviceId=1
Device* device = new Device(fd, deviceId, String8(devicePath), identifier);
//参数分析:
//此处结合是getevent工具分析的
//fd是dev/input/event0的设备的描述符
//deviceid=1
//devicePath=dev/input/event0
//identifier存储了此设备所有的厂商信息
loadConfigurationLocked(device);//加载device的配置文件。主要是例如:device.type和device.internal等信息
// 详细事件报告的类型,从fd对应的device中读取各种信息,并保存到device的keyBitmask或absBitmask中,
//例如:如果是键盘设备,则device->keyBitmask有数据,而device->absBitmask无数据
ioctl(fd, EVIOCGBIT(EV_KEY, sizeof(device->keyBitmask)), device->keyBitmask);//按键类型
ioctl(fd, EVIOCGBIT(EV_ABS, sizeof(device->absBitmask)), device->absBitmask);//绝对坐标类型
ioctl(fd, EVIOCGBIT(EV_REL, sizeof(device->relBitmask)), device->relBitmask);//相对坐标类型,只要用于motion
ioctl(fd, EVIOCGBIT(EV_SW, sizeof(device->swBitmask)), device->swBitmask);//开关类型
ioctl(fd, EVIOCGBIT(EV_LED, sizeof(device->ledBitmask)), device->ledBitmask);//led等类型
ioctl(fd, EVIOCGBIT(EV_FF, sizeof(device->ffBitmask)), device->ffBitmask);//力反馈类型
ioctl(fd, EVIOCGPROP(sizeof(device->propBitmask)), device->propBitmask);
//Device结构体的事件位掩码描述了6种类型的输入事件:
//EV_KEY,按键类型的事件。能够上报这类事件的设备有键盘、鼠标、手柄、手写板
//等一切拥有按钮的设备(包括手机上的实体按键)。在Device结构体中,对应的事件
//位掩码keyBitmask描述了设备可以产生的按键事件的集合。按键事件的全集包括字
//符按键、方向键、控制键、鼠标键、游戏按键等。
//EV_ABS,绝对坐标类型的事件。这类事件描述了在空间中的一个点,触控板、触
//摸屏等使用绝对坐标的输入设备可以上报这类事件。事件位掩码absBitmask描述了
//设备可以上报的事件的维度信息(ABS_X、ABS_Y、ABS_Z),以及是否支持多点
//事件。
//EV_REL,相对坐标类型的事件。这类事件描述了事件在空间中相对于上次事件
//的偏移量。鼠标、轨迹球等基于游标指针的设备可以上报此类事件。事件位掩码
relBitmask描述了设备可以上报的事件的维度信息(REL_X、REL_Y、REL_Z)。
//EV_SW,开关类型的事件。这类事件描述了若干固定状态之间的切换。手机上的静
//音模式开关按钮、模式切换拨盘等设备可以上报此类事件。事件位掩码swBitmask表
//示了设备可切换的状态列表。
//EV_LED,光反馈类型事件。ledBitmask描述了设备是否支持光
//EV_FF,力反馈类型,ffBitmask则描述了设备是否支持力反馈。
//INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_KEYBOARD,可以上报鼠标按键以外的EV_KEY类型事件的设备都属于此类。如键
//盘、机身按钮(音量键、电源键等)。
//INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_ALPHAKEY,可以上报字符按键的设备,例如键盘。此类型的设备必定同时属于KEYBOARD。
//INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_DPAD,可以上报方向键的设备。例如键盘、手机导航键等。这类设备同时也属于KEYBOARD。
//INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_GAMEPAD,可以上报游戏按键的设备,如游戏手柄。这类设备同时也属于KEYBOARD。
//INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH,可以上报EV_ABS类型事件的设备都属于此类,如触摸屏和触控板。
//INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH_MT,可以上报EV_ABS类型事件,并且其事件位掩码指示其支持多点事件
//的设备属于此类。例如多点触摸屏。这类设备同时也属于TOUCH类型。
//INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_CURSOR,可以上报EV_REL类型的事件,并且可以上报BTN_MOUSE子类的
//EV_KEY事件的设备属于此类,例如鼠标和轨迹球。
//INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_SWITCH,可以上报EV_SW类型事件的设备。
//INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_JOYSTICK,属于GAMEPAD类型,并且属于TOUCH类型的设备。
//INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_VIBRATOR,支持力反馈的设备。
//INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_VIRTUAL,虚拟设备。
//INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_EXTERNAL,外部设备,即非内建设备。如外接鼠标、键盘、游戏手柄等。
//通过查看device->keyBitmask是否有数据,查看此设备是不是键盘类型
bool haveKeyboardKeys = containsNonZeroByte(device->keyBitmask, 0, sizeof_bit_array(BTN_MISC))
|| containsNonZeroByte(device->keyBitmask, sizeof_bit_array(KEY_OK),
sizeof_bit_array(KEY_MAX + 1));
bool haveGamepadButtons = containsNonZeroByte(device->keyBitmask, sizeof_bit_array(BTN_MISC),
sizeof_bit_array(BTN_MOUSE))
|| containsNonZeroByte(device->keyBitmask, sizeof_bit_array(BTN_JOYSTICK),
sizeof_bit_array(BTN_DIGI));
if (haveKeyboardKeys || haveGamepadButtons) {//如果是键盘类型或者游戏按键类型,
//则设置device->classes为INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_KEYBOARD
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_KEYBOARD;
}
//通过查看device->keyBitmask中是否有BTN_MOUSE对应的比特位和device->relBitmask是否对应的REL_X和REL_Y比特位,确认这是不是一个光标设备,如轨迹球或鼠标。
if (test_bit(BTN_MOUSE, device->keyBitmask)
&& test_bit(REL_X, device->relBitmask)
&& test_bit(REL_Y, device->relBitmask)) {
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_CURSOR;
}
// 查看是否是旋转编码器类型的设备.
String8 deviceType = String8();
if (device->configuration &&
device->configuration->tryGetProperty(String8("device.type"), deviceType)) {
if (!deviceType.compare(String8("rotaryEncoder"))) {
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_ROTARY_ENCODER;
}
}
//通过查看device->absBitmask,查看这是不是触摸板。
if (test_bit(ABS_MT_POSITION_X, device->absBitmask)
&& test_bit(ABS_MT_POSITION_Y, device->absBitmask)) {
if (test_bit(BTN_TOUCH, device->keyBitmask) || !haveGamepadButtons) {//尝试确认设备确实触摸屏。
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH | INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH_MT;
}
// 查看这是不是旧式的单触的驱动
} else if (test_bit(BTN_TOUCH, device->keyBitmask)
&& test_bit(ABS_X, device->absBitmask)
&& test_bit(ABS_Y, device->absBitmask)) {
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH;
// 查看不是外部手写笔
} else if ((test_bit(ABS_PRESSURE, device->absBitmask) ||
test_bit(BTN_TOUCH, device->keyBitmask))
&& !test_bit(ABS_X, device->absBitmask)
&& !test_bit(ABS_Y, device->absBitmask)) {
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_EXTERNAL_STYLUS;
device->classes &= ~INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_KEYBOARD;//有的事件键盘会和手写笔要配合执行一些操作。
}
//查看这个设备是否是操纵杆。
//假设操纵杆总是有游戏板按钮,以便与其他设备(如也有绝对轴的加速计)区分开来。
if (haveGamepadButtons) {
uint32_t assumedClasses = device->classes | INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_JOYSTICK;
for (int i = 0; i <= ABS_MAX; i++) {
if (test_bit(i, device->absBitmask)
&& (getAbsAxisUsage(i, assumedClasses) & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_JOYSTICK)) {
device->classes = assumedClasses;
break;
}
}
}
//查看此device是否有开关
for (int i = 0; i <= SW_MAX; i++) {
if (test_bit(i, device->swBitmask)) {
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_SWITCH;
break;
}
}
// 检查此设备是否支持可控震源。
if (test_bit(FF_RUMBLE, device->ffBitmask)) {
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_VIBRATOR;
}
// 如果是触摸屏,则为其配置虚拟键盘
if ((device->classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH)) {
//加载触摸屏的虚拟键(如果有)。
status_t status = loadVirtualKeyMapLocked(device);//loadVirtualKeyMapLocked函数的作用大致为
//加载系统提供的虚拟键盘的文件,然后将其键值对保存到virtualKeyMap中
if (!status) {
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_KEYBOARD;
}
}
//加载kepMap,键盘映射表
//我们为操纵杆或者键盘加载映射表
status_t keyMapStatus = NAME_NOT_FOUND;
if (device->classes & (INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_KEYBOARD | INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_JOYSTICK)) {
keyMapStatus = loadKeyMapLocked(device);//从device中加载keymap,键盘映射表
}
// 配置键盘、游戏板或虚拟键盘。
if (device->classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_KEYBOARD) {
if (!keyMapStatus
&& mBuiltInKeyboardId == NO_BUILT_IN_KEYBOARD//表示此时并未任何内置键盘配置过
&& isEligibleBuiltInKeyboard(device->identifier,
device->configuration, &device->keyMap)) //如果符合条件,会将键盘注册为内置键盘,
//然后device->keyMap保存着键盘映射表信息
{
mBuiltInKeyboardId = device->id;//mBuiltInKeyboardId内置键盘id,如果是第一次打开设备,则此时id为1
}
if (hasKeycodeLocked(device, AKEYCODE_Q)) {
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_ALPHAKEY;
}
//查看设备是否有方向键
if (hasKeycodeLocked(device, AKEYCODE_DPAD_UP) &&
hasKeycodeLocked(device, AKEYCODE_DPAD_DOWN) &&
hasKeycodeLocked(device, AKEYCODE_DPAD_LEFT) &&
hasKeycodeLocked(device, AKEYCODE_DPAD_RIGHT) &&
hasKeycodeLocked(device, AKEYCODE_DPAD_CENTER)) {
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_DPAD;
}
// 查看此设备是否有游戏板。
for (size_t i = 0; i < sizeof(GAMEPAD_KEYCODES)/sizeof(GAMEPAD_KEYCODES[0]); i++) {
if (hasKeycodeLocked(device, GAMEPAD_KEYCODES[i])) {
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_GAMEPAD;
break;
}
}
}
// 如果设备未识别类型,删除设备,直接返回
if (device->classes == 0) {
ALOGV("Dropping device: id=%d, path='%s', name='%s'",
deviceId, devicePath, device->identifier.name.string());
delete device;
return -1;
}
// 确定设备是否有麦克风。
if (deviceHasMicLocked(device)) {
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_MIC;
}
// 确定设备是外部设备还是内部设备
if (device->classes & (device->classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH)
|| (device->classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH_MT)) {
int devType = getTouchInputDeviceType(device);
if ( devType == 1)
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_EXTERNAL;
else if ( devType == 2)
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TERTIARY1;
else if ( devType == 3)
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TERTIARY2;
} else if (isExternalDeviceLocked(device))
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_EXTERNAL;
//确认设备是不是操控杆或者是不是游戏键盘,为其设置led灯效
if (device->classes & (INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_JOYSTICK | INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_DPAD)
&& device->classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_GAMEPAD) {
device->controllerNumber = getNextControllerNumberLocked(device);
setLedForControllerLocked(device);
}
if (registerDeviceForEpollLocked(device) != OK) {//将设备节点描述符的可读事件添加到Epoll中,
//当此设备的输入事件到来时,Epoll会在getEvents()函数的调用中产生一条epoll事件
delete device;
return -1;
}
configureFd(device);//给device对应的设备,通过ioctl设置重复设置为禁用
addDeviceLocked(device);//将设备添加到Device容器中
return OK;
}2.31 registerDeviceForEpollLocked
上面完成了/dev/input/xxxx设备节点到Device类的生成,Device类包含各个设备节点的厂商信息、设备类别、上报的事件种类、设备的映射表等诸多信息,然后注册设备节点到epoll中,开始监听各个设备节点下是否有可读事件,即监听设备的原始输入事件。
input事件主要分为两种:
一:原始输入事件,就是当触摸屏幕等操作时,产生的事件。
二:设备的增删事件。
status_t EventHub::registerDeviceForEpollLocked(Device* device) {
struct epoll_event eventItem;
memset(&eventItem, 0, sizeof(eventItem));
eventItem.events = EPOLLIN;//监听的文件描述符是否有可读事件
if (mUsingEpollWakeup) {//EPOLLWAKEUP标志就能保证事件在挂起或处理时,系统不会挂起或休眠。
eventItem.events |= EPOLLWAKEUP;
}
eventItem.data.u32 = device->id;//事件触发时会返回eventItem.data数据
if (epoll_ctl(mEpollFd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, device->fd, &eventItem)) {//监听device->fd对应的设备是否有可读事件。
//如果有事件可读,则返回eventItem.data
ALOGE("Could not add device fd to epoll instance. errno=%d", errno);
return -errno;
}
return OK;
}void EventHub::addDeviceLocked(Device* device) {
mDevices.add(device->id, device);//mDevices的定义是一个容器,KeyedVector<int32_t, Device*> mDevices;
device->next = mOpeningDevices;//Device结构体是一个单链表,其next指向下一个设备,但此时mOpeningDevices在初始化时值为0,0代表最近无设备打开
mOpeningDevices = device;//mOpeningDevices也是一个Device*指针,指向此device,代表最近打开的设备。
}2.32 processEventsLocked
经过前面分析我们知道,input系统第一次启动时候,会先扫描/dev/input下的所有设备,并对所有设备进行信息的读取和配置文件的加载,并生成对应的Device类对象。然后会生成设备添加的事件,当完成所有设备的扫描后,会生成一个设备扫描完成事件。
RawEvent事件含义如下:
struct RawEvent {
nsecs_t when;//时间
int32_t deviceId;//事件发生的设备id
int32_t type;//类型,例如按键事件等
int32_t code;//扫描码,按键对应的扫描码
int32_t value;//值,表示按键按下,或者抬起等
};
void InputReader::processEventsLocked(const RawEvent* rawEvents, size_t count) {//用rawEvents指针接收传入的从传入的mEventBuffer数组的首地址
for (const RawEvent* rawEvent = rawEvents; count;) {//for循环遍历数组
int32_t type = rawEvent->type;//取出数组中第0号的元素rawEvent的type.
size_t batchSize = 1;
//事件信息有两种,一种是设备节点的增加和删除事件,统称为设备事件,另一种是原始输入事件。
//此处满足条件,则是对设备事件进行处理
if (type < EventHubInterface::FIRST_SYNTHETIC_EVENT) {
} else {
switch (rawEvent->type) {//处理设备添加事件
case EventHubInterface::DEVICE_ADDED://设备添加事件。同时为其创建对应的mapper
addDeviceLocked(rawEvent->when, rawEvent->deviceId);
break;
case EventHubInterface::DEVICE_REMOVED://设备删除事件
removeDeviceLocked(rawEvent->when, rawEvent->deviceId);
break;
case EventHubInterface::FINISHED_DEVICE_SCAN://扫描完成事件
handleConfigurationChangedLocked(rawEvent->when);//生成一个通知的事件塞进队列
break;
default:
ALOG_ASSERT(false);
break;
}
}
count -= batchSize;
rawEvent += batchSize;
}
}2.33 addDeviceLocked
此处先分析设备添加事件。主要根据Device对象的一些信息生成InputDevice对象。InputDevice对象中会根据其设备是开关设备、键盘设备、还是滚轮式设备生成诸多对应的mapper对象。
Device类和InputDevice类非常相似,其主要区别是InputDevice相对于Device结构体多了一个
InputMapper列表。
InputMapper有一系列的子类,分别用于加工不同类型的原始输入事件。
void InputReader::addDeviceLocked(nsecs_t when, int32_t deviceId) {
ssize_t deviceIndex = mDevices.indexOfKey(deviceId);
InputDeviceIdentifier identifier = mEventHub->getDeviceIdentifier(deviceId);//mEventHub是在inputreader初始化时赋值的,
//是EventHub类对象,此处只是将device->identifier取出来
uint32_t classes = mEventHub->getDeviceClasses(deviceId);//取出device->classes
int32_t controllerNumber = mEventHub->getDeviceControllerNumber(deviceId);
InputDevice* device = createDeviceLocked(deviceId, controllerNumber, identifier, classes);//创建InputDevice
device->configure(when, &mConfig, 0);//对设备一些厂商信息进行配置,对按键等布局信息进行加载到map中,并对生成的mapper进行配置。配置坐标系映射等
device->reset(when);//重置所有mapper,比如按键mapper是将保存所有按键按下的vector清空。
if (device->isIgnored()) {//isIgnored()函数返回的是mMapper容器是否为空,一般不为空,除非出错
ALOGI("Device added: id=%d, name='%s' (ignored non-input device)", deviceId,
identifier.name.string());
} else {
ALOGI("Device added: id=%d, name='%s', sources=0x%08x", deviceId,
identifier.name.string(), device->getSources());
}
mDevices.add(deviceId, device);
bumpGenerationLocked();
if (device->getClasses() & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_EXTERNAL_STYLUS) {
notifyExternalStylusPresenceChanged();
}
}2.34 createDeviceLocked
1.生成了InputDevice类对象。
2.根据设备的class类型生成了多个对应的inputMapper对象。并将inputMapper对象存储在InputDevice类的一个容器中。
其事件类型、设备类型和InputMapper对应关系如下:

(图片来自参考文章)
InputDevice* InputReader::createDeviceLocked(int32_t deviceId, int32_t controllerNumber,
const InputDeviceIdentifier& identifier, uint32_t classes) {
InputDevice* device = new InputDevice(&mContext, deviceId, bumpGenerationLocked(),controllerNumber, identifier, classes);
//此处本质是通过Device结构体,生成InputReader类的InputDevice对象,InputDevice表示的是单个设备的状态。单个很重要
//根据Device结构体指针的class属性,为InputReader类赋值
//参数分析:
//mContext是inputreader对象
//bumpGenerationLocked函数会将Generation值加1.故此时是2
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_EXTERNAL) {
device->setExternal(true);//源码为inline void setExternal(bool external) { mIsExternal = external; }
}
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TERTIARY1) {
device->setTertiary(1);//源码为inline void setTertiary(int tertiary) { mIsTertiary = tertiary; }
}
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TERTIARY2) {
device->setTertiary(2);//源码为inline void setTertiary(int tertiary) { mIsTertiary = tertiary; }
}
// 设备有麦克风
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_MIC) {
device->setMic(true);//源码为inline void setMic(bool hasMic) { mHasMic = hasMic; }
}
// 开关设备
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_SWITCH) {
device->addMapper(new SwitchInputMapper(device));//源码为
//1.SwitchInputMapper::SwitchInputMapper(InputDevice* device) :InputMapper(device), mSwitchValues(0), mUpdatedSwitchMask(0)
//2.void InputDevice::addMapper(InputMapper* mapper) {mMappers.add(mapper);}
//含义:如果是开关设备,则初始化一个SwitchInputMapper,并添加到存储InputMapper*指针的容器mMappers中。
}
// 滚动滚轮式设备。
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_ROTARY_ENCODER) {
device->addMapper(new RotaryEncoderInputMapper(device));
}
// 力反馈设备,类似振动器
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_VIBRATOR) {
device->addMapper(new VibratorInputMapper(device));
}
// 类似键盘设备.
uint32_t keyboardSource = 0;
int32_t keyboardType = AINPUT_KEYBOARD_TYPE_NON_ALPHABETIC;
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_KEYBOARD) {//可以上报鼠标按键以外的EV_KEY类型事件的设备都属于此类。如键盘、机身按钮(音量键、电源键等)。
keyboardSource |= AINPUT_SOURCE_KEYBOARD;
}
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_ALPHAKEY) {//表示可以上报字符按键的设备,此类型的设备必定同时属于keyboard
keyboardType = AINPUT_KEYBOARD_TYPE_ALPHABETIC;//有字母的键盘按键
}
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_DPAD) {//可以上报方向键的设备。例如键盘、手机导航键等
keyboardSource |= AINPUT_SOURCE_DPAD;
}
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_GAMEPAD) {//可以上报游戏按键的设备,如游戏手柄。这类设备同时也属于KEYBOARD
keyboardSource |= AINPUT_SOURCE_GAMEPAD;
}
if (keyboardSource != 0) {
device->addMapper(new KeyboardInputMapper(device, keyboardSource, keyboardType));//创建了一个KeyboardInputMapper,
//并添加到存储InputMapper*指针的容器mMappers中
}
// 类似光标的设备,如鼠标
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_CURSOR) {
device->addMapper(new CursorInputMapper(device));
}
// 触摸屏或者触摸平板设备
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH_MT) {
device->addMapper(new MultiTouchInputMapper(device));//new了一个多点触摸的Mapper
} else if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH) {
device->addMapper(new SingleTouchInputMapper(device));//new了一个单点触摸的Mapper
}
// 类似操纵手柄的设备
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_JOYSTICK) {
device->addMapper(new JoystickInputMapper(device));
}
// 外部类似手写笔的设备。
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_EXTERNAL_STYLUS) {
device->addMapper(new ExternalStylusInputMapper(device));
}
return device;
}2.35 configure
1.主要是对mapper循环调用configure,后续文章会对键盘和触摸屏进行配置的分析。
void InputDevice::configure(nsecs_t when, const InputReaderConfiguration* config, uint32_t changes) {
mSources = 0;
if (!isIgnored()) {//isIgnored()函数返回的是mMapper容器是否为空,一般不为空,除非出错
if (!changes) { // 仅设备第一次添加时,此处执行
mContext->getEventHub()->getConfiguration(mId, &mConfiguration);//从Device类的对象中获取configuration,
//赋值给传入的inputDevice类对象的mConfiguration,mId是deviceid
}
if (!changes || (changes & InputReaderConfiguration::CHANGE_KEYBOARD_LAYOUTS)) {//第一次配置设备时,必会执行,
//否则就是当键盘布局发生改变时,changes会等于CHANGE_KEYBOARD_LAYOUTS时,下列代码才执行。
if (!(mClasses & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_VIRTUAL)) {//此处含义为:当不是虚拟键盘时,从供应商信息中获取键盘布局,
//并保存到keyboardLayout这个KeyCharacterMap中。
sp<KeyCharacterMap> keyboardLayout =
mContext->getPolicy()->getKeyboardLayoutOverlay(mIdentifier);
if (mContext->getEventHub()->setKeyboardLayoutOverlay(mId, keyboardLayout)) {
bumpGeneration();
}
}
}
if (!changes || (changes & InputReaderConfiguration::CHANGE_DEVICE_ALIAS)) {//第一次配置设备时,必会执行,
//否则就是当设备的别名发生改变时,changes会等于CHANGE_KEYBOARD_LAYOUTS时,下列代码才执行。
if (!(mClasses & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_VIRTUAL)) {//此处含义为:当不是虚拟键盘时,从供应商信息中获取别名,
//并重新给设备的别名赋值
String8 alias = mContext->getPolicy()->getDeviceAlias(mIdentifier);
if (mAlias != alias) {
mAlias = alias;
bumpGeneration();
}
}
}
if (!changes || (changes & InputReaderConfiguration::CHANGE_ENABLED_STATE)) {//第一次必定执行,
//CHANGE_ENABLED_STATE表示的含义是CHANGE_ENABLED_STATE表示的含义是禁用的输入设备已更改。当chnages等于时,下列代码才执行
ssize_t index = config->disabledDevices.indexOf(mId);//disabledDevices是一个有序的容器,存储的是禁用的设备。
//从禁用的设备容器中,根据deviceid查询
bool enabled = index < 0;//第一次配置设备时enabled为ture,
setEnabled(enabled, when);//enabled值为ture就设置Device*类的device->enabled属性为true
}
size_t numMappers = mMappers.size();
for (size_t i = 0; i < numMappers; i++) {//循环对具体的mapper进行配置
InputMapper* mapper = mMappers[i];
mapper->configure(when, config, changes);//此函数是根据具体的map进行配置的,//此处仅分析touch的配置和keyboard的配置。
mSources |= mapper->getSources();
}
}
}2.36 removeDeviceLocked
如果是删除设备事件,则:
1.删除对应的InputDevice设备
2.重置其所有的mapper
void InputReader::removeDeviceLocked(nsecs_t when, int32_t deviceId) {
InputDevice* device = NULL;
ssize_t deviceIndex = mDevices.indexOfKey(deviceId);
if (deviceIndex < 0) {
ALOGW("Ignoring spurious device removed event for deviceId %d.", deviceId);
return;
}
device = mDevices.valueAt(deviceIndex);
mDevices.removeItemsAt(deviceIndex, 1);//从mDevices中删除InputDevice指针
bumpGenerationLocked();//值+1,表示设备有变化
if (device->isIgnored()) {
ALOGI("Device removed: id=%d, name='%s' (ignored non-input device)",
device->getId(), device->getName().string());
} else {
ALOGI("Device removed: id=%d, name='%s', sources=0x%08x",
device->getId(), device->getName().string(), device->getSources());
}
if (device->getClasses() & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_EXTERNAL_STYLUS) {
notifyExternalStylusPresenceChanged();//如果是外部手写笔,则通知
}
device->reset(when);//重置device中的所有mapper
delete device;
}2.37 handleConfigurationChangedLocked
1.生成了一个NotifyConfigurationChangedArgs消息,然后进入派发队列。
//设备完成扫描时,生成一个通知arg
void InputReader::handleConfigurationChangedLocked(nsecs_t when) {
// Reset global meta state because it depends on the list of all configured devices.
