Features
- Several levels of brutality when rotating connections:
-
Session pooling
- Most polite method. When client connects, a server connection will be assigned to it for the whole duration it stays connected. When client disconnects, the server connection will be put back into pool. This mode supports all PostgeSQL features. Transaction pooling
- Server connection is assigned to client only during a transaction. When PgBouncer notices that transaction is over, the server will be put back into pool.
- This mode breaks few session-based features of PostgreSQL. You can use it only when application cooperates by not using features that break. See the table below for incompatible features. Statement pooling
- Most aggressive method. This is transaction pooling with a twist - multi-statement transactions are disallowed. This is meant to enforce "autocommit" mode on client, mostly targeted for PL/Proxy.
- Low memory requirements (2k per connection by default). This is due to the fact that PgBouncer does not need to see full packet at once.
- It is not tied to one backend server, the destination databases can reside on different hosts.
- Supports online reconfiguration for most of the settings.
- Supports online restart/upgrade without dropping client connections.
- Supports protocol V3 only, so backend version must be >= 7.4.
-
feature matrix for pooling modes
Following table list various PostgreSQL features and whether they are compatible with PgBouncer pooling modes. Note that 'transaction' pooling breaks client expectations of serverby designand can be used only if application cooperates by not using non-working features.
Supported PostgreSQL features. Feature Session pooling [1] Transaction pooling Startup parameters [2] Yes Yes SET/RESET Yes No LISTEN/NOTIFY Yes No WITHOUT HOLD CURSOR Yes Yes WITH HOLD CURSOR Yes No Protocol-level prepared plans Yes No [3] PREPARE / DEALLOCATE Yes No ON COMMIT DROP temp tables Yes Yes PRESERVE/DELETE ROWS temp tables Yes No Cached plan reset Yes Yes [1] LOAD statement Yes No UDFs with session state Yes No - [1] - Full transparency requires PostgreSQL 8.3 and PgBouncer 1.1+ with server_reset_query = DISCARD ALL
- [2] - Startup parameters are: client_encoding, datestyle, timezone, standard_conforming_strings and application_name. PgBouncer can detect their changes so it can guarantee they remain consistent for client. Available from PgBouncer 1.1.
- [3] - It is possible to add support for that into PgBouncer.
以上摘自wiki
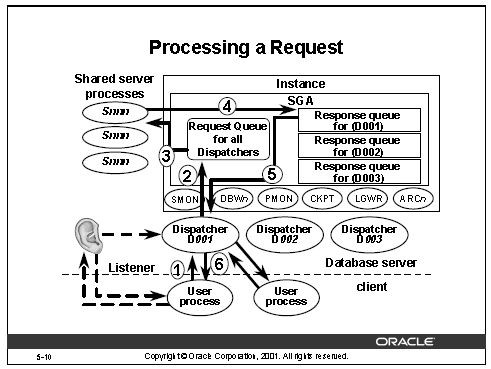
| ①.用户将请求发送给调度程序。 |
| ②.调度程序将请求置入“系统全局区”(SystemGlobalArea,SGA)中的请求队列(公共队列)。 |
| ③.共享服务器从请求队列选择该请求,然后处理该请求。 |
| ④.共享服务器将响应放入请求调度程序的响应队列。 |
| ⑤.该响应被传送给调度程序。 |
| ⑥.调度程序将该响应返回给用户。 |
| 请求队列: | ||
| ⊙ 所有调度程序共享一个请求队列。 | ||
| ⊙ 共享服务器监视请求队列以查看是否有新的请求。 | ||
| ⊙ 请求的处理采取先进先出(FIFO)的原则。 | ||
| ⊙ 共享服务器将完成的所有请求放入请求调度程序的响应队列。 | ||
| ⊙ 每个调度程序在SGA中都有自己的响应队列。
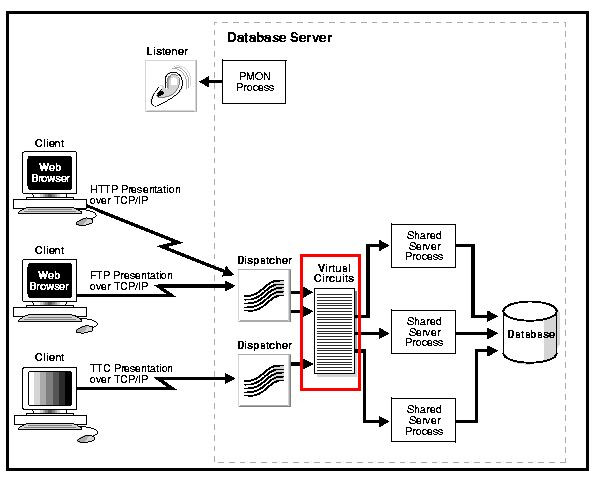
CIRCUITS
|




















 1882
1882

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








