文章目录
Spring Boot学习笔记-进阶(3)
一、Spring Boot与缓存
JSR-107、Spring缓存抽象、整合Redis







package com.atguigu.cache.service;
import com.atguigu.cache.bean.Employee;
import com.atguigu.cache.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@CacheConfig(cacheNames="emp"/*,cacheManager = "employeeCacheManager"*/) //抽取缓存的公共配置
@Service
public class EmployeeService {
@Autowired
EmployeeMapper employeeMapper;
/**
* 将方法的运行结果进行缓存;以后再要相同的数据,直接从缓存中获取,不用调用方法;
* CacheManager管理多个Cache组件的,对缓存的真正CRUD操作在Cache组件中,每一个缓存组件有自己唯一一个名字;
*
*
* 原理:
* 1、自动配置类;CacheAutoConfiguration
* 2、缓存的配置类
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.GenericCacheConfiguration
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.JCacheCacheConfiguration
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.EhCacheCacheConfiguration
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.HazelcastCacheConfiguration
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.InfinispanCacheConfiguration
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CouchbaseCacheConfiguration
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CaffeineCacheConfiguration
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.GuavaCacheConfiguration
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.SimpleCacheConfiguration【默认】
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.NoOpCacheConfiguration
* 3、哪个配置类默认生效:SimpleCacheConfiguration;
*
* 4、给容器中注册了一个CacheManager:ConcurrentMapCacheManager
* 5、可以获取和创建ConcurrentMapCache类型的缓存组件;他的作用将数据保存在ConcurrentMap中;
*
* 运行流程:
* @Cacheable:
* 1、方法运行之前,先去查询Cache(缓存组件),按照cacheNames指定的名字获取;
* (CacheManager先获取相应的缓存),第一次获取缓存如果没有Cache组件会自动创建。
* 2、去Cache中查找缓存的内容,使用一个key,默认就是方法的参数;
* key是按照某种策略生成的;默认是使用keyGenerator生成的,默认使用SimpleKeyGenerator生成key;
* SimpleKeyGenerator生成key的默认策略;
* 如果没有参数;key=new SimpleKey();
* 如果有一个参数:key=参数的值
* 如果有多个参数:key=new SimpleKey(params);
* 3、没有查到缓存就调用目标方法;
* 4、将目标方法返回的结果,放进缓存中
*
* @Cacheable标注的方法执行之前先来检查缓存中有没有这个数据,默认按照参数的值作为key去查询缓存,
* 如果没有就运行方法并将结果放入缓存;以后再来调用就可以直接使用缓存中的数据;
*
* 核心:
* 1)、使用CacheManager【ConcurrentMapCacheManager】按照名字得到Cache【ConcurrentMapCache】组件
* 2)、key使用keyGenerator生成的,默认是SimpleKeyGenerator
*
*
* 几个属性:
* cacheNames/value:指定缓存组件的名字;将方法的返回结果放在哪个缓存中,是数组的方式,可以指定多个缓存;
*
* key:缓存数据使用的key;可以用它来指定。默认是使用方法参数的值 1-方法的返回值
* 编写SpEL; #i d;参数id的值 #a0 #p0 #root.args[0]
* getEmp[2]
*
* keyGenerator:key的生成器;可以自己指定key的生成器的组件id
* key/keyGenerator:二选一使用;
*
*
* cacheManager:指定缓存管理器;或者cacheResolver指定获取解析器
*
* condition:指定符合条件的情况下才缓存;
* ,condition = "#id>0"
* condition = "#a0>1":第一个参数的值》1的时候才进行缓存
*
* unless:否定缓存;当unless指定的条件为true,方法的返回值就不会被缓存;可以获取到结果进行判断
* unless = "#result == null"
* unless = "#a0==2":如果第一个参数的值是2,结果不缓存;
* sync:是否使用异步模式
* @param id
* @return
*
*/
@Cacheable(value = {"emp"}/*,keyGenerator = "myKeyGenerator",condition = "#a0>1",unless = "#a0==2"*/)
public Employee getEmp(Integer id){
System.out.println("查询"+id+"号员工");
Employee emp = employeeMapper.getEmpById(id);
return emp;
}
/**
* @CachePut:既调用方法,又更新缓存数据;同步更新缓存
* 修改了数据库的某个数据,同时更新缓存;
* 运行时机:
* 1、先调用目标方法
* 2、将目标方法的结果缓存起来
*
* 测试步骤:
* 1、查询1号员工;查到的结果会放在缓存中;
* key:1 value:lastName:张三
* 2、以后查询还是之前的结果
* 3、更新1号员工;【lastName:zhangsan;gender:0】
* 将方法的返回值也放进缓存了;
* key:传入的employee对象 值:返回的employee对象;
* 4、查询1号员工?
