普通的哈希算法采用简单取模的方式,将缓存服务器进行散列,通常情况下是没有问题的,但是当缓存服务器的个数发生变动时,将会产生较大的影响
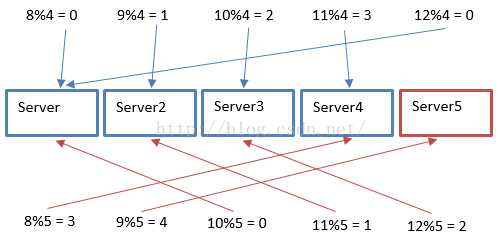
如上图所示,之前有4台缓存服务器,当增加1台缓存服务器之后,除数的变化(4 -> 5)导致求模结果变化,所有缓存查询均未命中
即缓存服务器的个数发生变化时,在一段时间内(缓存重建完毕之前),会有大量缓存查询未命中,导致这段时间内的服务整体性能下降特别严重
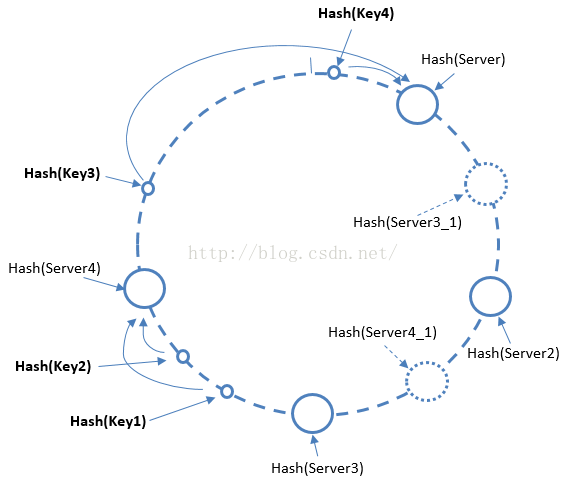
一致性哈希算法能有效降低服务器个数变化对整体缓存的影响,基本实现原理是将Hash函数的值域空间组织成一个圆环,将服务器节点进行哈希,并将哈希结果映射到圆环上,当有一个写入缓存的请求到来时,使用相同的Hash函数,计算Key的哈希值在圆环上对应的位置,按顺时针方向,将请求定位至离其最近的服务器节点
如下图所见,当增加一台缓存服务器Server5后,Server4和Server5之间的点将被定位至Server5,Server5和Server之间的点依然定位至Server,并且对Server2,Server3和Server4没影响,比起简单的求模哈希,未命中的缓存查询少了很多,整体服务性能不会下降过大
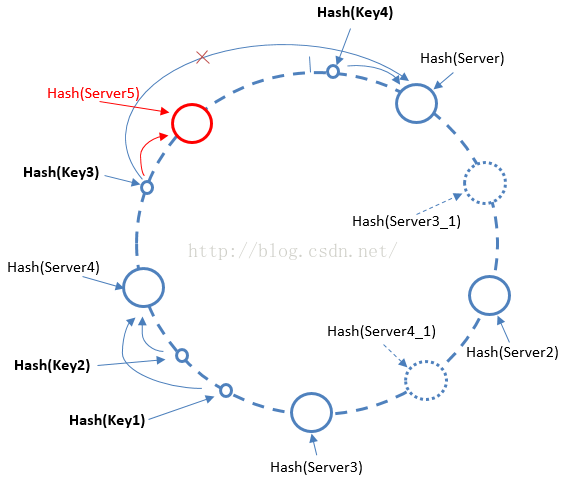
当然在实际使用过程中会在圆环上添加很多虚拟缓存服务器节点,以便缓存分布更加均匀
介绍完原理,我们再来看一下具体实现,以Memcached-java-client为例
如果我们想使用一致性哈希算法,只需要添加pool.setHashingAlg(SockIOPool.CONSISTENT_HASH);这行代码即可
import com.danga.MemCached.MemCachedClient;
import com.danga.MemCached.SockIOPool;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MemCachedClient client = new MemCachedClient();
String[] servers = {"192.168.52.129:9999",
"192.168.52.131:9999"};
Integer[] weights = {1, 1};
SockIOPool pool = SockIOPool.getInstance();
pool.setServers(servers);
pool.setWeights(weights);
pool.setInitConn(5);
pool.setMinConn(5);
pool.setMaxConn(250);
pool.setMaxIdle(1000 * 60 * 60 * 6);
pool.setMaintSleep(30);
pool.setNagle(false);
pool.setSocketTO(3000);
pool.setSocketConnectTO(0);
pool.setHashingAlg(SockIOPool.CONSISTENT_HASH);
pool.initialize();
client.set("test", "This is a test String");
String test = (String) client.get("test");
System.out.println(test);
}
}来看下实际效果
sean@ubuntu1:~$ telnet 192.168.52.131 9999
Trying 192.168.52.131...
