
硬实时Linux(RT-Preempt Patch)在PC上的编译、使用和测试
Vanilla kernel的问题
Linux kernel在spinlock、irq上下文方面无法抢占,因此高优先级任务被唤醒到得以执行的时间并不能完全确定。同时,Linux kernel本身也不处理优先级反转。RT-Preempt Patch是在Linux社区kernel的基础上,加上相关的补丁,以使得Linux满足硬实时的需求。本文描述了该patch在PC上的实践。我们的 测试环境为Ubuntu 10.10,默认情况下使用Ubuntu 10.10自带的kernel:

在Ubuntu 10.10,apt-get install rt-tests安装rt测试工具集,运行其中的cyclictest测试工具,默认创建5个SCHED_FIFO策略的realtime线程,优先级 76-80,运行周期是1000,1500,2000,2500,3000微秒:
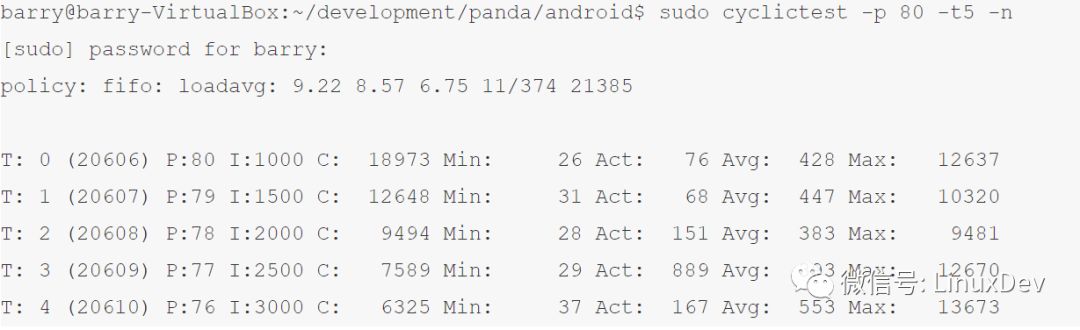
由此可见在标准Linux内,rt线程投入运行的jitter非常不稳定,最小值在26-37微秒,平均值为68-889微秒,而最大值则分布在9481-13673微秒之间。
我们还是运行这个测试,但是在运行这个测试的过程中引入更多干扰,如mount /dev/sdb1 ~/development,则结果变为:
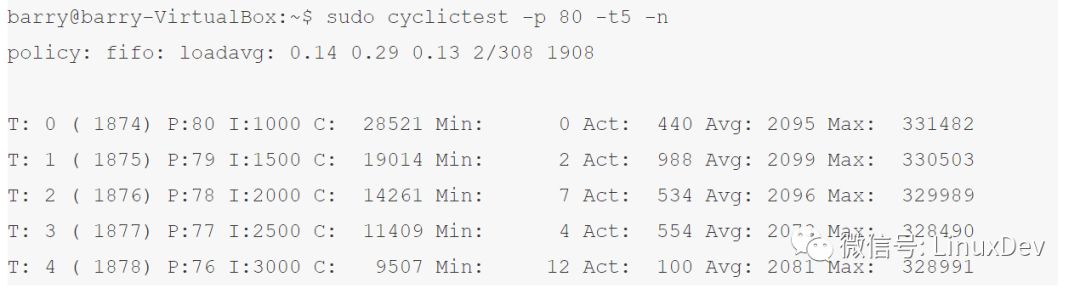
mount过程中引入的irq、softirq和spinlock导致最大jitter明显地加大甚至达到了331482us,充分显示出了标准Linux内核中RT线程投入运行时间的不可预期性(硬实时要求意味着可预期)。
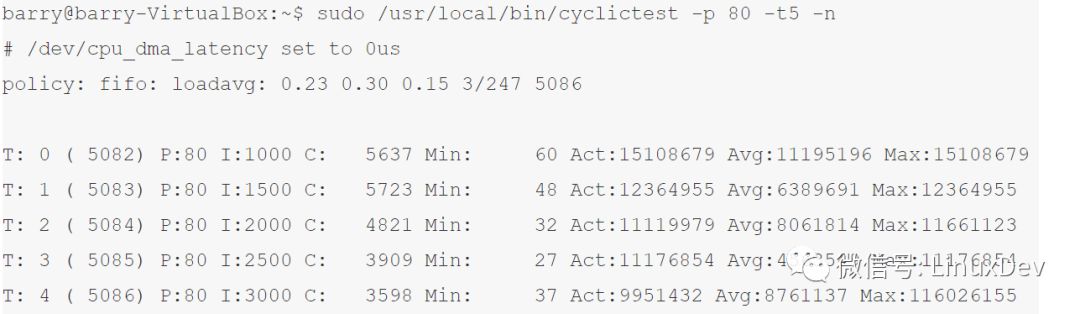
如果我们编译一份kernel,选择的是“Voluntary Kernel Preemption (Desktop)“,这类似于2.4不支持kernel抢占的情况,我们运行同样的case,时间的不确定性大地几乎让我们无法接受:
RT-Preempt Patch使能
RT-Preempt Patch对Linux kernel的主要改造包括:
Making in-kernel locking-primitives (using spinlocks) preemptible though reimplementation with rtmutexes:
Critical sections protected by i.e. spinlock_t and rwlock_t are now preemptible. The creation of non-preemptible sections (in kernel) is still possible with raw_spinlock_t (same APIs like spinlock_t)