updateGlobalMetaStateLocked();
NotifyConfigurationChangedArgs args(when);//生成了一个NotifyConfigurationChangedArgs消息
mQueuedListener->notifyConfigurationChanged(&args);//进入派发队列
}进入派发队列,然后等待唤醒派发线程。
void QueuedInputListener::notifyConfigurationChanged(
const NotifyConfigurationChangedArgs* args) {
mArgsQueue.push(new NotifyConfigurationChangedArgs(*args));//将此消息放入队列中
}再次回到inputreader第一次启动执行的代码块,注意,看此时会调用notifyInputDevicesChanged来通知java层IMS设备发生变化。
//第一次启动时,执行的代码块
void InputReader::loopOnce() {
int32_t oldGeneration;
int32_t timeoutMillis;
bool inputDevicesChanged = false;
Vector<InputDeviceInfo> inputDevices;
{
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
oldGeneration = mGeneration;//值为1,在inputreader构造函数中mGeneration=1,
timeoutMillis = -1;
uint32_t changes = mConfigurationChangesToRefresh;//值为0,初始化时设置为0,代表无变化,不刷新配置
// if (changes) {//此处刚开始代码不执行,
// mConfigurationChangesToRefresh = 0;
// timeoutMillis = 0;
// refreshConfigurationLocked(changes);
// } else if (mNextTimeout != LLONG_MAX) {//在inputreader构造函数中,mNextTimeout是LLONG_MAX,此处代码不会执行
// //此处的含义本人认为,mNextTimeout代表了下一次线程唤醒的时间点,如果mNextTimeout不是LLONG_MAX,则需要计算休眠的时间
// nsecs_t now = systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC);
// timeoutMillis = toMillisecondTimeoutDelay(now, mNextTimeout);//线程休眠时间
// }
}
size_t count = mEventHub->getEvents(timeoutMillis, mEventBuffer, EVENT_BUFFER_SIZE);//通过EventHub的getEvents函数获取事件,
//并存放在mEventBuffer中。此时可以知道刚启动时,只是会生成所有已经扫描的设备的add类型的事件和一个完成设备扫描的事件
//参数分析:timeoutMillis=-1,代表啥意思不清楚,感觉如果数字为0代表立即执行
//mEventBuffer是一个存放从eventhub中读取的rawevent结构体类型的数组,源代码是:RawEvent mEventBuffer[EVENT_BUFFER_SIZE];
//EVENT_BUFFER_SIZE值是256,代表最大可以读取256个原始事件,RawEvent结构体如下
////从EventHub检索到的原始事件
//struct RawEvent {
//nsecs_t when;//时间
//int32_t deviceId;//事件发生的设备id
//int32_t type;//类型,例如按键事件等
//int32_t code;//扫描码,按键对应的扫描码
//int32_t value;//值,表示按键按下,或者抬起等
//};
{ // acquire lock
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
mReaderIsAliveCondition.broadcast();
if (count) {//返回的事件数量大于,则调用processEventsLocked处理事件
processEventsLocked(mEventBuffer, count);
}
/*
if (mNextTimeout != LLONG_MAX) //此时mNextTimeout是LLONG_MAX
{
nsecs_t now = systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC);
if (now >= mNextTimeout) {
#if DEBUG_RAW_EVENTS
ALOGD("Timeout expired, latency=%0.3fms", (now - mNextTimeout) * 0.000001f);
#endif
mNextTimeout = LLONG_MAX;
timeoutExpiredLocked(now);
}
}*/
if (oldGeneration != mGeneration) {//此处是不等于的,因为当有add设备事件时processEventsLocked函数中调用addDeviceLocked,addDeviceLocked在完成设备配置后
//会调用bumpGenerationLocked函数,使得mGeneration+1,从而不相等
inputDevicesChanged = true;
getInputDevicesLocked(inputDevices);//获取所有的新的设备信息到inputDevices容器中
}
} // release lock
//
if (inputDevicesChanged) {//如果设备发生变化,生成一个通知设备事件的通知
mPolicy->notifyInputDevicesChanged(inputDevices);//此时mPolicy是NativeInputManager对象,所以此时调用到了NativeInputManager::notifyInputDevicesChanged
}
//发布事件。 一般此处只会处理加工后的原始输入事件,而此时开机启动只有设备添加和删除的事件,但是当设备完成扫描时会生成一个通知事件
//放入此队列。所以启动后,扫描完设备后,此容器只有一个扫描设备完成的通知事件
// mQueuedListener中。在循环的最后,通过调用flush()函数将所有事件交付给InputDispatcher
mQueuedListener->flush();
}2.38 notifyInputDevicesChanged
mpolicy对象本质是NativeInputManager对象。
此处主要作用是:
当开机启动后,扫描完所有设备会生成InputDevice对象,然后根据InputDevice对象会生成对应的
InputDeviceInfo类对象,其同样包含设备的所有信息,然后通过jni通知到java层的IMS,用于通知给java层通知设备监听的listener。
void NativeInputManager::notifyInputDevicesChanged(const Vector<InputDeviceInfo>& inputDevices) {
//inputDevices存储了所有刚开机启动添加的所有的设备信息。
ATRACE_CALL();
JNIEnv* env = jniEnv();
size_t count = inputDevices.size();
jobjectArray inputDevicesObjArray = env->NewObjectArray(count, gInputDeviceClassInfo.clazz, NULL);//创建一个保存类的对象数组大小为count
//static struct {
//jclass clazz;
//} gInputDeviceClassInfo;
if (inputDevicesObjArray) {
bool error = false;
for (size_t i = 0; i < count; i++) {
jobject inputDeviceObj = android_view_InputDevice_create(env, inputDevices.itemAt(i));//根据c++的InputDeviceInfo类的对象创建对应的inputDeviceObj对象
if (!inputDeviceObj) {
error = true;
break;
}
env->SetObjectArrayElement(inputDevicesObjArray, i, inputDeviceObj);//将生成的inputDeviceObj对象设置进对象数组中
env->DeleteLocalRef(inputDeviceObj);//删除本地引用
}
if (!error) {//如果没有出错,则通过jni调用java层的notifyInputDevicesChanged方法,传递参数为inputDevicesObjArray
env->CallVoidMethod(mServiceObj, gServiceClassInfo.notifyInputDevicesChanged,inputDevicesObjArray);
}
env->DeleteLocalRef(inputDevicesObjArray);
}
checkAndClearExceptionFromCallback(env, "notifyInputDevicesChanged");
}我们可以看到函数形参上存在,存储InputDeviceInfo的容器,那么InputDeviceInfo是何时被创建的呢?
查看InputReader::loopOnce() 存在getInputDevicesLocked函数。
此函数主要是为所有的InputDevice生成对应的InputDeviceInfo对象。
void InputReader::getInputDevicesLocked(Vector<InputDeviceInfo>& outInputDevices) {
outInputDevices.clear();//Vector<InputDeviceInfo> inputDevices;,保存的是所有的设备信息。当设备发生变化时,先清除所有的信息
size_t numDevices = mDevices.size();
for (size_t i = 0; i < numDevices; i++) {//循环为所有的InputDevice生成对应的InputDeviceInfo类对象
InputDevice* device = mDevices.valueAt(i);
if (!device->isIgnored()) {
outInputDevices.push();//往inputDevices中添加一个InputDeviceInfo
device->getDeviceInfo(&outInputDevices.editTop());
}
}
}void InputDevice::getDeviceInfo(InputDeviceInfo* outDeviceInfo) {
outDeviceInfo->initialize(mId, mGeneration, mControllerNumber, mIdentifier, mAlias,
mIsExternal, mHasMic);
//mId是设备id
//mGeneration 主要用于判断设备是否发生了变化的参数
//mControllerNumber,控制器编号 默认是0
//mIdentifier,主要包含了设备厂商信息
//mAlias,代表别名
//mIsExternal代表是不是外接设备
//mHasMic是否有麦克风
size_t numMappers = mMappers.size();
for (size_t i = 0; i < numMappers; i++) {
InputMapper* mapper = mMappers[i];
mapper->populateDeviceInfo(outDeviceInfo);//此处会根据不同的mapper执行不同的操作。此处暂时分析KeyboardInputMapper,因为一个设备可能有多个maper
}
}void InputDeviceInfo::initialize(int32_t id, int32_t generation, int32_t controllerNumber,
const InputDeviceIdentifier& identifier, const String8& alias, bool isExternal,
bool hasMic) {
mId = id;
mGeneration = generation;
mControllerNumber = controllerNumber;
mIdentifier = identifier;
mAlias = alias;
mIsExternal = isExternal;
mHasMic = hasMic;
mSources = 0;
mKeyboardType = AINPUT_KEYBOARD_TYPE_NONE;
mHasVibrator = false;
mHasButtonUnderPad = false;
mMotionRanges.clear();
}void KeyboardInputMapper::populateDeviceInfo(InputDeviceInfo* info) {
InputMapper::populateDeviceInfo(info);//调用了父类的populateDeviceInfo
//主要是设置source类型
info->setKeyboardType(mKeyboardType);//设置按键的type
/*
enum {
AINPUT_KEYBOARD_TYPE_NONE = 0,
// 无字母的键盘按键
AINPUT_KEYBOARD_TYPE_NON_ALPHABETIC = 1,
// 有字母的键盘按键
AINPUT_KEYBOARD_TYPE_ALPHABETIC = 2,
};*/
info->setKeyCharacterMap(getEventHub()->getKeyCharacterMap(getDeviceId()));//设置其按键映射表到InputDeviceInfo中
}
void InputMapper::populateDeviceInfo(InputDeviceInfo* info) {
info->addSource(getSources());//soucre采用的是|的运算方式,因为一个InputDeviceInfo可能对应多个InputMapper
}
void InputDeviceInfo::addSource(uint32_t source) {
mSources |= source;
//AINPUT_SOURCE_KEYBOARD可以上报鼠标按键以外的EV_KEY类型事件的设备都属于此类。如键盘、机身按钮(音量键、电源键等)。
//AINPUT_SOURCE_DPAD表示可以上报字符按键的设备,此类型的设备必定同时属于keyboard
//AINPUT_SOURCE_GAMEPAD可以上报游戏按键的设备,如游戏手柄。这类设备同时也属于KEYBOARD
}找到了InputDeviceInfo的创建,那么我们此时需要再回到notifyInputDevicesChanged函数,其中
android_view_InputDevice_create是根据C++层的InputDeviceInfo类的对象创建java层的inputDeviceObj对象,然后通过jni机制调用java层的notifyInputDevicesChanged函数。
jobject android_view_InputDevice_create(JNIEnv* env, const InputDeviceInfo& deviceInfo) {
ScopedLocalRef<jstring> nameObj(env, env->NewStringUTF(deviceInfo.getDisplayName().string()));//生成jni的nameObj,此时是设备厂商的名称
if (!nameObj.get()) {
return NULL;
}
ScopedLocalRef<jstring> descriptorObj(env,env->NewStringUTF(deviceInfo.getIdentifier().descriptor.string()));//生成jni的描述符
if (!descriptorObj.get()) {
return NULL;
}
ScopedLocalRef<jobject> kcmObj(env,
android_view_KeyCharacterMap_create(env, deviceInfo.getId(),
deviceInfo.getKeyCharacterMap()));//根据c++层的键盘布局的map生成jni层的键盘布局map
if (!kcmObj.get()) {
return NULL;
}
const InputDeviceIdentifier& ident = deviceInfo.getIdentifier();
// Not sure why, but JNI is complaining when I pass this through directly.
jboolean hasMic = deviceInfo.hasMic() ? JNI_TRUE : JNI_FALSE;
ScopedLocalRef<jobject> inputDeviceObj(env, env->NewObject(gInputDeviceClassInfo.clazz,//生成对应的inputDeviceObj
gInputDeviceClassInfo.ctor, deviceInfo.getId(), deviceInfo.getGeneration(),
deviceInfo.getControllerNumber(), nameObj.get(),
static_cast<int32_t>(ident.vendor), static_cast<int32_t>(ident.product),
descriptorObj.get(), deviceInfo.isExternal(), deviceInfo.getSources(),
deviceInfo.getKeyboardType(), kcmObj.get(), deviceInfo.hasVibrator(),
hasMic, deviceInfo.hasButtonUnderPad()));
const Vector<InputDeviceInfo::MotionRange>& ranges = deviceInfo.getMotionRanges();//添加motion相关的设备信息,键盘的话,是为空的
for (size_t i = 0; i < ranges.size(); i++) {
const InputDeviceInfo::MotionRange& range = ranges.itemAt(i);
env->CallVoidMethod(inputDeviceObj.get(), gInputDeviceClassInfo.addMotionRange, range.axis,
range.source, range.min, range.max, range.flat, range.fuzz, range.resolution);
if (env->ExceptionCheck()) {
return NULL;
}
}
return env->NewLocalRef(inputDeviceObj.get());
}//IMS.java
private void notifyInputDevicesChanged(InputDevice[] inputDevices) {
synchronized (mInputDevicesLock) {
if (!mInputDevicesChangedPending) {
mInputDevicesChangedPending = true;
mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_DELIVER_INPUT_DEVICES_CHANGED,mInputDevices).sendToTarget();//mHandler是InputManager对象,
//Handler获取一个消息,触发mHandler的handleMessage函数。
}
mInputDevices = inputDevices;
}
} public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case MSG_DELIVER_INPUT_DEVICES_CHANGED:
deliverInputDevicesChanged((InputDevice[])msg.obj);
break;
case MSG_SWITCH_KEYBOARD_LAYOUT:
handleSwitchKeyboardLayout(msg.arg1, msg.arg2);
break;
case MSG_RELOAD_KEYBOARD_LAYOUTS:
reloadKeyboardLayouts();
break;
case MSG_UPDATE_KEYBOARD_LAYOUTS:
updateKeyboardLayouts();
break;
case MSG_RELOAD_DEVICE_ALIASES:
reloadDeviceAliases();
break;
case MSG_DELIVER_TABLET_MODE_CHANGED:
SomeArgs args = (SomeArgs) msg.obj;
long whenNanos = (args.argi1 & 0xFFFFFFFFl) | ((long) args.argi2 << 32);
boolean inTabletMode = (boolean) args.arg1;
deliverTabletModeChanged(whenNanos, inTabletMode);
break;
}
} private void deliverInputDevicesChanged(InputDevice[] oldInputDevices) {
// Scan for changes.
int numFullKeyboardsAdded = 0;
mTempInputDevicesChangedListenersToNotify.clear();
mTempFullKeyboards.clear();
final int numListeners;
final int[] deviceIdAndGeneration;
synchronized (mInputDevicesLock) {
if (!mInputDevicesChangedPending) {//刚才mInputDevicesChangedPending值为true
return;
}
mInputDevicesChangedPending = false;
numListeners = mInputDevicesChangedListeners.size();//mInputDevicesChangedListeners存储着监听device设备的listener,这些listener会在java层调用registerInputDeviceListener
//注册input的设备增加和删除
for (int i = 0; i < numListeners; i++) {
mTempInputDevicesChangedListenersToNotify.add(//取出所有的监听设备add,放入mTempInputDevicesChangedListenersToNotify中
mInputDevicesChangedListeners.valueAt(i));
}
final int numDevices = mInputDevices.length;
deviceIdAndGeneration = new int[numDevices * 2];
for (int i = 0; i < numDevices; i++) {
final InputDevice inputDevice = mInputDevices[i];
deviceIdAndGeneration[i * 2] = inputDevice.getId();
deviceIdAndGeneration[i * 2 + 1] = inputDevice.getGeneration();
if (!inputDevice.isVirtual() && inputDevice.isFullKeyboard()) {//如果设备不是虚拟键盘,并且是有字母的键盘
if (!containsInputDeviceWithDescriptor(oldInputDevices,
inputDevice.getDescriptor())) {//如果旧的inputDevice和更新后的inputDevice对应的设备描述符不一样
mTempFullKeyboards.add(numFullKeyboardsAdded++, inputDevice);
} else {
mTempFullKeyboards.add(inputDevice);//保存所有设备中是有字母键盘的,后面由于检查键盘布局
}
}
}
}
// Notify listeners.
for (int i = 0; i < numListeners; i++) {
mTempInputDevicesChangedListenersToNotify.get(i).notifyInputDevicesChanged(
deviceIdAndGeneration);//通知所有的客户端设备add和remove的消息
}
mTempInputDevicesChangedListenersToNotify.clear();
//检查是否缺少键盘布局
List<InputDevice> keyboardsMissingLayout = new ArrayList<>();
final int numFullKeyboards = mTempFullKeyboards.size();
synchronized (mDataStore) {
for (int i = 0; i < numFullKeyboards; i++) {
final InputDevice inputDevice = mTempFullKeyboards.get(i);
String layout =
getCurrentKeyboardLayoutForInputDevice(inputDevice.getIdentifier());//获取当前键盘布局
if (layout == null) {
layout = getDefaultKeyboardLayout(inputDevice);//如果布局为空,则获取默认的布局
if (layout != null) {//如果布局不为空
setCurrentKeyboardLayoutForInputDevice(
inputDevice.getIdentifier(), layout);//设置当前布局
}
}
if (layout == null) {//如果布局为空
keyboardsMissingLayout.add(inputDevice);//则将此键盘添加缺少布局
}
}
}
if (mNotificationManager != null) {
if (!keyboardsMissingLayout.isEmpty()) {
if (keyboardsMissingLayout.size() > 1) {//发送缺少键盘布局的通知
showMissingKeyboardLayoutNotification(null);
} else {
showMissingKeyboardLayoutNotification(keyboardsMissingLayout.get(0));
}
} else if (mKeyboardLayoutNotificationShown) {
hideMissingKeyboardLayoutNotification();
}
}
mTempFullKeyboards.clear();
}2.39 QueuedInputListener::flush
void QueuedInputListener::flush() {
size_t count = mArgsQueue.size();
for (size_t i = 0; i < count; i++) {//从存储NotifyArgs的容器中循环取出并调用notify
NotifyArgs* args = mArgsQueue[i];
args->notify(mInnerListener);//传入的参数mInnerListener是InputDispatcher类对象
delete args;
}
mArgsQueue.clear();
}2.40 NotifyConfigurationChangedArgs::notify
void NotifyConfigurationChangedArgs::notify(const sp<InputListenerInterface>& listener) const {
listener->notifyConfigurationChanged(this);//此处listener是InputDispatcher类对象,this是调用者也就是一个NotifyConfigurationChangedArgs对象
}2.41 notifyConfigurationChanged
1生成了一个ConfigurationChangedEntry事件,并将此事件放入InboundQueue中,然后唤醒派发线程,派发线程会取出消息进行派发。
void InputDispatcher::notifyConfigurationChanged(const NotifyConfigurationChangedArgs* args) {
#if DEBUG_INBOUND_EVENT_DETAILS
ALOGD("notifyConfigurationChanged - eventTime=%" PRId64, args->eventTime);
#endif
bool needWake;
{ // acquire lock
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
ConfigurationChangedEntry* newEntry = new ConfigurationChangedEntry(args->eventTime);//生成ConfigurationChangedEntry事件
needWake = enqueueInboundEventLocked(newEntry);//将事件放入队列中
} // release lock
if (needWake) {
mLooper->wake();//需要唤醒分发线程的looper
}
}查看2.22知道,此时的派发线程在休眠状态,mLooper->pollOnce(timeoutMillis);然后唤醒后,会进入下一次dispatchOnce的调用。此时分析第二次执行的代码块。
2.42 dispatchOnce
//唤醒线程后,第二次执行的代码块
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce() {
nsecs_t nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MAX;//下一次唤醒该线程的时间,也可以说是下一次线程循环的执行时间点
{
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
mDispatcherIsAliveCondition.broadcast();//分发线程处于活跃状态,进行广播
if (!haveCommandsLocked()) {//此时mCommandQueue中无命令。作用:检查inputdispatcher的缓存队列中是否有还未处理的命令,
//只有无命令时才会执行dispatchOnceInnerLocked方法,进行事件的分发。
dispatchOnceInnerLocked(&nextWakeupTime);// 传入的nextWakeupTime决定了下次派发线程循环的执行时间点,
}
if (runCommandsLockedInterruptible()) {//此时dispatchOnceInnerLocked在处理设备变化的消息时,调用dispatchConfigurationChangedLocked
//向命令队列中添加了一条命令,所以不为空
//如果此时缓存队列中有命令,则立即执行该命令,
//并将下一次线程循环的执行时间点设置为LONG_LONG_MIN,将使派发线程立刻开始下次线程。
//最小值定义为0,最大值是unsigned long long的最大值:1844674407370955161
nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MIN;//会执行,并立即开启第三次线程循环
}
} // release lock
nsecs_t currentTime = now();//获取当前时间点
int timeoutMillis = toMillisecondTimeoutDelay(currentTime, nextWakeupTime);//下一次唤醒时间点-当前时间点=线程休眠时间
mLooper->pollOnce(timeoutMillis);//调用pollOnce使线程休眠,等待回调,唤醒或超时。
//Looper的pollOnce()的实质就是epoll_wait()。 因此派发线程的休眠在三种情况下可能被唤醒:
1.调用Looper::wake()函数主动唤醒(有输入事件注入派发队列中时),
2.到达nextWakeupTime的事件点时唤醒
3.epoll_waitepoll_wait()监听的fd有epoll_event发生时唤醒(这种唤醒方式将在介绍ANR机制时讨论)。
}2.43 dispatchOnceInnerLocked
1.生成ConfigurationChangedEntry事件,用于表示配置发生变化
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnceInnerLocked(nsecs_t* nextWakeupTime) {
nsecs_t currentTime = now();
if (!mDispatchEnabled) {//默认值为flase
resetKeyRepeatLocked();//重置上一个事件
}
// 如果mDispatch被冻结,则不派发事件
if (mDispatchFrozen) {
#if DEBUG_FOCUS
ALOGD("Dispatch frozen. Waiting some more.");
#endif
return;
}
bool isAppSwitchDue = mAppSwitchDueTime <= currentTime;//第二次循环时mAppSwitchDueTime值是LONG_LONG_MAX,所以isAppSwitchDue是false
//如果没有待发送的事件,则从mInboundQueue队列中取出一个事件,进行分发
if (! mPendingEvent) {//此时mPendingEvent= null
///if (mInboundQueue.isEmpty())
{
} else {//此时不会空
//从派发队列中将位于队首的一条EventEntry取出并保存在mPendingEvent成员变量中。
// mPendingEvent表示处于派发过程中的一个输入事件
mPendingEvent = mInboundQueue.dequeueAtHead();
traceInboundQueueLengthLocked();//更新一下队列长度
}
/// Poke user activity for this event.
