什么是程序库?
库是写好的现有的,成熟的,可以复用的代码。现实中每个程序都要依赖很多基础的底层库,不可能每个人的代码都从零开始,因此库的存在意义非同寻常。比如你经常使用的STL(Standard Template Library)也是库,有了STL你才能方便地使用std::string、std::cout这些类。
本质上来说库是一种可执行代码的二进制形式,可以被操作系统载入内存,被别的程序调用执行。C++的库有两种:静态库和动态库。将一个程序编译成可执行文件一般经过 预编译–>编译–>链接 这几个过程,而静态库与动态库的区别主要体现在链接这个过程。
静态库:
在链接阶段,会将编译的目标文件.obj 与引用到的库.lib 一起链接打包到可执行文件exe(也称为目标代码)中,程序运行时将不再需要该静态库。
因此最终链接成的可执行文件(.exe)体积较大。在Windows中一般以.lib为后缀名,在Linux中一般以.a为后缀名。
动态库:
在链接阶段,动态库.dll并没有真正被连接到目标代码中,只是将这个动态库的声明链接到目标代码中(这样程序运行时才知道怎样使用这个动态库),动态库.dll依然是独立存在的,只有在程序运行是才会将.dll载入到内存中被程序调用。因此程序运行时必须要有这个动态库且放在正确的路径中。
因此最终链接成的可执行文件(.exe)体积较小。在Windows中一般以.dll为后缀名,在Linux中一般以.so为后缀名。
静态库与动态库的区别:
| 特点 | 静态库 | 动态库 |
|---|
| 对函数库的链接时机 | 在编译的链接阶段完成的 | 推迟到程序运行的时期 |
| 运行过程与库的关系 | 程序在运行时与静态库再无瓜葛 | 程序在运行时与动态库库需要一直存在且路径正确 |
| 是否链接到可执行文件 | 静态库被链接合成一个可执行文件 | 动态库不会被链接到可执行文件中 |
| 目标文件大小 | 体积较大 | 体积较小 |
| 内存占用度 | 占用内存。如果多个程序使用了同一个静态库,每一个程序者会包含这个静态库 | 节约内存。如果多个程序使用了同一个动态库,可以实现进程之间的资源共享(因此动态库也称为共享库) |
| 程序移植 | 移植方便 | 移植不太方便,需要所有动态库的头文件 |
| 程序升级 | 程序升级麻烦,需要下载整个程序进行升级 | 程序升级更简单,只需要升级某个DLL或某个程序,下载一个升级包即可 |
| 编译出的结果文件 | ProjectName.lib | ProjectName.lib+ProjectName.dll, 这里的ProjectName.lib与静态库的.lib文件不同,这只是一个导入库,只包含了地址符号表等,以便调用方的程序能找到对应的函数,真正的库文件是ProjectName.dll |
编译自己的工程库
假设我们有这样一个工程,这个工程的作用就是提供一些常用的工具类和方法,然后我们要将这个工程编译成库提供给别人使用。
编译静态库
假设我们已经建好工程并写好了相应的代码:
工程目录
Utils.h:
- //===============================================================
- //Summary:
- // Utils 类, 工具类
- //FileName:
- // Utils.h
- //Remarks:
- // ...
- //Date:
- // 2015/10/4
- //Author:
- // Administrator(luoweifu@126.com)
- //===============================================================
-
- #ifndef __UTILS_H__
- #define __UTILS_H__
-
- #include <string>
- #include <strstream>
- //#include <cstdlib>
-
- class Utils
- {
- public:
- Utils(void);
- ~Utils(void);
-
- public:
- //---------------------------------------------------------------
- //function:
- // WString2String wstring 到 string 的转换
- //Access:
- // public
- //Parameter:
- // [in] const std::wstring & ws - wstring字符串
- //Returns:
- // std::string - string字符串
- //Remarks:
- // 些方法跨平台,可移植版本
- //author: luoweifu
- //---------------------------------------------------------------
- static std::string WString2String(const std::wstring& ws);
-
- //---------------------------------------------------------------
- //function:
- // String2WString string 到 wstring 的转换
- //Access:
- // public
- //Parameter:
- // [in] const std::string & s - string 字符串
- //Returns:
- // std::wstring - wstring字符串
- //Remarks:
- // 些方法跨平台,可移植版本
- //author: luoweifu
- //---------------------------------------------------------------
- static std::wstring String2WString(const std::string& s);
-
- };
-
- //---------------------------------------------------------------
- //function:
- // ConvertToString 将int转换成string
- //Parameter:
- // [in] int val - 要转换的变量
- //Returns:
- // std::string - 转换后的字符串
- //Remarks:
- // ...
