一、环境准备
测试环境使用的cdh提供的quickstart vm
Hadoop版本:2.5.0-cdh5.2.0
Spark版本:1.1.0
二、Hello Spark
- 将/usr/lib/spark/examples/lib/spark-examples-1.1.0-cdh5.2.0-hadoop2.5.0-cdh5.2.0.jar移动到/usr/lib/spark/lib/spark-examples-1.1.0-cdh5.2.0-hadoop2.5.0-cdh5.2.0.jar
- 执行程序 ./bin/run-example SparkPi 10
- 日志分析:
- 程序检查ip,host,SecurityManager
- 启动sparkDriver。通过akka工具启动一个tcp监听 [akka.tcp://sparkDriver@192.168.128.131:42960]
- 启动MapOutputTracker,BlockManagerMaster
- 启动一个block manager,也就是ConnectionManagerId(192.168.128.131,41898),其中包含一个MemoryStore
- 通过netty启动一个HTTP file server:SocketConnector@0.0.0.0:55161
- 启动一个sparkUI:http://192.168.128.131:4040
- 通过http上传本地程序运行Jar包
- 连接HeartbeatReceiver: akka.tcp://sparkDriver@192.168.128.131:42960/user/HeartbeatReceiver
- Starting job: reduce
- 分析中job,有stage 0 (MappedRDD[1])
- 添加并启动运行task Submitting 10 missing tasks from Stage 0
- 通过http协议获取程序jar包,并添加到classloader
- 完成task后,将结果发送到driver
- scheduler.DAGScheduler完成Stage的所有task
- 在localhost的scheduler.TaskSetManager收集完成的task
- job finished
- Stop Spark Web UI
- Stop DAGScheduler
- MapOutputTrackerActor stopped
- stopConnectionManager
- MemoryStore cleared
- BlockManager stopped
- Shutting down remote daemon.
- Successfully stopped SparkContext
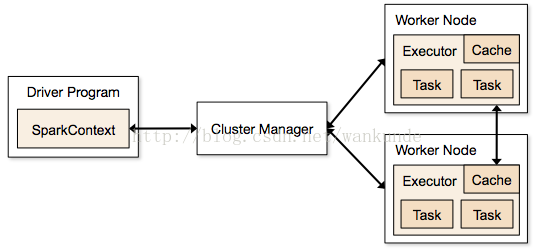
三、cluster mode运行模式
运行流程::
- SparkContext 连接cluster Manager (either Spark’s own standalone cluster manager or Mesos/YARN),
- spark Application向Cluster Manager请求资源 executors (运行计算和存储数据的线程)
- 将程序Jar包或者python程序分发到executors
- SparkContext发送tasks到executors上运行
Cluster Manager类型:
- Standalone Spark 内置的cluster manager,可以快速启动一个集群
- Apache Mesos 一个通用的Cluster manger,可以运行hadoop的Mapreduce和其他Service applications
- Hadoop YARN Hadoop 2中的Clustger Manager
主要概念
| Term | Meaning |
| Application | User program built on Spark. Consists of a driver program and executors on the cluster. |
| Application jar | A jar containing the user's Spark application. In some cases users will want to create an "uber jar" containing their application along with its dependencies. The user's jar should never include hadoop or Spark libraries, however, these will be added at runtime. |
| Driver program | The process running the main() function of the application and creating the SparkContext |
| Cluster manager | An external service for acquiring resources on the cluster (e.g. standalone manager, Mesos, YARN) |
| Deploy mode | Distinguishes where the driver process runs. In "cluster" mode, the framework launches the driver inside of the cluster. In "client" mode, the submitter launches the driver outside of the cluster. |
| Worker node | Any node that can run application code in the cluster |
| Executor | A process launched for an application on a worker node, that runs tasks and keeps data in memory or disk storage across them. Each application has its own executors. |
| Task | A unit of work that will be sent to one executor |
| Job | A parallel computation consisting of multiple tasks that gets spawned in response to a Spark action (e.g. save, collect); you'll see this term used in the driver's logs. |