///if (mPendingEvent->policyFlags & POLICY_FLAG_PASS_TO_USER) {//判断此key是否需要发送到应用程序。此时启动后只是一个设备变化的通知,故不执行
/// pokeUserActivityLocked(mPendingEvent);
///}
// Get ready to dispatch the event.
resetANRTimeoutsLocked();//重置anr
}
bool done = false;
DropReason dropReason = DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED;//默认丢弃原因为不丢弃
if (!(mPendingEvent->policyFlags & POLICY_FLAG_PASS_TO_USER)) {//在将事件注入派发队列时曾向DispatcherPolicy询间过派发策略
//倘若派发策略不允许此事件被派发给用户,则设置对应的dropReason
dropReason = DROP_REASON_POLICY;
}
///if (mNextUnblockedEvent == mPendingEvent) {//mNextUnblockedEvent此时为null,不执行
/// mNextUnblockedEvent = NULL;
///}
switch (mPendingEvent->type) {
case EventEntry::TYPE_CONFIGURATION_CHANGED: {
ConfigurationChangedEntry* typedEntry =static_cast<ConfigurationChangedEntry*>(mPendingEvent);
done = dispatchConfigurationChangedLocked(currentTime, typedEntry);//取出事件的type,发现是配置文件发生变化类型,则调用dispatchConfigurationChangedLocked
dropReason = DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED; // 配置发生变化类型永远也不会被丢弃
break;
}
default:
break;
}
if (done) {
mLastDropReason = dropReason;//mLastDropReason等于不丢弃
releasePendingEventLocked(); //释放此Event事件
*nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MIN; // 设置唤醒时间为LONG_LONG_MIN,表示立刻唤醒下次循环
}
}2.44 dispatchConfigurationChangedLocked
1.生成一个command命令事件。为了告诉policy配置已发生变化。并将此命令放入命令队列中。
bool InputDispatcher::dispatchConfigurationChangedLocked(nsecs_t currentTime, ConfigurationChangedEntry* entry) {
//在添加或删除键盘设备或其他情况下重置重复键。
resetKeyRepeatLocked();
//生成一个command命令事件。为了告诉policy配置已发生变化
CommandEntry* commandEntry = postCommandLocked(& InputDispatcher::doNotifyConfigurationChangedInterruptible);//传入了一个函数地址作为命令
commandEntry->eventTime = entry->eventTime;
return true;
}
InputDispatcher::CommandEntry* InputDispatcher::postCommandLocked(Command command) {
CommandEntry* commandEntry = new CommandEntry(command);
mCommandQueue.enqueueAtTail(commandEntry);//入队命令队列
return commandEntry;
}此时,我们可以知道,dispatchOnceInnerLocked是往命令队列中插入了一条命令。因此再回到
2.42的dispatchOnce函数的runCommandsLockedInterruptible这一行。
2.45 runCommandsLockedInterruptible
主要作用:
从命令队列中取出命令,然后执行doNotifyConfigurationChangedInterruptible函数,并将commandEntry作为参传递进去
bool InputDispatcher::runCommandsLockedInterruptible() {
///if (mCommandQueue.isEmpty()) {
/// return false;//不为空
///}
do {
CommandEntry* commandEntry = mCommandQueue.dequeueAtHead();//取出命令
Command command = commandEntry->command;
(this->*command)(commandEntry); // 执行doNotifyConfigurationChangedInterruptible函数,并传入commandEntry作为参数
commandEntry->connection.clear();//清除connection
delete commandEntry;
} while (! mCommandQueue.isEmpty());
return true;
}2.46 doNotifyConfigurationChangedInterruptible
void InputDispatcher::doNotifyConfigurationChangedInterruptible(CommandEntry* commandEntry) {
mLock.unlock();
mPolicy->notifyConfigurationChanged(commandEntry->eventTime);//调用NativeInputManager类对象的notifyConfigurationChanged方法,通知配置发生变化
mLock.lock();
}2.47 notifyConfigurationChanged
void NativeInputManager::notifyConfigurationChanged(nsecs_t when) {
JNIEnv* env = jniEnv();
env->CallVoidMethod(mServiceObj, gServiceClassInfo.notifyConfigurationChanged, when);
checkAndClearExceptionFromCallback(env, "notifyConfigurationChanged");
}
//java层IMS
private void notifyConfigurationChanged(long whenNanos) {//此处调用到了wms的notifyConfigurationChanged
mWindowManagerCallbacks.notifyConfigurationChanged();//mWindowManagerCallbacks就是WMS中的InputManagerCallback,此时便走到了WMS中
}
2.48 notifyConfigurationChanged
java层InputMontior.java,此类是在WMS类中的ims回调类的实现类,此时便通知到了WMS。
1.通知与此输入设备相关联的显示器。
2.当系统刚启动的时候,因为WMS会等待IMS将输入设备配置好,才唤醒派发事件。因此当IMS第一次配置好设备后,唤醒再此等待的线程。
//InputMontior.java
public void notifyConfigurationChanged() {
//通知与此输入设备相关联的正确显示器。
mService.sendNewConfiguration(DEFAULT_DISPLAY);//mService是wms对象
synchronized (mInputDevicesReadyMonitor) {
if (!mInputDevicesReady) {
mInputDevicesReady = true;//当第一次接收到输入设备配置改变通知以指示输入设备已准备好时,设置为true。
mInputDevicesReadyMonitor.notifyAll();//唤醒在mInputDevicesReadyMonitor等待的线程,因为在startOtherServices中,会调用waitForInputDevicesReady进行等待
//WMS需要等待开机后Ims将第一次设备已经配置好才派发事件。
}
}
}WMS会等待IMS将输入设备配置如下:
private void startOtherServices() {
final boolean safeMode = wm.detectSafeMode();
}//windowmanagerservice.java
public boolean detectSafeMode() {
if (!mInputMonitor.waitForInputDevicesReady(
INPUT_DEVICES_READY_FOR_SAFE_MODE_DETECTION_TIMEOUT_MILLIS)) {
Slog.w(TAG_WM, "Devices still not ready after waiting "
+ INPUT_DEVICES_READY_FOR_SAFE_MODE_DETECTION_TIMEOUT_MILLIS
+ " milliseconds before attempting to detect safe mode.");
}
} public boolean waitForInputDevicesReady(long timeoutMillis) {
synchronized (mInputDevicesReadyMonitor) {
if (!mInputDevicesReady) {
try {
mInputDevicesReadyMonitor.wait(timeoutMillis);
} catch (InterruptedException ex) {
}
}
return mInputDevicesReady;
}
}2.49
然后由于是立即唤醒,分发线程再次被唤醒,此时分发线程无消息,则陷入无线等待。
然后读取线程也进入第二次循环,epoll_wait等待输入事件的发生。
//唤醒线程后,第三次执行的代码块,然后分发线程陷入无线等待。
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce() {
nsecs_t nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MAX;//下一次唤醒该线程的时间,也可以说是下一次线程循环的执行时间点
{
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
mDispatcherIsAliveCondition.broadcast();//分发线程处于活跃状态,进行广播
if (!haveCommandsLocked()) {//此时mCommandQueue中无命令。
dispatchOnceInnerLocked(&nextWakeupTime);// 传入的nextWakeupTime决定了下次派发线程循环的执行时间点,
}
///if (runCommandsLockedInterruptible()) {//此时dispatchOnceInnerLocked无命令
/// nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MIN;//会执行,并立即开启第三次线程循环
///}
}
nsecs_t currentTime = now();//获取当前时间点
int timeoutMillis = toMillisecondTimeoutDelay(currentTime, nextWakeupTime);//下一次唤醒时间点-当前时间点=线程休眠时间
mLooper->pollOnce(timeoutMillis);//调用pollOnce使线程休眠,等待回调,唤醒或超时。
//Looper的pollOnce()的实质就是epoll_wait()。 因此派发线程的休眠在三种情况下可能被唤醒:
1.调用Looper::wake()函数主动唤醒(有输入事件注入派发队列中时),
2.到达nextWakeupTime的事件点时唤醒
3.epoll_waitepoll_wait()监听的fd有epoll_event发生时唤醒(这种唤醒方式将在介绍ANR机制时讨论)。
}//读取线程第二次循环时
void InputReader::loopOnce() {
int32_t oldGeneration;
int32_t timeoutMillis;
bool inputDevicesChanged = false;
Vector<InputDeviceInfo> inputDevices;
{ // acquire lock
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
oldGeneration = mGeneration;//新的值
timeoutMillis = -1;
size_t count = mEventHub->getEvents(timeoutMillis, mEventBuffer, EVENT_BUFFER_SIZE);//通过EventHub的getEvents函数获取事件,
//并存放在mEventBuffer中。
//参数分析:timeoutMillis=-1,代表啥意思不清楚,感觉如果数字为0代表立即执行
//mEventBuffer是一个存放从eventhub中读取的rawevent结构体类型的数组,源代码是:RawEvent mEventBuffer[EVENT_BUFFER_SIZE];
//EVENT_BUFFER_SIZE值是256,代表最大可以读取256个原始事件,RawEvent结构体如下
.......
}
size_t EventHub::getEvents(int timeoutMillis, RawEvent* buffer, size_t bufferSize) {
ALOG_ASSERT(bufferSize >= 1);
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
struct input_event readBuffer[bufferSize];//bufferSize值为传入的256
RawEvent* event = buffer;//event指针指向传入的buffer首地址,每存入一个事件,event指针向后移动一个元素
size_t capacity = bufferSize;//capacity表示buffer中剩余端元素数量,capacity为0,表示buffer已满
bool awoken = false;
for (;;) {
nsecs_t now = systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC);//获取当前时间
mPendingEventIndex = 0;//此时mPendingEventItems数组中未处理的事件已经处理完了,将mPendingEventIndex设置为0
mLock.unlock();
release_wake_lock(WAKE_LOCK_ID);
int pollResult = epoll_wait(mEpollFd, mPendingEventItems, EPOLL_MAX_EVENTS, timeoutMillis);//此时第二次读线程会阻塞在此处,等待有消息的事件发生
......
}3.总结
我们再次梳理一下主要流程:
1.首先,在systemserver启动中创建了java层的InputManagerService对象,
2.在framwork层的InputManagerService构造函数中,创建了NativeInputManager对象,由此通过jni进入native层。
3.在NativeInputManager对象中创建EventHub类对象,此对象通过epoil和notify监听/dev/input路径下是否有设备添加和删除事件
4.在NativeInputManager对象中创建InputManager类对象,InputManager类对象中创建了InputDispatcher和InputReader对象,并创建了分发线程和读取线程。
5.启动WMS对象,将IMS引用传入WMS中,这样WMS可以实时更新窗口信息到IMS中,IMS又保存着MWS实现的回调类,将用于派发消息到WMS。
6.先启动分发线程,分发线程无消息陷入休眠,然后启动读取线程。
7.因为是开机刚启动,因此要扫描/dev/input的所有设备节点,并读取设备并配置。每扫描完成一个设备,就生成对应的add事件,当设备全部扫描完成后,则生成扫描完成事件。此时是在在读取线程的mEventHub->getEvents函数中完成的。
8.处理设备add事件,即读取所有设备信息,生成对应的InputDevice对象,并配置好inputmapper。
9.处理设备完成扫描事件。唤醒分发线程,先通知java层监听设备变化的listener,然后派发消息到WMS,告诉系统设备已经完成配置。
4.启动流程——全源码全解析
此章节可不用阅读,绝大多数内容已经在第二节进行了描述、,此节每一行代码都会有笔者的注释,主要用于读者源码阅读时答疑解惑和参考。
主要包含第二章节中,相对于启动流程来讲一些不太重要的琐碎内容。
4.1 systemserver启动
从systemserver的main函数开始分析。
//frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SystemServer().run();
}//frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java
protected void run() {
.....
traceBeginAndSlog("StartServices")
startBootstrapServices();//启动引导服务,如AMS
startCoreServices();//启动核心服务
startOtherServices();//启动其他服务,如IMS,WMS
....
}4.2 startOtherServices
//frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java
private void startOtherServices() {
......
startInputManagerService();
startWindowManagerService();
startInputManager();
......
}
4.3 startInputManagerService
//frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java
protected void startInputManagerService() {
mInputManager = new InputManagerService(mSystemContext);//new了一个InputManagerService类的对象,但此时并未调用其start方法。
}
4.4 InputManagerService
//frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/input/InputManagerService.java
public InputManagerService(Context context) {
this.mContext = context;//其实就是systemserver的context
this.mHandler = new InputManagerHandler(DisplayThread.get().getLooper());//使用display的looper创建了InputManagerHandler
mUseDevInputEventForAudioJack =context.getResources().getBoolean(R.bool.config_useDevInputEventForAudioJack);
mPtr = nativeInit(this, mContext, mHandler.getLooper().getQueue());//调用了nativeInit方法在,
//传入参数为this=InputManagerService对象,mContext是systemserver的context,getQueue是display的looper的消息队列
//mPtr是nativeInit返回的值,是指向NativeInputManager的指针。
String doubleTouchGestureEnablePath = context.getResources().getString(R.string.config_doubleTouchGestureEnableFile);//获取多指触摸的文件路径
mDoubleTouchGestureEnableFile = TextUtils.isEmpty(doubleTouchGestureEnablePath) ? null :new File(doubleTouchGestureEnablePath);//获取多指触摸的文件
LocalServices.addService(InputManagerInternal.class, new LocalService());
}4.5 nativeInit
//frameworks/base/services/core/jni/com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp
static jlong nativeInit(JNIEnv* env, jclass /* clazz */,jobject serviceObj, jobject contextObj, jobject messageQueueObj) {
sp<MessageQueue> messageQueue = android_os_MessageQueue_getMessageQueue(env, messageQueueObj);//根据传入的java队列,获取native的消息队列
if (messageQueue == NULL) {
jniThrowRuntimeException(env, "MessageQueue is not initialized.");
return 0;
}
NativeInputManager* im = new NativeInputManager(contextObj, serviceObj,
messageQueue->getLooper());//创建了NativeInputManager类指针,
//传入参数:contextObj=systemserver的context,serviceObj=InputManagerService对象,looper是display的native的looper的消息队列
im->incStrong(0);//智能指针
return reinterpret_cast<jlong>(im);//将NativeInputManager类指针用reinterpret_cast强制转化为jlong并返回
}4.6 NativeInputManager
//frameworks/base/services/core/jni/com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp
NativeInputManager::NativeInputManager(jobject contextObj,jobject serviceObj, const sp<Looper>& looper) :mLooper(looper), mInteractive(true) {
JNIEnv* env = jniEnv();
mContextObj = env->NewGlobalRef(contextObj);//java层systemserver的context对象
mServiceObj = env->NewGlobalRef(serviceObj);//java层IMS对象
{
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
mLocked.systemUiVisibility = ASYSTEM_UI_VISIBILITY_STATUS_BAR_VISIBLE;
mLocked.pointerSpeed = 0;
mLocked.pointerGesturesEnabled = true;
mLocked.showTouches = false;
mLocked.pointerCapture = false;
}
mInteractive = true;
sp<EventHub> eventHub = new EventHub();//创建了EventHub类的对象,并用强指针指向它
mInputManager = new InputManager(eventHub, this, this);//创建了InputManager对象,并将EventHub类对象传入。
//参数分析:第二个this是NativeInputManager对象,第三个也是NativeInputManager对象,但代表的含义不同
//第一个this指,NativeInputManager继承自InputReaderPolicyInterface,
//第二个this指,NativeInputManager继承自InputDispatcherPolicyInterface
}4.7 EventHub
1.此处主要作用是:创建Epoll和iNotify对象,用于监听/dev/input节点下是否有设备增删。
当然,此时Epoll还未监听。因为并为调用epoll_wait函数,陷入等待事件发生。后续会调用。
简单介绍一下:
1.首先,要创建一个iNotify对象fd。此fd会监听/dev/input节点下时候有设备增删事件。
2.然后,将此iNotify对象添加到Epoll中监听,然后调用epoll_wait陷入等待状态,等待设备增删事件的发生。
3.当/dev/input节点下有设备增删的时候,epoll_wait会返回一个epoll_event的数组,此数组携带对应的iNotify对象fd和其他信息。
4.然后,iNotify对象就可以调用read读取其中的事件。
此处涉及知识点:Epoll和iNotify机制。请查看笔者另外一篇。
//frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/EventHub.cpp
EventHub::EventHub(void) :
mBuiltInKeyboardId(NO_BUILT_IN_KEYBOARD), mNextDeviceId(1), mControllerNumbers(),
mOpeningDevices(0), mClosingDevices(0),
mNeedToSendFinishedDeviceScan(false),
mNeedToReopenDevices(false), mNeedToScanDevices(true),
mPendingEventCount(0), mPendingEventIndex(0), mPendingINotify(false)
//参数分析:
//mBuiltInKeyboardId(NO_BUILT_IN_KEYBOARD),NO_BUILT_IN_KEYBOARD代表默认无内置键盘。
//mNextDeviceId,代表下一个设备id
//mOpeningDevices最近一次打开的设备,0代表最近无设备打开
//mClosingDevices,最近一次关闭的设备,0代表最近无设备关闭
//mNeedToSendFinishedDeviceScan,表示当设备扫描完成后,是否需要发送设备扫描完成的信号,默认为false
//mNeedToReopenDevices,表示是否需要重新打开设备
//mNeedToScanDevices,表示是否需要扫描设备,此处为是
//mPendingEventCount目前还未处理,正在等待处理的事件数量
//mPendingEventCount目前还未处理,马上要处理的下一个事件的索引。事件是由mPendingEventItems结构体数组存储。
//mPendingINotify,代表待定的通知
///struct epoll_event mPendingEventItems[EPOLL_MAX_EVENTS];
///size_t mPendingEventCount;
///size_t mPendingEventIndex;
{
acquire_wake_lock(PARTIAL_WAKE_LOCK, WAKE_LOCK_ID);//获取唤醒锁定 partial_wake_lock,部分唤醒锁定,wake_lock_id,唤醒锁定的id
#ifdef TERTIARY_TOUCH
//ng8 mBuiltinTouchScreenPhy;//内置触摸屏
//String8 mExternalTouchScreenPhy;//外部触摸屏
//String8 mTertiaryTouchScreenPhy1;//第三方的触摸屏1
//String8 mTertiaryTouchScreenPhy2;//第三方的触摸屏2
char p[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
property_get("persist.mtmd.display0_touch", p, "usb-xhci-hcd.0.auto-1.1/input0");//从系统属性中获取key为persist.mtmd.display0_touch的value值,存储于字符数组p中,
//如果系统属性中没有此值,则存储默认值为usb-xhci-hcd.0.auto-1.1/input0
mBuiltinTouchScreenPhy.setTo(p);//将字符串mBuiltinTouchScreenPhy内置触摸屏设置为p
memset(p, 0, PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX);//将字符数组p重置为0
property_get("persist.mtmd.display1_touch", p, "usb-xhci-hcd.0.auto-1.2/input0");
mExternalTouchScreenPhy.setTo(p);
memset(p, 0, PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX);
property_get("persist.mtmd.display2_touch", p, "usb-xhci-hcd.0.auto-1.3/input0");
mTertiaryTouchScreenPhy1.setTo(p);
memset(p, 0, PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX);
property_get("persist.mtmd.display3_touch", p, "usb-xhci-hcd.0.auto-1.4/input0");
mTertiaryTouchScreenPhy2.setTo(p);
memset(p, 0, PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX);
#endif
mEpollFd = epoll_create(EPOLL_SIZE_HINT);//创建epoll对象,mEpollFd为此对象的描述符
mINotifyFd = inotify_init();//创建inotify对象,mINotifyFd为此对象的描述符
int result = inotify_add_watch(mINotifyFd, DEVICE_PATH, IN_DELETE | IN_CREATE);//将一个用于监听输入设备节点的创建与删除的watch对象,
//添加到inotify对象中,此处DEVICE_PATH为"/dev/input",监听该目录下的设备节点创建与删除操作。
//当/dev/input/下的设备节点发生创建与删除操作时,都会将相应的事件信息写入到inotifyFd所描述的inotify对象中,
//此时可以通过read()函数从inotifyFd描述符中将事件信息读取出来。
struct epoll_event eventItem;//创建epoll_event结构体,此结构体
//struct epoll_event {
//__uint32_t events; /* 事件掩码,指明了需要监听的事件种类,
//常用的事件有EPOLLIN(可读),EPOLLOUT(可写),EPOLLERR(描述符发生错误),EPOLLHUP(描述符被挂起)
//epoll_data_t data; /* 使用者自定义的数据,当此事件发生时该数据将原封不动地返回给使用者 */
//};
memset(&eventItem, 0, sizeof(eventItem));//初始值为0
eventItem.events = EPOLLIN;//可读,代表监听可读事件
eventItem.data.u32 = EPOLL_ID_INOTIFY;//EPOLL_ID_INOTIFY代表用于与设备无关的epoll通知的ID。此处为Epoll的通知id
result = epoll_ctl(mEpollFd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, mINotifyFd, &eventItem);//添加刚才监听目录下设备创建和删除的INotify到epoll实例,EPOLL_CTL_ADD表示增加事件
//epoll_ctl将事件监听添加到epoll对象中去。
//当/dev/input/下的设备节点发生创建与删除操作时,首先会将相应的事件信息写入到inotifyFd所描述的inotify对象中,又因为该inotifyFd被epoll监听可读,
//故直接生成eventItem事件
int wakeFds[2];
result = pipe(wakeFds);//创建管道
mWakeReadPipeFd = wakeFds[0];//管道读端
mWakeWritePipeFd = wakeFds[1];//管道写端
result = fcntl(mWakeReadPipeFd, F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK);//将管道的读设置为非阻塞
result = fcntl(mWakeWritePipeFd, F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK);//将管道的写设置为非阻塞
eventItem.data.u32 = EPOLL_ID_WAKE;//Epoll监听事件触发后返回的epoll_event数组中,events事件,此处代表EPOLL唤醒事件的id
result = epoll_ctl(mEpollFd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, mWakeReadPipeFd, &eventItem);//将管道的读端添加到epoll实例中,当管道有数据可读时,此事件返回events中带有id值。
int major, minor;
getLinuxRelease(&major, &minor);
// EPOLLWAKEUP was introduced in kernel 3.5
mUsingEpollWakeup = major > 3 || (major == 3 && minor >= 5);
}4.8 InputManager
主要作用:
1.创建InputDispatcher对象,用于事件的分发。
2.创建InputReader对象,并将eventHub对象传递进去。用于事件的读取和加工。
3.在initialize函数中,创建了InputDispatcherThread线程和InputReaderThread线程。
//frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/InputManager.cpp
InputManager::InputManager(
const sp<EventHubInterface>& eventHub,
const sp<InputReaderPolicyInterface>& readerPolicy,
const sp<InputDispatcherPolicyInterface>& dispatcherPolicy) {
mDispatcher = new InputDispatcher(dispatcherPolicy);//创建InputDispatcher对象,传入的参数为NativeInputManager
mReader = new InputReader(eventHub, readerPolicy, mDispatcher);//创建InputReader对象,
//传入参数:
//eventHub=EventHub类对象,
//readerPolicy=NativeInputManager类对象,
//mDispatcher=InputDispatcher对象,此处作用简单说一下
//大致为当inputreader从eventHub中读取到数据后,对数据进行加工包装后,会添加到InputDispatcher的一个队列中,并唤醒他,然后执行分发。
initialize();//初始化
}4.9 InputDispatcher
//frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/InputDispatcher.cpp
InputDispatcher::InputDispatcher(const sp<InputDispatcherPolicyInterface>& policy) :
mPolicy(policy),
mPendingEvent(NULL), mLastDropReason(DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED),
mAppSwitchSawKeyDown(false), mAppSwitchDueTime(LONG_LONG_MAX),
mNextUnblockedEvent(NULL),
mDispatchEnabled(false), mDispatchFrozen(false), mInputFilterEnabled(false),
mInputTargetWaitCause(INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_NONE)
//参数分析:
//mPolicy=NativeInputManager类对象
//mPendingEvent,含义为还未处理的事件,此处为NULL
//mLastDropReason,最近一次丢弃事件的原因,默认为DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED,表示不丢弃。
//mAppSwitchSawKeyDown,表示是否按下Home健,此处为flase
//mAppSwitchDueTime,代表,当用户按home健时,该操作事件最迟的分发时间。对于特殊按键 HOME, END_CALL, APP_SWITCH 增加了 0.5s 超时时间
// 超时之后会丢弃其他即将处理的按键事件。如果超时,则即 isAppSwitchDue 为 true 的情况,说明没有及时响应 HOME 键等操作
// 目的是优化 app 切换延迟,当切换超时,则抢占分发,丢弃其他所有即将要处理的事件
//mNextUnblockedEvent,下一个取消阻止的事件,含义为阻塞事件延迟优化。当用户打算将焦点转移到新应用程序时,会删除旧事件。直接到下一个事件。
//mDispatchEnabled,是否可以分发事件,此处为false,因为只是创建了对象,其工作线程还未启动。
//mDispatchFrozen,分发是否冻结,此处为false,如果为true则,不进行分发操作。InputDispatcher有三种状态,1.正常状态,2冻结状态,3.禁用状态。
//例如:当手机进入休眠状态时,InputDispatcher 会被禁用,而屏幕旋转过程中,InputDispatcher 会被暂时冻结
//mInputFilterEnabled,表示输入过滤是否使用,默认为false
//mInputTargetWaitCause,表示输入目标等待原因,即anr的原因,默认为无原因
// 跟踪ANR超时。
//enum InputTargetWaitCause {
//INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_NONE,//anr无原因
//INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_SYSTEM_NOT_READY,//系统无响应
//INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_APPLICATION_NOT_READY,//应用无响应
//};
{
mLooper = new Looper(false);//创建了自己的looper对象
mKeyRepeatState.lastKeyEntry = NULL;//按键重复状态,上一次按键事件
//按键重复追踪
//struct KeyRepeatState {
//yEntry* lastKeyEntry; // 如果不重复则为null
//nsecs_t nextRepeatTime;
//} mKeyRepeatState;
policy->getDispatcherConfiguration(&mConfig);//获取分发超时参数。此处调用了NativeInputManager类对象的getDispatcherConfiguration方法,
//超时参数来自于 IMS,参数默认值 keyRepeatTimeout = 500,超时时间为0.5秒,keyRepeatDelay = 50,按键重复按键间延迟为0.05秒
//InputDispatcher的配置。
//指定修改InputDispatcher的各种选项。
//这里提供的值只是默认值。实际值将来自ViewConfiguration,并在初始化期间传递给InputDispatcher
//struct InputDispatcherConfiguration {
// 重复按键超时
//nsecs_t keyRepeatTimeout;
// 重复按键按键间延迟
//nsecs_t keyRepeatDelay;
//InputDispatcherConfiguration() :
// keyRepeatTimeout(500 * 1000000LL),
// keyRepeatDelay(50 * 1000000LL) { }
//};
}void NativeInputManager::getDispatcherConfiguration(InputDispatcherConfiguration* outConfig) {
ATRACE_CALL();//用于统计函数的调用情况
JNIEnv* env = jniEnv();
jint keyRepeatTimeout = env->CallIntMethod(mServiceObj,
gServiceClassInfo.getKeyRepeatTimeout);//gServiceClassInfo是一个结构体,存储了java的所有方法。
//通过jni调用java层方法。mServiceObj是java层IMS对象。
if (!checkAndClearExceptionFromCallback(env, "getKeyRepeatTimeout")) {//检查并清除回调异常,如果回调无异常,则将值赋值给传入的outConfig
outConfig->keyRepeatTimeout = milliseconds_to_nanoseconds(keyRepeatTimeout);
}
jint keyRepeatDelay = env->CallIntMethod(mServiceObj,
gServiceClassInfo.getKeyRepeatDelay);//此变量的含义是连续按键重复之间的时间。通过jni调用java层方法。mServiceObj是java层IMS对象。
if (!checkAndClearExceptionFromCallback(env, "getKeyRepeatDelay")) {////检查并清除回调异常,如果回调无异常,则将值赋值给传入的outConfig
outConfig->keyRepeatDelay = milliseconds_to_nanoseconds(keyRepeatDelay);
}
}// Native callback.此时在java层的IMS.java中