* 应该是更新后的员工;
* key = "#employee.id":使用传入的参数的员工id;
* key = "#result.id":使用返回后的id
* @Cacheable的key是不能用#result
* 为什么是没更新前的?【1号员工没有在缓存中更新】
*
*/
@CachePut(/*value = "emp",*/key = "#result.id")
public Employee updateEmp(Employee employee){
System.out.println("updateEmp:"+employee);
employeeMapper.updateEmp(employee);
return employee;
}
/**
* @CacheEvict:缓存清除
* key:指定要清除的数据
* allEntries = true:指定清除这个缓存中所有的数据
* beforeInvocation = false:缓存的清除是否在方法之前执行
* 默认代表缓存清除操作是在方法执行之后执行;如果出现异常缓存就不会清除
*
* beforeInvocation = true:
* 代表清除缓存操作是在方法运行之前执行,无论方法是否出现异常,缓存都清除
*
*
*/
@CacheEvict(value="emp",beforeInvocation = true/*key = "#id",*/)
public void deleteEmp(Integer id){
System.out.println("deleteEmp:"+id);
//employeeMapper.deleteEmpById(id);
int i = 10/0;
}
// @Caching 定义复杂的缓存规则
@Caching(
cacheable = {
@Cacheable(/*value="emp",*/key = "#lastName")
},
put = {
@CachePut(/*value="emp",*/key = "#result.id"),
@CachePut(/*value="emp",*/key = "#result.email")
}
)
public Employee getEmpByLastName(String lastName){
return employeeMapper.getEmpByLastName(lastName);
}
}
package com.atguigu.cache;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
/**
* 一、搭建基本环境
* 1、导入数据库文件 创建出department和employee表
* 2、创建javaBean封装数据
* 3、整合MyBatis操作数据库
* 1.配置数据源信息
* 2.使用注解版的MyBatis;
* 1)、@MapperScan指定需要扫描的mapper接口所在的包
* 二、快速体验缓存
* 步骤:
* 1、开启基于注解的缓存 @EnableCaching
* 2、标注缓存注解即可
* @Cacheable
* @CacheEvict
* @CachePut
*
*
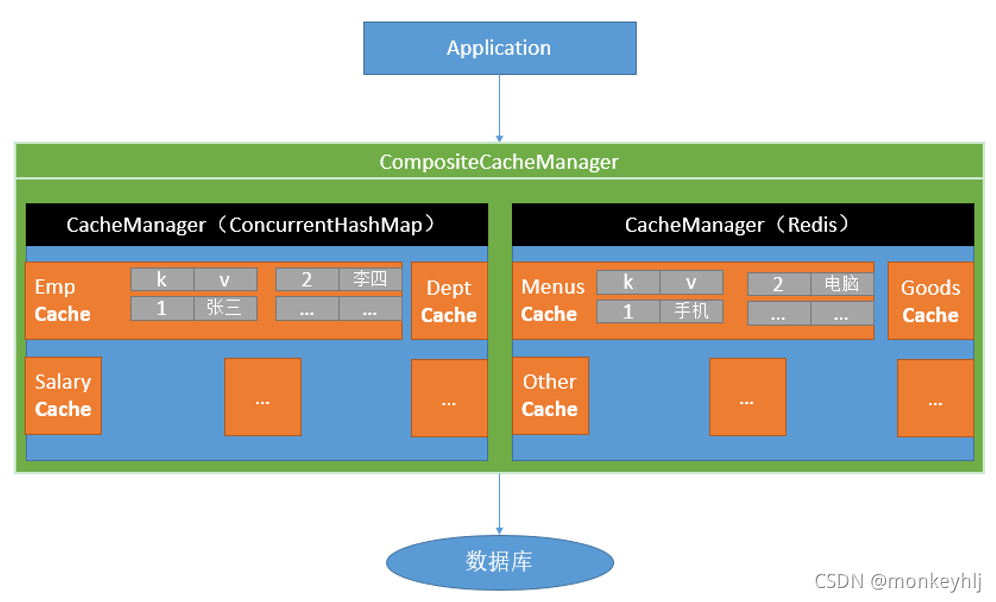
* 默认使用的是ConcurrentMapCacheManager==ConcurrentMapCache;将数据保存在 ConcurrentMap<Object, Object>中
* 开发中使用缓存中间件;redis、memcached、ehcache;
* 三、整合redis作为缓存
* Redis 是一个开源(BSD许可)的,内存中的数据结构存储系统,它可以用作数据库、缓存和消息中间件。
* 1、安装redis:使用docker;
* 2、引入redis的starter
* 3、配置redis
* 4、测试缓存
* 原理:CacheManager===Cache 缓存组件来实际给缓存中存取数据
* 1)、引入redis的starter,容器中保存的是 RedisCacheManager;
* 2)、RedisCacheManager 帮我们创建 RedisCache 来作为缓存组件;RedisCache通过操作redis缓存数据的