- //author: luoweifu
- //---------------------------------------------------------------
- std::string ConvertToString(int val);
-
- #endif //__UTILS_H__
上述声明的实现参考后面的附录Utils.cpp。
要编译成静态库,我们可以这样设置我们的工程:
右键工程->Properties
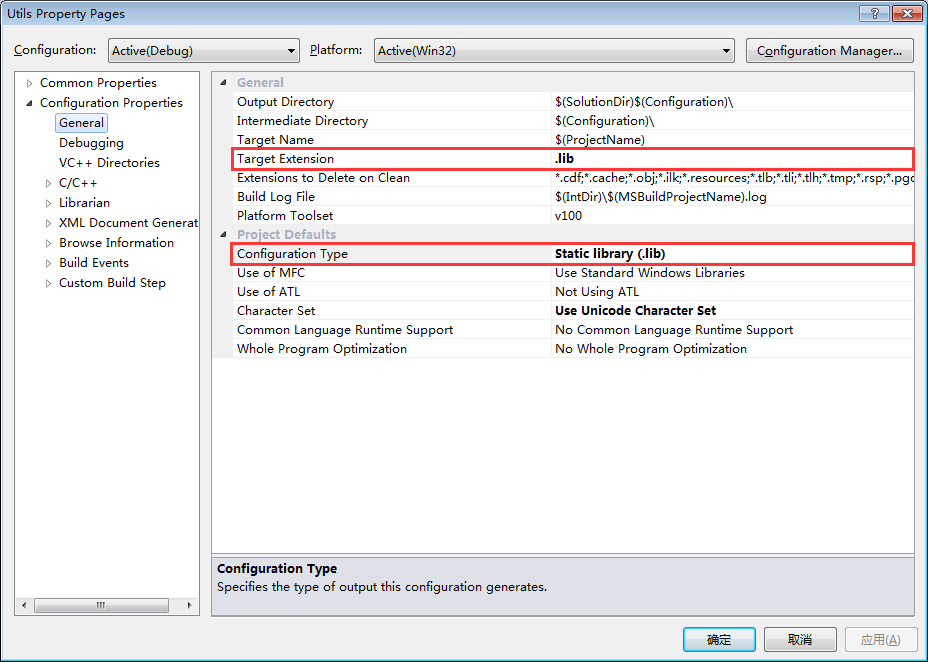
编译成静态库
然后右键Build就可以了,你可以在解决方案下的Debug(实际的情况中一般要编译成Release版本,设置的方法一样,这里的内容后一章中再讲)目录下就能看到Utils.lib,这就是编译出的库。要将这个库给别人使用,只要提供这个Utils.lib和这个工程的头文件就可以。将Utils.h拷贝到D:\ReleaseLibs\StaticLib\Includes,将Utils.lib拷贝到D:\ReleaseLibs\StaticLib\Libs,把D:\ReleaseLibs\StaticLib这个文件提供出去就可以了。静态库的使用请看后一小节使用静态库
编译动态库
与静态库相比,编译动态库要麻烦一些,一般要在导出函数的声明处加上_declspec(dllexport)关键字前缀。
1. *Utils.h的声明如下
- //===============================================================
- //Summary:
- // Utils 类, 工具类
- //FileName:
- // Utils.h
- //Remarks:
- // ...