| Stage | Each job gets divided into smaller sets of tasks called stages that depend on each other (similar to the map and reduce stages in MapReduce); you'll see this term used in the driver's logs. |
源文档 <http://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/cluster-overview.html>
四、yarn mode 运行模式
yarn集群方式运行
spark-submit
--classcom.wankun.sparktest.WordCount
--masteryarn-cluster
target/sparktest-1.0.0.jar/tmp/test1 2
运行命令:
yarn-cluster
spark-submit --classcom.wankun.sparktest.WordCount --master yarn-cluster --driver-memory 385m--executor-memory 410m target/sparktest-1.0.0.jar /tmp/test1 2
特点:
- 运行成功后,无任何输出,输出都在日志中
- 程序的运行有yarn来控制,spark只是检测程序的状态,状态为success,即运行成功
yarn-client
spark-submit--class com.wankun.sparktest.WordCount --master yarn-client --driver-memory 385m --executor-memory 410m target/sparktest-1.0.0.jar /tmp/test1 2
yarn-cluster的driver programcontainer是在集群里的,yarn-client的driver programcontainer是spark在集群外自己启动的
运行原理:
scheduler.DAGScheduler,scheduler.TaskSetManager,cluster.YarnClusterScheduler
- spark向RM申请一个Container作为调度container(此时启动的SparkUI端口随机)
- 请求Executors(默认2个, Container request (host: Any, priority: 1, capability: <memory:1408, vCores:1>)
- Received new token for : quickstart.cloudera:48622
- 根据resources and environment and commands, open proxy
- start progress reporter
- 在YarnClusterSchedulerBackend,BlockManagerMasterActor,MemoryStore等服务启动
- 在SparkContext中Starting job
- TasksetManager中starting task with TID 0,1
- 任务调度由scheduler.DAGScheduler执行,根据job和job中tasks进行任务执行,Taskset will be removed ,when completed
- job全部执行结束,Stopped Spark web UI,Stopping DAGScheduler,Shutting down all executors
executors
- executors应该是可以重用
- executors通过CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend获取分配的任务,关闭的时候,Driver commanded a shutdown
- 在关闭http file server进程时,遇到错误
| 14/11/05 20:17:40 WARN thread.QueuedThreadPool: 1 threads could not be stopped 14/11/05 20:17:40 INFO thread.QueuedThreadPool: Couldn't stop Thread[qtp26737473-36 Acceptor0 SocketConnector@0.0.0.0:39213,5,main] 14/11/05 20:17:41 INFO thread.QueuedThreadPool: at Java.NET.PlainSocketImpl.socketAccept(Native Method) 14/11/05 20:17:41 INFO thread.QueuedThreadPool: at java.net.AbstractPlainSocketImpl.accept(AbstractPlainSocketImpl.java:398) 14/11/05 20:17:41 INFO thread.QueuedThreadPool: at java.Net.ServerSocket.implAccept(ServerSocket.java:530) 14/11/05 20:17:41 INFO thread.QueuedThreadPool: at java.net.ServerSocket.accept(ServerSocket.java:498) 14/11/05 20:17:41 INFO thread.QueuedThreadPool: at org.eclipse.jetty.server.bio.SocketConnector.accept(SocketConnector.java:117) 14/11/05 20:17:41 INFO thread.QueuedThreadPool: at org.eclipse.jetty.server.AbstractConnector$Acceptor.run(AbstractConnector.java:938) 14/11/05 20:17:41 INFO thread.QueuedThreadPool: at org.eclipse.jetty.util.thread.QueuedThreadPool.runJob(QueuedThreadPool.java:608) 14/11/05 20:17:41 INFO thread.QueuedThreadPool: at org.eclipse.jetty.util.thread.QueuedThreadPool$3.run(QueuedThreadPool.java:543) 14/11/05 20:17:41 INFO thread.QueuedThreadPool: at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:745) 14/11/05 20:17:41 INFO network.ConnectionManager: Key not valid ? sun.nio.ch.SelectionKeyImpl@2cc51248 14/11/05 20:17:41 INFO spark.MapOutputTrackerMasterActor: MapOutputTrackerActor stopped! 