移动平均,滤波,平滑等,这些概念其实都大同小异,其作用都是希望能把信号数值中的毛刺、噪点,给去掉抹平捋顺,留下真值。
这类的程序和工作做了不少,一直没有机会总结归纳整理下。趁着这次空挡的时间,写了一个算法调试工具,顺便写篇博客总结一下。
至于写了算法调试工具的目的,主要是为了提高效率。
我们一般调试算法的步骤是:
如果使用算法调试工具,那我们的流程就可以变成这样
按照之前的流程,可能要走很多遍,效率不高。
有了算法调试工具后,理想情况下,一次搞定。
当然这种效率的提高,也是因为前期工作的准备(算法调试工具的开发)。
目前市面上有很多类似的,且更好用的工具,不过自己还是想要结合自身所学,综合考虑,自己开发一个算法调试工具。如下,目前功能还不多,慢慢增加。

简单移动平均
原理
若依次得到一组原始测定值时,按顺序取一定数量的数据并算得其全部算术平均值,得到的数据就叫做移动平均值。
假设:
原始测定值为:
x
1
,
x
2
,
x
3
,
x
4...
,
x
n
x1,x2,x3,x4...,x_{n}
x1,x2,x3,x4...,xn
一定数量L 为:
3
3
3(移动平均的窗口长度)
则:
移动平均值:
x
1
+
x
2
+
x
3
3
,
x
2
+
x
3
+
x
4
3
,
x
3
+
x
4
+
x
5
3
,
x
4
+
x
5
+
x
6
3
.
.
.
.
.
.
\cfrac{x1+x2+x3}{3} , \cfrac{x2+x3+x4}{3},\cfrac{x3+x4+x5}{3},\cfrac{x4+x5+x6}{3}......
3x1+x2+x3,3x2+x3+x4,3x3+x4+x5,3x4+x5+x6......
代码(C#)
int len = (int)simpleLenUpDown.Value; //移动平均的窗口长度
simpleList.Clear();//移动平均值队列
List<double> bufferList = new List<double>();//移动平均窗口队列
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
if (i >= sourceList.Count)
break;
bufferList.Add(sourceList[i]);
simpleList.Add(sourceList[i]);
}
for (int i = len; i < sourceList.Count; i++)
{
simpleList.Add(bufferList.Average());
bufferList.RemoveAt(0);
bufferList.Add(sourceList[i]);//移动
}
//刷新结果
chartControl.BeginInit();
Series series = new Series(simpleStr, ViewType.Line);
series.Label.ResolveOverlappingMode = ResolveOverlappingMode.HideOverlapped;
for (int i = 0; i < simpleList.Count; i++)
{
SeriesPoint seriesPoint = new SeriesPoint(i, simpleList[i]);
series.Points.Add(seriesPoint);
}
chartControl.Series.Add(series);
series.ArgumentScaleType = ScaleType.Numerical;
chartControl.EndInit();
效果图
移动平均的窗口长度L=5

移动平均的窗口长度L=50

分析
两张效果图已经很明细了,窗口L如果太小,则平滑效果不好。
窗口L如果太大,则会有明显的迟滞效应。
所以这种简单移动平均的应用很有局限性,需要你小心的调整这个窗口L的大小。
加权移动平均
原理
主要方法是,通过给较近的数值分配较高的权重,给较远的数值分配较低的权重。
主要目的是,在有不错的平滑效果情况下,尽量的减少其迟滞效应,更能反映当前的真值和未来的预测值。
权重分配的方法有很多,用的比较多的是线性法和指数法。以下以线性加权移动平均为例。
假设:
原始测定值为:
x
1
,
x
2
,
x
3
,
x
4...
,
x
n
x1,x2,x3,x4...,x_{n}
x1,x2,x3,x4...,xn
一定数量L 为:
3
3
3(移动平均的窗口长度)
则:
线性加权移动平均值:
1
×
x
1
+
2
×
x
2
+
3
×
x
3
3
,
1
×
x
2
+
2
×
x
3
+
3
×
x
4
3
,
1
×
x
3
+
2
×
x
4
+
3
×
x
5
3
,
1
×
x
4
+
2
×
x
5
+
3
×
x
6
3
.
.
.
.
.
.
\cfrac{1 \times x1+ 2 \times x2+3 \times x3}{3} , \cfrac{1 \times x2+2 \times x3+3 \times x4}{3},\cfrac{1 \times x3+2 \times x4+3 \times x5}{3},\cfrac{1 \times x4+2 \times x5+3 \times x6}{3}......
31×x1+2×x2+3×x3,31×x2+2×x3+3×x4,31×x3+2×x4+3×x5,31×x4+2×x5+3×x6......
