作者:朱金灿
来源:http://blog.csdn.net/clever101
首先请先编译或安装boost库,使用CodeBlocks编译boost库具体见:Boost库在CodeBlocks环境下的编译。
以下内容主要翻译自:BoostWindows Quick Ref ,我所用的编译环境为Win 7家庭版,CodeBlocks V10.05, mingw32 v4.4.1,boostv1.42
1. 为boost库创建一个CodeBlocks全局变量
1)打开“Settings”菜单——>"Global variables..."菜单项,弹出如下对话框,单击下图的对话框上的New按钮,
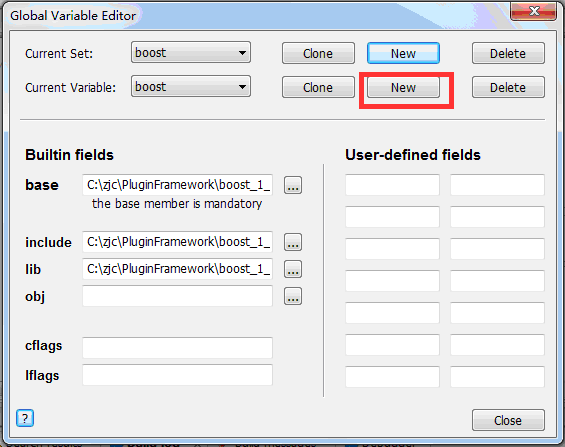
2) 在弹出的对话框上输入你要新建的全部变量名,例如boost,如下图:

3)设置全局变量的base目录、lib目录和include目录,具体如下图:

Base目录为你的boost安装目录,也是你在编译boost库的—prefix选项的参数值,如:
你的bjam命令为:
bjam install--toolset=gcc--prefix="C:\zjc\PluginFramework\boost_1_42_0"--build-type=complete
那么base目录为C:\zjc\PluginFramework\boost_1_42_0
Include和lib目录很容易理解,就是boost库的头文件和库文件所在的目录。
现在我们使用一下这个全局变量,
1. CodeBlocks新建一个控制台工程TestConsole,敲入如下代码:
- <SPAN style="FONT-SIZE: 18px"> #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <iostream>
- using std::cout;
- using std::wcout;
- using std::endl;
- #include <string>
- using std::string;
- using std::wstring;
- #include <boost/algorithm/string.hpp>
- #include <boost/filesystem/path.hpp>
- #include "boost/filesystem/operations.hpp"
- #include <boost/format.hpp>
- int main()
- {
- // ANSI字符的格式化
- cout << boost::format( "%1% %2%" ) % "Hell" % "Low" <<endl;
- string s1 = boost::str( boost::format( "%2% %1%" ) % "Hell" % "Low" );
- cout << s1 << endl;
- // UNICODE字符的格式化
- wcout << boost::wformat( L"%s %X" ) % L"-1 is" % -1 << endl;
- wstring s2 = boost::str( boost::wformat( L"%2$s %1$.2f" ) % 3.141592 % L"Version" );
- wcout << s2 << endl;
- // 获取应用程序所在目录(ANSI字符),注意是boost::filesystem::path
- string AnsiPath = boost::filesystem::initial_path<boost::filesystem::path>().string();
- cout<<AnsiPath<<endl;
- // 获取应用程序所在目录(UNICODE字符),注意是boost::filesystem::wpath
- wstring UnicodePath = boost::filesystem::initial_path<boost::filesystem::wpath>().string();
- wcout<<UnicodePath<<endl;
- system("PAUSE");
- return 0;
- }
- </SPAN>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::wcout;
using std::endl;
#include <string>
using std::string;
using std::wstring;
#include <boost/algorithm/string.hpp>
#include <boost/filesystem/path.hpp>
#include "boost/filesystem/operations.hpp"
#include <boost/format.hpp>
int main()
{
// ANSI字符的格式化
cout << boost::format( "%1% %2%" ) % "Hell" % "Low" <<endl;
string s1 = boost::str( boost::format( "%2% %1%" ) % "Hell" % "Low" );
cout << s1 << endl;
// UNICODE字符的格式化
wcout << boost::wformat( L"%s %X" ) % L"-1 is" % -1 << endl;
wstring s2 = boost::str( boost::wformat( L"%2$s %1$.2f" ) % 3.141592 % L"Version" );
wcout << s2 << endl;
// 获取应用程序所在目录(ANSI字符),注意是boost::filesystem::path
string AnsiPath = boost::filesystem::initial_path<boost::filesystem::path>().string();
cout<<AnsiPath<<endl;
// 获取应用程序所在目录(UNICODE字符),注意是boost::filesystem::wpath
wstring UnicodePath = boost::filesystem::initial_path<boost::filesystem::wpath>().string();
wcout<<UnicodePath<<endl;
system("PAUSE");
return 0;
}
2. 在工程树节点上右键单击,在弹出的右键菜单上单击Build Option…菜单项,如下图:

3.在弹出的对话框中选择Search directories选项卡,然后单击对话框中的add按钮,在弹出的对话框中输入:$(#boost),具体如下图:
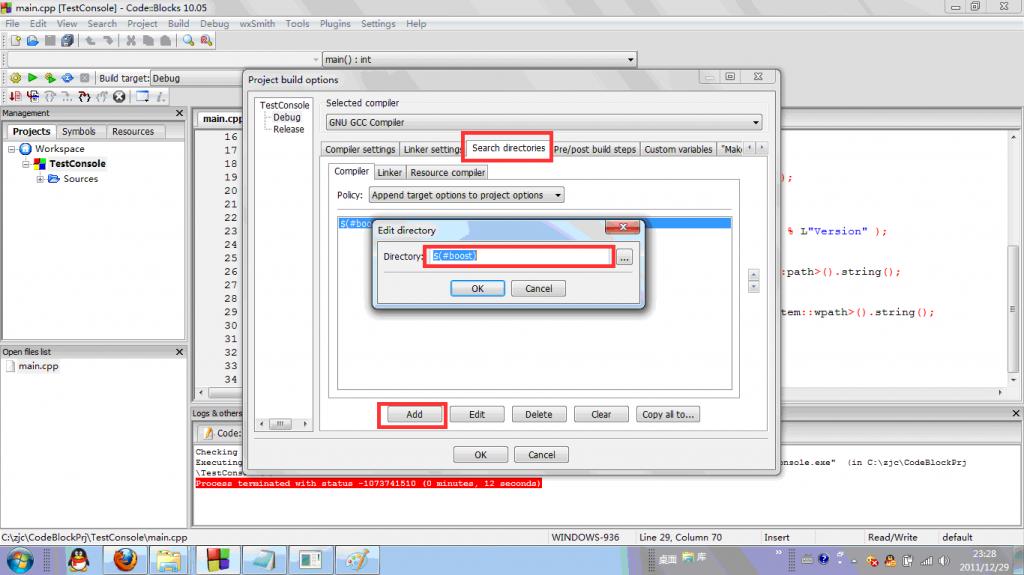
看到这,你可能觉得比较熟悉,这个CodeBlocks全局变量不相当于一个操作系统环境变量吗?是的,它起的正是这个作用。
4.选择“Linker setting”选项卡,填入你的工程要链接到到的具体的boost库,具体如下图:
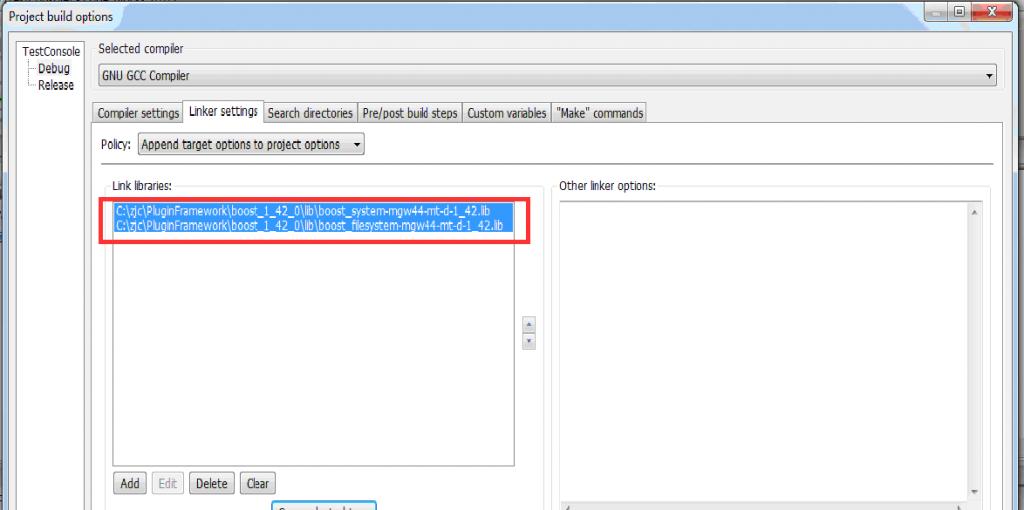
一个小小的问题,在使用boost库时只需在定义了BOOST_ALL_DYN_LINK宏,同时指定了库文件所在的文件夹就能实现自动链接而不必指定要链接到的具体库,这个我在VS环境下已经多次使用过,但我在CodeBlocks下定义了BOOST_ALL_DYN_LINK,如下图:

但是还是得指定链接到的具体库,这是为什么呢?知道的大侠请具体指点下。
参考文献:






















 288
288

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