private int getKeyRepeatTimeout() {
return ViewConfiguration.getKeyRepeatTimeout(); //此处获取的值是400 ms
}
private int getKeyRepeatDelay() {
return ViewConfiguration.getKeyRepeatDelay(); //从ViewConfiguration中获取按键重复按键间延迟50 ms
}4.10 InputReader
构造函数中保存了InputDispatcher对象,即listener,这里说明了inputreader线程加工好了消息后如何通知InputDispatcher线程去派发消息。
//frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/InputReader.cpp
InputReader::InputReader(const sp<EventHubInterface>& eventHub,
const sp<InputReaderPolicyInterface>& policy,
const sp<InputListenerInterface>& listener) :
mContext(this), mEventHub(eventHub), mPolicy(policy),
mGlobalMetaState(0), mGeneration(1),
mDisableVirtualKeysTimeout(LLONG_MIN), mNextTimeout(LLONG_MAX),
mConfigurationChangesToRefresh(0)
//参数分析:
//此处需要重点查看传入的参数listener,
//InputDispatcher继承自InputDispatcherInterface,InputDispatcherInterface继承自InputListenerInterface
//mContext=InputReader类对象
//mEventHub=传入的eventHub类对象
//mPolicy=传入的NativeInputManager类对象
//mGlobalMetaState,全局元状态,是int类型,不知道干啥的,后续瞅瞅
//mGeneration,用于表示设备更新的次数
//mDisableVirtualKeysTimeout,禁用虚拟键超时,不知道干啥的,后续瞅瞅
//NextTimeout,下一次唤醒的时间
//mConfigurationChangesToRefres,当Configuration变化时,进行刷新,0代表无变化,1代表有变化,当为1时需要执行刷新的函数
{
mQueuedListener = new QueuedInputListener(listener);//创建输入监听对象,listener是传入的参数,是一个InputDispatcher类的对象,
{ // 请求锁
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
refreshConfigurationLocked(0);//调用refreshConfigurationLocked()方法,刷新配置
updateGlobalMetaStateLocked();//调用updateGlobalMetaStateLocked()方法。更新GlobalMetaState的值。
} // 释放锁
}此处是将传入的dispatcher对象保存起来。
QueuedInputListener::QueuedInputListener(const sp<InputListenerInterface>& innerListener) :
mInnerListener(innerListener) {//将传入的InputDispatcher类的对象赋值给QueuedInputListener类的mInnerListener
}void InputReader::refreshConfigurationLocked(uint32_t changes) {//此时chenages传入为0
mPolicy->getReaderConfiguration(&mConfig);//mPolicy是NativeInputManager类对象,此函数会将获取的配置参数赋值给mConfig
mEventHub->setExcludedDevices(mConfig.excludedDeviceNames);//设置排除的设备名称。
/// if (changes) {//此时为0,不执行。
/// ALOGI("Reconfiguring input devices. changes=0x%08x", changes);
/// nsecs_t now = systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC);//获取当前时间
///
/// if (changes & InputReaderConfiguration::CHANGE_MUST_REOPEN) {//如果change为1,表示有变化,并且配置的属性为CHANGE_MUST_REOPEN,
/// //则调用requestReopenDevices,重新打开设备。
/// mEventHub->requestReopenDevices();
/// } else {
/// for (size_t i = 0; i < mDevices.size(); i++) {//此处简单描述一下,mDevices是一个容器,存储的是InputDevice类在
/// //此处代码并未调用,暂不分析。
/// InputDevice* device = mDevices.valueAt(i);
/// device->configure(now, &mConfig, changes);
/// }
/// }
/// }
}主要作用是:
1.读取触摸屏幕后禁用虚拟键的时间
2.从/system/etc/excluded-input-devices.xml读取要排除的设备
3.获取点击超时时间
4.获取双击超时时间
5.获取长按超时时间
6.获取点击事件最大移动距离
7.获取一些窗口的配置。
void NativeInputManager::getReaderConfiguration(InputReaderConfiguration* outConfig) {
ATRACE_CALL();
JNIEnv* env = jniEnv();
jint virtualKeyQuietTime = env->CallIntMethod(mServiceObj,
gServiceClassInfo.getVirtualKeyQuietTimeMillis);//virtualKeyQuietTime作用是指定在触摸屏幕后禁用虚拟键的时间量,
//以过滤由于在显示器边缘附近滑动手势或敲击而导致的意外虚拟键按下。此时是调用jni,到java层,获取的值是0,
//即不禁用虚拟键
if (!checkAndClearExceptionFromCallback(env, "getVirtualKeyQuietTimeMillis")) {//检查返回值是否存在异常
outConfig->virtualKeyQuietTime = milliseconds_to_nanoseconds(virtualKeyQuietTime);
}
outConfig->excludedDeviceNames.clear();
jobjectArray excludedDeviceNames = jobjectArray(env->CallObjectMethod(mServiceObj,
gServiceClassInfo.getExcludedDeviceNames));//通过jni从/system/etc/excluded-input-devices.xml读取要排除的设备
if (!checkAndClearExceptionFromCallback(env, "getExcludedDeviceNames") && excludedDeviceNames) {//检查返回值是否存在异常
jsize length = env->GetArrayLength(excludedDeviceNames);
for (jsize i = 0; i < length; i++) {//此处是提取获取的排除的设备的值,放入outConfig中
jstring item = jstring(env->GetObjectArrayElement(excludedDeviceNames, i));
const char* deviceNameChars = env->GetStringUTFChars(item, NULL);
outConfig->excludedDeviceNames.add(String8(deviceNameChars));
env->ReleaseStringUTFChars(item, deviceNameChars);
env->DeleteLocalRef(item);
}
env->DeleteLocalRef(excludedDeviceNames);
}
jint hoverTapTimeout = env->CallIntMethod(mServiceObj,
gServiceClassInfo.getHoverTapTimeout);//150毫秒,调用jni从java层的IMS中获取超时时间
//此变量的含义是,如果motion事件的触摸和释放之间的间距不超过此时间,即把此事件认为是点击事件,而非移动事件
if (!checkAndClearExceptionFromCallback(env, "getHoverTapTimeout")) {
jint doubleTapTimeout = env->CallIntMethod(mServiceObj,
gServiceClassInfo.getDoubleTapTimeout);//300毫秒,第一次点击的向上事件和第二次点击的向下事件之间的持续时间,视为双击。
if (!checkAndClearExceptionFromCallback(env, "getDoubleTapTimeout")) {
jint longPressTimeout = env->CallIntMethod(mServiceObj,
gServiceClassInfo.getLongPressTimeout);//获取长按时间,500毫秒
if (!checkAndClearExceptionFromCallback(env, "getLongPressTimeout")) {
outConfig->pointerGestureTapInterval = milliseconds_to_nanoseconds(hoverTapTimeout);
//此处是为了确保按下和滑动的时间间隔要小于长按,大于点击
jint tapDragInterval = max(min(longPressTimeout - 100,
doubleTapTimeout), hoverTapTimeout);//此时是300毫秒
outConfig->pointerGestureTapDragInterval =
milliseconds_to_nanoseconds(tapDragInterval);
}
}
}
jint hoverTapSlop = env->CallIntMethod(mServiceObj,
gServiceClassInfo.getHoverTapSlop);//20像素。为了区分点击和移动事件,定义在点击事件是在手指触摸释放之前可以移动的最大距离(以像素为单位
if (!checkAndClearExceptionFromCallback(env, "getHoverTapSlop")) {
outConfig->pointerGestureTapSlop = hoverTapSlop;
}
{ // acquire lock
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
outConfig->pointerVelocityControlParameters.scale = exp2f(mLocked.pointerSpeed
* POINTER_SPEED_EXPONENT);//鼠标指针移动的速度控制参数。初始值是0
outConfig->pointerGesturesEnabled = mLocked.pointerGesturesEnabled;//此时是true,启用了pointer手势。
outConfig->showTouches = mLocked.showTouches;//此时是false,如果为true,则将触摸屏上的触摸位置显示为点。
outConfig->pointerCapture = mLocked.pointerCapture;
outConfig->setPhysicalDisplayViewport(ViewportType::VIEWPORT_INTERNAL,//设置物理的视图窗口
mLocked.internalViewport);
outConfig->setPhysicalDisplayViewport(ViewportType::VIEWPORT_EXTERNAL,
mLocked.externalViewport);
outConfig->setVirtualDisplayViewports(mLocked.virtualViewports);
outConfig->disabledDevices = mLocked.disabledInputDevices;
} // release lock
}// Native callback.
private int getVirtualKeyQuietTimeMillis() {
return mContext.getResources().getInteger(
com.android.internal.R.integer.config_virtualKeyQuietTimeMillis);//virtualKeyQuietTime作用是指定在触摸屏幕后禁用虚拟键的时间量,
//以过滤由于在显示器边缘附近滑动手势或敲击而导致的意外虚拟键按下。此时是调用jni,到java层,获取的值是0,
//即不禁用虚拟键
}// Native callback.
private String[] getExcludedDeviceNames() {
ArrayList<String> names = new ArrayList<String>();
// 读取要排除在外的设备
XmlPullParser parser = null;
// 从安卓或者"/system".
File confFile = new File(Environment.getRootDirectory(), EXCLUDED_DEVICES_PATH);//从安卓etc/excluded-input-devices.xml
//或者/system/etc/excluded-input-devices.xml读取消息
FileReader confreader = null;
try {
confreader = new FileReader(confFile);
parser = Xml.newPullParser();
parser.setInput(confreader);
XmlUtils.beginDocument(parser, "devices");
while (true) {
XmlUtils.nextElement(parser);
if (!"device".equals(parser.getName())) {
break;
}
String name = parser.getAttributeValue(null, "name");
if (name != null) {
names.add(name);//读取排除的设备的名称
}
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// It's ok if the file does not exist.
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Exception while parsing '" + confFile.getAbsolutePath() + "'", e);
} finally {
try { if (confreader != null) confreader.close(); } catch (IOException e) { }
}
return names.toArray(new String[names.size()]);
}// Native callback.
private int getHoverTapTimeout() {
return ViewConfiguration.getHoverTapTimeout();
}
public static int getHoverTapTimeout() {
return HOVER_TAP_TIMEOUT; //150ms
}
// Native callback.
private int getDoubleTapTimeout() {
return ViewConfiguration.getDoubleTapTimeout();//第一次点击的向上事件和第二次点击的向下事件之间的持续时间,视为双击。
}
public static int getDoubleTapTimeout() {
return DOUBLE_TAP_TIMEOUT;
}
private static final int DOUBLE_TAP_TIMEOUT = 300;
// Native callback.
private int getLongPressTimeout() {
return ViewConfiguration.getLongPressTimeout();//长按,值为500毫秒
}
public static int getLongPressTimeout() {
return AppGlobals.getIntCoreSetting(Settings.Secure.LONG_PRESS_TIMEOUT,
DEFAULT_LONG_PRESS_TIMEOUT);
}
private static final int DEFAULT_LONG_PRESS_TIMEOUT = 500;
// Native callback.
private int getHoverTapSlop() {
return ViewConfiguration.getHoverTapSlop();
}
void EventHub::setExcludedDevices(const Vector<String8>& devices) {
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
mExcludedDevices = devices;//取出从上层获取的排除哪些设备,设置到EventHub中
}void InputReader::updateGlobalMetaStateLocked() {
mGlobalMetaState = 0;
/// for (size_t i = 0; i < mDevices.size(); i++) {//刚开始mDevices值为0,此循环不执行
/// InputDevice* device = mDevices.valueAt(i);
/// mGlobalMetaState |= device->getMetaState();//0与获取的getMetaState值进行或运算。
/// }
}4.11 initialize
主要作用为:
1.创建了inputreader线程,此线程的作用是从eventHub中无休止的读取原始的事件,并进行加工,最终会得出三种事件类型,然后将事件会加入到InputDispatcher的一个队列中进行分发
2.创建了InputDispatcherThread线程,此线程主要进行事件的分发,其保存者wms的窗口信息,通过相关函数将事件准确的发送到指定窗口。
void InputManager::initialize() {
mReaderThread = new InputReaderThread(mReader);//创建了inputreader线程,传入了inputreader类对象,
//此线程的作用是从eventHub中无休止的读取原始的事件,并进行加工,最终会得出三种事件类型
//1.key事件,NotifyKeyArgs,
//2.Motion事件,NotifyMotionArgs,
//3.Switch事件,NotifySwitchArgs,
//然后会加入到InputDispatcher的一个队列中进行分发
mDispatcherThread = new InputDispatcherThread(mDispatcher);//创建了InputDispatcher线程,传入了InputDispatcher类对象
}4.12 InputReaderThread
InputReaderThread::InputReaderThread(const sp<InputReaderInterface>& reader) :
Thread(/*canCallJava*/ true), mReader(reader) {//给mReader赋了个值为inputreader类
//此线程会从eventHub中无休止的读取原始的事件,并进行加工
}4.13 InputDispatcherThread
InputDispatcherThread::InputDispatcherThread(const sp<InputDispatcherInterface>& dispatcher)
: Thread(/*canCallJava*/ true), mDispatcher(dispatcher) {}
//此线程会无休止地入队和分发输入事件4.14 startWindowManagerService
主要作用:
1.执行WMS的main方法,此时将mInputManager的引用传递到WMS中,因为当应用向WMS申请创建窗口是随时的,那么WMS就必须及时将窗口信息更新到IMS中,以便input消息能正确的发送给指定窗口。
protected void startWindowManagerService() {
//WMS需要传感器服务先启动
ConcurrentUtils.waitForFutureNoInterrupt(mSensorServiceStart, START_SENSOR_SERVICE);//启动传感器服务
mSensorServiceStart = null;
mWm = WindowManagerService.main(mSystemContext, mInputManager,
mFactoryTestMode != FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL,
!mFirstBoot, mOnlyCore, new CarWindowManager());//调用WMS的main方法,把inputManager的引用放到WMS中,建立联系
//传入的参数mSystemContext=systemserver对象,mInputManager=InputManagerService对象,CarWindowManager对象。
ServiceManager.addService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE, mWm, /* allowIsolated= */ false,DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_CRITICAL | DUMP_FLAG_PROTO);//WMS添加进ServiceManager中,
ServiceManager.addService(Context.INPUT_SERVICE, mInputManager,/* allowIsolated= */ false, DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_CRITICAL);//IMS添加进ServiceManager中
}4.15 WindowManagerService.main
public static WindowManagerService main(final Context context, final InputManagerService im,
final boolean haveInputMethods, final boolean showBootMsgs, final boolean onlyCore,
WindowManagerPolicy policy) {
//接收参数分析:
//context=systemserver对象
//im = InputManagerService对象
//haveInputMethods应该是true
//policy接收一个PhoneWindowManager类对象
DisplayThread.getHandler().runWithScissors(() ->
sInstance = new WindowManagerService(context, im, haveInputMethods, showBootMsgs,
onlyCore, policy), 0);
return sInstance;
}4.16 startInputManager
1.IMS保存了InputMonitor对象,InputMonitor类是在WMS侧实现的IMS的回调类,此处说明了消息最终如何回调到WMS。
protected void startInputManager() {
mInputManager.setWindowManagerCallbacks(mWm.getInputMonitor());//设置回调,将WMS中的InputManagerCallback设置到inputManager中,
//这里说明了最终如何回调到WMS
mInputManager.start();//启动IMS
}
class InputMonitor implements InputManagerService.WindowManagerCallbacks
//继承自WindowManagerCallbacks,此回调类需要WMS是实现,主要是一些回调函数。此类的内部
//有一个内部类EventReceiverInputConsumer,用于接受IMS的消息。
public void setWindowManagerCallbacks(WindowManagerCallbacks callbacks) {
mWindowManagerCallbacks = callbacks;//此处证明后续如何回到wms中
}
//WMS.java
public InputMonitor getInputMonitor() {
return mInputMonitor;
}4.17 InputManager.start
public void start() {
Slog.i(TAG, "Starting input manager");
nativeStart(mPtr);//mPtr是nativeInit返回的值,是指向NativeInputManager的指针。
// Add ourself to the Watchdog monitors.
Watchdog.getInstance().addMonitor(this);//将InputManagerService服务添加到Watchdog中监控,Watchdog的作用是每隔一段时间监控线程是否异常
registerPointerSpeedSettingObserver();//注册触摸点速度的观察者
registerShowTouchesSettingObserver();//注册是否展示触摸屏的位置为一个点的观察者
registerAccessibilityLargePointerSettingObserver();
mContext.registerReceiver(new BroadcastReceiver() {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {//注册回调
updatePointerSpeedFromSettings();
updateShowTouchesFromSettings();
updateAccessibilityLargePointerFromSettings();
}
}, new IntentFilter(Intent.ACTION_USER_SWITCHED), null, mHandler);
updatePointerSpeedFromSettings();//更新触摸点的速度
updateShowTouchesFromSettings();//更新是否显示触摸屏位置为一个点
updateAccessibilityLargePointerFromSettings();//最大支持手指数量
}4.18 nativeStart
1.主要用于调用InputManager.start方法。
static void nativeStart(JNIEnv* env, jclass /* clazz */, jlong ptr) {
NativeInputManager* im = reinterpret_cast<NativeInputManager*>(ptr);//将ptr指针转化为NativeInputManager类指针
status_t result = im->getInputManager()->start();//调用了mInputManager.start()方法。
//而mInputManager是在NativeInputManager::NativeInputManager构造函数中,创建的指向inputManager对象的指针
}4.19 InputManager.start
1.DispatcherThread线程启动
2.ReaderThread线程启动
status_t InputManager::start() {
status_t result = mDispatcherThread->run("InputDispatcher", PRIORITY_URGENT_DISPLAY);//开启分发线程,
//PRIORITY_URGENT_DISPLAY重要显示线程的优先级,屏幕合成和获取输入事件使用这个级别
if (result) {
ALOGE("Could not start InputDispatcher thread due to error %d.", result);
return result;
}
result = mReaderThread->run("InputReader", PRIORITY_URGENT_DISPLAY);//开启reader线程
if (result) {
ALOGE("Could not start InputReader thread due to error %d.", result);
mDispatcherThread->requestExit();//如果inputreader线程开启发生错误,则调用requestExit方法停止Dispatcher线程
return result;
}
return OK;
}4.20 mDispatcherThread->run
1.分发线程启动。
线程调用run方法后,会调用threadLoop方法,当其返回true并且没有调用requsetexit函数时,会一直循环的调用threadLoop函数
此处涉及Android侧的多线程篇,原理请查看本人的另一篇博客
4.21 InputDispatcherThread::threadLoop
bool InputDispatcherThread::threadLoop() {//线程调用run方法后,会调用threadLoop方法,
//当其返回true并且没有调用requsetexit函数时,会一直循环的调用threadLoop函数
mDispatcher->dispatchOnce();
return true;
}4.22 InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce
1.此时分发线程刚启动,消息和命令都没有,然后就陷入了无限等待inputreader线程唤醒状态。
//刚启动第一次循环时,分发线程执行的代码块
//本质上,第一次循环时,什么消息都没有,所以就是相当于任何函数都没执行,然后就陷入了无线等待唤醒
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce() {
nsecs_t nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MAX;//下一次唤醒该线程的时间,也可以说是下一次线程循环的执行时间点,默认最大值,即刚开始InputDispatcherThread线程无限等待
{
if (!haveCommandsLocked()) {//此时无命令。
//作用:检查inputdispatcher的缓存队列中是否有还未处理的命令
//只有无命令时才会执行dispatchOnceInnerLocked方法,进行事件的分发。
dispatchOnceInnerLocked(&nextWakeupTime);// 传入的nextWakeupTime决定了下次派发线程循环的执行时间点,
}
}
nsecs_t currentTime = now();//获取当前时间点
int timeoutMillis = toMillisecondTimeoutDelay(currentTime, nextWakeupTime);//下一次唤醒时间点-当前时间点=线程休眠时间
mLooper->pollOnce(timeoutMillis);//调用pollOnce使线程休眠,等待回调,唤醒或超时。
//Looper的pollOnce()的实质就是epoll_wait()。 因此派发线程的休眠在三种情况下可能被唤醒:
//1.调用Looper::wake()函数主动唤醒(有输入事件注入派发队列中时),
//2.到达nextWakeupTime的事件点时唤醒
//3.epoll_wait()监听的fd有epoll_event发生时唤醒(这种唤醒方式将在介绍ANR机制时讨论)。
}
bool InputDispatcher::haveCommandsLocked() const {//第一次线程循环执行,返回为false
return !mCommandQueue.isEmpty();
}4.23 dispatchOnceInnerLocked
//刚开机启动后,第一次执行代码块为
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnceInnerLocked(nsecs_t* nextWakeupTime) {
nsecs_t currentTime = now();
if (!mDispatchEnabled) {//默认值为flase
resetKeyRepeatLocked();//将上一个事件指向的对象删除,并置空
}
//优化应用程序交换机的延迟。
//本质上,当按下应用程序切换键(HOME/ENDCALL)时,我们会开始短暂的超时。当它过期时,我们抢占分派并丢弃所有其他挂起的事件。
bool isAppSwitchDue = mAppSwitchDueTime <= currentTime;//mAppSwitchDueTime这个值是在EventEntry进入队列时设置的,默认值是最大值
//第一次循环时mAppSwitchDueTime值是LONG_LONG_MAX,所以isAppSwitchDue是false
//如果mAppSwitchDueTime小于当前时间,说明约定的最迟分发时间已经过去了,即没有即使响应home建等操作。
if (! mPendingEvent) {//如果没有待发送的事件,则从mInboundQueue队列中取出一个事件,进行分发
if (mInboundQueue.isEmpty()) {
//如果不需要生成重复按键事件,或还没有到达合适的时间点,
//则直接返回,派发线程再次沉睡
if (!mPendingEvent) {
return;
}
}
}
}
void InputDispatcher::resetKeyRepeatLocked() {
/// if (mKeyRepeatState.lastKeyEntry) {//默认是空,所以不执行
/// mKeyRepeatState.lastKeyEntry->release();
/// mKeyRepeatState.lastKeyEntry = NULL;
/// }
}
4.24 mReaderThread->run
1.读取线程启动。
线程调用run方法后,会调用threadLoop方法,当其返回true并且没有调用requsetexit函数时,会一直循环的调用threadLoop函数
4.25 threadLoop
bool InputReaderThread::threadLoop() {//inputreader线程调用run方法后,会调用threadLoop方法,
//当其返回true并且没有调用requsetexit函数时,会一直循环的调用threadLoop函数
mReader->loopOnce();
return true;
}4.26 InputReader::loopOnce
//第一次启动时,执行的代码块
void InputReader::loopOnce() {
int32_t oldGeneration;
int32_t timeoutMillis;
bool inputDevicesChanged = false;
Vector<InputDeviceInfo> inputDevices;
{
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
oldGeneration = mGeneration;//值为1,在inputreader构造函数中mGeneration=1,
timeoutMillis = -1;
uint32_t changes = mConfigurationChangesToRefresh;//值为0,初始化时设置为0,代表无变化,不刷新配置
// if (changes) {//此处刚开始代码不执行,
// mConfigurationChangesToRefresh = 0;
// timeoutMillis = 0;
// refreshConfigurationLocked(changes);
// } else if (mNextTimeout != LLONG_MAX) {//在inputreader构造函数中,mNextTimeout是LLONG_MAX,此处代码不会执行
// //此处的含义本人认为,mNextTimeout代表了下一次线程唤醒的时间点,如果mNextTimeout不是LLONG_MAX,则需要计算休眠的时间
// nsecs_t now = systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC);
// timeoutMillis = toMillisecondTimeoutDelay(now, mNextTimeout);//线程休眠时间
// }
}
size_t count = mEventHub->getEvents(timeoutMillis, mEventBuffer, EVENT_BUFFER_SIZE);//通过EventHub的getEvents函数获取事件,
//并存放在mEventBuffer中。此时可以知道刚启动时,只是会生成所有已经扫描的设备的add类型的事件和一个完成设备扫描的事件
//参数分析:timeoutMillis=-1,代表啥意思不清楚,感觉如果数字为0代表立即执行
//mEventBuffer是一个存放从eventhub中读取的rawevent结构体类型的数组,源代码是:RawEvent mEventBuffer[EVENT_BUFFER_SIZE];
//EVENT_BUFFER_SIZE值是256,代表最大可以读取256个原始事件,RawEvent结构体如下
////从EventHub检索到的原始事件
//struct RawEvent {
//nsecs_t when;//时间
//int32_t deviceId;//事件发生的设备id
//int32_t type;//类型,例如按键事件等
//int32_t code;//扫描码,按键对应的扫描码
//int32_t value;//值,表示按键按下,或者抬起等
//};
{ // acquire lock
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
mReaderIsAliveCondition.broadcast();
if (count) {//返回的事件数量大于,则调用processEventsLocked处理事件
processEventsLocked(mEventBuffer, count);
}
/*
if (mNextTimeout != LLONG_MAX) //此时mNextTimeout是LLONG_MAX
{
nsecs_t now = systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC);
if (now >= mNextTimeout) {
#if DEBUG_RAW_EVENTS
ALOGD("Timeout expired, latency=%0.3fms", (now - mNextTimeout) * 0.000001f);
#endif
mNextTimeout = LLONG_MAX;
timeoutExpiredLocked(now);
}
}*/
if (oldGeneration != mGeneration) {//此处是不等于的,因为当有add设备事件时processEventsLocked函数中调用addDeviceLocked,addDeviceLocked在完成设备配置后
//会调用bumpGenerationLocked函数,使得mGeneration+1,从而不相等
inputDevicesChanged = true;
getInputDevicesLocked(inputDevices);//获取所有的新的设备信息到inputDevices容器中
}
} // release lock
//
if (inputDevicesChanged) {//如果设备发生变化,生成一个通知设备事件的通知
mPolicy->notifyInputDevicesChanged(inputDevices);//此时mPolicy是NativeInputManager对象,所以此时调用到了NativeInputManager::notifyInputDevicesChanged
}
//发布事件。 一般此处只会处理加工后的原始输入事件,而此时开机启动只有设备添加和删除的事件,但是当设备完成扫描时会生成一个通知事件
//放入此队列。所以启动后,扫描完设备后,此容器只有一个扫描设备完成的通知事件
// mQueuedListener中。在循环的最后,通过调用flush()函数将所有事件交付给InputDispatcher
mQueuedListener->flush();
}4.27 mEventHub->getEvents
1.设备刚启动,扫描/dev/input下的所有输入设备,用Device类保存其信息,并生成DEVICE_ADDED类型的事件(设备增加类型事件)放入消息数组中
2.当完成所有设备扫描后,生成FINISHED_DEVICE_SCAN类型的事件,并通过event指针存放于buffer数组中。
3.返回存在设备增加事件和设备完成扫描事件的数组,让inputreader进行处理。
size_t EventHub::getEvents(int timeoutMillis, RawEvent* buffer, size_t bufferSize) {
ALOG_ASSERT(bufferSize >= 1);
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
struct input_event readBuffer[bufferSize];//bufferSize值为传入的256
RawEvent* event = buffer;//event指针指向传入的buffer首地址,每存入一个事件,event指针向后移动一个元素
size_t capacity = bufferSize;//capacity表示buffer中剩余端元素数量,capacity为0,表示buffer已满
bool awoken = false;
for (;;) {//死循环
nsecs_t now = systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC);//获取当前时间
// // 是否需要重新打开设备,主要用于设备配置发生改变等原因
// if (mNeedToReopenDevices) {//EventHub构造函数中初始化时,其值为false,第一次getevent时,后续代码不执行
// mNeedToReopenDevices = false;
// ALOGI("Reopening all input devices due to a configuration change.");
// closeAllDevicesLocked();//关闭所有devices
// mNeedToScanDevices = true;//设置需要扫描设备为true
// break; //真正扫描设备之前,退出循环
// }
// Report any devices that had last been added/removed.