- //Date:
- // 2015/10/4
- //Author:
- // Administrator(luoweifu@126.com)
- //===============================================================
-
- #ifndef __UTILS_H__
- #define __UTILS_H__
-
- #include <string>
- #include <strstream>
- //#include <cstdlib>
-
- //===============================================================
-
- //===============================================================
-
- class Utils
- {
- public:
- Utils(void);
- ~Utils(void);
-
- public:
- //---------------------------------------------------------------
- //function:
- // Max 获得两个数中的最大值
- //Access:
- // public
- //Parameter:
- // [in] int nValue1 - 第一个数
- // [in] int nValue2 - 每二个数
- //Returns:
- // int - 最大值
- //Remarks:
- // ...
- //author: luoweifu
- //---------------------------------------------------------------
- static int Max(int nValue1, int nValue2);
-
- //---------------------------------------------------------------
- //function:
- // Min 获得两个数中的最小值
- //Access:
- // public
- //Parameter:
- // [in] int nValue1 - 第一个值
- // [in] int nValue2 - 第二个值
- //Returns:
- // int - 最小值
- //Remarks:
- // ...
- //author: luoweifu
- //---------------------------------------------------------------
- static int Min(int nValue1, int nValue2);
-
- //---------------------------------------------------------------
- //function:
- // Range 将一值限定在一个范围内
- //Access:
- // public
- //Parameter:
- // [in] int nMin - 最小值
- // [in] int nMax - 最大值
- //Returns:
- // int - 返回在限制在该范围内的一个值
- //Remarks:
- // ...
- //author: luoweifu
- //---------------------------------------------------------------
- static int Range(int nMin, int nMax, int nValue);
- };
-
-
- //---------------------------------------------------------------
- //function:
- // ConvertToInt 将一个常量字符串转换成int类型数据
- //Access:
- // public
- //Parameter:
- // [in] const char * pStr - 常量字符串
- //Returns:
- // int - 转换成的int值
- //Remarks:
- // ...
- //author: luoweifu
- //---------------------------------------------------------------
- int ConvertToInt(const char* pStr);
-
- #endif //__UTILS_H__
- 要编译成动态库,我们可以这样设置我们的工程:
右键工程->Properties
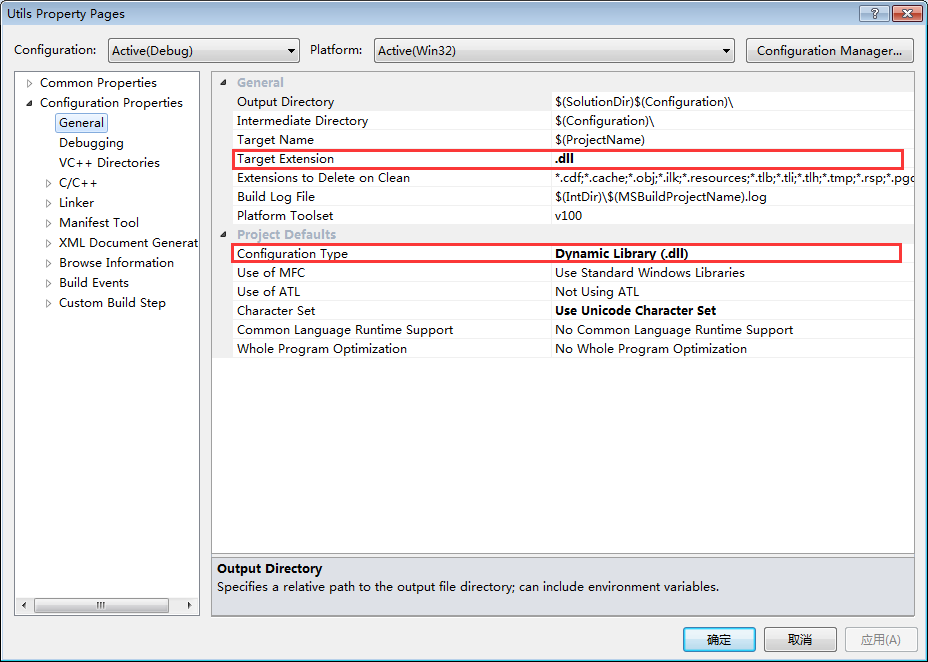
设置编译的目标类型
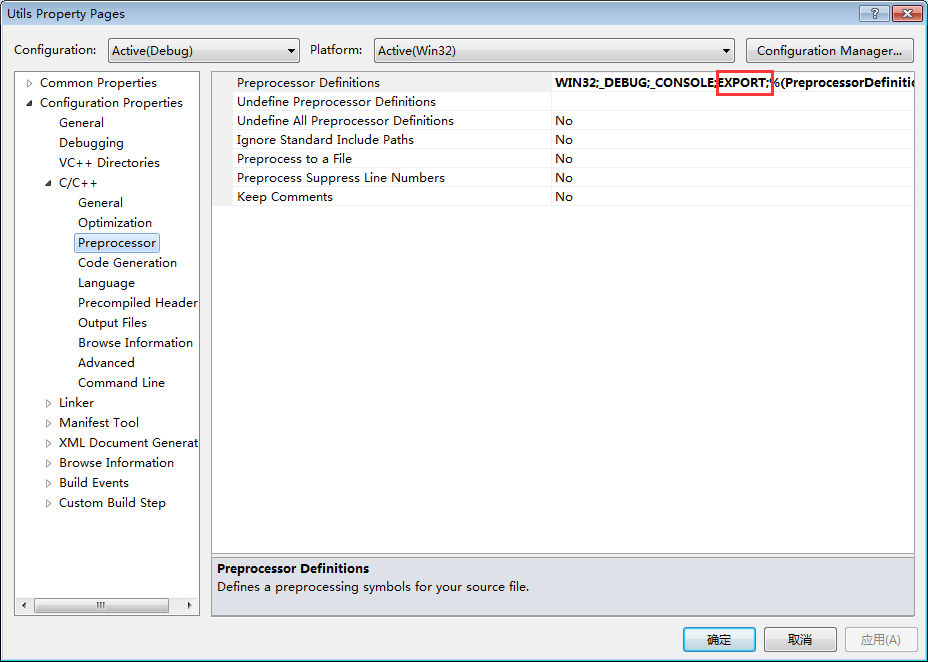
设置预编译宏
然后右键Build就可以了,你可以在解决方案下的Debug(实际的情况中一般要编译成Release版本,设置的方法一样,这里的内容后一章中再讲)目录下就能看到Utils.dll和Utils.lib,这就是编译出的库。要将这个库给别人使用,只要提供这个Utils.dll、Utils.lib和这个工程的头文件就可以。将Utils.h拷贝到D:\ReleaseLibs\DynamicLib\Includes,将Utils.dll和Utils.lib拷贝到D:\ReleaseLibs\DynamicLib\Libs,把D:\ReleaseLibs\DynamicLib这个文件提供出去就可以了。动态库的使用请看后一小节使用动态库
也许你要问为什么编译出的静态库是Utils.lib,编译出的动态库也有Utils.lib,这两个.lib文件是一样的吗?