* 3)、默认保存数据 k-v 都是Object;利用序列化保存;如何保存为json
* 1、引入了redis的starter,cacheManager变为 RedisCacheManager;
* 2、默认创建的 RedisCacheManager 操作redis的时候使用的是 RedisTemplate<Object, Object>
* 3、RedisTemplate<Object, Object> 是 默认使用jdk的序列化机制
* 4)、自定义CacheManager;
*
*/
@MapperScan("com.atguigu.cache.mapper")
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableCaching
public class Springboot01CacheApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Springboot01CacheApplication.class, args);
}
}

【redis中文网】http://www.redis.cn/
package com.atguigu.cache.service;
import com.atguigu.cache.bean.Department;
import com.atguigu.cache.mapper.DepartmentMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.cache.Cache;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheConfig;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class DeptService {
@Autowired
DepartmentMapper departmentMapper;
@Qualifier("deptCacheManager")
@Autowired
RedisCacheManager deptCacheManager;
/**
* 缓存的数据能存入redis;
* 第二次从缓存中查询就不能反序列化回来;
* 存的是dept的json数据;CacheManager默认使用RedisTemplate<Object, Employee>操作Redis
*
*
* @param id
* @return
*/
// @Cacheable(cacheNames = "dept",cacheManager = "deptCacheManager")
// public Department getDeptById(Integer id){
// System.out.println("查询部门"+id);
// Department department = departmentMapper.getDeptById(id);
// return department;
// }
// 使用缓存管理器得到缓存,进行api调用
public Department getDeptById(Integer id){
System.out.println("查询部门"+id);
Department department = departmentMapper.getDeptById(id);
//获取某个缓存
Cache dept = deptCacheManager.getCache("dept");
dept.put("dept:1",department);
return department;
}
}
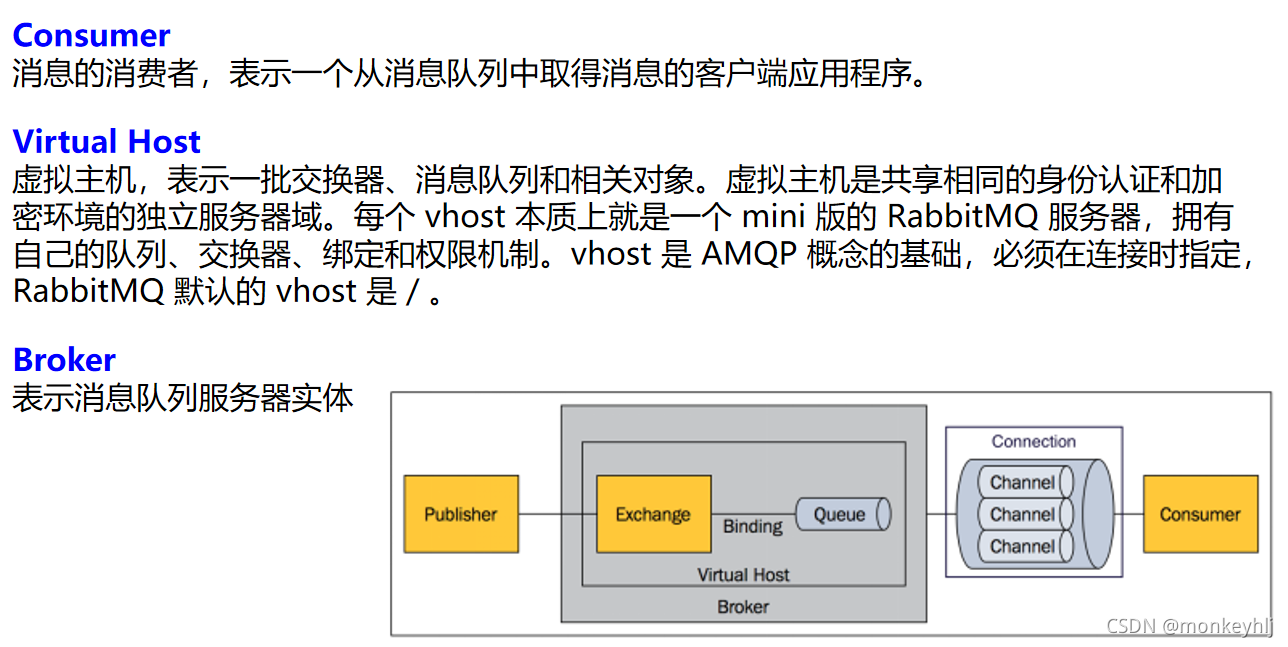
二、Spring Boot与消息












package com.atguigu.amqp;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.EnableRabbit;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
