Codeforces 359 Div2
A. Free Ice Cream
| time limit per test2 seconds | memory limit per test256 megabytes |
|---|
After their adventure with the magic mirror Kay and Gerda have returned home and sometimes give free ice cream to kids in the summer.
At the start of the day they have x ice cream packs. Since the ice cream is free, people start standing in the queue before Kay and Gerda’s house even in the night. Each person in the queue wants either to take several ice cream packs for himself and his friends or to give several ice cream packs to Kay and Gerda (carriers that bring ice cream have to stand in the same queue).
If a carrier with d ice cream packs comes to the house, then Kay and Gerda take all his packs. If a child who wants to take d ice cream packs comes to the house, then Kay and Gerda will give him d packs if they have enough ice cream, otherwise the child will get no ice cream at all and will leave in distress.
Kay wants to find the amount of ice cream they will have after all people will leave from the queue, and Gerda wants to find the number of distressed kids.
Input
The first line contains two space-separated integers n and x (1 ≤ n ≤ 1000, 0 ≤ x ≤
109
).
Each of the next n lines contains a character ‘+’ or ‘-‘, and an integer di, separated by a space (1 ≤ di ≤ 109). Record “+ di” in i-th line means that a carrier with di ice cream packs occupies i-th place from the start of the queue, and record “- di” means that a child who wants to take di packs stands in i-th place.
Output
Print two space-separated integers — number of ice cream packs left after all operations, and number of kids that left the house in distress.
Examples
input
5 7
+ 5
- 10
- 20
+ 40
- 20
output
22 1
input
5 17
- 16
- 2
- 98
+ 100
- 98
output
3 2
Note
Consider the first sample.
Initially Kay and Gerda have 7 packs of ice cream.
Carrier brings 5 more, so now they have 12 packs.
A kid asks for 10 packs and receives them. There are only 2 packs remaining.
Another kid asks for 20 packs. Kay and Gerda do not have them, so the kid goes away distressed.
Carrier bring 40 packs, now Kay and Gerda have 42 packs.
Kid asks for 20 packs and receives them. There are 22 packs remaining.
题意:简单题,根据提议直接模拟就行。
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: A.cpp
> Author: JueChen
> Mail:libiao0730@gmail.com
> Created Time: 2016年06月27日 星期一 15时41分06秒
************************************************************************/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
int n;
LL m,data;
char op[2];
int main()
{
cin>>n>>m;
int sum = 0 ;
while(n--)
{
cin>>op>>data;
if(op[0] == '+')
{
m+=data;
}
else
{
if(m>=data)
{
m-=data;
}
else
{
sum++;
}
}
}
cout<<m<<" "<<sum<<endl;
return 0;
}
B. Little Robber Girl’s Zoo
| time limit per test2 seconds | memory limit per test256 megabytes |
|---|---|
| inputstandard input | outputstandard output |
Little Robber Girl likes to scare animals in her zoo for fun. She decided to arrange the animals in a row in the order of non-decreasing height. However, the animals were so scared that they couldn’t stay in the right places.
The robber girl was angry at first, but then she decided to arrange the animals herself. She repeatedly names numbers l and r such that r - l + 1 is even. After that animals that occupy positions between l and r inclusively are rearranged as follows: the animal at position l swaps places with the animal at position l + 1, the animal l + 2 swaps with the animal l + 3, …, finally, the animal at position r - 1 swaps with the animal r.
Help the robber girl to arrange the animals in the order of non-decreasing height. You should name at most 20 000 segments, since otherwise the robber girl will become bored and will start scaring the animals again.
Input
The first line contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 100) — number of animals in the robber girl’s zoo.
The second line contains n space-separated integers a1, a2, …, an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109), where ai is the height of the animal occupying the i-th place.
Output
Print the sequence of operations that will rearrange the animals by non-decreasing height.
The output should contain several lines, i-th of the lines should contain two space-separated integers li and ri (1 ≤ li < ri ≤ n) — descriptions of segments the robber girl should name. The segments should be described in the order the operations are performed.
The number of operations should not exceed 20 000.
If the animals are arranged correctly from the start, you are allowed to output nothing.
