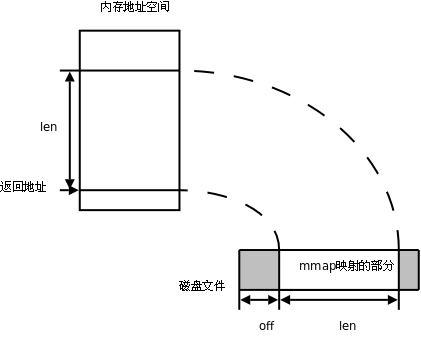
鉴于linux,window系统为mmap所提供的API大同小异(见下图)。这里仅以mongodb对window系统的mmap调用机制为例,来说 明一下其具体的实现方式,以及在mongodb启动时,客户端提交查询和插入操作请求时mongodb的mmap执行流程。

上面类图中:
MongoFile :定义了mongo文件对象常用操作,包括创建,关闭,设置名称,flushAll,获取MongoFile文件总尺寸等。
MMF : 一个类型定义,其声明:typedef MemoryMappedFile MMF;
MongoMMF :为了便于journaling/durability操作,对MemoryMappedFile进行了一些封装(特别是对private views )
下面着重看一下windows提供的mmap的常用API:
MapViewOfFile (): 把文件数据映射到进程的地址空间
CreateFileMapping () : 创建一个新的文件映射内核对象
FlushViewOfFile (): 强制系统将内存中修改过的数据重新写入磁盘映像,从而可以确保所有的数据更新能及时保存到磁盘
CloseHandle (): 关闭文件映射对象和文件对象
MapViewOfFileEx (): 将文件映射到指定的进程地址空间
参数说明:
- MapViewOfFile(
- __in HANDLE hFileMappingObject, /*hFileMappingObject是共享文件对象*/
- __in DWORD dwDesiredAccess, /*dwDesiredAccess是文件共享属性*/
- __in DWORD dwFileOffsetHigh, /*dwFileOffsetHigh是文件共享区的偏移地址*/
- __in DWORD dwFileOffsetLow, /*dwFileOffsetLow是文件共享区的偏移地址*/
- __in SIZE_T dwNumberOfBytesToMap /*dwNumberOfBytesToMap是共享数据长度*/
- );
- //winbase.h
- CreateFileMappingW(
- __in HANDLE hFile, /*hFile是创建共享文件的句柄*/
- __in_opt LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpFileMappingAttributes, /*lpFileMappingAttributes是文件共享的属性*/
- __in DWORD flProtect, /*flProtect是当文件映射时读写文件的属性*/
- __in DWORD dwMaximumSizeHigh, /*是文件共享的大小高位字节*/
- __in DWORD dwMaximumSizeLow, /*是文件共享的大小低位字节*/
- __in_opt LPCWSTR lpName /*lpName是共享文件对象名称*/
- );
- #ifdef UNICODE
- #define CreateFileMapping CreateFileMappingW
- #else
- #define CreateFileMapping CreateFileMappingA
- #endif // !UNICODE
- FlushViewOfFile(
- __in LPCVOID lpBaseAddress, /*内存映射文件中的视图的一个字节的地址*/
- __in SIZE_T dwNumberOfBytesToFlush /*想要刷新的字节数*/
- );
- MapViewOfFileEx(
- __in HANDLE hFileMappingObject, /*共享文件对象*/
- __in DWORD dwDesiredAccess, /*文件共享属性*/
- __in DWORD dwFileOffsetHigh, /*文件共享区的偏移地址*/
- __in DWORD dwFileOffsetLow, /*文件共享区的偏移地址*/
- __in SIZE_T dwNumberOfBytesToMap /*共享数据长度*/
- __in_opt LPVOID lpBaseAddress /*指定映射文件映射对象的地址。如这个地址处没有足够的内存空间,
- 那么对MapViewOfFileEx的调用会失效*/
- );
下面我们看一下mongodb如何使用上述API,来实现windows环境下对mongofile进行mmap操作的.