14/11/05 20:17:41 INFO network.ConnectionManager: Removing SendingConnection to ConnectionManagerId(quickstart.cloudera,48234) 14/11/05 20:17:41 INFO network.ConnectionManager: Removing SendingConnection to ConnectionManagerId(quickstart.cloudera,52620) 14/11/05 20:17:42 INFO network.ConnectionManager: key already cancelled ? sun.nio.ch.SelectionKeyImpl@2cc51248 java.nio.channels.CancelledKeyException at org.apache.spark.network.ConnectionManager.run(ConnectionManager.Scala:386) at org.apache.spark.network.ConnectionManager$$anon$4.run(ConnectionManager.scala:139) 14/11/05 20:17:42 INFO network.ConnectionManager: Key not valid ? sun.nio.ch.SelectionKeyImpl@69aaccdf 14/11/05 20:17:42 INFO network.ConnectionManager: key already cancelled ? sun.nio.ch.SelectionKeyImpl@69aaccdf java.nio.channels.CancelledKeyException at org.apache.spark.network.ConnectionManager.run(ConnectionManager.scala:386) at org.apache.spark.network.ConnectionManager$$anon$4.run(ConnectionManager.scala:139) |
日志查看
方式一:yarnlogs -applicationId application_1415100770125_0002
方式二:通过Rm:8088端口进入Spark history Server:18088端口查看
- 配置spark-defaults.conf中jobhistory中的配置
spark.eventLog.enabled=true
spark.eventLog.dir=hdfs:///user/spark/applicationHistory
spark.yarn.historyServer.address=http://quickstart.cloudera:18088
- 启动 spark-history-server服务
- 此时,在yarn集群中提交的服务日志会上传的hdfs上,在RM:8088页面中可以直接调整到spark页面进行查看
提交参数:
- spark-submit --class com.wankun.sparktest.WordCount --master yarn-cluster --driver-memory 385m --executor-memory 410m target/sparktest-1.0.0.jar /tmp/test1 2
实际上,driverExecutor和task Executor 占用那个的内存显示并没有这么多,不清楚什么原因
- 支持参数
14/11/05 11:56:14ERROR yarn.Client: Error: Executor memory sizemust be greater than: 384
Exception in thread"main" java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Usage:org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.Client [options]
Options:
--jar JAR_PATH Path to your application's JARfile (required in yarn-cluster mode)
--class CLASS_NAME Name of your application's main class(required)
--arg ARGS Argument to be passed to yourapplication's main class.
Multipleinvocations are possible, each will be passed in order.
--num-executors NUM Number of executors to start (Default:2)
--executor-cores NUM Number of cores for the executors(Default: 1).
--driver-memory MEM Memory for driver (e.g. 1000M, 2G)(Default: 512 Mb)
--executor-memory MEM Memory per executor (e.g. 1000M, 2G)(Default: 1G)
--name NAME The name of your application(Default: Spark)
--queue QUEUE The hadoop queue to use forallocation requests (Default: 'default')
--addJars jars Comma separated list of local jarsthat want SparkContext.addJar to work with.
--files files Comma separated list of files tobe distributed with the job.
--archives archives Comma separated list of archives to bedistributed with the job.