/**
* 自动配置
* 1、RabbitAutoConfiguration
* 2、有自动配置了连接工厂ConnectionFactory;
* 3、RabbitProperties 封装了 RabbitMQ的配置
* 4、 RabbitTemplate :给RabbitMQ发送和接受消息;
* 5、 AmqpAdmin : RabbitMQ系统管理功能组件;
* AmqpAdmin:创建和删除 Queue,Exchange,Binding
* 6、@EnableRabbit + @RabbitListener 监听消息队列的内容
*
*/
@EnableRabbit //开启基于注解的RabbitMQ模式
@SpringBootApplication
public class Springboot02AmqpApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Springboot02AmqpApplication.class, args);
}
}
package com.atguigu.amqp;
import com.atguigu.amqp.bean.Book;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpAdmin;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.DirectExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class Springboot02AmqpApplicationTests {
@Autowired
RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@Autowired
AmqpAdmin amqpAdmin;
@Test
public void createExchange(){
// amqpAdmin.declareExchange(new DirectExchange("amqpadmin.exchange"));
// System.out.println("创建完成");
// amqpAdmin.declareQueue(new Queue("amqpadmin.queue",true));
//创建绑定规则
// amqpAdmin.declareBinding(new Binding("amqpadmin.queue", Binding.DestinationType.QUEUE,"amqpadmin.exchange","amqp.haha",null));
//amqpAdmin.de
}
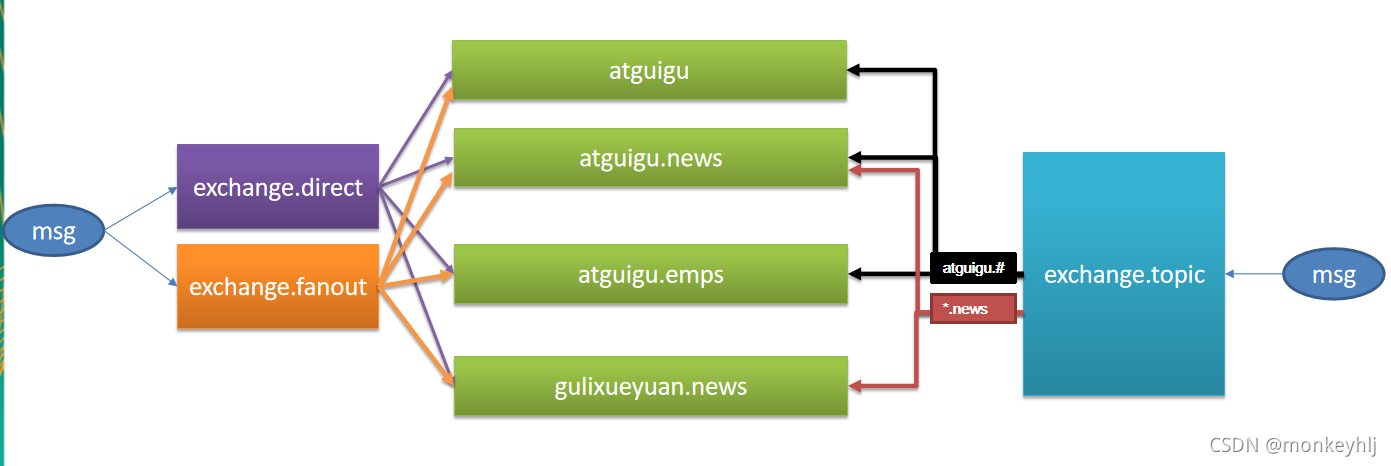
/**
* 1、单播(点对点)
*/
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
//Message需要自己构造一个;定义消息体内容和消息头
//rabbitTemplate.send(exchage,routeKey,message);
//object默认当成消息体,只需要传入要发送的对象,自动序列化发送给rabbitmq;
//rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchage,routeKey,object);
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("msg","这是第一个消息");
map.put("data", Arrays.asList("helloworld",123,true));
//对象被默认序列化以后发送出去
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("exchange.direct","atguigu.news",new Book("西游记","吴承恩"));
}
//接受数据,如何将数据自动的转为json发送出去