- //mmap_win.cpp
- mutex mapViewMutex("mapView");//声明mapView的互斥体(mutex)对象
- ourbitset writable;
- /** unmapping 通知,以便清空 writable bits */
- void MemoryMappedFile::clearWritableBits(void *p) {
- for( unsigned i = ((size_t)p)/ChunkSize; i <= (((size_t)p)+len)/ChunkSize; i++ ) {
- writable.clear(i);
- assert( !writable.get(i) );
- }
- }
- MemoryMappedFile::MemoryMappedFile()
- : _flushMutex(new mutex("flushMutex")) {
- fd = 0;
- maphandle = 0;
- len = 0;
- created();
- }
- //关闭文件MemoryMappedFile
- void MemoryMappedFile::close() {
- for( vector<void*>::iterator i = views.begin(); i != views.end(); i++ ) {
- clearWritableBits(*i);
- UnmapViewOfFile(*i);
- }
- views.clear();
- if ( maphandle )
- CloseHandle(maphandle);//关闭文件映射对象和文件对象
- maphandle = 0;
- if ( fd )
- CloseHandle(fd);//关闭文件映射对象和文件对象
- fd = 0;
- }
- unsigned long long mapped = 0;
- //创建只读map
- void* MemoryMappedFile::createReadOnlyMap() {
- assert( maphandle );
- scoped_lock lk(mapViewMutex);
- void *p = MapViewOfFile(maphandle, FILE_MAP_READ, /*f ofs hi*/0, /*f ofs lo*/ 0, /*dwNumberOfBytesToMap 0 means to eof*/0);
- if ( p == 0 ) {
- DWORD e = GetLastError();
- log() << "FILE_MAP_READ MapViewOfFile failed " << filename() << " " << errnoWithDescription(e) << endl;
- }
- else {
- views.push_back(p);
- }
- return p;
- }
- //创建指定名称和大小的MapViewOfFile
- void* MemoryMappedFile::map(const char *filenameIn, unsigned long long &length, int options) {
- assert( fd == 0 && len == 0 ); // 仅能打开一次
- setFilename(filenameIn);
- /* big hack here: Babble uses db names with colons. doesn't seem to work on windows. temporary perhaps. */
- char filename[256];
- strncpy(filename, filenameIn, 255);
- filename[255] = 0;
- {
- size_t len = strlen( filename );
- for ( size_t i=len-1; i>=0; i-- ) {
- if ( filename[i] == '/' ||
- filename[i] == '//' )
- break;
- if ( filename[i] == ':' )
- filename[i] = '_';
- }
- }
- updateLength( filename, length );//如果指定文件已存在,则用已存在的文件长度更新length值
- {
- DWORD createOptions = FILE_ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL;
- if ( options & SEQUENTIAL )
- createOptions |= FILE_FLAG_SEQUENTIAL_SCAN;//针对连续访问对文件缓冲进行优化选项
- DWORD rw = GENERIC_READ | GENERIC_WRITE;//普通读/写
- fd = CreateFile(//创建相关文件
- toNativeString(filename).c_str(),//创建的文件名称
- rw, // desired access
- FILE_SHARE_WRITE | FILE_SHARE_READ, // share mode
- NULL, // security
- OPEN_ALWAYS, // create disposition
- createOptions , // flags
- NULL); // hTempl
- if ( fd == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE ) {
- DWORD e = GetLastError();
- log() << "Create/OpenFile failed " << filename << " errno:" << e << endl;
- return 0;
- }
- }
- mapped += length;
- {
- //采用“读写文件数据”方式的页面保护属性
- DWORD flProtect = PAGE_READWRITE;
- //创建一个文件映射内核对象并告诉系统文件的尺寸以及访问文件的方式
- maphandle = CreateFileMapping(fd, NULL, flProtect,
- length >> 32 /*maxsizehigh*/,
- (unsigned) length /*maxsizelow*/,
- NULL/*lpName*/);
- if ( maphandle == NULL ) {
- // 先获取操作信息, 因为下面的log()要删除lasterror信息
- DWORD e = GetLastError();
- log() << "CreateFileMapping failed " << filename << ' ' << errnoWithDescription(e) << endl;
- close();
- return 0;
- }
- }
- void *view = 0;
- {
- scoped_lock lk(mapViewMutex);
- DWORD access = (options&READONLY)? FILE_MAP_READ : FILE_MAP_ALL_ACCESS;
- //把文件数据映射到进程的地址空间
- view = MapViewOfFile(maphandle, access, /*f ofs hi*/0, /*f ofs lo*/ 0, /*dwNumberOfBytesToMap 0 means to eof*/0);