Examples
input
4
2 1 4 3
output
1 4
input
7
36 28 57 39 66 69 68
output
1 4
6 7
input
5
1 2 1 2 1
output
2 5
3 4
1 4
1 4
Note
Note that you don’t have to minimize the number of operations. Any solution that performs at most 20 000 operations is allowed.
题意:给你一个数组,规定每次让你找一个偶数个数元素的区间,交换区间相邻的两个书,判断多少次可以交换为一个不降的序列。
思路:开始的时候没有思路,读错题意,以为是求最少的次数,但是后来发现题意要求的只是能够交换到规定的状态举行,那么我们直接用冒泡的方式就可以了。
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: B.cpp
> Author: JueChen
> Mail:libiao0730@gmail.com
> Created Time: 2016年06月27日 星期一 15时47分13秒
************************************************************************/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int a[110];
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
}
for(int i = n;i >= 1; i--)
{
for(int j = 1;j<i;j++)
{
if(a[j]>a[j+1])
{
swap(a[j],a[j+1]);
printf("%d %d\n",j,j+1);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
C. Robbers’ watch
| time limit per test2 seconds | memory limit per test256 megabytes |
|---|
Robbers, who attacked the Gerda’s cab, are very successful in covering from the kingdom police. To make the goal of catching them even harder, they use their own watches.
First, as they know that kingdom police is bad at math, robbers use the positional numeral system with base 7. Second, they divide one day in n hours, and each hour in m minutes. Personal watches of each robber are divided in two parts: first of them has the smallest possible number of places that is necessary to display any integer from 0 to n - 1, while the second has the smallest possible number of places that is necessary to display any integer from 0 to m - 1. Finally, if some value of hours or minutes can be displayed using less number of places in base 7 than this watches have, the required number of zeroes is added at the beginning of notation.
Note that to display number 0 section of the watches is required to have at least one place.
Little robber wants to know the number of moments of time (particular values of hours and minutes), such that all digits displayed on the watches are distinct. Help her calculate this number.
Input
The first line of the input contains two integers, given in the decimal notation, n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 109) — the number of hours in one day and the number of minutes in one hour, respectively.
Output
Print one integer in decimal notation — the number of different pairs of hour and minute, such that all digits displayed on the watches are distinct.
Examples
input
2 3
output
4
input
8 2
output
5
Note
In the first sample, possible pairs are: (0: 1), (0: 2), (1: 0), (1: 2).
In the second sample, possible pairs are: (02: 1), (03: 1), (04: 1), (05: 1), (06: 1).
题意:给你时钟的n和m,7进制数,判断有多少种显示的方式使得每一数字没有重复的。
思路:由于只有7个数,所以n和m转化为7进制以后,如果位数多余7则一定没有解,所以只有当两个数的位数之和小于等于7的时候才有解,那么我们会发现此时的数是比较小的,所以我们可以直接暴力计算结果。
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: C.cpp
> Author: JueChen
> Mail:libiao0730@gmail.com
> Created Time: 2016年06月27日 星期一 16时21分58秒
************************************************************************/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
bool vis[10];
bool Judge(int n ,int len)
{
int sum = 0;
while(n)
{
if(vis[n%7])
{
return false;
}
vis[n%7] = true;
n/=7;
sum++;
}
for(int i = sum;i<len;i++)
{
if(vis[0]) return false;
vis[0] = true;
}
return true;
}
int n,m;
int main()
{
cin>>n>>m;
int len1 = 1 ,len2 = 1;
int nn = n,mm = m;
for(int i = 7;i<n;i*=7) len1++;
for(int i = 7;i<m;i*=7) len2++;
int ans = 0 ;
if(len1+len2 <= 7)
{
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j = 0;j<m;j++)
{
memset(vis,false,sizeof(vis));
if((i == j) || (!Judge(i,len1)) || (!Judge(j,len2))) continue;
ans++;
}
}
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
return 0;
}
D. Kay and Snowflake
| time limit per test3 seconds | memory limit per test256 megabytes |
|---|
After the piece of a devilish mirror hit the Kay’s eye, he is no longer interested in the beauty of the roses. Now he likes to watch snowflakes.
Once upon a time, he found a huge snowflake that has a form of the tree (connected acyclic graph) consisting of n nodes. The root of tree has index 1. Kay is very interested in the structure of this tree.