// while (mClosingDevices) {//EventHub构造函数中初始化时,其值为0,此代码块不执行
// Device* device = mClosingDevices;
// ALOGV("Reporting device closed: id=%d, name=%s\n",
// device->id, device->path.string());
// mClosingDevices = device->next;
// event->when = now;
// event->deviceId = device->id == mBuiltInKeyboardId ? BUILT_IN_KEYBOARD_ID : device->id;
// event->type = DEVICE_REMOVED;
// event += 1;
// delete device;
// mNeedToSendFinishedDeviceScan = true;
// if (--capacity == 0) {
// break;
// }
// }
if (mNeedToScanDevices) {//默认值为true,即第一次调用getevent时,会扫描/dev/input下的设备
mNeedToScanDevices = false;//设置为false,避免重复扫描设备
scanDevicesLocked();//执行扫描设备的函数。扫描/dev/input下的设备
mNeedToSendFinishedDeviceScan = true;//mNeedToSendFinishedDeviceScan值为true,用于生成FINISHED_DEVICE_SCAN事件
}
while (mOpeningDevices != NULL) {
Device* device = mOpeningDevices;//此时mOpeningDevices值是刚打开过的device
mOpeningDevices = device->next;//device->next值为0,指向下一个设备
//生成DEVICE_ADDED类型的事件,并通过event指针存放于buffer数组中
event->when = now;
event->deviceId = device->id == mBuiltInKeyboardId ? 0 : device->id;//如果是内置键盘,则其id为0,如果不是则是device->id
event->type = DEVICE_ADDED;//类型
event += 1;//event的定义是RawEvent* event = buffer,event指针指向传入的buffer数组的首地址,即第0个元素,
//每存入一个事件,event指针向后移动一个元素
mNeedToSendFinishedDeviceScan = true;
if (--capacity == 0) {//buffer数组可容量-1
break;
}
}
if (mNeedToSendFinishedDeviceScan) {
mNeedToSendFinishedDeviceScan = false;
//生成FINISHED_DEVICE_SCAN类型的事件,并通过event指针存放于buffer数组中
event->when = now;
event->type = FINISHED_DEVICE_SCAN;
event += 1;
if (--capacity == 0) {
break;
}
}
bool deviceChanged = false;
/*如果存在未处理的事件,则从mPendingEventItems数组中取出事件
while (mPendingEventIndex < mPendingEventCount) {//此时刚开机启动。mPendingEventIndex和mPendingEventCount都为0
.......
}
*/
// 当event的指针不再指向buffer的首地址时,代表里面有数据,或者被唤醒时,立即退出循环
if (event != buffer || awoken) {//此时生成了两种事件,一个是扫描的所有打开设备的事件,还有一个是完成设备扫描报告的事件,故退出循环
break;
}
}
// 全部完成后,返回我们读取的事件数。
return event - buffer;
}4.28 scanDevicesLocked
void EventHub::scanDevicesLocked() {
status_t res = scanDirLocked(DEVICE_PATH);//调用scanDirLocked方法,DEVICE_PATH=/dev/input,返回0代表成功
if(res < 0) {
ALOGE("scan dir failed for %s\n", DEVICE_PATH);
}
if (mDevices.indexOfKey(VIRTUAL_KEYBOARD_ID) < 0) {//
//mDevices的定义是一个map容器,KeyedVector<int32_t, Device*> mDevices;mDevices中存放的是已经扫描完成的设备,即
//已经完成设备厂商信息的获取和注册进epoll监听的设备。VIRTUAL_KEYBOARD_ID的值等于-1
//此处如果从mDevice中没有找到虚拟键盘,则调用createVirtualKeyboardLocked方法创建虚拟键盘。
createVirtualKeyboardLocked();
}
}void EventHub::createVirtualKeyboardLocked() {
InputDeviceIdentifier identifier;//存储厂商信息的结构体
identifier.name = "Virtual";
identifier.uniqueId = "<virtual>";
assignDescriptorLocked(identifier);
Device* device = new Device(-1, VIRTUAL_KEYBOARD_ID, String8("<virtual>"), identifier);//创建了一个Device对象
device->classes = INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_KEYBOARD | INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_ALPHAKEY |
INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_DPAD | INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_VIRTUAL;//设置属性calss
loadKeyMapLocked(device);//加载kepMap,键盘映射表,保存到device->keyMap中。
addDeviceLocked(device);//添加设备到mDevices的map容器中
}
status_t EventHub::loadKeyMapLocked(Device* device) {
return device->keyMap.load(device->identifier, device->configuration);
}
void EventHub::addDeviceLocked(Device* device) {
mDevices.add(device->id, device);//mDevices的定义是一个容器,KeyedVector<int32_t, Device*> mDevices;
device->next = mOpeningDevices;//Device结构体是一个单链表,其next指向下一个设备,但此时mOpeningDevices在初始化时值为0,0代表最近无设备打开
mOpeningDevices = device;//mOpeningDevices也是一个Device*指针,指向此device,代表最近打开的设备。
}
4.29 scanDirLocked
1.循环打开/dev/input下的所有设备节点。
status_t EventHub::scanDirLocked(const char *dirname)
{
char devname[PATH_MAX];
char *filename;
DIR *dir;
struct dirent *de;
dir = opendir(dirname);
if(dir == NULL)
return -1;
strcpy(devname, dirname);
filename = devname + strlen(devname);
*filename++ = '/';
while((de = readdir(dir))) {//循环打开目录下的所有设备
if(de->d_name[0] == '.' &&
(de->d_name[1] == '\0' ||
(de->d_name[1] == '.' && de->d_name[2] == '\0')))
continue;
strcpy(filename, de->d_name);
openDeviceLocked(devname);//打开设备
}
closedir(dir);//关闭目录
return 0;
}
4.30 openDeviceLocked
主要作用为:
1.打开/dev/input/xxxx的设备,然后获取设备的驱动版本,设备产品,设备供应商,设备物理地址,设备标识符将信息保存到InputDeviceIdentifier类的identifier对象中,此对象主要用于存储设备厂商的所有信息。
2.假设此时有一个设备/dev/input/event0,根据其dentifier对象生成对应的Device类对象。然后加载设备的配置文件到device类对象的PropertyMap中。
配置文件主要有三类。
一.idc文件,主要用于触摸屏配置。
二.kl文件,主要用于键盘的扫描码和keycode的转化。
三.kcm文件,主要作用是将 Android按键代码与修饰符的组合映射到 Unicode。
3.从设备的fd中读取数据判断其设备类型为EV_KEY、EV_ABS、EV_REL、EV_SW、EV_LED、EV_FF类型。
一:EV_KEY,按键类型的事件。能够上报这类事件的设备有键盘、鼠标、手柄、手写板
等一切拥有按钮的设备(包括手机上的实体按键)。在Device结构体中,对应的事件
位掩码keyBitmask描述了设备可以产生的按键事件的集合。按键事件的全集包括字
符按键、方向键、控制键、鼠标键、游戏按键等。
二:EV_ABS,绝对坐标类型的事件。这类事件描述了在空间中的一个点,触控板、触
摸屏等使用绝对坐标的输入设备可以上报这类事件。事件位掩码absBitmask描述了
设备可以上报的事件的维度信息(ABS_X、ABS_Y、ABS_Z),以及是否支持多点
事件。
三:EV_REL,相对坐标类型的事件。这类事件描述了事件在空间中相对于上次事件
的偏移量。鼠标、轨迹球等基于游标指针的设备可以上报此类事件。事件位掩码
relBitmask描述了设备可以上报的事件的维度信息(REL_X、REL_Y、REL_Z)。
四:EV_SW,开关类型的事件。这类事件描述了若干固定状态之间的切换。手机上的静
音模式开关按钮、模式切换拨盘等设备可以上报此类事件。事件位掩码swBitmask表
示了设备可切换的状态列表。
五:EV_LED,光反馈类型事件。ledBitmask描述了设备是否支持光
六:EV_FF,力反馈类型,ffBitmask则描述了设备是否支持力反馈。
4.根据上诉大类型,生成更细分的类型——INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_xxx类型。如L按键事件可再通过有无X,y比特位,区分是键盘还是蓝牙手柄。
一:INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_KEYBOARD,可以上报鼠标按键以外的EV_KEY类型事件的设备都属于此类。如键盘、机身按钮(音量键、电源键等)。
二:INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_ALPHAKEY,可以上报字符按键的设备,例如键盘。此类 型的设备必定同时属于KEYBOARD。
三:INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_DPAD,可以上报方向键的设备。例如键盘、手机导航键
等。这类设备同时也属于KEYBOARD。
四:INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_GAMEPAD,可以上报游戏按键的设备,如游戏手柄。这类设备同时也属于KEYBOARD。
五:INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH,可以上报EV_ABS类型事件的设备都属于此类,如触摸屏和触控板。
六:INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH_MT,可以上报EV_ABS类型事件,并且其事件位掩码指示其支持多点事件的设备属于此类。例如多点触摸屏。这类设备同时也属于TOUCH类型。
七:INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_CURSOR,可以上报EV_REL类型的事件,并且可以上报BTN_MOUSE子类的EV_KEY事件的设备属于此类,例如鼠标和轨迹球。
八:INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_SWITCH,可以上报EV_SW类型事件的设备。
九:INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_JOYSTICK,属于GAMEPAD类型,并且属于TOUCH类型的设备。
十:INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_VIBRATOR,支持力反馈的设备。
十一:INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_VIRTUAL,虚拟设备。
十二:INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_EXTERNAL,外部设备,即非内建设备。如外接鼠标、键盘、游戏手柄等。
status_t EventHub::openDeviceLocked(const char *devicePath) {
char buffer[80];
int fd = open(devicePath, O_RDWR | O_CLOEXEC | O_NONBLOCK);//以读写,非阻塞,原子方式打开设备
//打开设备节点的文件描述符,用于获取设备信息以及读取原始输入事件
InputDeviceIdentifier identifier;//存储厂商的信息
//接下来的代码通过ioctl()函数从设备节点中获取输入设备的厂商信息
if(ioctl(fd, EVIOCGNAME(sizeof(buffer) - 1), &buffer) < 1) {//通过设备的fd,向驱动发送EVIOCGNAME指令,
//获取设备名称,写入buffer中
} else {
buffer[sizeof(buffer) - 1] = '\0';
identifier.name.setTo(buffer);//从buffer中取出名称信息,赋值给identifier的name属性
}
// 检查获取的设备名称是否在排除列表中下
for (size_t i = 0; i < mExcludedDevices.size(); i++) {// 检查获取的设备名称是否在排除列表中下,
//如果在mExcludedDevices列表中,则关闭此设备,并返回,mExcludedDevices列表在setExcludedDevices方法中赋值的,
//而setExcludedDevices方法是在inputreader构造函数中的refreshConfigurationLocked方法中调用的,
//同时mExcludedDevices最后是调用到java层ims中获取的。
const String8& item = mExcludedDevices.itemAt(i);
if (identifier.name == item) {
ALOGI("ignoring event id %s driver %s\n", devicePath, item.string());
close(fd);
return -1;
}
}
//获取设备驱动版本
int driverVersion;
if(ioctl(fd, EVIOCGVERSION, &driverVersion)) {//从驱动中获取的信息赋值给driverVersion
ALOGE("could not get driver version for %s, %s\n", devicePath, strerror(errno));
close(fd);
return -1;
}
//获取设备标识符
struct input_id inputId;
if(ioctl(fd, EVIOCGID, &inputId)) {//赋值给inputId
ALOGE("could not get device input id for %s, %s\n", devicePath, strerror(errno));
close(fd);
return -1;
}
identifier.bus = inputId.bustype;
identifier.product = inputId.product;//设备产品
identifier.vendor = inputId.vendor;//供应商
identifier.version = inputId.version;//版本
// 获取设备物理地址
if(ioctl(fd, EVIOCGPHYS(sizeof(buffer) - 1), &buffer) < 1) {//放于buffer中
//fprintf(stderr, "could not get location for %s, %s\n", devicePath, strerror(errno));
} else {
buffer[sizeof(buffer) - 1] = '\0';
identifier.location.setTo(buffer);//赋值给location
}
//获取设备唯一的id
if(ioctl(fd, EVIOCGUNIQ(sizeof(buffer) - 1), &buffer) < 1) {
//fprintf(stderr, "could not get idstring for %s, %s\n", devicePath, strerror(errno));
} else {
buffer[sizeof(buffer) - 1] = '\0';
identifier.uniqueId.setTo(buffer);//赋值给uniqueId
}
assignDescriptorLocked(identifier);//将identifier信息填充到fd,分配唯一标识设备的设备描述符,主要作用是填写identifier.nonce字段。
// 分配device,device对象获取fd的所有权
int32_t deviceId = mNextDeviceId++;//mNextDeviceId初始值为1,故deviceId=1
Device* device = new Device(fd, deviceId, String8(devicePath), identifier);
//参数分析:
//此处结合是getevent工具分析的
//fd是dev/input/event0的设备的描述符
//deviceid=1
//devicePath=dev/input/event0
//identifier存储了此设备所有的厂商信息
loadConfigurationLocked(device);//加载device的配置文件。主要是例如:device.type和device.internal等信息
// 详细事件报告的类型,从fd对应的device中读取各种信息,并保存到device的keyBitmask或absBitmask中,
//例如:如果是键盘设备,则device->keyBitmask有数据,而device->absBitmask无数据
ioctl(fd, EVIOCGBIT(EV_KEY, sizeof(device->keyBitmask)), device->keyBitmask);//按键类型
ioctl(fd, EVIOCGBIT(EV_ABS, sizeof(device->absBitmask)), device->absBitmask);//绝对坐标类型
ioctl(fd, EVIOCGBIT(EV_REL, sizeof(device->relBitmask)), device->relBitmask);//相对坐标类型,只要用于motion
ioctl(fd, EVIOCGBIT(EV_SW, sizeof(device->swBitmask)), device->swBitmask);//开关类型
ioctl(fd, EVIOCGBIT(EV_LED, sizeof(device->ledBitmask)), device->ledBitmask);//led等类型
ioctl(fd, EVIOCGBIT(EV_FF, sizeof(device->ffBitmask)), device->ffBitmask);//力反馈类型
ioctl(fd, EVIOCGPROP(sizeof(device->propBitmask)), device->propBitmask);
//Device结构体的事件位掩码描述了6种类型的输入事件:
//EV_KEY,按键类型的事件。能够上报这类事件的设备有键盘、鼠标、手柄、手写板
//等一切拥有按钮的设备(包括手机上的实体按键)。在Device结构体中,对应的事件
//位掩码keyBitmask描述了设备可以产生的按键事件的集合。按键事件的全集包括字
//符按键、方向键、控制键、鼠标键、游戏按键等。
//EV_ABS,绝对坐标类型的事件。这类事件描述了在空间中的一个点,触控板、触
//摸屏等使用绝对坐标的输入设备可以上报这类事件。事件位掩码absBitmask描述了
//设备可以上报的事件的维度信息(ABS_X、ABS_Y、ABS_Z),以及是否支持多点
//事件。
//EV_REL,相对坐标类型的事件。这类事件描述了事件在空间中相对于上次事件
//的偏移量。鼠标、轨迹球等基于游标指针的设备可以上报此类事件。事件位掩码
relBitmask描述了设备可以上报的事件的维度信息(REL_X、REL_Y、REL_Z)。
//EV_SW,开关类型的事件。这类事件描述了若干固定状态之间的切换。手机上的静
//音模式开关按钮、模式切换拨盘等设备可以上报此类事件。事件位掩码swBitmask表
//示了设备可切换的状态列表。
//EV_LED,光反馈类型事件。ledBitmask描述了设备是否支持光
//EV_FF,力反馈类型,ffBitmask则描述了设备是否支持力反馈。
//INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_KEYBOARD,可以上报鼠标按键以外的EV_KEY类型事件的设备都属于此类。如键
//盘、机身按钮(音量键、电源键等)。
//INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_ALPHAKEY,可以上报字符按键的设备,例如键盘。此类型的设备必定同时属于KEYBOARD。
//INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_DPAD,可以上报方向键的设备。例如键盘、手机导航键等。这类设备同时也属于KEYBOARD。
//INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_GAMEPAD,可以上报游戏按键的设备,如游戏手柄。这类设备同时也属于KEYBOARD。
//INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH,可以上报EV_ABS类型事件的设备都属于此类,如触摸屏和触控板。
//INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH_MT,可以上报EV_ABS类型事件,并且其事件位掩码指示其支持多点事件
//的设备属于此类。例如多点触摸屏。这类设备同时也属于TOUCH类型。
//INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_CURSOR,可以上报EV_REL类型的事件,并且可以上报BTN_MOUSE子类的
//EV_KEY事件的设备属于此类,例如鼠标和轨迹球。
//INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_SWITCH,可以上报EV_SW类型事件的设备。
//INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_JOYSTICK,属于GAMEPAD类型,并且属于TOUCH类型的设备。
//INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_VIBRATOR,支持力反馈的设备。
//INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_VIRTUAL,虚拟设备。
//INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_EXTERNAL,外部设备,即非内建设备。如外接鼠标、键盘、游戏手柄等。
//通过查看device->keyBitmask是否有数据,查看此设备是不是键盘类型
bool haveKeyboardKeys = containsNonZeroByte(device->keyBitmask, 0, sizeof_bit_array(BTN_MISC))
|| containsNonZeroByte(device->keyBitmask, sizeof_bit_array(KEY_OK),
sizeof_bit_array(KEY_MAX + 1));
bool haveGamepadButtons = containsNonZeroByte(device->keyBitmask, sizeof_bit_array(BTN_MISC),
sizeof_bit_array(BTN_MOUSE))
|| containsNonZeroByte(device->keyBitmask, sizeof_bit_array(BTN_JOYSTICK),
sizeof_bit_array(BTN_DIGI));
if (haveKeyboardKeys || haveGamepadButtons) {//如果是键盘类型或者游戏按键类型,
//则设置device->classes为INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_KEYBOARD
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_KEYBOARD;
}
//通过查看device->keyBitmask中是否有BTN_MOUSE对应的比特位和device->relBitmask是否对应的REL_X和REL_Y比特位,确认这是不是一个光标设备,如轨迹球或鼠标。
if (test_bit(BTN_MOUSE, device->keyBitmask)
&& test_bit(REL_X, device->relBitmask)
&& test_bit(REL_Y, device->relBitmask)) {
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_CURSOR;
}
// 查看是否是旋转编码器类型的设备.