- }
- if ( view == 0 ) {
- DWORD e = GetLastError();
- log() << "MapViewOfFile failed " << filename << " " << errnoWithDescription(e) << endl;
- close();
- }
- else {
- views.push_back(view);
- }
- len = length;
- return view;
- }
- class WindowsFlushable : public MemoryMappedFile::Flushable {
- public:
- WindowsFlushable( void * view , HANDLE fd , string filename , boost::shared_ptr<mutex> flushMutex )
- : _view(view) , _fd(fd) , _filename(filename) , _flushMutex(flushMutex)
- {}
- void flush() {
- if (!_view || !_fd)
- return;
- scoped_lock lk(*_flushMutex);
- // 强制系统将内存中修改过的数据重新写入磁盘映像,从而可以确保所有的数据更新能及时保存到磁盘。
- bool success = FlushViewOfFile(_view, 0 /*0表示全部mapping*/);
- if (!success) {
- int err = GetLastError();
- out() << "FlushViewOfFile failed " << err << " file: " << _filename << endl;
- }
- success = FlushFileBuffers(_fd);//刷新内部文件缓冲区的数据刷到磁盘上
- if (!success) {
- int err = GetLastError();
- out() << "FlushFileBuffers failed " << err << " file: " << _filename << endl;
- }
- }
- void * _view;
- HANDLE _fd;
- string _filename;
- boost::shared_ptr<mutex> _flushMutex;
- };
- //是否进行异步的flush操作(该操作会将修改过的数据部分或全部重新写入磁盘映像)
- void MemoryMappedFile::flush(bool sync) {
- uassert(13056, "Async flushing not supported on windows", sync);//windows系统不支持异步flush
- if( !views.empty() ) {
- WindowsFlushable f( views[0] , fd , filename() , _flushMutex);
- f.flush();
- }
- }
- //预先刷数据操作,该方法确保这个对象是可以执行flush()操作,以便在调用该方法之后执行flush操作.
- //参见mmap.cpp flushAll操作
- MemoryMappedFile::Flushable * MemoryMappedFile::prepareFlush() {
- return new WindowsFlushable( views.empty() ? 0 : views[0] , fd , filename() , _flushMutex );
- }
- void MemoryMappedFile::_lock() {}
- void MemoryMappedFile::_unlock() {}
上面的代码比较简单,大家看一下注释就可以了,下面看一下mmf对于上面的MemoryMappedFile类实现是如何封装的,因为mmf会在journaling/durability这类场景下使用PrivateMap():
- //mongommf.cpp文件
- //构造PrivateMap
- void* MemoryMappedFile::createPrivateMap() {
- assert( maphandle );
- scoped_lock lk(mapViewMutex);
- //void *p = mapaligned(maphandle, len);
- void *p = MapViewOfFile(maphandle, FILE_MAP_READ, 0, 0, 0);
- if ( p == 0 ) {
- DWORD e = GetLastError();
- log() << "createPrivateMap failed " << filename() << " " << errnoWithDescription(e) << endl;
- }
- else {
- clearWritableBits(p);
- views.push_back(p);
- }
- return p;
- }
- //重新映射PrivateView
- void* MemoryMappedFile::remapPrivateView(void *oldPrivateAddr) {
- dbMutex.assertWriteLocked(); // short window where we are unmapped so must be exclusive
- // mapViewMutex确保在重新映射时获得相同的地址
- scoped_lock lk(mapViewMutex);
- //清空 writable bits
- clearWritableBits(oldPrivateAddr);
- //从进程的地址空间(oldPrivateAddr)撤消文件数据的映像
- if( !UnmapViewOfFile(oldPrivateAddr) ) {
- DWORD e = GetLastError();
- log() << "UnMapViewOfFile failed " << filename() << ' ' << errnoWithDescription(e) << endl;
- assert(false);
- }
- // 将文件映射到指定的进程地址空间
- void *p = MapViewOfFileEx(maphandle, FILE_MAP_READ, 0, 0,
- /*dwNumberOfBytesToMap 0 means to eof*/0 /*len*/,
- oldPrivateAddr);
- if ( p == 0 ) {
- DWORD e = GetLastError();
- log() << "MapViewOfFileEx failed " << filename() << " " << errnoWithDescription(e) << endl;
- assert(p);
- }
- assert(p == oldPrivateAddr);
- return p;
- }
- #endif
- //重新映射PrivateView
- void MongoMMF::remapThePrivateView() {
- assert( cmdLine.dur );
- // todo 1.9 : it turns out we require that we always remap to the same address.