@Test
public void receive(){
Object o = rabbitTemplate.receiveAndConvert("atguigu.news");
System.out.println(o.getClass());
System.out.println(o);
}
/**
* 广播
*/
@Test
public void sendMsg(){
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("exchange.fanout","",new Book("红楼梦","曹雪芹"));
}
}
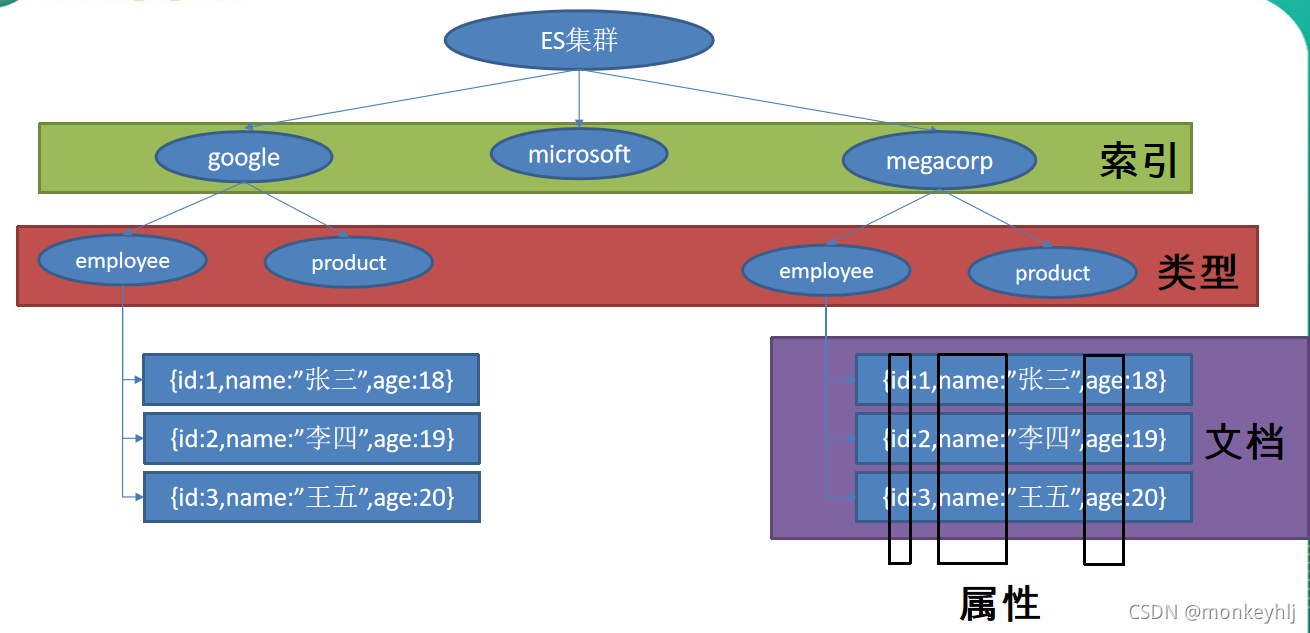
三、Spring Boot与检索



package com.atguigu.elastic;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
/**
* SpringBoot默认支持两种技术来和ES交互;
* 1、Jest(默认不生效)
* 需要导入jest的工具包(io.searchbox.client.JestClient)
*
* 2、SpringData ElasticSearch【ES版本有可能不合适】
* 版本适配说明:https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-data-elasticsearch
* 如果版本不适配:2.4.6
* 1)、升级SpringBoot版本
* 2)、安装对应版本的ES
*
* 1)、Client 节点信息clusterNodes;clusterName
* 2)、ElasticsearchTemplate 操作es
* 3)、编写一个 ElasticsearchRepository 的子接口来操作ES;
* 两种用法:https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-data-elasticsearch
* 1)、编写一个 ElasticsearchRepository
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class Springboot03ElasticApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Springboot03ElasticApplication.class, args);
}
}
package com.atguigu.elastic.repository;
import com.atguigu.elastic.bean.Book;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.repository.ElasticsearchRepository;
import java.util.List;
public interface BookRepository extends ElasticsearchRepository<Book,Integer> {
//参照
// https://docs.spring.io/spring-data/elasticsearch/docs/3.0.6.RELEASE/reference/html/
public List<Book> findByBookNameLike(String bookName);
}
package com.atguigu.elastic;
import com.atguigu.elastic.bean.Article;
import com.atguigu.elastic.bean.Book;
import com.atguigu.elastic.repository.BookRepository;
import io.searchbox.client.JestClient;
import io.searchbox.core.Index;
import io.searchbox.core.Search;