你比较一下两个.lib文件的大小就会发现相差很大(静态库的lib有235KB,动态库的lib只有2.7KB),所以肯定不是一样的啦!动态库对应的lib文件叫“导入库”,导入库只包含了地址符号表等,确保调用方的程序能找到对应函数的一些基本地址信息,而实际的执行代码位于DLL文件中。静态库的lib文件本身就包含了实际执行代码、符号表等。
使用导入(第三方)库
在实际的开发中经常要用第三方提供的库,如开源库,或大型系统中合作方提供的组件。如果使用呢?我们就以上面自己制作的库为例进行讲解。假设我们有一个工程TestProject要使用上面自己制作的Utils库。
使用静态库
-
右键工程->Properties,进行如下的设置。
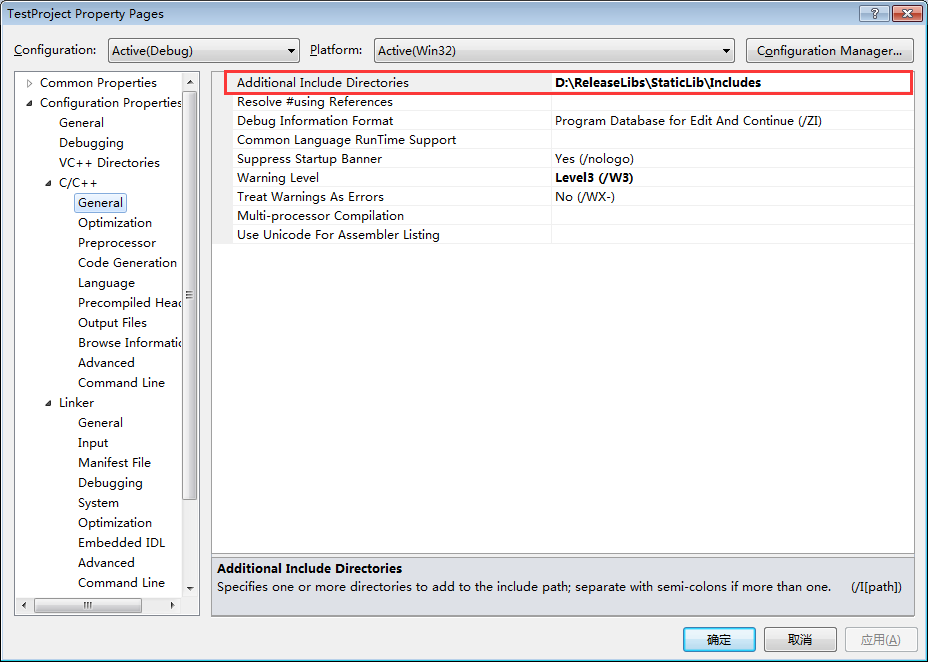
设置头文件所在的路径
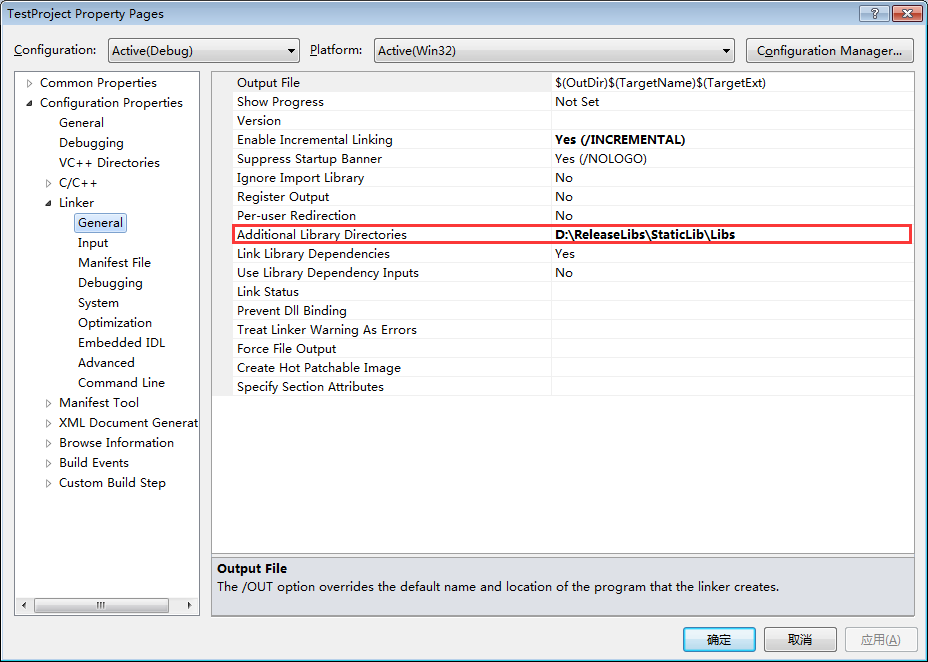
设置lib库所在的路径
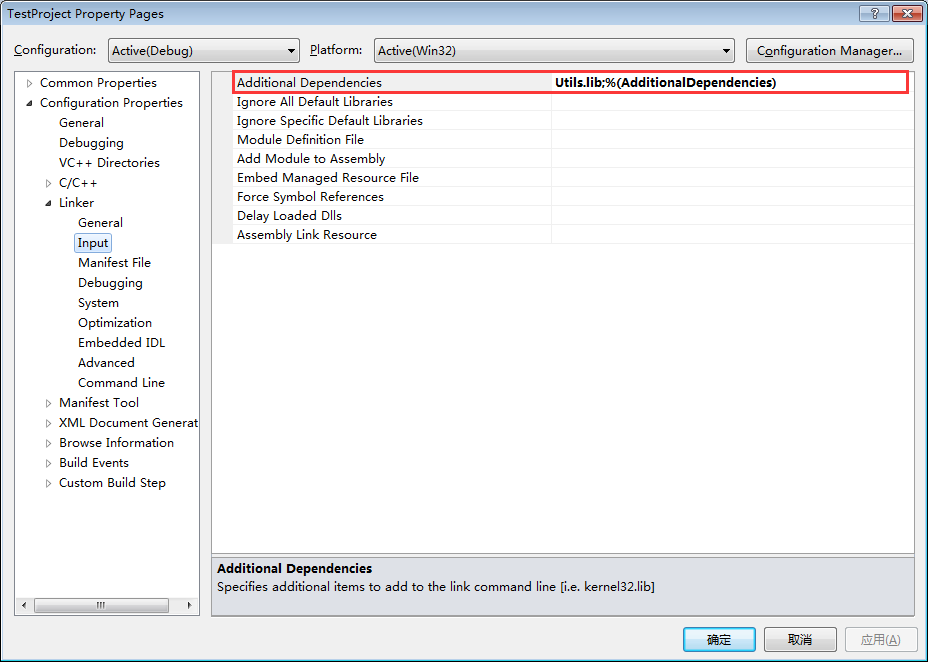
设置要导入哪个lib库
-
测试代码如下:
- #include <iostream>
- #include <tchar.h>