String8 deviceType = String8();
if (device->configuration &&
device->configuration->tryGetProperty(String8("device.type"), deviceType)) {
if (!deviceType.compare(String8("rotaryEncoder"))) {
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_ROTARY_ENCODER;
}
}
//通过查看device->absBitmask,查看这是不是触摸板。
if (test_bit(ABS_MT_POSITION_X, device->absBitmask)
&& test_bit(ABS_MT_POSITION_Y, device->absBitmask)) {
if (test_bit(BTN_TOUCH, device->keyBitmask) || !haveGamepadButtons) {//尝试确认设备确实触摸屏。
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH | INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH_MT;
}
// 查看这是不是旧式的单触的驱动
} else if (test_bit(BTN_TOUCH, device->keyBitmask)
&& test_bit(ABS_X, device->absBitmask)
&& test_bit(ABS_Y, device->absBitmask)) {
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH;
// 查看不是外部手写笔
} else if ((test_bit(ABS_PRESSURE, device->absBitmask) ||
test_bit(BTN_TOUCH, device->keyBitmask))
&& !test_bit(ABS_X, device->absBitmask)
&& !test_bit(ABS_Y, device->absBitmask)) {
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_EXTERNAL_STYLUS;
device->classes &= ~INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_KEYBOARD;//有的事件键盘会和手写笔要配合执行一些操作。
}
//查看这个设备是否是操纵杆。
//假设操纵杆总是有游戏板按钮,以便与其他设备(如也有绝对轴的加速计)区分开来。
if (haveGamepadButtons) {
uint32_t assumedClasses = device->classes | INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_JOYSTICK;
for (int i = 0; i <= ABS_MAX; i++) {
if (test_bit(i, device->absBitmask)
&& (getAbsAxisUsage(i, assumedClasses) & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_JOYSTICK)) {
device->classes = assumedClasses;
break;
}
}
}
//查看此device是否有开关
for (int i = 0; i <= SW_MAX; i++) {
if (test_bit(i, device->swBitmask)) {
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_SWITCH;
break;
}
}
// 检查此设备是否支持可控震源。
if (test_bit(FF_RUMBLE, device->ffBitmask)) {
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_VIBRATOR;
}
// 如果是触摸屏,则为其配置虚拟键盘
if ((device->classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH)) {
//加载触摸屏的虚拟键(如果有)。
status_t status = loadVirtualKeyMapLocked(device);//loadVirtualKeyMapLocked函数的作用大致为
//加载系统提供的虚拟键盘的文件,然后将其键值对保存到virtualKeyMap中
if (!status) {
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_KEYBOARD;
}
}
//加载kepMap,键盘映射表
//我们为操纵杆或者键盘加载映射表
status_t keyMapStatus = NAME_NOT_FOUND;
if (device->classes & (INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_KEYBOARD | INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_JOYSTICK)) {
keyMapStatus = loadKeyMapLocked(device);//从device中加载keymap,键盘映射表
}
// 配置键盘、游戏板或虚拟键盘。
if (device->classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_KEYBOARD) {
if (!keyMapStatus
&& mBuiltInKeyboardId == NO_BUILT_IN_KEYBOARD//表示此时并未任何内置键盘配置过
&& isEligibleBuiltInKeyboard(device->identifier,
device->configuration, &device->keyMap)) //如果符合条件,会将键盘注册为内置键盘,
//然后device->keyMap保存着键盘映射表信息
{
mBuiltInKeyboardId = device->id;//mBuiltInKeyboardId内置键盘id,如果是第一次打开设备,则此时id为1
}
if (hasKeycodeLocked(device, AKEYCODE_Q)) {
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_ALPHAKEY;
}
//查看设备是否有方向键
if (hasKeycodeLocked(device, AKEYCODE_DPAD_UP) &&
hasKeycodeLocked(device, AKEYCODE_DPAD_DOWN) &&
hasKeycodeLocked(device, AKEYCODE_DPAD_LEFT) &&
hasKeycodeLocked(device, AKEYCODE_DPAD_RIGHT) &&
hasKeycodeLocked(device, AKEYCODE_DPAD_CENTER)) {
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_DPAD;
}
// 查看此设备是否有游戏板。
for (size_t i = 0; i < sizeof(GAMEPAD_KEYCODES)/sizeof(GAMEPAD_KEYCODES[0]); i++) {
if (hasKeycodeLocked(device, GAMEPAD_KEYCODES[i])) {
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_GAMEPAD;
break;
}
}
}
// 如果设备未识别类型,删除设备,直接返回
if (device->classes == 0) {
ALOGV("Dropping device: id=%d, path='%s', name='%s'",
deviceId, devicePath, device->identifier.name.string());
delete device;
return -1;
}
// 确定设备是否有麦克风。
if (deviceHasMicLocked(device)) {
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_MIC;
}
// 确定设备是外部设备还是内部设备
if (device->classes & (device->classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH)
|| (device->classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH_MT)) {
int devType = getTouchInputDeviceType(device);
if ( devType == 1)
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_EXTERNAL;
else if ( devType == 2)
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TERTIARY1;
else if ( devType == 3)
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TERTIARY2;
} else if (isExternalDeviceLocked(device))
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_EXTERNAL;
//确认设备是不是操控杆或者是不是游戏键盘,为其设置led灯效
if (device->classes & (INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_JOYSTICK | INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_DPAD)
&& device->classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_GAMEPAD) {
device->controllerNumber = getNextControllerNumberLocked(device);
setLedForControllerLocked(device);
}
if (registerDeviceForEpollLocked(device) != OK) {//将设备节点描述符的可读事件添加到Epoll中,
//当此设备的输入事件到来时,Epoll会在getEvents()函数的调用中产生一条epoll事件
delete device;
return -1;
}
configureFd(device);//给device对应的设备,通过ioctl设置重复设置为禁用
addDeviceLocked(device);//将设备添加到Device容器中
return OK;
} 主要作用是:
1.分配唯一标识设备的设备描述符。Descriptor用与唯一的表示设备
此处的逻辑为:
如果identifier中有uniqueId表示设备的唯一id,则不用干啥。如果identifier中没有uniqueId表示设备的唯一,则通过vendor,product等生成可以唯一表示设备的描述符,如果有vendor,product重名的,则用nonce区分。
void EventHub::assignDescriptorLocked(InputDeviceIdentifier& identifier) {
//分配唯一标识设备的设备描述符。
identifier.nonce = 0;
String8 rawDescriptor = generateDescriptor(identifier);
if (identifier.uniqueId.isEmpty()) {//如果没有唯一的uniqueId,则循环查找identifier.descriptor字段,
//如果已经获取过的device的identifier.descriptor存在重复,则强制加1,然后重新获取独一无二的Descriptor字段
while (getDeviceByDescriptorLocked(identifier.descriptor) != NULL) {
identifier.nonce++;
rawDescriptor = generateDescriptor(identifier);//重新生成identifier.descriptor字段
}
}
ALOGV("Created descriptor: raw=%s, cooked=%s", rawDescriptor.string(),
identifier.descriptor.string());
}
static String8 generateDescriptor(InputDeviceIdentifier& identifier) {
String8 rawDescriptor;
rawDescriptor.appendFormat(":%04x:%04x:", identifier.vendor, identifier.product);//为vendor和product自定义格式,并追加到rawDescriptor中
if (!identifier.uniqueId.isEmpty()) {
rawDescriptor.append("uniqueId:");
rawDescriptor.append(identifier.uniqueId);
} else if (identifier.nonce != 0) {
rawDescriptor.appendFormat("nonce:%04x", identifier.nonce);
}
if (identifier.vendor == 0 && identifier.product == 0) {
//如果我们不知道供应商和产品id,那么设备可能是内置的,因此我们需要依赖其他信息来唯一标识输入设备。
//通常,我们尽量避免依赖设备名称或位置,但对于内置输入设备,它们不太可能更改。
if (!identifier.name.isEmpty()) {
rawDescriptor.append("name:");
rawDescriptor.append(identifier.name);//如果是虚拟键盘,rawDescriptor大致变为:uniqueId:<virtual> name:Virtual
} else if (!identifier.location.isEmpty()) {
rawDescriptor.append("location:");
rawDescriptor.append(identifier.location);
}
}
identifier.descriptor = sha1(rawDescriptor);//sha1是用来将字符串加密成十六进制的一串字符
return rawDescriptor;
}
EventHub::Device* EventHub::getDeviceByDescriptorLocked(String8& descriptor) const {
size_t size = mDevices.size();
for (size_t i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Device* device = mDevices.valueAt(i);
if (descriptor.compare(device->identifier.descriptor) == 0) {//如果已扫描过的device中的descriptor等于传入的descriptor,则返回此device
return device;
}
}
return NULL;
}1.主要用于加载设备的触摸屏配置文件,读取其属性到PropertyMap中
void EventHub::loadConfigurationLocked(Device* device) {
device->configurationFile = getInputDeviceConfigurationFilePathByDeviceIdentifier(//从供应商信息中获取此设备的device配置文件
device->identifier, INPUT_DEVICE_CONFIGURATION_FILE_TYPE_CONFIGURATION);//代表idc文件
///enum InputDeviceConfigurationFileType {
///INPUT_DEVICE_CONFIGURATION_FILE_TYPE_CONFIGURATION = 0, /* .idc file *//idc文件,主要用于触摸屏配置
///INPUT_DEVICE_CONFIGURATION_FILE_TYPE_KEY_LAYOUT = 1, /* .kl file *//主要用于键盘的扫描码和keycode的转化
///INPUT_DEVICE_CONFIGURATION_FILE_TYPE_KEY_CHARACTER_MAP = 2, /* .kcm file *///.kcm"文件意为按键字符映射文件,作用是将 Android按键代码与修饰符的组合映射到 Unicode字符
//};
if (device->configurationFile.isEmpty()) {//如果供应商信息的文件为空
ALOGD("No input device configuration file found for device '%s'.",
device->identifier.name.string());
} else {
status_t status = PropertyMap::load(device->configurationFile,
&device->configuration);//源文件路径为device->configurationFile,读取属性并输出到device->configuration这个PropertyMap下
if (status) {
ALOGE("Error loading input device configuration file for device '%s'. "
"Using default configuration.",
device->identifier.name.string());
}
}
//idc文件的命名方式有三种
//Vendor_xxxx_Product_xxxx_Version_xxxx.idc
//Vendor_xxxx_Product_xxxx.idc
//device-name.idc
String8 getInputDeviceConfigurationFilePathByDeviceIdentifier(const InputDeviceIdentifier& deviceIdentifier,InputDeviceConfigurationFileType type) {
if (deviceIdentifier.vendor !=0 && deviceIdentifier.product != 0) {
if (deviceIdentifier.version != 0) {//根据vendor,product,version获取配置文件路径
// Try vendor product version.
String8 versionPath(getInputDeviceConfigurationFilePathByName(
String8::format("Vendor_%04x_Product_%04x_Version_%04x",//拼接字符串为此格式
deviceIdentifier.vendor, deviceIdentifier.product,
deviceIdentifier.version),
type));
if (!versionPath.isEmpty()) {
return versionPath;
}
}
// Try vendor product.
String8 productPath(getInputDeviceConfigurationFilePathByName(//根据vendor和product获取配置文件路径
String8::format("Vendor_%04x_Product_%04x",
deviceIdentifier.vendor, deviceIdentifier.product),
type));
if (!productPath.isEmpty()) {
return productPath;
}
}
// Try device name.
return getInputDeviceConfigurationFilePathByName(deviceIdentifier.name, type);//根据deice名称获取配置文件路径
}
String8 getInputDeviceConfigurationFilePathByName(const String8& name, InputDeviceConfigurationFileType type) {
// Search system repository.
//搜索系统存储库
String8 path;
// Treblized input device config files will be located /odm/usr or /vendor/usr.
//input设备的配置文件将会坐落于/odm/usr或者/vendor/usr
const char *rootsForPartition[] {"/odm", "/vendor", getenv("ANDROID_ROOT")};
for (size_t i = 0; i < size(rootsForPartition); i++) {
path.setTo(rootsForPartition[i]);
path.append("/usr/");
appendInputDeviceConfigurationFileRelativePath(path, name, type);//传入的path是/vendor/usr/,name是Vendor_xxxx_Product_xxxx_Version_xxxx.idc,type是0
#if DEBUG_PROBE
ALOGD("Probing for system provided input device configuration file: path='%s'",
path.string());
#endif
if (!access(path.string(), R_OK)) {
#if DEBUG_PROBE
ALOGD("Found");
#endif
return path;
}
}
// Search user repository.
//搜索用户存储库
// TODO Should only look here if not in safe mode.
path.setTo(getenv("ANDROID_DATA"));
path.append("/system/devices/");
appendInputDeviceConfigurationFileRelativePath(path, name, type);
#if DEBUG_PROBE
ALOGD("Probing for system user input device configuration file: path='%s'", path.string());
#endif
if (!access(path.string(), R_OK)) {
#if DEBUG_PROBE
ALOGD("Found");
#endif
return path;
}
// Not found.
#if DEBUG_PROBE
ALOGD("Probe failed to find input device configuration file: name='%s', type=%d",
name.string(), type);
#endif
return String8();
}
String8 getInputDeviceConfigurationFilePathByName(const String8& name, InputDeviceConfigurationFileType type) {
// Search system repository.
//搜索系统存储库
String8 path;
// Treblized input device config files will be located /odm/usr or /vendor/usr.
//input设备的配置文件将会坐落于/odm/usr或者/vendor/usr
const char *rootsForPartition[] {"/odm", "/vendor", getenv("ANDROID_ROOT")};
for (size_t i = 0; i < size(rootsForPartition); i++) {
path.setTo(rootsForPartition[i]);
path.append("/usr/");
appendInputDeviceConfigurationFileRelativePath(path, name, type);//传入的path是/vendor/usr/,name是Vendor_xxxx_Product_xxxx_Version_xxxx.idc,type是0
#if DEBUG_PROBE
ALOGD("Probing for system provided input device configuration file: path='%s'",
path.string());
#endif
if (!access(path.string(), R_OK)) {
#if DEBUG_PROBE
ALOGD("Found");
#endif
return path;
}
}
// Search user repository.
//搜索用户存储库
// TODO Should only look here if not in safe mode.
path.setTo(getenv("ANDROID_DATA"));
path.append("/system/devices/");
appendInputDeviceConfigurationFileRelativePath(path, name, type);
#if DEBUG_PROBE
ALOGD("Probing for system user input device configuration file: path='%s'", path.string());
#endif
if (!access(path.string(), R_OK)) {
#if DEBUG_PROBE
ALOGD("Found");
#endif
return path;
}
// Not found.
#if DEBUG_PROBE
ALOGD("Probe failed to find input device configuration file: name='%s', type=%d",
name.string(), type);
#endif
return String8();
}
static const char* CONFIGURATION_FILE_DIR[] = {
"idc/",
"keylayout/",
"keychars/",
};
static const char* CONFIGURATION_FILE_EXTENSION[] = {
".idc",
".kl",
".kcm",
} 主要作用是:
加载虚拟键盘映射表到VirtualKeyMap中.
status_t EventHub::loadVirtualKeyMapLocked(Device* device) {
//virtualKeyMap,虚拟键盘映射表由内核作为主板属性文件提供
String8 path;
path.append("/sys/board_properties/virtualkeys.");//路径
path.append(device->identifier.name);//路径+文件名
if (access(path.string(), R_OK)) {
return NAME_NOT_FOUND;
}
return VirtualKeyMap::load(path, &device->virtualKeyMap);//加载path的键值对到virtualKeyMap中,
//注意返回值,0代表真,1代表假,大致返回0
} 主要作用是:
加载键盘映射表到VirtualKeyMap中
status_t EventHub::loadKeyMapLocked(Device* device) {
return device->keyMap.load(device->identifier, device->configuration);
}void EventHub::configureFd(Device* device) {
// Set fd parameters with ioctl, such as key repeat, suspend block, and clock type
//使用ioctl设置fd参数,如key重复、挂起块和时钟类型
if (device->classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_KEYBOARD) {
// 禁用内核按键重复,因为我们自己处理它
unsigned int repeatRate[] = {0, 0};
if (ioctl(device->fd, EVIOCSREP, repeatRate)) {
ALOGW("Unable to disable kernel key repeat for %s: %s",
device->path.string(), strerror(errno));
}
}
String8 wakeMechanism("EPOLLWAKEUP");
if (!mUsingEpollWakeup) {
#ifndef EVIOCSSUSPENDBLOCK
// uapi headers don't include EVIOCSSUSPENDBLOCK, and future kernels
// will use an epoll flag instead, so as long as we want to support
// this feature, we need to be prepared to define the ioctl ourselves.
#define EVIOCSSUSPENDBLOCK _IOW('E', 0x91, int)
#endif
if (ioctl(device->fd, EVIOCSSUSPENDBLOCK, 1)) {
wakeMechanism = "<none>";
} else {
wakeMechanism = "EVIOCSSUSPENDBLOCK";
}
}
//告诉内核,我们希望使用单调时钟来报告与输入事件相关联的时间戳。这一点很重要,因为输入系统广泛使用时间戳,并假设它们是使用单调时钟记录的。
int clockId = CLOCK_MONOTONIC;//这个时钟不受系统时间
bool usingClockIoctl = !ioctl(device->fd, EVIOCSCLOCKID, &clockId);
ALOGI("wakeMechanism=%s, usingClockIoctl=%s", wakeMechanism.string(),
toString(usingClockIoctl));
}void EventHub::addDeviceLocked(Device* device) {
mDevices.add(device->id, device);//mDevices的定义是一个容器,KeyedVector<int32_t, Device*> mDevices;
device->next = mOpeningDevices;//Device结构体是一个单链表,其next指向下一个设备,但此时mOpeningDevices在初始化时值为0,0代表最近无设备打开
mOpeningDevices = device;//mOpeningDevices也是一个Device*指针,指向此device,代表最近打开的设备。
}4.31 registerDeviceForEpollLocked
上面完成了/dev/input/xxxx设备节点到Device类的生成,Device类包含各个设备节点的厂商信息、设备类别、上报的事件种类、设备的映射表等诸多信息,然后注册设备节点到epoll中,开始监听各个设备节点下是否有可读事件,即监听设备的原始输入事件。
input事件主要分为两种:
一:原始输入事件,就是当触摸屏幕等操作时,产生的事件。
二:设备的增删事件。
status_t EventHub::registerDeviceForEpollLocked(Device* device) {
struct epoll_event eventItem;
memset(&eventItem, 0, sizeof(eventItem));
eventItem.events = EPOLLIN;//监听的文件描述符是否有可读事件
if (mUsingEpollWakeup) {//EPOLLWAKEUP标志就能保证事件在挂起或处理时,系统不会挂起或休眠。
eventItem.events |= EPOLLWAKEUP;
}
eventItem.data.u32 = device->id;//事件触发时会返回eventItem.data数据
if (epoll_ctl(mEpollFd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, device->fd, &eventItem)) {//监听device->fd对应的设备是否有可读事件。
//如果有事件可读,则返回eventItem.data
ALOGE("Could not add device fd to epoll instance. errno=%d", errno);
return -errno;
}
return OK;
}4.32 processEventsLocked
经过前面分析我们知道,input系统第一次启动时候,会先扫描/dev/input下的所有设备,并对所有设备进行信息的读取和配置文件的加载,并生成对应的Device类对象。然后会生成设备添加的事件,当完成所有设备的扫描后,会生成一个设备扫描完成事件。
RawEvent事件含义如下:
struct RawEvent {
nsecs_t when;//时间
int32_t deviceId;//事件发生的设备id
int32_t type;//类型,例如按键事件等
int32_t code;//扫描码,按键对应的扫描码
int32_t value;//值,表示按键按下,或者抬起等
};
void InputReader::processEventsLocked(const RawEvent* rawEvents, size_t count) {//用rawEvents指针接收传入的从传入的mEventBuffer数组的首地址
for (const RawEvent* rawEvent = rawEvents; count;) {//for循环遍历数组
int32_t type = rawEvent->type;//取出数组中第0号的元素rawEvent的type.
size_t batchSize = 1;
//事件信息有两种,一种是设备节点的增加和删除事件,统称为设备事件,另一种是原始输入事件。
//此处满足条件,则是对设备事件进行处理
if (type < EventHubInterface::FIRST_SYNTHETIC_EVENT) {
} else {
switch (rawEvent->type) {//处理设备添加事件
case EventHubInterface::DEVICE_ADDED://设备添加事件。同时为其创建对应的mapper
addDeviceLocked(rawEvent->when, rawEvent->deviceId);
break;
case EventHubInterface::DEVICE_REMOVED://设备删除事件
removeDeviceLocked(rawEvent->when, rawEvent->deviceId);
break;
case EventHubInterface::FINISHED_DEVICE_SCAN://扫描完成事件
handleConfigurationChangedLocked(rawEvent->when);//生成一个通知的事件塞进队列
break;
default:
ALOG_ASSERT(false);
break;
}
}
count -= batchSize;
rawEvent += batchSize;
}
}4.33 addDeviceLocked
此处先分析设备添加事件。主要根据Device对象的一些信息生成InputDevice对象。InputDevice对象中会根据其设备是开关设备、键盘设备、还是滚轮式设备生成诸多对应的mapper对象。
Device类和InputDevice类非常相似,其主要区别是InputDevice相对于Device结构体多了一个
InputMapper列表。
InputMapper有一系列的子类,分别用于加工不同类型的原始输入事件。
void InputReader::addDeviceLocked(nsecs_t when, int32_t deviceId) {
ssize_t deviceIndex = mDevices.indexOfKey(deviceId);
InputDeviceIdentifier identifier = mEventHub->getDeviceIdentifier(deviceId);//mEventHub是在inputreader初始化时赋值的,
//是EventHub类对象,此处只是将device->identifier取出来
uint32_t classes = mEventHub->getDeviceClasses(deviceId);//取出device->classes
int32_t controllerNumber = mEventHub->getDeviceControllerNumber(deviceId);
InputDevice* device = createDeviceLocked(deviceId, controllerNumber, identifier, classes);//创建InputDevice
device->configure(when, &mConfig, 0);//对设备一些厂商信息进行配置,对按键等布局信息进行加载到map中,并对生成的mapper进行配置。配置坐标系映射等
device->reset(when);//重置所有mapper,比如按键mapper是将保存所有按键按下的vector清空。
if (device->isIgnored()) {//isIgnored()函数返回的是mMapper容器是否为空,一般不为空,除非出错
ALOGI("Device added: id=%d, name='%s' (ignored non-input device)", deviceId,
identifier.name.string());
} else {
ALOGI("Device added: id=%d, name='%s', sources=0x%08x", deviceId,
identifier.name.string(), device->getSources());
}
mDevices.add(deviceId, device);
bumpGenerationLocked();
if (device->getClasses() & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_EXTERNAL_STYLUS) {
notifyExternalStylusPresenceChanged();
}
}2.34 createDeviceLocked
1.生成了InputDevice类对象。
2.根据设备的class类型生成了多个对应的inputMapper对象。并将inputMapper对象存储在InputDevice类的一个容器中。
其事件类型、设备类型和InputMapper对应关系如下:

(图片来自参考文章)
InputDevice* InputReader::createDeviceLocked(int32_t deviceId, int32_t controllerNumber,
const InputDeviceIdentifier& identifier, uint32_t classes) {
InputDevice* device = new InputDevice(&mContext, deviceId, bumpGenerationLocked(),controllerNumber, identifier, classes);
//此处本质是通过Device结构体,生成InputReader类的InputDevice对象,InputDevice表示的是单个设备的状态。单个很重要
//根据Device结构体指针的class属性,为InputReader类赋值
//参数分析:
//mContext是inputreader对象
//bumpGenerationLocked函数会将Generation值加1.故此时是2
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_EXTERNAL) {
device->setExternal(true);//源码为inline void setExternal(bool external) { mIsExternal = external; }
}
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TERTIARY1) {
device->setTertiary(1);//源码为inline void setTertiary(int tertiary) { mIsTertiary = tertiary; }
}
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TERTIARY2) {
device->setTertiary(2);//源码为inline void setTertiary(int tertiary) { mIsTertiary = tertiary; }
}
// 设备有麦克风
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_MIC) {
device->setMic(true);//源码为inline void setMic(bool hasMic) { mHasMic = hasMic; }
}
// 开关设备
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_SWITCH) {
device->addMapper(new SwitchInputMapper(device));//源码为
//1.SwitchInputMapper::SwitchInputMapper(InputDevice* device) :InputMapper(device), mSwitchValues(0), mUpdatedSwitchMask(0)
//2.void InputDevice::addMapper(InputMapper* mapper) {mMappers.add(mapper);}
//含义:如果是开关设备,则初始化一个SwitchInputMapper,并添加到存储InputMapper*指针的容器mMappers中。
}
// 滚动滚轮式设备。
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_ROTARY_ENCODER) {
device->addMapper(new RotaryEncoderInputMapper(device));
}
// 力反馈设备,类似振动器
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_VIBRATOR) {
device->addMapper(new VibratorInputMapper(device));
}
// 类似键盘设备.