- // so the remove / add isn't necessary and can be removed
- privateViews.remove(_view_private);
- _view_private = remapPrivateView(_view_private);
- privateViews.add(_view_private, this);
- }
- ......
- //打开指定的文件并执行mmap操作
- bool MongoMMF::open(string fname, bool sequentialHint) {
- setPath(fname);
- _view_write = mapWithOptions(fname.c_str(), sequentialHint ? SEQUENTIAL : 0);
- return finishOpening();
- }
- //创建指定名称的文件并执行mmap操作
- bool MongoMMF::create(string fname, unsigned long long& len, bool sequentialHint) {
- setPath(fname);
- _view_write = map(fname.c_str(), len, sequentialHint ? SEQUENTIAL : 0);
- return finishOpening();
- }
- //创建PrivateMap并加载到privateViews集合中
- bool MongoMMF::finishOpening() {
- if( _view_write ) {
- if( cmdLine.dur ) {
- _view_private = createPrivateMap();
- if( _view_private == 0 ) {
- massert( 13636 , "createPrivateMap failed (look in log for error)" , false );
- }
- privateViews.add(_view_private, this); // note that testIntent builds use this, even though it points to view_write then...
- }
- else {
- _view_private = _view_write;
- }
- return true;
- }
- return false;
- }
- ......
- //从privateViews集合中移除当前 _view_private,并关闭文件映射对象和文件对象
- void MongoMMF::close() {
- {
- if( cmdLine.dur && _view_write/*actually was opened*/ ) {
- if( debug )
- log() << "closingFileNotication:" << filename() << endl;
- dur::closingFileNotification();
- }
- privateViews.remove(_view_private);
- }
- _view_write = _view_private = 0;
- MemoryMappedFile::close();//关闭文件映射对象和文件对象
- }
mongodb完成了上面的工具类的声明定义之后,就会在前台使用这些类了,下面通过插入数据操作(之前主要流程我已在这篇文章 中有所描述)过程中,对上面类的使用来进行阐述.
首先需要说明的是,如果是首次在本地运行mongod,则不会在指定的数据库目录(dbpath 参数)下生成数据库文件,但如果有数据插入时,则会生成相应文件,这里可以理解为生成文件的过程就是mmap的创建过程。
之前的文章中提到过,当客户端要插入记录时,则系统会根据客户端的操作枚举信息来调用相应的操作,这里它会执行instance.cpp 文件中的receivedInsert方法,并进而调用 pdfile.cpp 文件的 insert ()函数,而在该方法下有如下一段代码:
- DiskLoc DataFileMgr::insert(const char *ns, const void *obuf, int len, bool god, const BSONElement &writeId, bool mayAddIndex) {
- ......
- NamespaceDetails *d = nsdetails(ns);//获取ns的详细信息
- if ( d == 0 ) {
- addNewNamespaceToCatalog(ns);//向system catalog添加新的名空间,它会再次调用当前insert()方法
- // 创建第一个数据库文件,方法位于database.cpp
- cc().database()->allocExtent(ns, Extent::initialSize(len), false);
- ......