Connected to 192.168.52.131.
Escape character is '^]'.
get test
END
sean1@ubuntu2:~$ telnet 192.168.52.129 9999
Trying 192.168.52.129...
Connected to 192.168.52.129.
Escape character is '^]'.
get test
VALUE test 32 21
This is a test String
END先从SockIOPool的初始化开始
public void initialize() {
......
if (this.hashingAlg == 3)
populateConsistentBuckets();
else
populateBuckets();
......
}构建一致性哈希算法中的整个圆环,当然从具体实现上来看只是构建虚拟节点的集合
private void populateConsistentBuckets(){
this.consistentBuckets = new TreeMap();
MessageDigest localMessageDigest = (MessageDigest)MD5.get();
// 获得总权重
// 如果指定了每个服务器的权重,则其和值为总权重
// 否则每个服务器权重为1,总权重为服务器个数
if ((this.totalWeight.intValue() <= 0) && (this.weights != null))
for (i = 0; i < this.weights.length; ++i){
SchoonerSockIOPool localSchoonerSockIOPool = this;
(localSchoonerSockIOPool.totalWeight = Integer.valueOf(localSchoonerSockIOPool.totalWeight.intValue()
+ ((this.weights[i] == null) ? 1 : this.weights[i].intValue())));
}
else if (this.weights == null)
this.totalWeight = Integer.valueOf(this.servers.length);
// 循环遍历每一个服务器以便创建其虚拟节点
for (int i = 0; i < this.servers.length; ++i){
int j = 1;
if ((this.weights != null) && (this.weights[i] != null))
j = this.weights[i].intValue();
// 每个服务器的虚拟节点个数需参照该服务器的权重
double d = Math.floor(40 * this.servers.length * j / this.totalWeight.intValue());
long l = 0L;
// 循环构建每一个节点
while (l < d){
byte[] arrayOfByte = localMessageDigest.digest(this.servers[i] + "-" + l.getBytes());
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k){
Long localLong = Long.valueOf((arrayOfByte[(3 + k * 4)] & 0xFF) << 24
| (arrayOfByte[(2 + k * 4)] & 0xFF) << 16
| (arrayOfByte[(1 + k * 4)] & 0xFF) << 8
| arrayOfByte[(0 + k * 4)] & 0xFF);
// 将每个虚拟节点添加到圆环中
this.consistentBuckets.put(localLong, this.servers[i]);
}
l += 1L;
}
Object localObject;
// 构建socket工厂类
if (this.authInfo != null)
localObject = new AuthSchoonerSockIOFactory(this.servers[i], this.isTcp, this.bufferSize,
this.socketTO, this.socketConnectTO, this.nagle, this.authInfo);
else
localObject = new SchoonerSockIOFactory(this.servers[i], this.isTcp, this.bufferSize,
this.socketTO, this.socketConnectTO, this.nagle);
// 使用socket工厂类创建连接池
GenericObjectPool localGenericObjectPool = new GenericObjectPool((PoolableObjectFactory)localObject,
this.maxConn, 1, this.maxIdle, this.maxConn);
((SchoonerSockIOFactory)localObject).setSockets(localGenericObjectPool);
// 每个服务器都有自己的连接池
this.socketPool.put(this.servers[i], localGenericObjectPool);
}
}MemcachedClient的初始化方法,通过该方法可确定Client的具体实现类为AscIIUDPClient
public MemCachedClient() {
this(null, true, false);
}
public MemCachedClient(String paramString, boolean paramBoolean1,
boolean paramBoolean2) {
this.BLAND_DATA_SIZE = " ".getBytes();
if (paramBoolean2)
this.client = new BinaryClient(paramString);
else
this.client = new AscIIUDPClient(paramString);
}当发送一个添加请求时,本质还是通过调用set方法实现的
public boolean add(String paramString, Object paramObject) {
return set("add", paramString, paramObject, null, null,
Long.valueOf(0L));
}
// paramInteger的值为null
private boolean set(String paramString1, String paramString2,
Object paramObject, Date paramDate, Integer paramInteger,
Long paramLong) {
......