Implementing priority inheritance for in-kernel spinlocks and semaphores. For more information on priority inversion and priority inheritance please consult Introduction to Priority Inversion (http://www.embedded.com/electronics-blogs/beginner-s-corner/4023947/Introduction-to-Priority-Inversion)
Converting interrupt handlers into preemptible kernel threads: The RT-Preempt patch treats soft interrupt handlers in kernel thread context, which is represented by a task_struct like a common userspace process. However it is also possible to register an IRQ in kernel context.
Converting the old Linux timer API into separate infrastructures for high resolution kernel timers plus one for timeouts, leading to userspace POSIX timers with high resolution.
在本试验中,我们取的带RT- Preempt Patch的kernel tree是git://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/rt/linux-stable- rt.git,使用其v3.4-rt-rebase branch,编译kernel时选中了"Fully Preemptible Kernel"抢占模型:
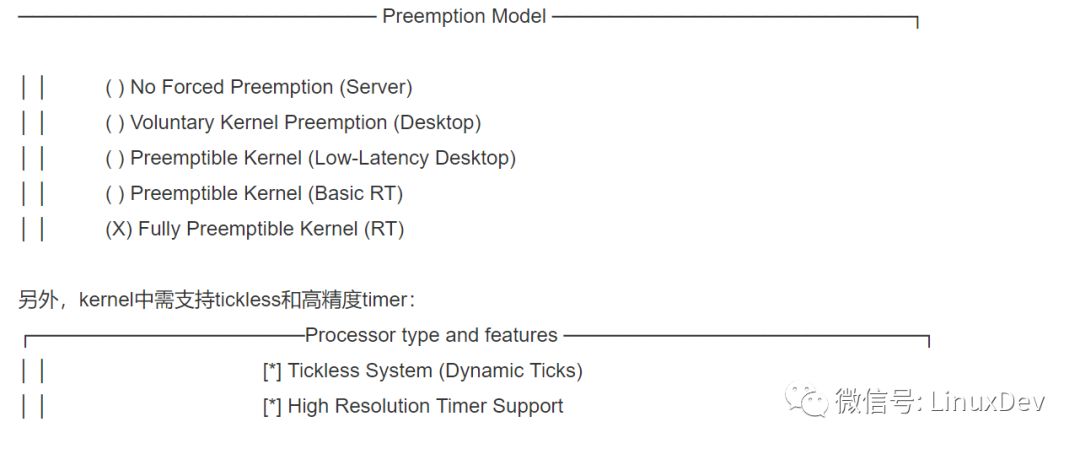
make modules_install、make install、mkintramfs后,我们得到一个可以在Ubuntu中启动的RT kernel。具体编译方法可详见http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2012-01/50749.htm,根据该文修改版本 号等信息即可,我们运行的命令包括:
安装模块
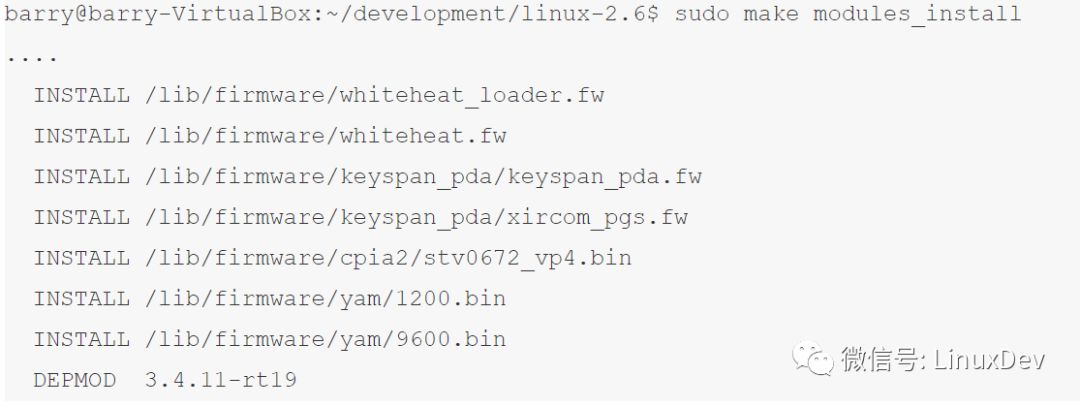