优化配置
将spark的hadoop类库上传到hdfs上,省的每次都上传
|
hdfs dfs -mkdir -p /user/spark/share/lib hadoop dfs -put /usr/lib/spark/assembly/lib/spark-assembly-1.1.0-cdh5.2.0-hadoop2.5.0-cdh5.2.0.jar /user/spark/share/lib/spark-assembly.jar hadoop dfs -chmod -R 777 /user/spark/
在spark-env.sh中配置 export SPARK_JAR=hdfs://quickstart.cloudera:8020/user/spark/share/lib/spark-assembly.jar |
五、spark cluster mode 运行模式
spark服务
启动服务:spark-history-server spark-master spark-worker
spark-master监控页面:
http://192.168.128.131:4040/ application detail 页面,如果有多个sparkContext,端口依次递增(如4041,4042…),程序结束后,关闭。页面主要内容
- stages and tasks,
- RDD sizes and memory usage
- Environmental
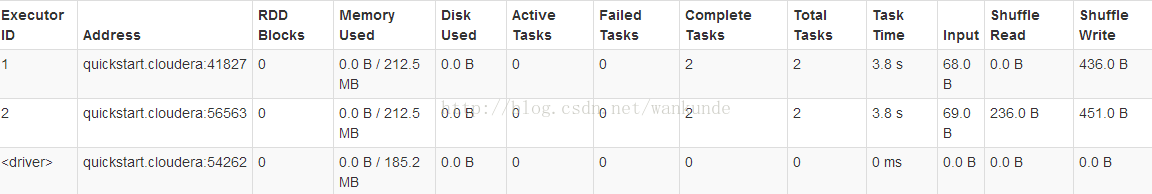
- executors
192.168.128.131 7077 master通信端口
spark-worker监控页面:
http://192.168.128.131:18081监控页面
192.168.128.131 7078 worker通信端口
spark-history-server监控页面:
spark master和worker之间的通信使用的是akka,tcp协议。例如:[akka.tcp://sparkWorker@192.168.128.131:7078]
备注:测试时,因为master绑定在了192.168.128.131 ip上了,所以必须在/etc/spark/con/spark-env.sh配置文件配置上exportSPARK_MASTER_IP=192.168.128.131参数
spark-env.sh主要配置
| export STANDALONE_SPARK_MASTER_HOST="192.168.128.131"
export SPARK_MASTER_IP=$STANDALONE_SPARK_MASTER_HOST
### Let's run everything with JVM runtime, instead of Scala export SPARK_LAUNCH_WITH_SCALA=0 export SPARK_LIBRARY_PATH=${SPARK_HOME}/lib export SCALA_LIBRARY_PATH=${SPARK_HOME}/lib export SPARK_MASTER_WEBUI_PORT=18080 export SPARK_MASTER_IP="192.168.128.131" export SPARK_MASTER_PORT=7077 export SPARK_WORKER_CORES=1 export SPARK_WORKER_MEMORY=100m export SPARK_WORKER_PORT=7078 export SPARK_WORKER_INSTANCES=1 export SPARK_WORKER_WEBUI_PORT=18081 export SPARK_WORKER_DIR=/var/run/spark/work export SPARK_LOG_DIR=/var/log/spark export SPARK_PID_DIR='/var/run/spark/'
if [ -n "$HADOOP_HOME" ]; then export SPARK_LIBRARY_PATH=$SPARK_LIBRARY_PATH:${HADOOP_HOME}/lib/native fi
export HADOOP_CONF_DIR=${HADOOP_CONF_DIR:-/etc/hadoop/conf} |
注意在cloudera提供的虚拟机中的配置文件有如下问题:
第一、master的7077端口并未绑定在0.0.0.0上,第二,HADOOP_CONF_DIR写错了,写成了etc/hadoop/conf。
第二、在/etc/hosts中将hostname配置上外网口ip,否则会造成master和worker通信失败,或者job无法正常提交的问题,提交job时也要使用hostname提交
六、spark-submit
spark-submit
--classcom.wankun.sparktest.JavaWordCount
--masterspark://quickstart.cloudera:7077
target/sparktest-1.0.0.jar/tmp/test1 2
其余常用参数:
--executor-memory 20G
--total-executor-cores 100
--master yarn-cluster\ # can also be `yarn-client` for clientmode
--masterlocal[8]\# Run application locally on 8 cores
--master yarn-cluster\ # can also be `yarn-client` for clientmode
Master URLs
The master URL passed to Spark can be in one of thefollowing formats:
| Master URL | Meaning |
| local | Run Spark locally with one worker thread (i.e. no parallelism at all). |
| local[K] | Run Spark locally with K worker threads (ideally, set this to the number of cores on your machine). |
| local[*] | Run Spark locally with as many worker threads as logical cores on your machine. |
| spark://HOST:PORT | Connect to the given Spark standalone cluster master. The port must be whichever one your master is configured to use, which is 7077 by default. |
| mesos://HOST:PORT | Connect to the given Mesos cluster. The port must be whichever one your is configured to use, which is 5050 by default. Or, for a Mesos cluster using ZooKeeper, use mesos://zk://.... |
| yarn-client | Connect to a YARN cluster in client mode. The cluster location will be found based on the HADOOP_CONF_DIR variable. |
| yarn-cluster | Connect to a YARN cluster in cluster mode. The cluster location will be found based on HADOOP_CONF_DIR. |
源文档 <http://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/submitting-applications.html>
Transformations
The following table listssome of the common transformations supported by Spark. Refer to the RDD API doc(Scala, Java, Python) and pair RDD functions doc (Scala, Java) for details.
