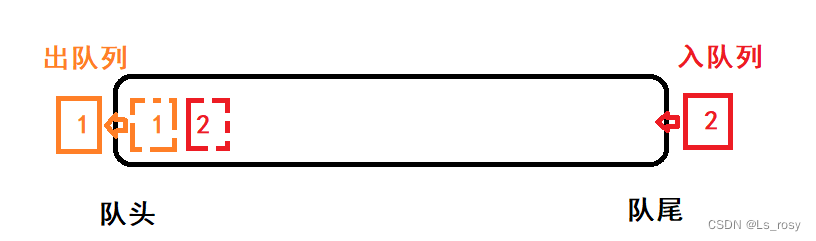
一.队列的概念
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有
先进先出
FIFO(First In First Out)的特性。
入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾。
出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头。
二.队列的存储形式
1.顺序表与链表的选择
顺序表:
优势:入队列时间复杂度O(1);
劣势:出队列,需要挪动数据,时间复杂度O(N);空间不足需要扩容。
链表:
优势:出队列时间复杂度O(1);不需要扩容。
劣势:入队列时间复杂度O(N);
这样看来,貌似两者差距不大,其实不然,链表的入队列我们可以定义一个尾指针记录,不用每次去找尾,时间复杂度可以简化成O(1)。而顺序表的出队列O(N)的时间复杂度,就算能优化,也到不了O(1)级别。
所以,我们选择链表存储。
2.队列的结构

这里我们需要两个结构体:1.链表的结构 ,2.队列的头尾指针、长度。
typedef int datatype;
typedef struct QNode
{
datatype data;
struct QNode* next;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* head;
QNode* tail;
int size;
}Queue;三.队列的基本操作
1.初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
2.入队列
入队列和单链表面临一样的问题,如果链表里面没有结点,则新节点就是头结点。
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, datatype x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* new = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (new==NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail\n");
return;
}
new->data = x;
new->next = NULL;
if (pq->head == NULL)
{
assert(pq->tail == NULL);
pq->head = new;
pq->tail = new;
}
else
{
pq->tail->next = new;
pq->tail = new;
}
pq->size++;
}3.出队列
出队列,如果只有一个结点,则直接置空。
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head != NULL);
if (pq->head->next == NULL)
{
free(pq->head);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
else
{
QNode* next = pq->head->next;
free(pq->head);
pq->head = next;
}
pq->size--;
}4.取队头
datatype QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->head->data;
}5.取队尾
datatype QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->tail->data;
}6.长度
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}7.判空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
if (pq->size == 0)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}8.销毁
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
QNode*next=cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}四.完整代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int datatype;
typedef struct QNode
{
datatype data;
struct QNode* next;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* head;
QNode* tail;
int size;
}Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
void QueuePush(Queue* pq,datatype x);
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
datatype QueueFront(Queue* pq);
datatype QueueBack(Queue* pq);
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, datatype x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* new = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (new==NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail\n");
return;
}
new->data = x;
new->next = NULL;
if (pq->head == NULL)
{
assert(pq->tail == NULL);
pq->head = new;
pq->tail = new;
}
else
{
pq->tail->next = new;
pq->tail = new;
}
pq->size++;
}
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head != NULL);
if (pq->head->next == NULL)
{
free(pq->head);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
else
{
QNode* next = pq->head->next;
free(pq->head);
pq->head = next;
}
pq->size--;
}
datatype QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->head->data;
}
datatype QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->tail->data;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
if (pq->size == 0)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
QNode*next=cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
int main()
{
Queue pq;
QueueInit(&pq);
QueuePush(&pq, 1);
QueuePush(&pq, 2);
QueuePop(&pq);
QueueFront(&pq);
QueueBack(&pq);
QueueSize(&pq);
QueueEmpty(&pq);
QueueDestroy(&pq);
}五.扩展:循环队列
typedef struct
{
int*a;
int front;
int rear;
int k;
} MyCircularQueue;
MyCircularQueue* myCircularQueueCreate(int k)
{
MyCircularQueue*obj=(MyCircularQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyCircularQueue));
obj->a=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(k+1));
obj->k=k;
obj->front=obj->rear=0;
return obj;
}
bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{
return (obj->front)==obj->rear;
}
bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{
return (obj->rear+1)%(obj->k+1)==obj->front;
}
bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj, int value)
{
if(myCircularQueueIsFull(obj))
{
return false;
}
obj->a[obj->rear++]=value; // rear 可能跑到后面去了
(obj->rear)%=(obj->k+1);
return true;
}
bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
{
return false;
}
obj->front++;
obj->front%=(obj->k+1);
return true;
}
int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
{
return -1;
}
return obj->a[obj->front];
}
int myCircularQueueRear(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
{
return -1;
}
return obj->a[(obj->rear-1+obj->k+1)%(obj->k+1)]; //注意是否进入循环了
}
void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
free(obj->a);
free(obj);
}







 本文介绍了队列的概念,强调其先进先出(FIFO)特性,并对比了使用顺序表和链表实现队列的优缺点,推荐使用链表。接着,详细展示了如何使用链表结构实现队列的基本操作,包括初始化、入队、出队、取队头和队尾、计算长度、判断队列是否为空以及销毁队列。最后,提到了循环队列的概念并给出了相关函数接口。
本文介绍了队列的概念,强调其先进先出(FIFO)特性,并对比了使用顺序表和链表实现队列的优缺点,推荐使用链表。接着,详细展示了如何使用链表结构实现队列的基本操作,包括初始化、入队、出队、取队头和队尾、计算长度、判断队列是否为空以及销毁队列。最后,提到了循环队列的概念并给出了相关函数接口。















 1006
1006

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










