二叉树的遍历是非常重要的基础算法,今天闲来无事,对二叉树的前序、中序、后序遍历使用递归和非递归进行了一个实现。
构造一个有9个节点的二叉树,如下
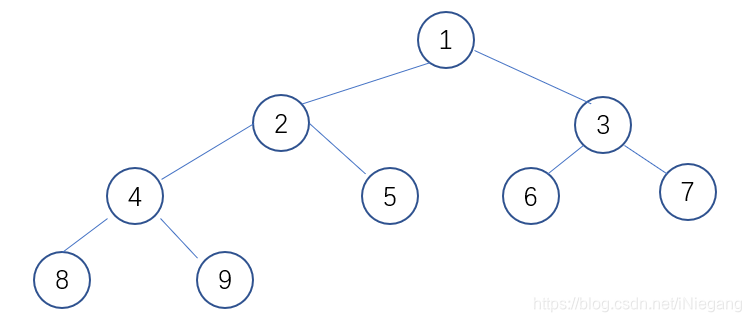
具体代码实现如下
public class BinaryTree {
private static class Tree {
private Integer value;
private Tree leftNode;
private Tree rightNode;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tree tree = new Tree();
createTree(1, tree);
List<Integer> rootFirstRecursiveResult = new ArrayList<>();
rootFirstRecursive(rootFirstRecursiveResult, tree);
System.out.println("Root First By Recursive: " + rootFirstRecursiveResult);
System.out.println("Root First By not Recursive: " + rootFirstNotRecursive(tree));
List<Integer> rootMiddleRecursiveResult = new ArrayList<>();
rootMiddleRecursive(rootMiddleRecursiveResult, tree);
System.out.println("Root Middle By Recursive: " + rootMiddleRecursiveResult);
System.out.println("Root Middle By not Recursive: " + rootMiddleNotRecursive(tree));
List<Integer> rootLastRecursiveResult = new ArrayList<>();
rootLastRecursive(rootLastRecursiveResult, tree);
System.out.println("Root Last By Recursive: " + rootLastRecursiveResult);
System.out.println("Root Last By not Recursive: " + rootLastNotRecursive(tree));
}
/**
* 创建一棵二叉树,最大节点的值为9
*/
private static void createTree(int value, Tree tree) {
if (value > 9) {
return;
}
tree.value = value;
if (2 * value > 9) {
return;
}
tree.leftNode = new Tree();
tree.rightNode = new Tree();
createTree(2 * tree.value, tree.leftNode);
createTree(2 * tree.value + 1, tree.rightNode);
}
/**
* 用递归实现先序遍历
*/
private static void rootFirstRecursive(List<Integer> visited, Tree tree) {
if (tree == null) {
return;
}
visited.add(tree.value);
rootFirstRecursive(visited, tree.leftNode);
rootFirstRecursive(visited, tree.rightNode);
}
/**
* 用非递归实现先序遍历
* 思路:利用栈先进后出的特性,将当前节点的右节点和左节点入栈,然后依次弹出
*/
private static List<Integer> rootFirstNotRecursive(Tree tree) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<Tree> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(tree);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
tree = stack.pop();
result.add(tree.value);
if (tree.rightNode != null) {
stack.push(tree.rightNode);
}
if (tree.leftNode != null) {
stack.push(tree.leftNode);
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* 用递归实现中序遍历
*/
private static void rootMiddleRecursive(List<Integer> visited, Tree tree) {
if (tree == null) {
return;
}
rootMiddleRecursive(visited, tree.leftNode);
visited.add(tree.value);
rootMiddleRecursive(visited, tree.rightNode);
}
/**
* 用非递归实现中序遍历
* 思路:利用栈先进后出的特性,首先找到其最左的节点,出栈,考虑到该节点可能有右子树,因此再考察其右子树
*/
private static List<Integer> rootMiddleNotRecursive(Tree tree) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<Tree> stack = new Stack<>();
while (!stack.isEmpty() || tree != null) {
while (tree != null) {
stack.push(tree);
tree = tree.leftNode;
}
if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
tree = stack.pop();
result.add(tree.value);
tree = tree.rightNode;
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* 用递归实现后序遍历
*/
private static void rootLastRecursive(List<Integer> visited, Tree tree) {
if (tree == null) {
return;
}
rootLastRecursive(visited, tree.leftNode);
rootLastRecursive(visited, tree.rightNode);
visited.add(tree.value);
}
/**
* 用非递归实现后序遍历
* 思路:先序遍历是根左右,后序遍历是左右根,那如果把先序遍历的代码改造为根右左,并把遍历结果存入一个新的栈中,再利用栈的先进后出的特性,即可得到左右根的结果
*/
private static List<Integer> rootLastNotRecursive(Tree tree) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<Tree> stack1 = new Stack<>();
Stack<Tree> stack2 = new Stack<>();
stack1.push(tree);
while (!stack1.isEmpty()) {
tree = stack1.pop();
stack2.push(tree);
if (tree.leftNode != null) {
stack1.push(tree.leftNode);
}
if (tree.rightNode != null) {
stack1.push(tree.rightNode);
}
}
while (!stack2.isEmpty()) {
result.add(stack2.pop().value);
}
return result;
}
}







 本文详细介绍了二叉树的前序、中序、后序遍历算法,包括递归和非递归两种实现方式,并通过示例代码展示了具体的实现过程。
本文详细介绍了二叉树的前序、中序、后序遍历算法,包括递归和非递归两种实现方式,并通过示例代码展示了具体的实现过程。
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