| Transformation | Meaning | |||
| map(func) | Return a new distributed dataset formed by passing each element of the source through a function func.
| |||
| filter(func) | Return a new dataset formed by selecting those elements of the source on which func returns true. | |||
| flatMap(func) | Similar to map, but each input item can be mapped to 0 or more output items (so func should return a Seq rather than a single item).
| |||
| mapPartitions(func) | Similar to map, but runs separately on each partition (block) of the RDD, so func must be of type Iterator<T> => Iterator<U> when running on an RDD of type T. | |||
| mapPartitionsWithIndex(func) | Similar to mapPartitions, but also provides func with an integer value representing the index of the partition, so func must be of type (Int, Iterator<T>) => Iterator<U> when running on an RDD of type T. | |||
| sample(withReplacement,fraction, seed) | Sample a fraction fraction of the data, with or without replacement, using a given random number generator seed. | |||
| union(otherDataset) | Return a new dataset that contains the union of the elements in the source dataset and the argument. | |||
| intersection(otherDataset) | Return a new RDD that contains the intersection of elements in the source dataset and the argument. | |||
| distinct([numTasks])) | Return a new dataset that contains the distinct elements of the source dataset. | |||
| groupByKey([numTasks]) | When called on a dataset of (K, V) pairs, returns a dataset of (K, Iterable<V>) pairs. Note: If you are grouping in order to perform an aggregation (such as a sum or average) over each key, using reduceByKey or combineByKey will yield much better performance. Note: By default, the level of parallelism in the output depends on the number of partitions of the parent RDD. You can pass an optional numTasks argument to set a different number of tasks. | |||
| reduceByKey(func, [numTasks]) | When called on a dataset of (K, V) pairs, returns a dataset of (K, V) pairs where the values for each key are aggregated using the given reduce function func, which must be of type (V,V) => V. Like ingroupByKey, the number of reduce tasks is configurable through an optional second argument. | |||
| aggregateByKey(zeroValue)(seqOp, combOp, [numTasks]) | When called on a dataset of (K, V) pairs, returns a dataset of (K, U) pairs where the values for each key are aggregated using the given combine functions and a neutral "zero" value. Allows an aggregated value type that is different than the input value type, while avoiding unnecessary allocations. Like in groupByKey, the number of reduce tasks is configurable through an optional second argument. | |||
| sortByKey([ascending], [numTasks]) | When called on a dataset of (K, V) pairs where K implements Ordered, returns a dataset of (K, V) pairs sorted by keys in ascending or descending order, as specified in the boolean ascending argument. | |||
| join(otherDataset, [numTasks]) | When called on datasets of type (K, V) and (K, W), returns a dataset of (K, (V, W)) pairs with all pairs of elements for each key. Outer joins are also supported through leftOuterJoin and rightOuterJoin. | |||
| cogroup(otherDataset, [numTasks]) | When called on datasets of type (K, V) and (K, W), returns a dataset of (K, Iterable<V>, Iterable<W>) tuples. This operation is also called groupWith. | |||
| cartesian(otherDataset) | When called on datasets of types T and U, returns a dataset of (T, U) pairs (all pairs of elements). | |||
| pipe(command, [envVars]) | Pipe each partition of the RDD through a shell command, e.g. a Perl or bash script. RDD elements are written to the process's stdin and lines output to its stdout are returned as an RDD of strings. | |||
| coalesce(numPartitions) | Decrease the number of partitions in the RDD to numPartitions. Useful for running operations more efficiently after filtering down a large dataset. | |||
| repartition(numPartitions) | Reshuffle the data in the RDD randomly to create either more or fewer partitions and balance it across them. This always shuffles all data over the network. | |||
| mapToPair
| JavaPairRDD ---> JavaPairRDD
JavaPairRDD<Integer, Integer> tc; JavaPairRDD<Integer, Integer> edges = tc.mapToPair( new PairFunction<Tuple2<Integer, Integer>, Integer, Integer>() { @Override public Tuple2<Integer, Integer> call(Tuple2<Integer, Integer> e) { return new Tuple2<Integer, Integer>(e._2(), e._1()); } }); |
Actions
The following table listssome of the common actions supported by Spark. Refer to the RDD API doc (Scala, Java, Python) and pair RDD functions doc (Scala, Java) for details.