- #include "Utils.h"
-
- int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
- {
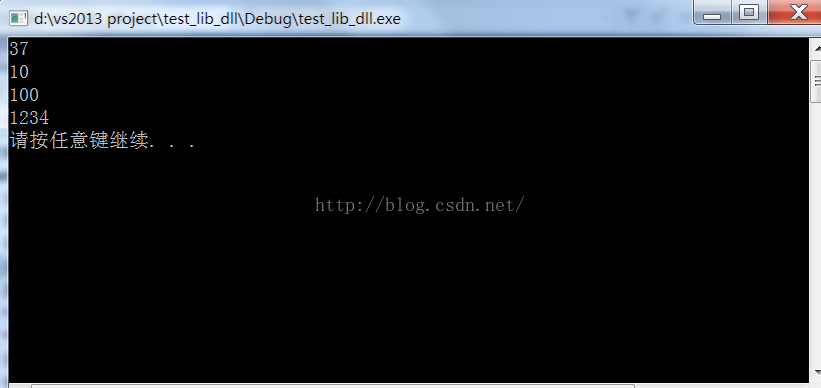
- int nMax = Utils::Max(25, 37);
- std::cout << nMax << std::endl;
- int nMin = Utils::Min(10, 44);
- std::cout << nMin << std::endl;
- int nValue = Utils::Range(0, 100, 115);
- std::cout << nValue << std::endl;
- char* pStr = "1234";
- int nValue2 = ConvertToInt(pStr);
- std::cout << nValue2 << std::endl;
- return 0;
- }
使用动态库
-
右键TestProject工程->Properties,进行如下的设置。
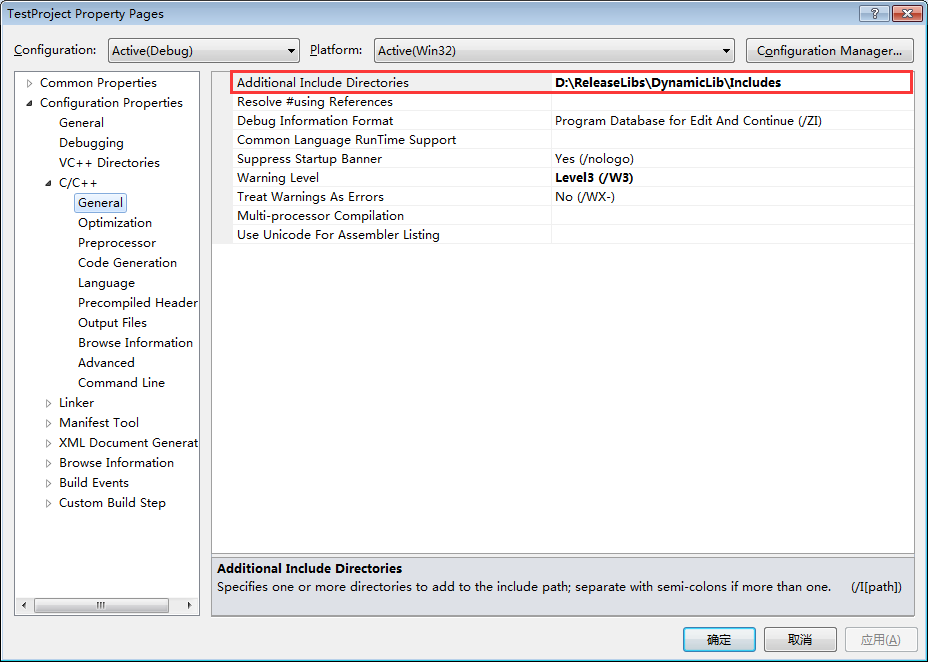
设置头文件所在的路径