SchoonerSockIO localSchoonerSockIO = this.pool.getSock(paramString2,
paramInteger);
......
}服务器的查找过程如下
public final SchoonerSockIO getSock(String paramString, Integer paramInteger) {
......
// 计算Key的哈希值,并根据该哈希值得到对应的服务器节点哈希值
long l = getBucket(paramString, paramInteger);
// 根据服务器节点哈希值得到对应的服务器
String str1 = (this.hashingAlg == 3) ? (String) this.consistentBuckets
.get(Long.valueOf(l)) : (String) this.buckets.get((int) l);
while (!(((Set) localObject).isEmpty())) {
// 从服务器连接池中获取到特定服务器的连接
SchoonerSockIO localSchoonerSockIO = getConnection(str1);
......
}首选根据Key值计算出其哈希值(getHash),然后根据得到的哈希值确定其在圆环上对应的服务器节点(findPointFor)
// paramInteger的值为null
private final long getBucket(String paramString, Integer paramInteger) {
long l1 = getHash(paramString, paramInteger);
if (this.hashingAlg == 3)
return findPointFor(Long.valueOf(l1)).longValue();
long l2 = l1 % this.buckets.size();
if (l2 < 0L)
l2 *= -1L;
return l2;
}Key的哈希值计算过程如下,和populateConsistentBuckets方法中用来生成服务器虚拟节点哈希值的算法是一样的
// paramInteger的值为null
private final long getHash(String paramString, Integer paramInteger) {
if (paramInteger != null) {
if (this.hashingAlg == 3)
return (paramInteger.longValue() & 0xFFFFFFFF);
return paramInteger.longValue();
}
switch (this.hashingAlg) {
case 0:
return paramString.hashCode();
case 1:
return origCompatHashingAlg(paramString);
case 2:
return newCompatHashingAlg(paramString);
case 3:
return md5HashingAlg(paramString);
}
this.hashingAlg = 0;
return paramString.hashCode();
}
private static long md5HashingAlg(String paramString) {
MessageDigest localMessageDigest = (MessageDigest) MD5.get();
localMessageDigest.reset();
localMessageDigest.update(paramString.getBytes());
byte[] arrayOfByte = localMessageDigest.digest();
long l = (arrayOfByte[3] & 0xFF) << 24 | (arrayOfByte[2] & 0xFF) << 16
| (arrayOfByte[1] & 0xFF) << 8 | arrayOfByte[0] & 0xFF;
return l;
}
在圆环上查找Key的哈希值对应的服务器节点哈希值
参照populateConsistentBuckets中的代码,所有虚拟节点被存放在一个TreeMap中,所以这里可以使用tailMap方法获得大于等于Key哈希值的子树,然后获取该树中最小值即可
private final Long findPointFor(Long paramLong) {
SortedMap localSortedMap = this.consistentBuckets.tailMap(paramLong);
return ((localSortedMap.isEmpty()) ? (Long) this.consistentBuckets
.firstKey() : (Long) localSortedMap.firstKey());
}



















 4万+
4万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