| Action | Meaning | |||
| reduce(func) | Aggregate the elements of the dataset using a function func (which takes two arguments and returns one). The function should be commutative and associative so that it can be computed correctly in parallel.
| |||
| collect() | Return all the elements of the dataset as an array at the driver program. This is usually useful after a filter or other operation that returns a sufficiently small subset of the data. | |||
| count() | Return the number of elements in the dataset. | |||
| first() | Return the first element of the dataset (similar to take(1)). | |||
| take(n) | Return an array with the first n elements of the dataset. Note that this is currently not executed in parallel. Instead, the driver program computes all the elements. | |||
| takeSample(withReplacement,num, [seed]) | Return an array with a random sample of num elements of the dataset, with or without replacement, optionally pre-specifying a random number generator seed. | |||
| takeOrdered(n, [ordering]) | Return the first n elements of the RDD using either their natural order or a custom comparator. | |||
| saveAsTextFile(path) | Write the elements of the dataset as a text file (or set of text files) in a given directory in the local filesystem, HDFS or any other Hadoop-supported file system. Spark will call toString on each element to convert it to a line of text in the file. | |||
| saveAsSequenceFile(path) (Java and Scala) | Write the elements of the dataset as a Hadoop SequenceFile in a given path in the local filesystem, HDFS or any other Hadoop-supported file system. This is available on RDDs of key-value pairs that either implement Hadoop's Writable interface. In Scala, it is also available on types that are implicitly convertible to Writable (Spark includes conversions for basic types like Int, Double, String, etc). | |||
| saveAsObjectFile(path) (java and Scala) | Write the elements of the dataset in a simple format using Java serialization, which can then be loaded usingSparkContext.objectFile(). | |||
| countByKey() | Only available on RDDs of type (K, V). Returns a hashmap of (K, Int) pairs with the count of each key. | |||
| foreach(func) | Run a function func on each element of the dataset. This is usually done for side effects such as updating an accumulator variable (see below) or interacting with external storage systems. |
源文档 <http://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/programming-guide.html>
action结果是一个数据,例如,正数,数组,对象等
transformation结果是一个RDD,完成从一个RDD到另一个RDD的转换
常用工具类说明:
JavaRDD<D>
JavaPairRDD<K,V>
Tuple2(K,V> 类似与map中的一个entry e._1() e._2()
相关资料
http://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/api/scala/index.html Scala API doc
http://mail-archives.apache.org/mod_mbox/incubator-spark-user/ Apache Spark mailing list
http://apache-spark-user-list.1001560.n3.nabble.com/
http://community.cloudera.com/t5/Advanced-Analytics-Apache-Spark/bd-p/Spark
https://github.com/apache/spark/tree/master/examples/src/main/java/org/apache/spark/examples spark examples





















 186
186











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








