一、String字符串
1、直接赋值
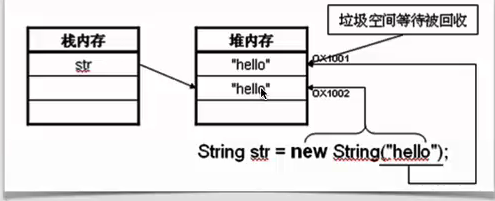
2、使用关键字new
用new关键字给String赋值,实际在堆内存中开辟两块空间各存储两个“hello”。
3、String内容比较
String str = “hello”;
String str1 = new String(“hello”);
System.out.println(str == str1);
//此时输出时false,因为“==”是比较地址
//正确应该是
System.out.println(str.equals(str2));
//此时才是比较内容
二、字符串常用方法
1、字符串长度:length()
String str = new String("helloworld");
System.out.println(str.length());
2、字符串转换数组:toCharArray()
String str = new String("helloworld");
char[] array = str.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
System.out.print(array[i]+" ");
}
3、从字符串中取出指定位置的字符:charAt()
String str = new String(“hello”);
System.out.println(str.charAt((2));
//输出的是'l'字符
4、字符串与byte数组的转换:getBytes()
byte bytes[ ] = str.getBytes();
for(int i = 0;i < bytes.length; i++)
{
System.out.println(new String(bytes)+"\t");
}
5、过滤字符串中存在的字符:indexOf()
String str = new String("hello");
System.out.println(str.indexOf("e"));
6、去掉字符串前后的空格:trim()
7、从字符串中取出子字符串:subString()
8、大小写转换:toLowerCase() toUpperCase()
9、判断字符串的开头结尾字符:endWith() startWith()
10、替换String字符串的一个字符:replace()
三、StringBuffer方法
1、它是缓冲区,本身也是操作字符串,但与String不同,StringBuffer是可以更改的。StringBuffer是一个操作类,必须通过实例化进行操作。
2、StringBuffer常用方法:append()追加内容、insert()、replace()、indexO()
四、StringBuilder
一个可变的字符序列,该类设计作用StringBuffer的一个简易替换,用在字符串缓冲区被单个线程使用的时候。建议优先考虑,速度比StringBuffer要快。






















 143
143

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