import io.searchbox.core.SearchResult;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class Springboot03ElasticApplicationTests {
@Autowired
JestClient jestClient;
@Autowired
BookRepository bookRepository;
@Test
public void test02(){
// Book book = new Book();
// book.setId(1);
// book.setBookName("西游记");
// book.setAuthor("吴承恩");
// bookRepository.index(book);
for (Book book : bookRepository.findByBookNameLike("游")) {
System.out.println(book);
}
;
}
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
//1、给Es中索引(保存)一个文档;
Article article = new Article();
article.setId(1);
article.setTitle("好消息");
article.setAuthor("zhangsan");
article.setContent("Hello World");
//构建一个索引功能
Index index = new Index.Builder(article).index("atguigu").type("news").build();
try {
//执行
jestClient.execute(index);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//测试搜索
@Test
public void search(){
//查询表达式
String json ="{\n" +
" \"query\" : {\n" +
" \"match\" : {\n" +
" \"content\" : \"hello\"\n" +
" }\n" +
" }\n" +
"}";
//更多操作:https://github.com/searchbox-io/Jest/tree/master/jest
//构建搜索功能
Search search = new Search.Builder(json).addIndex("atguigu").addType("news").build();
//执行
try {
SearchResult result = jestClient.execute(search);
System.out.println(result.getJsonString());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
四、Spring Boot与任务
package com.atguigu.task;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableScheduling;
@EnableAsync //开启异步注解功能
@EnableScheduling //开启基于注解的定时任务
@SpringBootApplication
public class Springboot04TaskApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Springboot04TaskApplication.class, args);
}
}
异步任务

package com.atguigu.task.service;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class AsyncService {
//告诉Spring这是一个异步方法
@Async
public void hello(){
