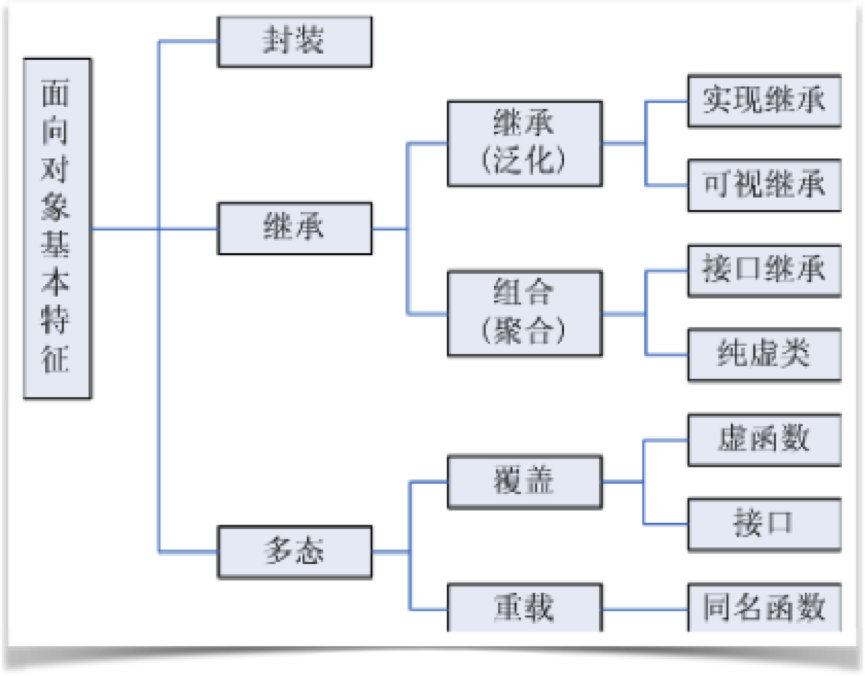
1.面向对象的3要素。
2.面向对象开发的6大原则。
1.单一职责原则
应该有且仅有一个原因引起类的变更。
2.里氏替换原则
只要父类能出现的地方,其子类就应该能出现。也就是用子类替换父类后,保证程序照样运行。
3.依赖倒置原则
面向接口编程。
4.接口隔离原则
接口细化,也就是接口中的方法要尽量少。
5.迪米特法则
也称为最少知识原则,其定义为:一个对象应当对其他对象有最少的了解。也就是一个类中不要有过多的其他类。
6.开闭原则
开闭原则的核心是:对扩展开放,对修改关闭。
3.圈复杂度(Cyclomatic Complexity,CC)
圈复杂度(以下简称CC)是一种度量方法,表明一个方法中执行路径的数量;
CC从1开始,每多一个条件语句(if,else,switch…case,while,for)CC值加1;
一个方法的CC值越大,表明该方法越复杂;
CC值指明了完全测试一个方法所需要的测试用例。
4.圈复杂度度量
CC∈[0,5]:代码质量不错;
CC∈[6,20]:可能存在需要拆分的代码,应该尽可能想办法重构;
CC∈[21, ∞ ):必须进行重构。如果你的代码CC经常达到这个水平,请重新整理Coding的思路;
请尽可能保证CC<10。
5.圈复杂度计算
V(G) = e – n + 2;
V(G):圈复杂度
e:程序流程图中的边数;
n:程序流程图中的节点数;
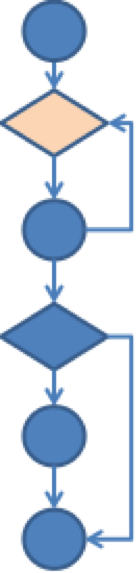
6.圈复杂度计算
代码:
void test() {
int cnt = 0;
for(int I = 0;I < 100;i++) {
cnt++;
}
if(cnt > 100) {
System.out.println();
}
…
}
相应流程图:


7.降低圈复杂度
方法一
提炼函数,抽取方法:
优化前:
Int getAppKey(String user, String package) {
String userId = “”;
String packageId = “”;
System.out.println(“=============”);
if(null == user) {
System.out.println(“user id is null.”);
} else {
userId = “user_” + id1;
System.out.println(“userid is ” + userId );
}
if(null == package) {
System.out.println(“packageId id is null.”);
} else {
packageId = “package_” + id2;
System.out.println(“packageId is ” + packageId );
}
System.out.println(“=============”);
return userId .hashCode() ^ packageId .hashCode();
}
优化后:
Int getAppKey(String user, String package) {
String userId = geId(“user_”, user);
String packageId = getId(“package_”, package);
printId(userId, packageId );
return userId .hashCode() ^ packageId .hashCode();
}
String getId(String head, String key) {
String id = “”;
if(key != null) {
id= head + user;
}
return id;
}
String getPrintInfo(String name, String value) {
String info = name + “is ” + value;
if(“”.equals(value)) {
info = name + “is null.”;
}
return id;
}
void printId(String userId , String packageId) {
System.out.println(“=============”);
System.out.println(getPrintInfo(“userId”, userId));
System.out.println(getPrintInfo(“packageId”, packageId));
System.out.println(“=============”);
}
方法二
用循环替代条件式:
优化前:
String getName(String id) {
String name = null;
if("0000".equals(id)) {
name = "小吴";
}
if("0001".equals(id)) {
name = "小王";
}
if("0002".equals(id)) {
name = "老赵";
}
if("0003".equals(id)) {
name = "小李";
}
if("0004".equals(id)) {
name = "小刘";
}
if("0005".equals(id)) {
name = "小张";
}
return name;
}
优化后:
private static String getName(String id) {
String name = null;
//当元素个数较多的时候,将数组替换成Map。数组对象可作为参数传入。
String[] idArray = new String[]{"0000", "0001", "0002", "0003", "0004", "0005"};
String[] nameArray = new String[]{"小吴", "小王", "老赵", "小李", "小刘", "小张"};
for(int i = 0;i < idArray.length;i++) {
Object peopleID = idArray[i];
if(peopleID.equals(id)) {
name = nameArray[i];
break;
}
}
return name;
}
方法三
用初始值消减条件分支:
优化前:
String getCode(String id) {
String code = "";
if(null == id) {
code = "0000";
} else {
code = "00" + id;
}
return code;
}
优化后:
String getCode(String id) {
//初始化时设为默认值
String code = "0000";
if(id != null) {
code = "00" + id;
}
return code;
}
方法四
函数代替参数:
优化前:
String getValue(String param) {
String value = null;
if("name".equals(param)) {
value = mName;
} else if("hight".equals(param)) {
value = mHight;
} else if("X".equals(param)) {
value = mX;
} else if("Y".equals(param)) {
value = mY;
}
return value;
}
优化后:
String getName() {
return mName;
}
private static String getHight() {
return mHight;
}
private static String getX() {
return mX;
}
private static String getY() {
return mY;
}
方法五
用参数应对变化:
优化前:
private static int getWidth(int val) {
int width = 0;
if(val == 10) {
width += ((val << 2) ^ 0x10) * 200;
} else if(val == 100) {
width += ((val << 2) ^ 0x1a) * 200;
}
return width;
}
优化后:
private static int getWidth(int val) {
int width = 10;
width += getDeta(val, 0x10);
width += getDeta(val, 0x1a);
return width;
}
private static int getDeta(int val, int trim) {
int deta = 0;
if(val == range) {
deta = ((val << 2) ^ trim) * 200;
}
return deta;
}








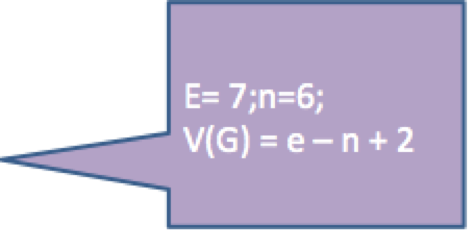














 1092
1092

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