- }
上面的allocExtent方法用于分配Extent要求的磁盘空间,其中Extent用于记录多个record记录信息,而record就是数据库中 的一条记录。这里可以将Extent看成是一个数据集合,但与我们通常所理解的"数据表"(datatable)有所差异,因为在同一个 namespace下可以有一个或多个extent(可以不连续),extent之间是一个双向链表结构,其通过cursor进行向前(forward) 或反转(reverse)的访问。有关这些内容,参见我之前写的这篇文章 。
言归正传,在上面的allocExtent方法中,会执行pdfile.cpp中的如下方法:
- //pdfile.cpp
- Extent* MongoDataFile::createExtent(const char *ns, int approxSize, bool newCapped, int loops) {
- .....
- int ExtentSize = approxSize <= header()->unusedLength ? approxSize : header()->unusedLength;
- DiskLoc loc;
- if ( ExtentSize < Extent::minSize() ) {//判断当前ExtentSize的大小
- ......
- //addAFile方法位于 database.cpp
- return cc().database()->addAFile( 0, true )->createExtent(ns, approxSize, newCapped, loops+1);
- .....
- }
最后在addAFile方法中,我们会看下如下代码段:
- //database.cpp
- MongoDataFile* Database::addAFile( int sizeNeeded, bool preallocateNextFile ) {
- int n = (int) files.size();
- MongoDataFile *ret = getFile( n, sizeNeeded );//调用下面的getFile方法
- .....
- }
- //database.cpp
- MongoDataFile* Database::getFile( int n, int sizeNeeded , bool preallocateOnly) {
- ......
- namespaceIndex.init();
- .....
- }
- //namespace.cpp
- void NamespaceIndex::init() {
- ......
- unsigned long long len = 0;
- boost::filesystem::path nsPath = path();
- string pathString = nsPath.string();
- void *p = 0;
- if( MMF::exists(nsPath) ) {//使用本文前面提到的MMF类,判断数据库文件是否存在
- if( f.open(pathString, true) ) {//打开指定的文件并执行mmap操作
- len = f.length();
- if ( len % (1024*1024) != 0 ) {
- log() << "bad .ns file: " << pathString << endl;
- uassert( 10079 , "bad .ns file length, cannot open database", len % (1024*1024) == 0 );
- }
- p = f.getView();//返回mapview
- }
- }
- else {//不存在
- // use lenForNewNsFiles, we are making a new database
- massert( 10343, "bad lenForNewNsFiles", lenForNewNsFiles >= 1024*1024 );
- maybeMkdir();//创建相应目录(如不存在)
- unsigned long long l = lenForNewNsFiles;
- if( f.create(pathString, l, true) ) {//创建指定名称的文件并执行mmap操作
- getDur().createdFile(pathString, l); // always a new file
- len = l;
- assert( len == lenForNewNsFiles );
- p = f.getView();//返回mapview
- }
- }
- ......
- }
下面用一张时序图来大体回顾一下这一流程:

在创建了该数据库文件及相应mmap操作之后,下面再重新启动mongod时,系统会通过构造client类的上下文对象 (context)方法来最终调用namespaceIndex.init()方法,其时序图如下,大家可以通过调试源码来难证这一流程:

好了,今天的内容到这里就告一段落。
参考链接:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mmap
http://linux.about.com/library/cmd/blcmdl2_mmap.htm
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa366761.aspx
http://hi.baidu.com/%B2%A4%B2%CB%B1%F9%B1%F9/blog/item/f6e6fb2561c0136a35a80f70.html
原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/daizhj/archive/2011/04/25/mongos_mmap_source_code.html
作者: daizhj, 代震军
微博: http://t.sina.com.cn/daizhj
Tags: mongodb,c++,mmap






















 362
362

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








