How to Use Grub Rescue to Fix Linux Boot Failure
------------------------------------------------------------------
要点:
如果要使用 boot-repair,最好使用 boot-repair-disk,这是一个在 Live cd 操作系统中自带的工具包。
单纯使用 boot-repair,如果采用 Ubuntu live cd,可能还会出现 “SMBus Host controller not enabled(虚拟机进入不了图形界面)” 问题需要处理。 https://blog.csdn.net/ken2232/article/details/134156698
======================================
What Is GRUB Bootloader in Linux? https://phoenixnap.com/kb/what-is-grub
How to Use GRUB Rescue to Fix Linux https://www.howtogeek.com/887757/how-to-use-grub-rescue-to-fix-linux/
How to Use Grub Rescue to Fix Linux Boot Failure
Introduction
The GRUB (Grand Unified Bootloader) is a tool for booting and loading operating system kernels and the default bootloader for systems based on the Linux kernel. Although it runs first when a machine is turned on, regular users rarely see GRUB in action. It functions automatically and requires no user input.
However, when attempting to boot another operating system alongside Linux on the same machine, the other system's bootloader may overwrite GRUB, resulting in the inability of the Linux system to boot up.
This article will show you how to fix Linux boot failure using GRUB Rescue commands and the Boot Repair tool.
Prerequisites
- An account with sudo privileges.
- Access to the command line.
Note: The tutorial below is written for GRUB 2, the current iteration of the GRUB bootloader.
GRUB Boot Issues
The most common reason for GRUB not booting into the operating system is another OS's bootloader overwriting GRUB boot configuration. The problem occurs during an attempt a dual boot with an existing Linux installation. Another reason is the accidental removal of GRUB configuration files.
When GRUB is not able to boot the system, the GRUB Rescue prompt appears.

The example above shows GRUB displaying the "no such partition" error before displaying the grub rescue prompt. Another common GRUB error is "unknown filesystem", followed by the same prompt.

Sometimes, the screen may show the grub prompt only.
![]()
GRUB Rescue Commands
Below is the list of the commonly used GRUB Rescue commands. Use the commands in the prompts mentioned in the previous section.
| Command | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
boot | Start booting (shortcuts: F10, CTRL + x). | The command is issued without arguments. |
cat | Write the contents of a file to standard output. | cat (hd0,1)/boot/grub/grub.cfg |
configfile | Load a configuration file. | configfile (hd0,1)/boot/grub/grub.cfg |
initrd | Load the initrd.img file. | initrd (hd0,1)/initrd.img |
insmod | Load a module. | insmod (hd0,1)/boot/grub/normal.mod |
loopback | Mount an image file as a device. | loopback loop0 (hd0,1)/iso/image.iso |
ls | Display the contents of a directory or partition. | ls (hd0,1) |
lsmod | Display a list of loaded modules. | The command is issued without arguments. |
normal | Activate the normal module. | The command is issued without arguments. |
search | Search for devices. Option --file searches for files, --label searches for labels, --fs-uuid searches for filesystem UUID. | search -file [filename] |
set | Set an environment variable. If issued with no arguments, the command prints the list of all environment variables and their values. | set [variable-name]=[value] |
Fixing Boot Failure
This tutorial covers two ways to resolve GRUB boot issues, using the GRUB Rescue prompt, and the Boot Repair tool.
Via Grub Terminal
1. Use the set command with no arguments to view the environment variables:
setThe example output shows that GRUB is set up to boot from (hd0,msdos3) partition:

2. The ls command lists the available partitions on the disk.
lsThe output shows the partition list.

Use the ls command to find the partition containing the boot directory.
ls [partition-name]The example shows the boot directory in the (hd0,msdos1) partition.
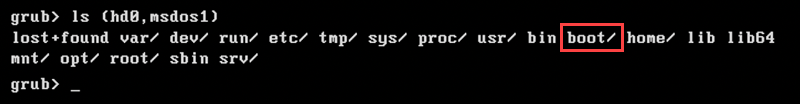
3. Set the boot partition as the value of the root variable. The example uses the partition named (hd0,msdos1).
set root=(hd0,msdos1)4. Load the normal boot mode.
insmod normal5. Start the normal boot mode.
normalThe normal mode enables you to issue more complex commands.
6. Load the Linux kernel using the linux command.
linux /boot/vmlinuz-4.2.0-16-generic root=/dev/sda1 ro7. Issue the boot command.
bootThe system now boots properly.
Via Live image
Another way to fix your GRUB boot issues is to use a Linux live image to boot from an external device.
1. Download a live Linux installer. This example uses the Ubuntu 20.04 ISO image.
2. Use a tool such as Etcher to write the Linux image to an SD card or a USB flash drive.
3. Insert the bootable device and start the computer.
4. Select Try Ubuntu on the welcome screen.

5. When the live system boots up, connect to the internet.
6. Open the terminal and type the following command to add the repository for the Boot Repair tool.
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:yannubuntu/boot-repair
Press Enter and wait for the repository to be added.
7. Update the repositories.
sudo apt update8. Install the Boot Repair tool.
sudo apt install boot-repair9. Start the Boot Repair tool via the terminal.
boot-repair10. Select Recommended repair.

Wait for the tool to finish repairing the bootloader.
Note: The Boot Repair tool is available as a live image, so you can boot it from an external drive without using another live OS.
Updating GRUB config file
When the system successfully boots up, make sure the GRUB configuration is up to date.
Run this command:
update-grub
Reinstalling GRUB
Follow the steps below to reinstall GRUB on your Linux system.
1. Mount the partition containing the OS installation. The example mounts the /dev/sda1 partition to the /mnt directory.
sudo mount /dev/sda1 /mnt2. Bind the /dev, /dev/pts, /proc, and /sys directories to the corresponding directories in the /mnt folder.
sudo mount --bind /dev /mnt/dev &&
sudo mount --bind /dev/pts /mnt/dev/pts &&
sudo mount --bind /proc /mnt/proc &&
sudo mount --bind /sys /mnt/sys3. Install GRUB.
sudo grub-install -root-directory=/mnt/ /dev/sda
4. Unmount the directories when the installation completes successfully.
sudo umount /mnt/sys &&
sudo umount /mnt/proc &&
sudo umount /mnt/dev/pts &&
sudo umount /mnt/dev &&
sudo umount /mntConclusion
After reading this article, you should be able to fix your Linux boot failure using GRUB Rescue or Boot Repair utilities. For another way to fix your boot-related issues, read How to Use fsck Command.
:https://phoenixnap.com/kb/grub-rescue










 本文详细介绍了如何使用GRUBRescue来解决Linux启动失败问题,包括在遇到SMBusHostController问题时的处理方法,以及通过GRUBRescue命令行和BootRepair工具进行修复的步骤。
本文详细介绍了如何使用GRUBRescue来解决Linux启动失败问题,包括在遇到SMBusHostController问题时的处理方法,以及通过GRUBRescue命令行和BootRepair工具进行修复的步骤。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