代码(C#)
private double getWeightListAverage(List<double> bufferList)
{
double sum = 0;
int sumIndex = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < bufferList.Count; i++)
{
sumIndex += i;
sum += (i * bufferList[i]);
}
return sum / sumIndex;
}
private void weightUpdateBtn_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
removeSeries(weightStr);
int len = (int)weightLenUpDown.Value;
weightList.Clear();
List<double> bufferList = new List<double>();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
if (i >= sourceList.Count)
break;
bufferList.Add(sourceList[i]);
weightList.Add(sourceList[i]);
}
for (int i = len; i < sourceList.Count; i++)
{
weightList.Add(getWeightListAverage(bufferList));
bufferList.RemoveAt(0);
bufferList.Add(sourceList[i]);
}
chartControl.BeginInit();
Series series = new Series(weightStr, ViewType.Line);
series.Label.ResolveOverlappingMode = ResolveOverlappingMode.HideOverlapped;
for (int i = 0; i < weightList.Count; i++)
{
SeriesPoint seriesPoint = new SeriesPoint(i, weightList[i]);
series.Points.Add(seriesPoint);
}
chartControl.Series.Add(series);
series.ArgumentScaleType = ScaleType.Numerical;
chartControl.EndInit();
}
效果图
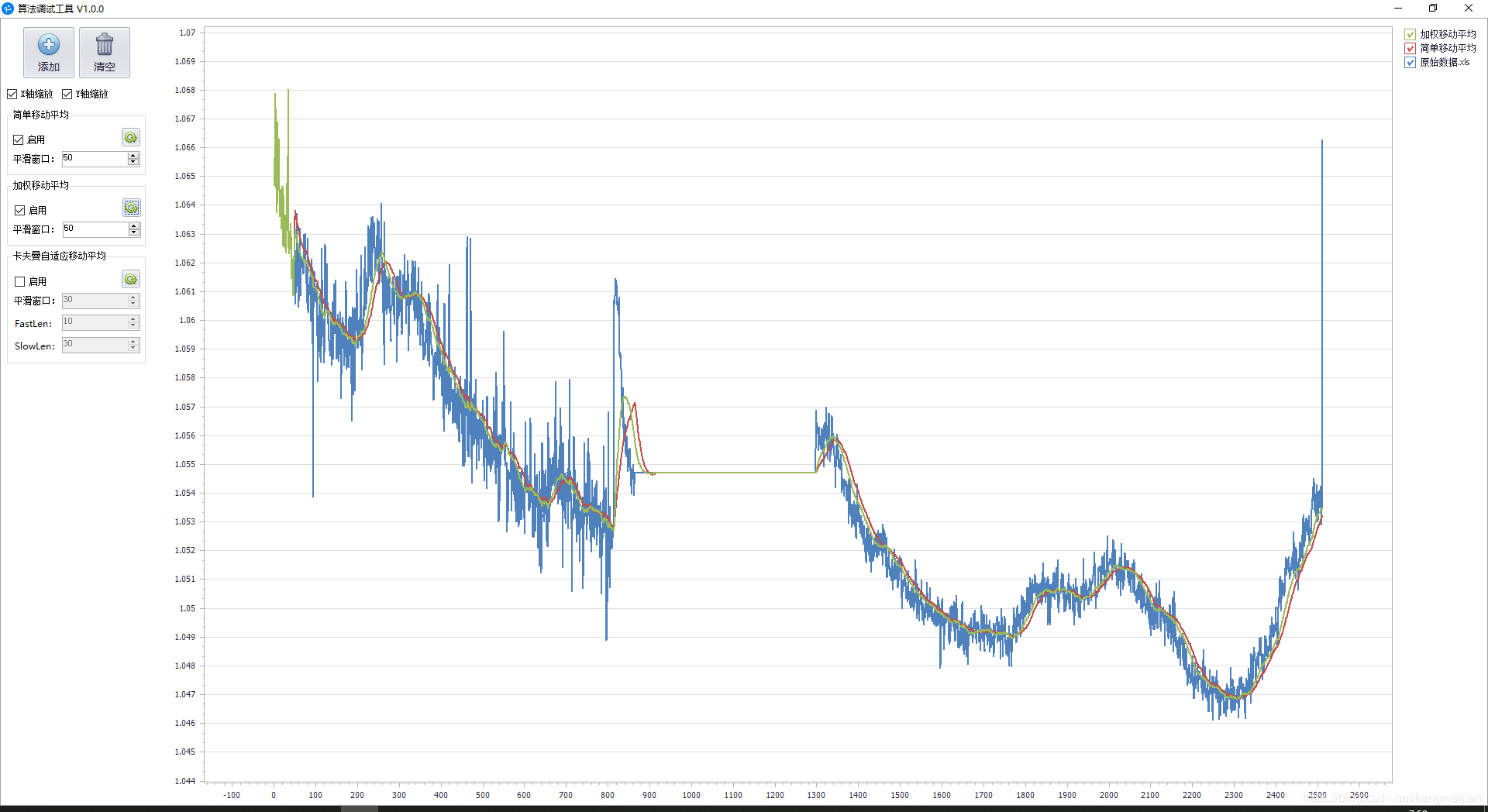
卡夫曼自适应移动平均
原理
卡夫曼自适应移动不同于以上两种的移动平均算法,它既能快速反应当前的真值和预测值,又能又较好的平滑效果。
原始测定值为:
x
1
,
x
2
,
x
3
,
x
4...