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("处理数据中...");
}
}
package com.atguigu.task.controller;
import com.atguigu.task.service.AsyncService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class AsyncController {
@Autowired
AsyncService asyncService;
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
asyncService.hello();
return "success";
}
}
定时任务

package com.atguigu.task.service;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class ScheduledService {
/**
* second(秒), minute(分), hour(时), day of month(日), month(月), day of week(周几).
* 0 * * * * MON-FRI
* 【0 0/5 14,18 * * ?】 每天14点整,和18点整,每隔5分钟执行一次
* 【0 15 10 ? * 1-6】 每个月的周一至周六10:15分执行一次
* 【0 0 2 ? * 6L】每个月的最后一个周六凌晨2点执行一次
* 【0 0 2 LW * ?】每个月的最后一个工作日凌晨2点执行一次
* 【0 0 2-4 ? * 1#1】每个月的第一个周一凌晨2点到4点期间,每个整点都执行一次;
*/
// @Scheduled(cron = "0 * * * * MON-SAT")
//@Scheduled(cron = "0,1,2,3,4 * * * * MON-SAT")
// @Scheduled(cron = "0-4 * * * * MON-SAT")
@Scheduled(cron = "0/4 * * * * MON-SAT") //每4秒执行一次
public void hello(){
System.out.println("hello ... ");
}
}
邮件任务

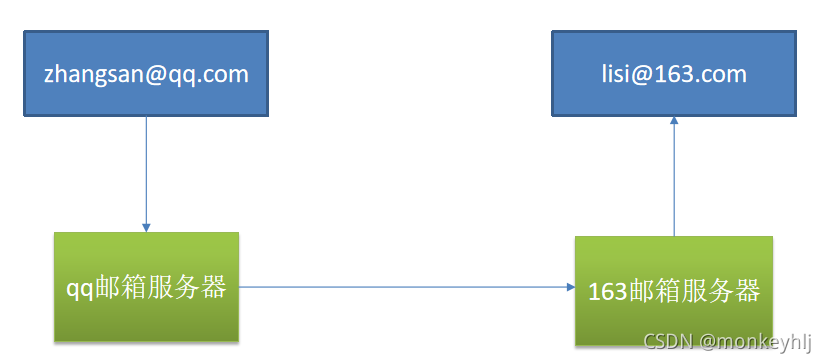
package com.atguigu.task;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.mail.SimpleMailMessage;
import org.springframework.mail.javamail.JavaMailSenderImpl;
import org.springframework.mail.javamail.MimeMessageHelper;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import javax.mail.internet.MimeMessage;
import java.io.File;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class Springboot04TaskApplicationTests {
@Autowired
JavaMailSenderImpl mailSender;
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
SimpleMailMessage message = new SimpleMailMessage();
//邮件设置
message.setSubject("通知-今晚开会");
message.setText("今晚7:30开会");
message.setTo("17512080612@163.com");
message.setFrom("534096094@qq.com");
mailSender.send(message);
}
@Test