uint32_t keyboardSource = 0;
int32_t keyboardType = AINPUT_KEYBOARD_TYPE_NON_ALPHABETIC;
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_KEYBOARD) {//可以上报鼠标按键以外的EV_KEY类型事件的设备都属于此类。如键盘、机身按钮(音量键、电源键等)。
keyboardSource |= AINPUT_SOURCE_KEYBOARD;
}
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_ALPHAKEY) {//表示可以上报字符按键的设备,此类型的设备必定同时属于keyboard
keyboardType = AINPUT_KEYBOARD_TYPE_ALPHABETIC;//有字母的键盘按键
}
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_DPAD) {//可以上报方向键的设备。例如键盘、手机导航键等
keyboardSource |= AINPUT_SOURCE_DPAD;
}
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_GAMEPAD) {//可以上报游戏按键的设备,如游戏手柄。这类设备同时也属于KEYBOARD
keyboardSource |= AINPUT_SOURCE_GAMEPAD;
}
if (keyboardSource != 0) {
device->addMapper(new KeyboardInputMapper(device, keyboardSource, keyboardType));//创建了一个KeyboardInputMapper,
//并添加到存储InputMapper*指针的容器mMappers中
}
// 类似光标的设备,如鼠标
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_CURSOR) {
device->addMapper(new CursorInputMapper(device));
}
// 触摸屏或者触摸平板设备
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH_MT) {
device->addMapper(new MultiTouchInputMapper(device));//new了一个多点触摸的Mapper
} else if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH) {
device->addMapper(new SingleTouchInputMapper(device));//new了一个单点触摸的Mapper
}
// 类似操纵手柄的设备
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_JOYSTICK) {
device->addMapper(new JoystickInputMapper(device));
}
// 外部类似手写笔的设备。
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_EXTERNAL_STYLUS) {
device->addMapper(new ExternalStylusInputMapper(device));
}
return device;
}
InputDevice::InputDevice(InputReaderContext* context, int32_t id, int32_t generation,
int32_t controllerNumber, const InputDeviceIdentifier& identifier, uint32_t classes) :
mContext(context), mId(id), mGeneration(generation), mControllerNumber(controllerNumber),
mIdentifier(identifier), mClasses(classes),
mSources(0), mIsExternal(false), mHasMic(false), mDropUntilNextSync(false) {
}4.35 configure
1.主要是对mapper循环调用configure,后续文章会对键盘和触摸屏进行配置的分析。
void InputDevice::configure(nsecs_t when, const InputReaderConfiguration* config, uint32_t changes) {
mSources = 0;
if (!isIgnored()) {//isIgnored()函数返回的是mMapper容器是否为空,一般不为空,除非出错
if (!changes) { // 仅设备第一次添加时,此处执行
mContext->getEventHub()->getConfiguration(mId, &mConfiguration);//从Device类的对象中获取configuration,
//赋值给传入的inputDevice类对象的mConfiguration,mId是deviceid
}
if (!changes || (changes & InputReaderConfiguration::CHANGE_KEYBOARD_LAYOUTS)) {//第一次配置设备时,必会执行,
//否则就是当键盘布局发生改变时,changes会等于CHANGE_KEYBOARD_LAYOUTS时,下列代码才执行。
if (!(mClasses & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_VIRTUAL)) {//此处含义为:当不是虚拟键盘时,从供应商信息中获取键盘布局,
//并保存到keyboardLayout这个KeyCharacterMap中。
sp<KeyCharacterMap> keyboardLayout =
mContext->getPolicy()->getKeyboardLayoutOverlay(mIdentifier);
if (mContext->getEventHub()->setKeyboardLayoutOverlay(mId, keyboardLayout)) {
bumpGeneration();
}
}
}
if (!changes || (changes & InputReaderConfiguration::CHANGE_DEVICE_ALIAS)) {//第一次配置设备时,必会执行,
//否则就是当设备的别名发生改变时,changes会等于CHANGE_KEYBOARD_LAYOUTS时,下列代码才执行。
if (!(mClasses & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_VIRTUAL)) {//此处含义为:当不是虚拟键盘时,从供应商信息中获取别名,
//并重新给设备的别名赋值
String8 alias = mContext->getPolicy()->getDeviceAlias(mIdentifier);
if (mAlias != alias) {
mAlias = alias;
bumpGeneration();
}
}
}
if (!changes || (changes & InputReaderConfiguration::CHANGE_ENABLED_STATE)) {//第一次必定执行,
//CHANGE_ENABLED_STATE表示的含义是CHANGE_ENABLED_STATE表示的含义是禁用的输入设备已更改。当chnages等于时,下列代码才执行
ssize_t index = config->disabledDevices.indexOf(mId);//disabledDevices是一个有序的容器,存储的是禁用的设备。
//从禁用的设备容器中,根据deviceid查询
bool enabled = index < 0;//第一次配置设备时enabled为ture,
setEnabled(enabled, when);//enabled值为ture就设置Device*类的device->enabled属性为true
}
size_t numMappers = mMappers.size();
for (size_t i = 0; i < numMappers; i++) {//循环对具体的mapper进行配置
InputMapper* mapper = mMappers[i];
mapper->configure(when, config, changes);//此函数是根据具体的map进行配置的,//此处仅分析touch的配置和keyboard的配置。
mSources |= mapper->getSources();
}
}
}4.36 removeDeviceLocked
如果是删除设备事件,则:
1.删除对应的InputDevice设备
2.重置其所有的mapper
void InputReader::removeDeviceLocked(nsecs_t when, int32_t deviceId) {
InputDevice* device = NULL;
ssize_t deviceIndex = mDevices.indexOfKey(deviceId);
if (deviceIndex < 0) {
ALOGW("Ignoring spurious device removed event for deviceId %d.", deviceId);
return;
}
device = mDevices.valueAt(deviceIndex);
mDevices.removeItemsAt(deviceIndex, 1);//从mDevices中删除InputDevice指针
bumpGenerationLocked();//值+1,表示设备有变化
if (device->isIgnored()) {
ALOGI("Device removed: id=%d, name='%s' (ignored non-input device)",
device->getId(), device->getName().string());
} else {
ALOGI("Device removed: id=%d, name='%s', sources=0x%08x",
device->getId(), device->getName().string(), device->getSources());
}
if (device->getClasses() & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_EXTERNAL_STYLUS) {
notifyExternalStylusPresenceChanged();//如果是外部手写笔,则通知
}
device->reset(when);//重置device中的所有mapper
delete device;
}4.37 handleConfigurationChangedLocked
1.生成了一个NotifyConfigurationChangedArgs消息,然后进入派发队列。
//设备完成扫描时,生成一个通知arg
void InputReader::handleConfigurationChangedLocked(nsecs_t when) {
// Reset global meta state because it depends on the list of all configured devices.
updateGlobalMetaStateLocked();
NotifyConfigurationChangedArgs args(when);//生成了一个NotifyConfigurationChangedArgs消息
mQueuedListener->notifyConfigurationChanged(&args);//进入派发队列
}进入派发队列,然后等待唤醒派发线程。
void QueuedInputListener::notifyConfigurationChanged(
const NotifyConfigurationChangedArgs* args) {
mArgsQueue.push(new NotifyConfigurationChangedArgs(*args));//将此消息放入队列中
}再次回到inputreader第一次启动执行的代码块,注意,看此时会调用notifyInputDevicesChanged来通知java层IMS设备发生变化。
//第一次启动时,执行的代码块
void InputReader::loopOnce() {
int32_t oldGeneration;
int32_t timeoutMillis;
bool inputDevicesChanged = false;
Vector<InputDeviceInfo> inputDevices;
{
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
oldGeneration = mGeneration;//值为1,在inputreader构造函数中mGeneration=1,
timeoutMillis = -1;
uint32_t changes = mConfigurationChangesToRefresh;//值为0,初始化时设置为0,代表无变化,不刷新配置
// if (changes) {//此处刚开始代码不执行,
// mConfigurationChangesToRefresh = 0;
// timeoutMillis = 0;
// refreshConfigurationLocked(changes);
// } else if (mNextTimeout != LLONG_MAX) {//在inputreader构造函数中,mNextTimeout是LLONG_MAX,此处代码不会执行
// //此处的含义本人认为,mNextTimeout代表了下一次线程唤醒的时间点,如果mNextTimeout不是LLONG_MAX,则需要计算休眠的时间
// nsecs_t now = systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC);
// timeoutMillis = toMillisecondTimeoutDelay(now, mNextTimeout);//线程休眠时间
// }
}
size_t count = mEventHub->getEvents(timeoutMillis, mEventBuffer, EVENT_BUFFER_SIZE);//通过EventHub的getEvents函数获取事件,
//并存放在mEventBuffer中。此时可以知道刚启动时,只是会生成所有已经扫描的设备的add类型的事件和一个完成设备扫描的事件
//参数分析:timeoutMillis=-1,代表啥意思不清楚,感觉如果数字为0代表立即执行
//mEventBuffer是一个存放从eventhub中读取的rawevent结构体类型的数组,源代码是:RawEvent mEventBuffer[EVENT_BUFFER_SIZE];
//EVENT_BUFFER_SIZE值是256,代表最大可以读取256个原始事件,RawEvent结构体如下
////从EventHub检索到的原始事件
//struct RawEvent {
//nsecs_t when;//时间
//int32_t deviceId;//事件发生的设备id
//int32_t type;//类型,例如按键事件等
//int32_t code;//扫描码,按键对应的扫描码
//int32_t value;//值,表示按键按下,或者抬起等
//};
{ // acquire lock
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
mReaderIsAliveCondition.broadcast();
if (count) {//返回的事件数量大于,则调用processEventsLocked处理事件
processEventsLocked(mEventBuffer, count);
}
/*
if (mNextTimeout != LLONG_MAX) //此时mNextTimeout是LLONG_MAX
{
nsecs_t now = systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC);
if (now >= mNextTimeout) {
#if DEBUG_RAW_EVENTS
ALOGD("Timeout expired, latency=%0.3fms", (now - mNextTimeout) * 0.000001f);
#endif
mNextTimeout = LLONG_MAX;
timeoutExpiredLocked(now);
}
}*/
if (oldGeneration != mGeneration) {//此处是不等于的,因为当有add设备事件时processEventsLocked函数中调用addDeviceLocked,addDeviceLocked在完成设备配置后
//会调用bumpGenerationLocked函数,使得mGeneration+1,从而不相等
inputDevicesChanged = true;
getInputDevicesLocked(inputDevices);//获取所有的新的设备信息到inputDevices容器中
}
} // release lock
//
if (inputDevicesChanged) {//如果设备发生变化,生成一个通知设备事件的通知
mPolicy->notifyInputDevicesChanged(inputDevices);//此时mPolicy是NativeInputManager对象,所以此时调用到了NativeInputManager::notifyInputDevicesChanged
}
//发布事件。 一般此处只会处理加工后的原始输入事件,而此时开机启动只有设备添加和删除的事件,但是当设备完成扫描时会生成一个通知事件
//放入此队列。所以启动后,扫描完设备后,此容器只有一个扫描设备完成的通知事件
// mQueuedListener中。在循环的最后,通过调用flush()函数将所有事件交付给InputDispatcher
mQueuedListener->flush();
}4.38 notifyInputDevicesChanged
mpolicy对象本质是NativeInputManager对象。
此处主要作用是:
当开机启动后,扫描完所有设备会生成InputDevice对象,然后根据InputDevice对象会生成对应的
InputDeviceInfo类对象,其同样包含设备的所有信息,然后通过jni通知到java层的IMS,用于通知给java层通知设备监听的listener。
void NativeInputManager::notifyInputDevicesChanged(const Vector<InputDeviceInfo>& inputDevices) {
//inputDevices存储了所有刚开机启动添加的所有的设备信息。
ATRACE_CALL();
JNIEnv* env = jniEnv();
size_t count = inputDevices.size();
jobjectArray inputDevicesObjArray = env->NewObjectArray(count, gInputDeviceClassInfo.clazz, NULL);//创建一个保存类的对象数组大小为count
//static struct {
//jclass clazz;
//} gInputDeviceClassInfo;
if (inputDevicesObjArray) {
bool error = false;
for (size_t i = 0; i < count; i++) {
jobject inputDeviceObj = android_view_InputDevice_create(env, inputDevices.itemAt(i));//根据c++的InputDeviceInfo类的对象创建对应的inputDeviceObj对象
if (!inputDeviceObj) {
error = true;
break;
}
env->SetObjectArrayElement(inputDevicesObjArray, i, inputDeviceObj);//将生成的inputDeviceObj对象设置进对象数组中
env->DeleteLocalRef(inputDeviceObj);//删除本地引用
}
if (!error) {//如果没有出错,则通过jni调用java层的notifyInputDevicesChanged方法,传递参数为inputDevicesObjArray
env->CallVoidMethod(mServiceObj, gServiceClassInfo.notifyInputDevicesChanged,inputDevicesObjArray);
}
env->DeleteLocalRef(inputDevicesObjArray);
}
checkAndClearExceptionFromCallback(env, "notifyInputDevicesChanged");
}我们可以看到函数形参上存在,存储InputDeviceInfo的容器,那么InputDeviceInfo是何时被创建的呢?
查看InputReader::loopOnce() 存在getInputDevicesLocked函数。
此函数主要是为所有的InputDevice生成对应的InputDeviceInfo对象。
void InputReader::getInputDevicesLocked(Vector<InputDeviceInfo>& outInputDevices) {
outInputDevices.clear();//Vector<InputDeviceInfo> inputDevices;,保存的是所有的设备信息。当设备发生变化时,先清除所有的信息
size_t numDevices = mDevices.size();
for (size_t i = 0; i < numDevices; i++) {//循环为所有的InputDevice生成对应的InputDeviceInfo类对象
InputDevice* device = mDevices.valueAt(i);
if (!device->isIgnored()) {
outInputDevices.push();//往inputDevices中添加一个InputDeviceInfo
device->getDeviceInfo(&outInputDevices.editTop());
}
}
}void InputDevice::getDeviceInfo(InputDeviceInfo* outDeviceInfo) {
outDeviceInfo->initialize(mId, mGeneration, mControllerNumber, mIdentifier, mAlias,
mIsExternal, mHasMic);
//mId是设备id
//mGeneration 主要用于判断设备是否发生了变化的参数
//mControllerNumber,控制器编号 默认是0
//mIdentifier,主要包含了设备厂商信息
//mAlias,代表别名
//mIsExternal代表是不是外接设备
//mHasMic是否有麦克风
size_t numMappers = mMappers.size();
for (size_t i = 0; i < numMappers; i++) {
InputMapper* mapper = mMappers[i];
mapper->populateDeviceInfo(outDeviceInfo);//此处会根据不同的mapper执行不同的操作。此处暂时分析KeyboardInputMapper,因为一个设备可能有多个maper
}
}void InputDeviceInfo::initialize(int32_t id, int32_t generation, int32_t controllerNumber,
const InputDeviceIdentifier& identifier, const String8& alias, bool isExternal,
bool hasMic) {
mId = id;
mGeneration = generation;
mControllerNumber = controllerNumber;
mIdentifier = identifier;
mAlias = alias;
mIsExternal = isExternal;
mHasMic = hasMic;
mSources = 0;
mKeyboardType = AINPUT_KEYBOARD_TYPE_NONE;
mHasVibrator = false;
mHasButtonUnderPad = false;
mMotionRanges.clear();
}void KeyboardInputMapper::populateDeviceInfo(InputDeviceInfo* info) {
InputMapper::populateDeviceInfo(info);//调用了父类的populateDeviceInfo
//主要是设置source类型
info->setKeyboardType(mKeyboardType);//设置按键的type
/*
enum {
AINPUT_KEYBOARD_TYPE_NONE = 0,
// 无字母的键盘按键
AINPUT_KEYBOARD_TYPE_NON_ALPHABETIC = 1,
// 有字母的键盘按键
AINPUT_KEYBOARD_TYPE_ALPHABETIC = 2,
};*/
info->setKeyCharacterMap(getEventHub()->getKeyCharacterMap(getDeviceId()));//设置其按键映射表到InputDeviceInfo中
}
void InputMapper::populateDeviceInfo(InputDeviceInfo* info) {
info->addSource(getSources());//soucre采用的是|的运算方式,因为一个InputDeviceInfo可能对应多个InputMapper
}
void InputDeviceInfo::addSource(uint32_t source) {
mSources |= source;
//AINPUT_SOURCE_KEYBOARD可以上报鼠标按键以外的EV_KEY类型事件的设备都属于此类。如键盘、机身按钮(音量键、电源键等)。
//AINPUT_SOURCE_DPAD表示可以上报字符按键的设备,此类型的设备必定同时属于keyboard
//AINPUT_SOURCE_GAMEPAD可以上报游戏按键的设备,如游戏手柄。这类设备同时也属于KEYBOARD
}找到了InputDeviceInfo的创建,那么我们此时需要再回到notifyInputDevicesChanged函数,其中
android_view_InputDevice_create是根据C++层的InputDeviceInfo类的对象创建java层的inputDeviceObj对象,然后通过jni机制调用java层的notifyInputDevicesChanged函数。
jobject android_view_InputDevice_create(JNIEnv* env, const InputDeviceInfo& deviceInfo) {
ScopedLocalRef<jstring> nameObj(env, env->NewStringUTF(deviceInfo.getDisplayName().string()));//生成jni的nameObj,此时是设备厂商的名称
if (!nameObj.get()) {
return NULL;
}
ScopedLocalRef<jstring> descriptorObj(env,env->NewStringUTF(deviceInfo.getIdentifier().descriptor.string()));//生成jni的描述符
if (!descriptorObj.get()) {
return NULL;
}
ScopedLocalRef<jobject> kcmObj(env,
android_view_KeyCharacterMap_create(env, deviceInfo.getId(),
deviceInfo.getKeyCharacterMap()));//根据c++层的键盘布局的map生成jni层的键盘布局map
if (!kcmObj.get()) {
return NULL;
}
const InputDeviceIdentifier& ident = deviceInfo.getIdentifier();
// Not sure why, but JNI is complaining when I pass this through directly.
jboolean hasMic = deviceInfo.hasMic() ? JNI_TRUE : JNI_FALSE;
ScopedLocalRef<jobject> inputDeviceObj(env, env->NewObject(gInputDeviceClassInfo.clazz,//生成对应的inputDeviceObj
gInputDeviceClassInfo.ctor, deviceInfo.getId(), deviceInfo.getGeneration(),
deviceInfo.getControllerNumber(), nameObj.get(),
static_cast<int32_t>(ident.vendor), static_cast<int32_t>(ident.product),
descriptorObj.get(), deviceInfo.isExternal(), deviceInfo.getSources(),
deviceInfo.getKeyboardType(), kcmObj.get(), deviceInfo.hasVibrator(),
hasMic, deviceInfo.hasButtonUnderPad()));
const Vector<InputDeviceInfo::MotionRange>& ranges = deviceInfo.getMotionRanges();//添加motion相关的设备信息,键盘的话,是为空的
for (size_t i = 0; i < ranges.size(); i++) {
const InputDeviceInfo::MotionRange& range = ranges.itemAt(i);
env->CallVoidMethod(inputDeviceObj.get(), gInputDeviceClassInfo.addMotionRange, range.axis,
range.source, range.min, range.max, range.flat, range.fuzz, range.resolution);
if (env->ExceptionCheck()) {
return NULL;
}
}
return env->NewLocalRef(inputDeviceObj.get());
}//IMS.java
private void notifyInputDevicesChanged(InputDevice[] inputDevices) {
synchronized (mInputDevicesLock) {
if (!mInputDevicesChangedPending) {
mInputDevicesChangedPending = true;
mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_DELIVER_INPUT_DEVICES_CHANGED,mInputDevices).sendToTarget();//mHandler是InputManager对象,
//Handler获取一个消息,触发mHandler的handleMessage函数。
}
mInputDevices = inputDevices;
}
} public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case MSG_DELIVER_INPUT_DEVICES_CHANGED:
deliverInputDevicesChanged((InputDevice[])msg.obj);
break;
case MSG_SWITCH_KEYBOARD_LAYOUT:
handleSwitchKeyboardLayout(msg.arg1, msg.arg2);
break;
case MSG_RELOAD_KEYBOARD_LAYOUTS:
reloadKeyboardLayouts();
break;
case MSG_UPDATE_KEYBOARD_LAYOUTS:
updateKeyboardLayouts();
break;
case MSG_RELOAD_DEVICE_ALIASES:
reloadDeviceAliases();
break;
case MSG_DELIVER_TABLET_MODE_CHANGED:
SomeArgs args = (SomeArgs) msg.obj;
long whenNanos = (args.argi1 & 0xFFFFFFFFl) | ((long) args.argi2 << 32);
boolean inTabletMode = (boolean) args.arg1;
deliverTabletModeChanged(whenNanos, inTabletMode);
break;
}
} private void deliverInputDevicesChanged(InputDevice[] oldInputDevices) {
// Scan for changes.
int numFullKeyboardsAdded = 0;
mTempInputDevicesChangedListenersToNotify.clear();
mTempFullKeyboards.clear();
final int numListeners;
final int[] deviceIdAndGeneration;
synchronized (mInputDevicesLock) {
if (!mInputDevicesChangedPending) {//刚才mInputDevicesChangedPending值为true
return;
}
mInputDevicesChangedPending = false;
numListeners = mInputDevicesChangedListeners.size();//mInputDevicesChangedListeners存储着监听device设备的listener,这些listener会在java层调用registerInputDeviceListener
//注册input的设备增加和删除
for (int i = 0; i < numListeners; i++) {
mTempInputDevicesChangedListenersToNotify.add(//取出所有的监听设备add,放入mTempInputDevicesChangedListenersToNotify中
mInputDevicesChangedListeners.valueAt(i));
}
final int numDevices = mInputDevices.length;
deviceIdAndGeneration = new int[numDevices * 2];
for (int i = 0; i < numDevices; i++) {
final InputDevice inputDevice = mInputDevices[i];
deviceIdAndGeneration[i * 2] = inputDevice.getId();
deviceIdAndGeneration[i * 2 + 1] = inputDevice.getGeneration();
if (!inputDevice.isVirtual() && inputDevice.isFullKeyboard()) {//如果设备不是虚拟键盘,并且是有字母的键盘
if (!containsInputDeviceWithDescriptor(oldInputDevices,
inputDevice.getDescriptor())) {//如果旧的inputDevice和更新后的inputDevice对应的设备描述符不一样
mTempFullKeyboards.add(numFullKeyboardsAdded++, inputDevice);
} else {
mTempFullKeyboards.add(inputDevice);//保存所有设备中是有字母键盘的,后面由于检查键盘布局
}
}
}
}
// Notify listeners.