,
x
n
x1,x2,x3,x4...,x_{n}
x1,x2,x3,x4...,xn
窗口长度:
L
L
L
短(快)周期长度:
f
a
s
t
L
e
n
fastLen
fastLen
长(慢)周期长度:
s
l
o
w
L
e
n
slowLen
slowLen
波动性
v
o
l
=
∑
i
i
+
L
∣
x
i
−
x
i
+
1
∣
vol = \sum_{i}^{i+L} \left| x_i-x_{i+1} \right|
vol=∑ii+L∣xi−xi+1∣
方向性
d
i
r
e
c
t
i
o
n
=
∣
x
i
−
x
i
−
L
∣
direction= \left| x_i-x_{i-L} \right|
direction=∣xi−xi−L∣
效率系数
e
r
=
d
i
r
e
c
t
i
o
n
v
o
l
er = \cfrac{direction}{vol}
er=voldirection
短周期均线系数
f
a
s
t
e
s
t
=
2
f
a
s
t
L
e
n
+
1
fastest = \cfrac{2}{fastLen+1}
fastest=fastLen+12
长周期均线系数
s
l
o
w
e
s
t
=
2
s
l
o
w
L
e
n
+
1
slowest= \cfrac{2}{slowLen+1}
slowest=slowLen+12
平滑系数
s
m
o
o
t
h
=
e
r
×
(
f
a
s
t
e
s
t
−
s
l
o
w
e
s
t
)
+
s
l
o
w
e
s
t
smooth= er \times (fastest - slowest) + slowest
smooth=er×(fastest−slowest)+slowest
c
=
s
m
o
o
t
h
×
s
m
o
o
t
h
c=smooth \times smooth
c=smooth×smooth
公式
a
m
a
=
l
a
s
t
A
m
a
+
c
×
(
x
i
−
l
a
s
t
A
m
a
)
;
ama = lastAma + c \times (x_i - lastAma);
ama=lastAma+c×(xi−lastAma);
代码(C#)
int len = (int)amaLenUpDown.Value;
int fastLen = (int)amaFastLenUpDown.Value;
int slowLen = (int)amaSlowLenUpDown.Value;
amaList.Clear();
double ama=0, lastAma=0;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
if (i >= sourceList.Count)
break;
lastAma = sourceList[i];
ama = lastAma;
amaList.Add(ama);
}
for (int i = len; i < sourceList.Count; i++)
{
double direction = 0, er = 0, smooth= 0, c = 0, vol = 0;
double fastest = 2.0 / (fastLen + 1);
double slowest = 2.0 / (slowLen + 1);
for (int j = i-len; j < i-1; j++)
vol += Math.Abs(sourceList[j] - sourceList[j + 1]);
if (vol != 0)
{
direction = Math.Abs(sourceList[i] - sourceList[i - len]);
er = direction / vol;
smooth1 = er * (fastest - slowest) + slowest;
c = smooth * smooth;
ama = lastAma + c * (sourceList[i] - lastAma);
if (c>1000)
{ //防止大跳跃,大突变
ama = sourceList[i];
}
lastAma = ama;
}
else
{
ama = lastAma;
}
amaList.Add(ama);
}
chartControl.BeginInit();
Series series = new Series(amaStr, ViewType.Line);
series.Label.ResolveOverlappingMode = ResolveOverlappingMode.HideOverlapped;
for (int i = 0; i < amaList.Count; i++)
{
SeriesPoint seriesPoint = new SeriesPoint(i, amaList[i]);
series.Points.Add(seriesPoint);
}
chartControl.Series.Add(series);
series.ArgumentScaleType = ScaleType.Numerical;
chartControl.EndInit();
效果图

分析
不需要很大的窗口,就能有很好的平滑效果,且迟滞性很低。
这次分享到此结束,这类博客还有很多可以写的,后面希望能写出一个系列,分享更多更优更好的算法,迭代功能更强的算法调试工具。
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