public void test02() throws Exception{
//1、创建一个复杂的消息邮件
MimeMessage mimeMessage = mailSender.createMimeMessage();
MimeMessageHelper helper = new MimeMessageHelper(mimeMessage, true);
//邮件设置
helper.setSubject("通知-今晚开会");
helper.setText("<b style='color:red'>今天 7:30 开会</b>",true);
helper.setTo("17512080612@163.com");
helper.setFrom("534096094@qq.com");
//上传文件
helper.addAttachment("1.jpg",new File("C:\\Users\\lfy\\Pictures\\Saved Pictures\\1.jpg"));
helper.addAttachment("2.jpg",new File("C:\\Users\\lfy\\Pictures\\Saved Pictures\\2.jpg"));
mailSender.send(mimeMessage);
}
}
五、Spring Boot与安全



package com.atguigu.security;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
/**
* 1、引入SpringSecurity;
* 2、编写SpringSecurity的配置类;
* @EnableWebSecurity extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter
* 3、控制请求的访问权限:
* configure(HttpSecurity http) {
* http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/").permitAll()
* .antMatchers("/level1/**").hasRole("VIP1")
* }
* 4、定义认证规则:
* configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth){
* auth.inMemoryAuthentication()
* .withUser("zhangsan").password("123456").roles("VIP1","VIP2")
* }
* 5、开启自动配置的登陆功能:
* configure(HttpSecurity http){
* http.formLogin();
* }
* 6、注销:http.logout();
* 7、记住我:Remeberme();
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class Springboot05SecurityApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Springboot05SecurityApplication.class, args);
}
}
六、Spring Boot与分布式








七、Spring Boot与开发热部署



八、Spring Boot与监控管理

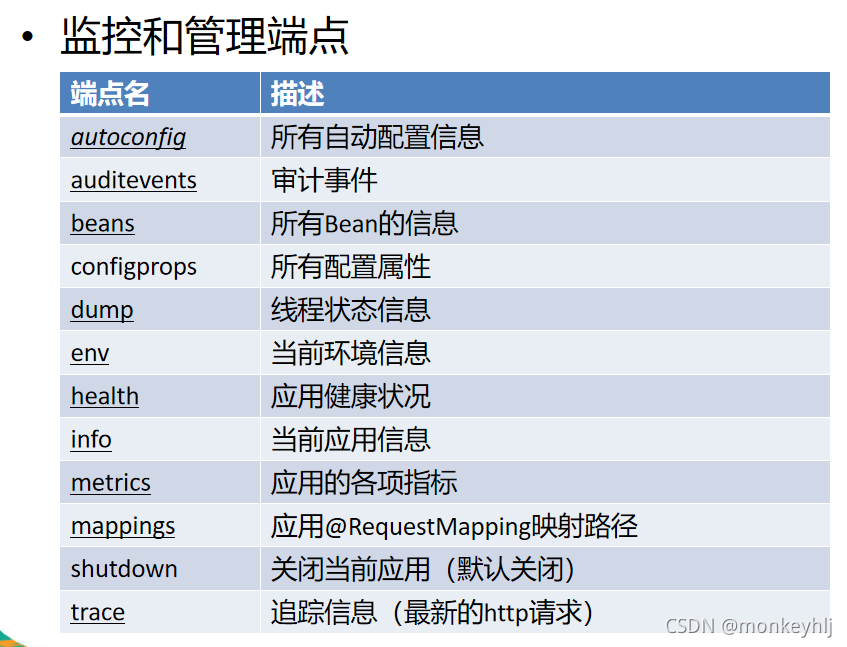

【学习视频参考】https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Ct411g78e
【代码参考】https://github.com/monkeyhlj/spring-study/tree/master/spring-boot-study-atguigu(2)



























 1081
1081

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