for (int i = 0; i < numListeners; i++) {
mTempInputDevicesChangedListenersToNotify.get(i).notifyInputDevicesChanged(
deviceIdAndGeneration);//通知所有的客户端设备add和remove的消息
}
mTempInputDevicesChangedListenersToNotify.clear();
//检查是否缺少键盘布局
List<InputDevice> keyboardsMissingLayout = new ArrayList<>();
final int numFullKeyboards = mTempFullKeyboards.size();
synchronized (mDataStore) {
for (int i = 0; i < numFullKeyboards; i++) {
final InputDevice inputDevice = mTempFullKeyboards.get(i);
String layout =
getCurrentKeyboardLayoutForInputDevice(inputDevice.getIdentifier());//获取当前键盘布局
if (layout == null) {
layout = getDefaultKeyboardLayout(inputDevice);//如果布局为空,则获取默认的布局
if (layout != null) {//如果布局不为空
setCurrentKeyboardLayoutForInputDevice(
inputDevice.getIdentifier(), layout);//设置当前布局
}
}
if (layout == null) {//如果布局为空
keyboardsMissingLayout.add(inputDevice);//则将此键盘添加缺少布局
}
}
}
if (mNotificationManager != null) {
if (!keyboardsMissingLayout.isEmpty()) {
if (keyboardsMissingLayout.size() > 1) {//发送缺少键盘布局的通知
showMissingKeyboardLayoutNotification(null);
} else {
showMissingKeyboardLayoutNotification(keyboardsMissingLayout.get(0));
}
} else if (mKeyboardLayoutNotificationShown) {
hideMissingKeyboardLayoutNotification();
}
}
mTempFullKeyboards.clear();
}4.39 QueuedInputListener::flush
void QueuedInputListener::flush() {
size_t count = mArgsQueue.size();
for (size_t i = 0; i < count; i++) {//从存储NotifyArgs的容器中循环取出并调用notify
NotifyArgs* args = mArgsQueue[i];
args->notify(mInnerListener);//传入的参数mInnerListener是InputDispatcher类对象
delete args;
}
mArgsQueue.clear();
}4.40 NotifyConfigurationChangedArgs::notify
void NotifyConfigurationChangedArgs::notify(const sp<InputListenerInterface>& listener) const {
listener->notifyConfigurationChanged(this);//此处listener是InputDispatcher类对象,this是调用者也就是一个NotifyConfigurationChangedArgs对象
}4.41 notifyConfigurationChanged
1生成了一个ConfigurationChangedEntry事件,并将此事件放入InboundQueue中,然后唤醒派发线程,派发线程会取出消息进行派发。
void InputDispatcher::notifyConfigurationChanged(const NotifyConfigurationChangedArgs* args) {
#if DEBUG_INBOUND_EVENT_DETAILS
ALOGD("notifyConfigurationChanged - eventTime=%" PRId64, args->eventTime);
#endif
bool needWake;
{ // acquire lock
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
ConfigurationChangedEntry* newEntry = new ConfigurationChangedEntry(args->eventTime);//生成ConfigurationChangedEntry事件
needWake = enqueueInboundEventLocked(newEntry);//将事件放入队列中
} // release lock
if (needWake) {
mLooper->wake();//需要唤醒分发线程的looper
}
}
bool InputDispatcher::enqueueInboundEventLocked(EventEntry* entry) {
bool needWake = mInboundQueue.isEmpty();
mInboundQueue.enqueueAtTail(entry);//将该事件放入mInboundQueue队列尾部
traceInboundQueueLengthLocked();//追踪队列的长度,打印了一条log
return needWake;
}查看2.22知道,此时的派发线程在休眠状态,mLooper->pollOnce(timeoutMillis);然后唤醒后,会进入下一次dispatchOnce的调用。此时分析第二次执行的代码块。
4.42 dispatchOnce
//唤醒线程后,第二次执行的代码块
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce() {
nsecs_t nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MAX;//下一次唤醒该线程的时间,也可以说是下一次线程循环的执行时间点
{
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
mDispatcherIsAliveCondition.broadcast();//分发线程处于活跃状态,进行广播
if (!haveCommandsLocked()) {//此时mCommandQueue中无命令。作用:检查inputdispatcher的缓存队列中是否有还未处理的命令,
//只有无命令时才会执行dispatchOnceInnerLocked方法,进行事件的分发。
dispatchOnceInnerLocked(&nextWakeupTime);// 传入的nextWakeupTime决定了下次派发线程循环的执行时间点,
}
if (runCommandsLockedInterruptible()) {//此时dispatchOnceInnerLocked在处理设备变化的消息时,调用dispatchConfigurationChangedLocked
//向命令队列中添加了一条命令,所以不为空
//如果此时缓存队列中有命令,则立即执行该命令,
//并将下一次线程循环的执行时间点设置为LONG_LONG_MIN,将使派发线程立刻开始下次线程。
//最小值定义为0,最大值是unsigned long long的最大值:1844674407370955161
nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MIN;//会执行,并立即开启第三次线程循环
}
} // release lock
nsecs_t currentTime = now();//获取当前时间点
int timeoutMillis = toMillisecondTimeoutDelay(currentTime, nextWakeupTime);//下一次唤醒时间点-当前时间点=线程休眠时间
mLooper->pollOnce(timeoutMillis);//调用pollOnce使线程休眠,等待回调,唤醒或超时。
//Looper的pollOnce()的实质就是epoll_wait()。 因此派发线程的休眠在三种情况下可能被唤醒:
1.调用Looper::wake()函数主动唤醒(有输入事件注入派发队列中时),
2.到达nextWakeupTime的事件点时唤醒
3.epoll_waitepoll_wait()监听的fd有epoll_event发生时唤醒(这种唤醒方式将在介绍ANR机制时讨论)。
}4.43 dispatchOnceInnerLocked
1.生成ConfigurationChangedEntry事件,用于表示配置发生变化
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnceInnerLocked(nsecs_t* nextWakeupTime) {
nsecs_t currentTime = now();
if (!mDispatchEnabled) {//默认值为flase
resetKeyRepeatLocked();//重置上一个事件
}
// 如果mDispatch被冻结,则不派发事件
if (mDispatchFrozen) {
#if DEBUG_FOCUS
ALOGD("Dispatch frozen. Waiting some more.");
#endif
return;
}
bool isAppSwitchDue = mAppSwitchDueTime <= currentTime;//第二次循环时mAppSwitchDueTime值是LONG_LONG_MAX,所以isAppSwitchDue是false
//如果没有待发送的事件,则从mInboundQueue队列中取出一个事件,进行分发
if (! mPendingEvent) {//此时mPendingEvent= null
///if (mInboundQueue.isEmpty())
{
} else {//此时不会空
//从派发队列中将位于队首的一条EventEntry取出并保存在mPendingEvent成员变量中。
// mPendingEvent表示处于派发过程中的一个输入事件
mPendingEvent = mInboundQueue.dequeueAtHead();
traceInboundQueueLengthLocked();//更新一下队列长度
}
/// Poke user activity for this event.
///if (mPendingEvent->policyFlags & POLICY_FLAG_PASS_TO_USER) {//判断此key是否需要发送到应用程序。此时启动后只是一个设备变化的通知,故不执行
/// pokeUserActivityLocked(mPendingEvent);
///}
// Get ready to dispatch the event.
resetANRTimeoutsLocked();//重置anr
}
bool done = false;
DropReason dropReason = DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED;//默认丢弃原因为不丢弃
if (!(mPendingEvent->policyFlags & POLICY_FLAG_PASS_TO_USER)) {//在将事件注入派发队列时曾向DispatcherPolicy询间过派发策略
//倘若派发策略不允许此事件被派发给用户,则设置对应的dropReason
dropReason = DROP_REASON_POLICY;
}
///if (mNextUnblockedEvent == mPendingEvent) {//mNextUnblockedEvent此时为null,不执行
/// mNextUnblockedEvent = NULL;
///}
switch (mPendingEvent->type) {
case EventEntry::TYPE_CONFIGURATION_CHANGED: {
ConfigurationChangedEntry* typedEntry =static_cast<ConfigurationChangedEntry*>(mPendingEvent);
done = dispatchConfigurationChangedLocked(currentTime, typedEntry);//取出事件的type,发现是配置文件发生变化类型,则调用dispatchConfigurationChangedLocked
dropReason = DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED; // 配置发生变化类型永远也不会被丢弃
break;
}
default:
break;
}
if (done) {
mLastDropReason = dropReason;//mLastDropReason等于不丢弃
releasePendingEventLocked(); //释放此Event事件
*nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MIN; // 设置唤醒时间为LONG_LONG_MIN,表示立刻唤醒下次循环
}
}void InputDispatcher::releasePendingEventLocked() {
if (mPendingEvent) {
resetANRTimeoutsLocked();//重置anr
releaseInboundEventLocked(mPendingEvent);//添加到最近的消息队列中,如果没添加成功,则删除此mPendingEvent事件
mPendingEvent = NULL;//置空
}
}
void InputDispatcher::releaseInboundEventLocked(EventEntry* entry) {
InjectionState* injectionState = entry->injectionState;
addRecentEventLocked(entry);//添加到最近的队列中
entry->release();//释放entry对象
}
void InputDispatcher::addRecentEventLocked(EventEntry* entry) {
entry->refCount += 1;
mRecentQueue.enqueueAtTail(entry);
if (mRecentQueue.count() > RECENT_QUEUE_MAX_SIZE) {
mRecentQueue.dequeueAtHead()->release();
}
}
void InputDispatcher::EventEntry::release() {
refCount -= 1;//引用计数减少1
if (refCount == 0) {//如果当前引用计数为0,则delete自己
delete this;
} else {
ALOG_ASSERT(refCount > 0);
}
}4.44 dispatchConfigurationChangedLocked
1.生成一个command命令事件。为了告诉policy配置已发生变化。并将此命令放入命令队列中。
bool InputDispatcher::dispatchConfigurationChangedLocked(nsecs_t currentTime, ConfigurationChangedEntry* entry) {
//在添加或删除键盘设备或其他情况下重置重复键。
resetKeyRepeatLocked();
//生成一个command命令事件。为了告诉policy配置已发生变化
CommandEntry* commandEntry = postCommandLocked(& InputDispatcher::doNotifyConfigurationChangedInterruptible);//传入了一个函数地址作为命令
commandEntry->eventTime = entry->eventTime;
return true;
}
InputDispatcher::CommandEntry* InputDispatcher::postCommandLocked(Command command) {
CommandEntry* commandEntry = new CommandEntry(command);
mCommandQueue.enqueueAtTail(commandEntry);//入队命令队列
return commandEntry;
}此时,我们可以知道,dispatchOnceInnerLocked是往命令队列中插入了一条命令。因此再回到
4.42的dispatchOnce函数的runCommandsLockedInterruptible这一行。
4.45 runCommandsLockedInterruptible
主要作用:
从命令队列中取出命令,然后执行doNotifyConfigurationChangedInterruptible函数,并将commandEntry作为参传递进去
bool InputDispatcher::runCommandsLockedInterruptible() {
///if (mCommandQueue.isEmpty()) {
/// return false;//不为空
///}
do {
CommandEntry* commandEntry = mCommandQueue.dequeueAtHead();//取出命令
Command command = commandEntry->command;
(this->*command)(commandEntry); // 执行doNotifyConfigurationChangedInterruptible函数,并传入commandEntry作为参数
commandEntry->connection.clear();//清除connection
delete commandEntry;
} while (! mCommandQueue.isEmpty());
return true;
}4.46 doNotifyConfigurationChangedInterruptible
void InputDispatcher::doNotifyConfigurationChangedInterruptible(CommandEntry* commandEntry) {
mLock.unlock();
mPolicy->notifyConfigurationChanged(commandEntry->eventTime);//调用NativeInputManager类对象的notifyConfigurationChanged方法,通知配置发生变化
mLock.lock();
}4.47 notifyConfigurationChanged
void NativeInputManager::notifyConfigurationChanged(nsecs_t when) {
JNIEnv* env = jniEnv();
env->CallVoidMethod(mServiceObj, gServiceClassInfo.notifyConfigurationChanged, when);
checkAndClearExceptionFromCallback(env, "notifyConfigurationChanged");
}
//java层IMS
private void notifyConfigurationChanged(long whenNanos) {//此处调用到了wms的notifyConfigurationChanged
mWindowManagerCallbacks.notifyConfigurationChanged();//mWindowManagerCallbacks就是WMS中的InputManagerCallback,此时便走到了WMS中
}
4.48 notifyConfigurationChanged
java层InputMontior.java,此类是在WMS类中的ims回调类的实现类,此时便通知到了WMS。
1.通知与此输入设备相关联的显示器。
2.当系统刚启动的时候,因为WMS会等待IMS将输入设备配置好,才唤醒派发事件。因此当IMS第一次配置好设备后,唤醒再此等待的线程。
//InputMontior.java
public void notifyConfigurationChanged() {
//通知与此输入设备相关联的正确显示器。
mService.sendNewConfiguration(DEFAULT_DISPLAY);//mService是wms对象
synchronized (mInputDevicesReadyMonitor) {
if (!mInputDevicesReady) {
mInputDevicesReady = true;//当第一次接收到输入设备配置改变通知以指示输入设备已准备好时,设置为true。
mInputDevicesReadyMonitor.notifyAll();//唤醒在mInputDevicesReadyMonitor等待的线程,因为在startOtherServices中,会调用waitForInputDevicesReady进行等待
//WMS需要等待开机后Ims将第一次设备已经配置好才派发事件。
}
}
}WMS会等待IMS将输入设备配置如下:
private void startOtherServices() {
final boolean safeMode = wm.detectSafeMode();
}//windowmanagerservice.java
public boolean detectSafeMode() {
if (!mInputMonitor.waitForInputDevicesReady(
INPUT_DEVICES_READY_FOR_SAFE_MODE_DETECTION_TIMEOUT_MILLIS)) {
Slog.w(TAG_WM, "Devices still not ready after waiting "
+ INPUT_DEVICES_READY_FOR_SAFE_MODE_DETECTION_TIMEOUT_MILLIS
+ " milliseconds before attempting to detect safe mode.");
}
}4.49
然后由于是立即唤醒,分发线程再次被唤醒,此时分发线程无消息,则陷入无线等待。
然后读取线程也进入第二次循环,epoll_wait等待输入事件的发生。
//唤醒线程后,第三次执行的代码块,然后分发线程陷入无线等待。
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce() {
nsecs_t nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MAX;//下一次唤醒该线程的时间,也可以说是下一次线程循环的执行时间点
{
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
mDispatcherIsAliveCondition.broadcast();//分发线程处于活跃状态,进行广播
if (!haveCommandsLocked()) {//此时mCommandQueue中无命令。
dispatchOnceInnerLocked(&nextWakeupTime);// 传入的nextWakeupTime决定了下次派发线程循环的执行时间点,
}
///if (runCommandsLockedInterruptible()) {//此时dispatchOnceInnerLocked无命令
/// nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MIN;//会执行,并立即开启第三次线程循环
///}
}
nsecs_t currentTime = now();//获取当前时间点
int timeoutMillis = toMillisecondTimeoutDelay(currentTime, nextWakeupTime);//下一次唤醒时间点-当前时间点=线程休眠时间
mLooper->pollOnce(timeoutMillis);//调用pollOnce使线程休眠,等待回调,唤醒或超时。
//Looper的pollOnce()的实质就是epoll_wait()。 因此派发线程的休眠在三种情况下可能被唤醒:
1.调用Looper::wake()函数主动唤醒(有输入事件注入派发队列中时),
2.到达nextWakeupTime的事件点时唤醒
3.epoll_waitepoll_wait()监听的fd有epoll_event发生时唤醒(这种唤醒方式将在介绍ANR机制时讨论)。
}//读取线程第二次循环时
void InputReader::loopOnce() {
int32_t oldGeneration;
int32_t timeoutMillis;
bool inputDevicesChanged = false;
Vector<InputDeviceInfo> inputDevices;
{ // acquire lock
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
oldGeneration = mGeneration;//新的值
timeoutMillis = -1;
size_t count = mEventHub->getEvents(timeoutMillis, mEventBuffer, EVENT_BUFFER_SIZE);//通过EventHub的getEvents函数获取事件,
//并存放在mEventBuffer中。
//参数分析:timeoutMillis=-1,代表啥意思不清楚,感觉如果数字为0代表立即执行
//mEventBuffer是一个存放从eventhub中读取的rawevent结构体类型的数组,源代码是:RawEvent mEventBuffer[EVENT_BUFFER_SIZE];
//EVENT_BUFFER_SIZE值是256,代表最大可以读取256个原始事件,RawEvent结构体如下
..........
}
size_t EventHub::getEvents(int timeoutMillis, RawEvent* buffer, size_t bufferSize) {
ALOG_ASSERT(bufferSize >= 1);
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
struct input_event readBuffer[bufferSize];//bufferSize值为传入的256
RawEvent* event = buffer;//event指针指向传入的buffer首地址,每存入一个事件,event指针向后移动一个元素
size_t capacity = bufferSize;//capacity表示buffer中剩余端元素数量,capacity为0,表示buffer已满
bool awoken = false;
for (;;) {
nsecs_t now = systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC);//获取当前时间
mPendingEventIndex = 0;//此时mPendingEventItems数组中未处理的事件已经处理完了,将mPendingEventIndex设置为0
mLock.unlock();
release_wake_lock(WAKE_LOCK_ID);
int pollResult = epoll_wait(mEpollFd, mPendingEventItems, EPOLL_MAX_EVENTS, timeoutMillis);//此时第二次读线程会阻塞在此处,等待有消息的事件发生
......
}5.常用结构体
5.1 epoll_event
struct epoll_event
{
__uint32_t events; /* 事件掩码,指明了需要监听的事件种类,
常用的事件有EPOLLIN(可读),EPOLLOUT(可写),EPOLLERR(描述符发生错误),EPOLLHUP(描述符被挂起)*/
epoll_data_t data; /* 使用者自定义的数据,当此事件发生时该数据将原封不动地返回给使用者 */
};5.2 Device
struct Device {
Device* next; //指向下一个Device设备
int fd; // fd表示此设备的设备节点的描述符,可以从此描述符中读取原始输入事件
const int32_t id;//id在input输入系统中的唯一标识的设备
const String8 path;//设备节点的路径
const InputDeviceIdentifier identifier;//存储了设备的厂商信息
uint32_t classes;//表示设备的类别,键盘设备、触摸设备、轨迹球设备等。
uint8_t keyBitmask[(KEY_MAX + 1) / 8];//
uint8_t absBitmask[(ABS_MAX + 1) / 8];
uint8_t relBitmask[(REL_MAX + 1) / 8];
uint8_t swBitmask[(SW_MAX + 1) / 8];
uint8_t ledBitmask[(LED_MAX + 1) / 8];
uint8_t ffBitmask[(FF_MAX + 1) / 8];
uint8_t propBitmask[(INPUT_PROP_MAX + 1) / 8];
String8 configurationFile; //配置信息。
PropertyMap* configuration;
VirtualKeyMap* virtualKeyMap;//虚拟键盘映射表
KeyMap keyMap; //按键映射表
sp<KeyCharacterMap> overlayKeyMap;
sp<KeyCharacterMap> combinedKeyMap;//组合建映射表
bool ffEffectPlaying; //力反馈相关信息
int16_t ffEffectId; // initially -1
int32_t controllerNumber;
int32_t timestampOverrideSec;
int32_t timestampOverrideUsec;
};5.3 InputReaderConfiguration
struct InputReaderConfiguration {
// 描述已发生的changes
enum {
// The pointer 速度改变
CHANGE_POINTER_SPEED = 1 << 0,
// The pointer 手势控制已改变.
CHANGE_POINTER_GESTURE_ENABLEMENT = 1 << 1,
// 显示大小或方向已改变
CHANGE_DISPLAY_INFO = 1 << 2,
// 可见触摸选项已改变
CHANGE_SHOW_TOUCHES = 1 << 3,
// 键盘布局必须重新加载
CHANGE_KEYBOARD_LAYOUTS = 1 << 4,
// 对于某些设备,由提供的设备名称别名可能已更改。
CHANGE_DEVICE_ALIAS = 1 << 5,
//位置校准矩阵已更改
CHANGE_TOUCH_AFFINE_TRANSFORMATION = 1 << 6,
// 外部手写笔的存在已更改
CHANGE_EXTERNAL_STYLUS_PRESENCE = 1 << 7,
// The pointer获取模式已更改
CHANGE_POINTER_CAPTURE = 1 << 8,
// 禁用的输入设备(disabledDevices)已更改。
CHANGE_ENABLED_STATE = 1 << 9,
// 所有设备必须重新打开
CHANGE_MUST_REOPEN = 1 << 31,
};
//获取触摸屏幕后禁用虚拟键的时间量,以过滤由于在屏幕边缘附近滑动手势或轻击而导致的意外虚拟键按下。可以为0以禁用该功能。
//比如:触摸了手机返回键边缘的屏幕
nsecs_t virtualKeyQuietTime;
// 平台的排除设备名称。将忽略具有这些名称的设备。
Vector<String8> excludedDeviceNames;
// 鼠标指针移动的速度控制参数。
VelocityControlParameters pointerVelocityControlParameters;
// 鼠标滚轮移动的速度控制参数。
VelocityControlParameters wheelVelocityControlParameters;
//如果启用了pointer手势,则为True。
bool pointerGesturesEnabled;
// 某些pointer手势转换之间的安静时间。
//在开始新手势之前,允许所有手指或按钮安置到稳定状态的时间。
nsecs_t pointerGestureQuietInterval;
//在拖动过程中,指针必须移动的最小速度,以便我们考虑将活动触摸指针切换到它。
//设置此阈值是为了避免由于手指放在触摸板上(可能只是按下它)产生的干扰信息而切换。
float pointerGestureDragMinSwitchSpeed; // in pixels per second
//轻触手势延迟时间。
//下降和上升之间的时间必须小于此值,才能视为轻敲。
nsecs_t pointerGestureTapInterval;
//点击拖动手势延迟时间。
//上一次点击抬起和下一次点击按下之间的时间必须小于此时间,才能被视为拖曳。否则,上一次点击结束,新的点击开始。
//请注意,上一次敲击将在整个持续时间内按住,因此此间隔必须短于长按超时。
nsecs_t pointerGestureTapDragInterval;
// 允许指针从初始位置向下移动到上的距离(以像素为单位),仍然称为轻敲。
float pointerGestureTapSlop; // in pixels
// 第一个触摸点按下到初始质心上的时间。
//这是为了有足够的时间来处理用户几乎同时但不完全同时放下两根手指的情况。
nsecs_t pointerGestureMultitouchSettleInterval;
// 当至少有两个指针从起始位置移动了至少这么远时,就会从PRESS(按压)模式转换到SWIPE(划动)或FREEFORM(自由)手势模式。
float pointerGestureMultitouchMinDistance; // in pixels
// 只有当两个矢量之间的角度余弦大于或等于该值时,才能从PRESS(按压)姿势模式转换为SWIPE(滑动)姿势模式,这表明矢量方向相同。
float pointerGestureSwipeTransitionAngleCosine;
// 只有当手指相对于触摸板的对角线尺寸不超过这个距离时,才能从按压手势模式转换为滑动手势模式。
//例如,0.5的比例意味着手指之间的间隔必须不超过触摸板对角线大小的一半。
float pointerGestureSwipeMaxWidthRatio;
// 相对于显示器大小的手势移动速度。
float pointerGestureMovementSpeedRatio;
//相对于显示器大小的手势缩放速度
//当手指主要相对于彼此移动时,缩放速度适用
//以执行缩放手势或类似动作。
float pointerGestureZoomSpeedRatio;
// True可将触摸屏上的触摸位置显示为点。
bool showTouches;
// True if pointer capture is enabled.
bool pointerCapture;
// 当前禁用的设备
SortedVector<int32_t> disabledDevices;
};5.4 InputDispatcherConfiguration
struct InputDispatcherConfiguration
{
nsecs_t keyRepeatTimeout;//重复按键超时
nsecs_t keyRepeatDelay;//重复按键按键间延迟
InputDispatcherConfiguration() :
keyRepeatTimeout(500 * 1000000LL),
keyRepeatDelay(50 * 1000000LL) { }
};5.5 VelocityControlParameters
//指定移动的加速度相关的参数
struct VelocityControlParameters {
//在应用任何其他速度控制因子之前,与原始速度增量相乘的比例因子。
//应使用比例因子使输入设备分辨率(例如每英寸计数)与输出设备分辨率(如每英寸像素)相适应。
float scale;
//开始施加加速度时的缩放速度。
//该值为在没有任何加速度的情况下进行的小的精确运动建立了低速状态的上限。
float lowThreshold;
//应用最大加速度时的缩放速度。
float highThreshold;
//加速度系数
float acceleration;
};
5.6 Locked
struct Locked {
// 显示大小信息
DisplayViewport internalViewport;
DisplayViewport externalViewport;
Vector<DisplayViewport> virtualViewports;
// 系统UI可见性。
int32_t systemUiVisibility;
// 指针速度
int32_t pointerSpeed;
// True if pointer gestures are enabled.
bool pointerGesturesEnabled;
// 显示触摸功能启用/禁用。
bool showTouches;
// Pointer capture feature enable/disable.
bool pointerCapture;
// Sprite controller singleton, created on first use.
sp<SpriteController> spriteController;
// Pointer controller singleton, created and destroyed as needed.
wp<PointerController> pointerController;//指针移动的控制器集合
// 要禁用的输入设备
SortedVector<int32_t> disabledInputDevices;
} mLocked;
5.7 RawEvent
struct RawEvent {
nsecs_t when;//时间
int32_t deviceId;//事件发生的设备id
int32_t type;//类型,例如按键事件等
int32_t code;//扫描码,按键对应的扫描码
int32_t value;//值,表示按键按下,或者抬起等
};5.8 InputDeviceConfigurationFileType
enum InputDeviceConfigurationFileType {
INPUT_DEVICE_CONFIGURATION_FILE_TYPE_CONFIGURATION = 0, /* .idc file *//idc文件,主要用于触摸屏配置
INPUT_DEVICE_CONFIGURATION_FILE_TYPE_KEY_LAYOUT = 1, /* .kl file *//主要用于键盘的扫描码和keycode的转化
INPUT_DEVICE_CONFIGURATION_FILE_TYPE_KEY_CHARACTER_MAP = 2, /* .kcm file *///.kcm"文件意为按键字符映射文件,作用是将 Android按键代码与修饰符的组合映射到 Unicode字符6 知识扩展
6.1 Epoll和Notify机制
请查看本人另外一篇 地址:
https://mp.csdn.net/mp_blog/creation/success/137793332
6.2 JNI机制
未整理完待更新
6.3 binder机制
未整理完待更新
6.4 安卓智能指针机制
未整理完待更新
6.5 Native层Thread类原理
未整理完待更新
参考:《深入理解Android 卷III》第五章 深入理解Android输入系统(完整版)_android 输入子系统slot协议的显式识别方式-CSDN博客Android Input系统2 输入系统启动_inputflinger 获取系统时间-CSDN博客





 https://blog.csdn.net/handsomethefirst/article/details/138226266?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
https://blog.csdn.net/handsomethefirst/article/details/138226266?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