安装kernel
barry@barry-VirtualBox:~/development/linux-2.6$ sudo make install
sh /home/barry/development/linux-2.6/arch/x86/boot/install.sh 3.4.11-rt19 arch/x86/boot/bzImage \
System.map "/boot"
制作initrd
barry@barry-VirtualBox:~/development/linux-2.6$ sudo mkinitramfs 3.4.11-rt19 -o /boot/initrd.img-3.4.11-rt19
修改grub配置
在grub.conf中增加新的启动entry,仿照现有的menuentry,增加一个新的,把其中的相关版本号都变更为3.4.11-rt19,我们的修改如下:
menuentry 'Ubuntu, with Linux 3.4.11-rt19' --class ubuntu --class gnu-linux --class gnu --class os {
recordfail
insmod part_msdos
insmod ext2
set root='(hd0,msdos1)'
search --no-floppy --fs-uuid --set a0db5cf0-6ce3-404f-9808-88ce18f0177a
linux /boot/vmlinuz-3.4.11-rt19 root=UUID=a0db5cf0-6ce3-404f-9808-88ce18f0177a ro quiet splash
initrd /boot/initrd.img-3.4.11-rt19
}
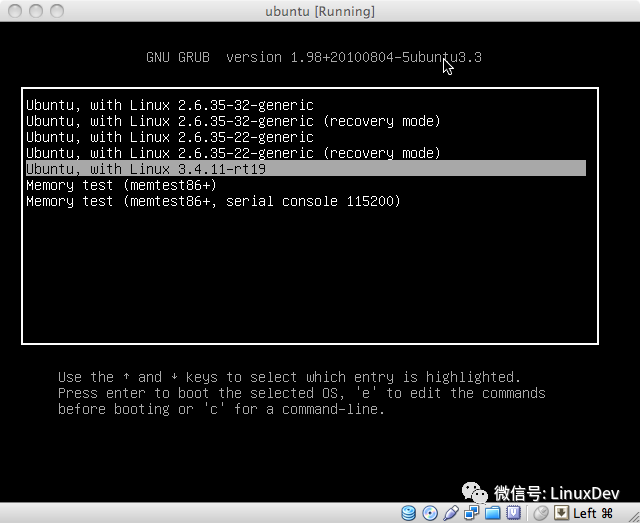
开机时选择3.4.11-rt19启动:
RT-Preempt Patch试用
运行同样的测试cyclictest benchmark工具,结果迥异:





 本文深入探讨了Linux系统的实时补丁原理,包括其如何在不重启系统的情况下更新内核,确保系统的稳定性和安全性。同时,通过实践案例,展示了实施实时补丁的过程和注意事项,为系统管理员提供了有效的维护策略。
本文深入探讨了Linux系统的实时补丁原理,包括其如何在不重启系统的情况下更新内核,确保系统的稳定性和安全性。同时,通过实践案例,展示了实施实时补丁的过程和注意事项,为系统管理员提供了有效的维护策略。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
















 1607
1607

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