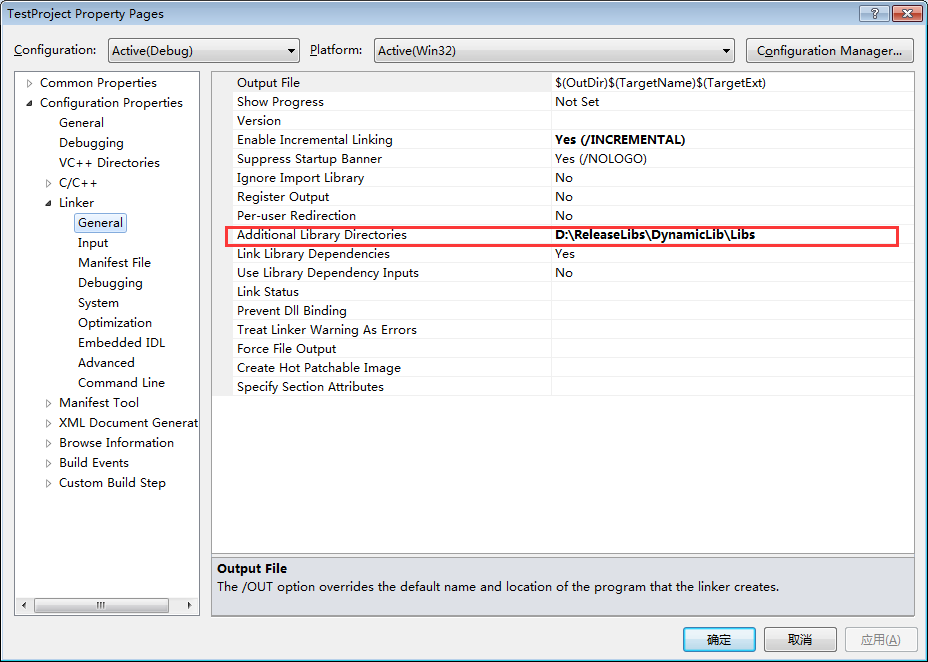
设置lib库所在的路径
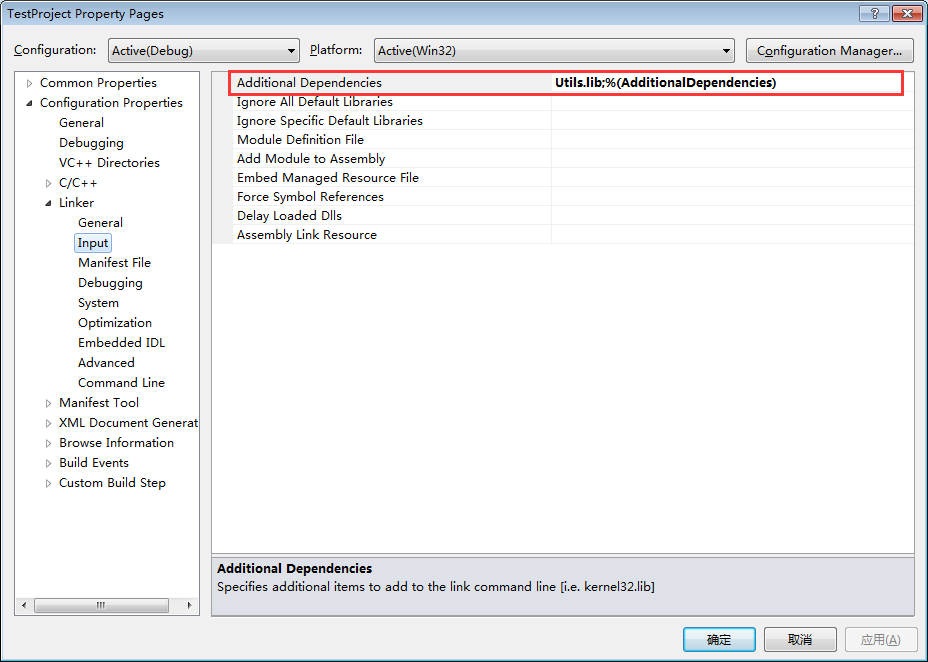
设置要导入哪个导入库
-
将Utils.dll放入与TestProject的输出文件TestProject.exe相同的路径下。这个很最重,不然会编译成功会是执行失败,因为找不到对应的.dll文件。
-
测试代码与静态库的一样。
附录
Utils.cpp
- #include "Utils.h"
-
- Utils::Utils(void)
- {
- }
-
- Utils::~Utils(void)
- {
- }
-
-
- int Utils::Max( int nValue1, int nValue2 )
- {
- return nValue1 > nValue2 ? nValue1 : nValue2;
- }
-
- int Utils::Min( int nValue1, int nValue2 )
- {
- return nValue1 < nValue2 ? nValue1 : nValue2;
- }
-
- int Utils::Range( int nMin, int nMax, int nValue )
- {
- if (nMax < nMin)
- {
- int temp = nMin;
- nMin = nMax;
- nMax = temp;
- }
-
- if (nValue < nMin)
- {
- return nMin;
- } else if (nValue > nMax)
- {
- return nMax;
- } else
- {
- return nValue;
- }
- }
-
- int ConvertToInt( const char* pStr )
- {
- int val;
- std::strstream ss;
- ss << pStr;
- ss >> val;
- return val;
- }
测试结果:
下面是一个非常赞的链接
推荐链接:
http://blog.csdn.net/luoweifu/article/category/5837703































 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