After doing some research he formed q queries he is interested in. The i-th query asks to find a centroid of the subtree of the node vi. Your goal is to answer all queries.
Subtree of a node is a part of tree consisting of this node and all it’s descendants (direct or not). In other words, subtree of node v is formed by nodes u, such that node v is present on the path from u to root.
Centroid of a tree (or a subtree) is a node, such that if we erase it from the tree, the maximum size of the connected component will be at least two times smaller than the size of the initial tree (or a subtree).
Input
The first line of the input contains two integers n and q (2 ≤ n ≤ 300 000, 1 ≤ q ≤ 300 000) — the size of the initial tree and the number of queries respectively.
The second line contains n - 1 integer p2, p3, …, pn (1 ≤ pi ≤ n) — the indices of the parents of the nodes from 2 to n. Node 1 is a root of the tree. It’s guaranteed that pi define a correct tree.
Each of the following q lines contain a single integer vi (1 ≤ vi ≤ n) — the index of the node, that define the subtree, for which we want to find a centroid.
Output
For each query print the index of a centroid of the corresponding subtree. If there are many suitable nodes, print any of them. It’s guaranteed, that each subtree has at least one centroid.
Example
input
7 4
1 1 3 3 5 3
1
2
3
5
output
3
2
3
6
Note
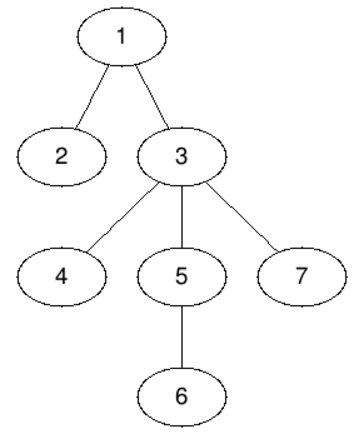
The first query asks for a centroid of the whole tree — this is node 3. If we delete node 3 the tree will split in four components, two of size 1 and two of size 2.
The subtree of the second node consists of this node only, so the answer is 2.
Node 3 is centroid of its own subtree.
The centroids of the subtree of the node 5 are nodes 5 and 6 — both answers are considered correct.
题意:给你一颗树,有n个节点,q次询问,每一给你一个节点,输出以这个节点为根的子树的重心(重心为子树的节点的数量的两倍大于等于所在树的节点的数量)。
思路:首先我们要知道每一个节点所在子树的节点的个数,那么对于一个树来说,重心要不是自己,要不就是在最大的子树上面,那么我们就可以先找出最大的子树,然后以这个子树的重心向上找重心,时间复杂度O(n+q).
/*****
********************************************************************
> File Name: D.cpp
> Author: JueChen
> Mail:libiao0730@gmail.com
> Created Time: 2016年06月27日 星期一 16时45分55秒
************************************************************************/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int Max = 300100;
vector<int>E[Max];
int pre[Max],Big[Max],num[Max];
int ans[Max];
void dfs1(int u)
{
num[u] = 1;
Big[u] = 0;
for(int i = 0 ;i<E[u].size();i++)
{
pre[E[u][i]] = u;
dfs1(E[u][i]);
num[u]+=num[E[u][i]];
Big[u] = max(Big[u],num[E[u][i]]);
}
}
bool Judge(int u,int v)
{
if(num[v]*2>=num[u]) return true;
return false;
}
void dfs2(int u)
{
if(num[u] == 1)
{
ans[u] = u;
return ;
}
int M = 0;
for(int i = 0;i<E[u].size();i++)
{
dfs2(E[u][i]);
if(num[E[u][M]]<num[E[u][i]])
{
M = i;
}
}
int c = ans[E[u][M]];
while(!Judge(u,c))
{
c = pre[c];
}
ans[u] = c;
}
int main()
{
int n,q,u;
scanf("%d %d",&n,&q);
for(int i = 2;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&u);
E[u].push_back(i);
}
pre[1] = 1;
dfs1(1);
dfs2(1);
for(int i = 0;i<q;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&u);
printf("%d\n",ans[u]);
}
return 0;
}






















 600
600











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








