一、Aggregate简介
db.collection.aggregate()是基于数据处理的聚合管道,每个文档通过一个由多个阶段(stage)组成的管道,可以对每个阶段的管道进行分组、过滤等功能,然后经过一系列的处理,输出相应的结果。
图来自https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/aggregation/ 官方网
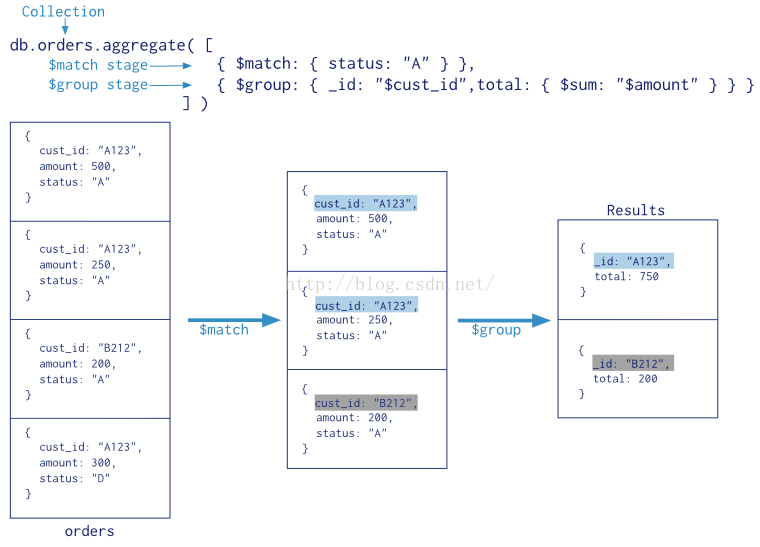
我们通过这张图,可以清晰的了解Aggregate处理的过程
1、db.collection.aggregate()可以多个管道,能方便的进行数据的处理。
2、db.collection.aggregate()使用了MongoDB内置的原生操作,聚合效率非常高,支持类似于SQL Group By操作的功能,而不再需要用户编写自定义的JavaScript例程。
3、 每个阶段管道限制为100MB的内存。如果一个节点管道超过这个极限,MongoDB将产生一个错误。为了能够在处理大型数据集,可以设置allowDiskUse为true来在聚合管道节点把数据写入临时文件。这样就可以解决100MB的内存的限制。
4、db.collection.aggregate()可以作用在分片集合,但结果不能输在分片集合,MapReduce可以 作用在分片集合,结果也可以输在分片集合。
5、db.collection.aggregate()方法可以返回一个指针(cursor),数据放在内存中,直接操作。跟Mongo shell 一样指针操作。
6、db.collection.aggregate()输出的结果只能保存在一个文档中,BSON Document大小限制为16M。可以通过返回指针解决,版本2.6中后面:DB.collect.aggregate()方法返回一个指针,可以返回任何结果集的大小。
二、aggregate语法:
db.collection.aggregate(pipeline, options)
【pipeline $group参数】
pipeline 类型是Array 语法: db.collection.aggregate( [ { <stage> }, ... ] )
$group : 将集合中的文档分组,可用于统计结果,$group首先将数据根据key进行分组。
$group语法: { $group: { _id: <expression>, <field1>: { <accumulator1> : <expression1> }, ... } }
_id 是要进行分组的key
$group:可以分组的数据执行如下的表达式计算:
$sum:计算总和。
$avg:计算平均值。
$min:根据分组,获取集合中所有文档对应值得最小值。
$max:根据分组,获取集合中所有文档对应值得最大值。
$push:将指定的表达式的值添加到一个数组中。
$addToSet:将表达式的值添加到一个集合中(无重复值)。
$first:返回每组第一个文档,如果有排序,按照排序,如果没有按照默认的存储的顺序的第一个文档。
$last:返回每组最后一个文档,如果有排序,按照排序,如果没有按照默认的存储的顺序的最后个文档。
我们可以通过Aggregation pipeline一些使用跟sql用法一样,我们能很清晰的怎么去使用
pipeline sql
$avg avg
$min min
$max max
$group group by
$sort order by
$limit limit
$sum sum()
$sum count()
三、pipeline $group 简单的例子
【数据 】
- db.items.insert( [
- {
- "quantity" : 2,
- "price" : 5.0,
- "pnumber" : "p003",
- },{
- "quantity" : 2,
- "price" : 8.0,
- "pnumber" : "p002"
- },{
- "quantity" : 1,
- "price" : 4.0,
- "pnumber" : "p002"
- },{
- "quantity" : 2,
- "price" : 4.0,
- "pnumber" : "p001"
- },{
- "quantity" : 4,
- "price" : 10.0,
- "pnumber" : "p003"
- },{
- "quantity" : 10,
- "price" : 20.0,
- "pnumber" : "p001"
- },{
- "quantity" : 10,
- "price" : 20.0,
- "pnumber" : "p003"
- },{
- "quantity" : 5,
- "price" : 10.0,
- "pnumber" : "p002"
- }
- ])
【$group】
1、将集合中的文档分组,可用于统计结果,$group首先将数据根据key进行分组。
_id 是要进行分组的key,如果_id为null 相当于select count(*) from table
【 $sum】
1、 我们统计items有几条,相当于SQL: select count(1) as count from items
- > db.items.count()
- 8
- > db.items.aggregate([{$group:{_id:null,count:{$sum:1}}}])
- { "_id" : null, "count" : 8 }
2、我们统计一下数量,相当于SQL: select sum(quantity) as total from items
- > db.items.aggregate([{$group:{_id:null,total:{$sum:"$quantity"}}}])
- { "_id" : null, "total" : 36 }
3、我们通过产品类型来进行分组,然后在统计卖出的数量是多少,相当于SQL:select sum(quantity) as total from items group by pnumber
- > db.items.aggregate([{$group:{_id:"$pnumber",total:{$sum:"$quantity"}}}])
- { "_id" : "p001", "total" : 12 }
- { "_id" : "p002", "total" : 8 }
- { "_id" : "p003", "total" : 16 }
【$min 、 $max 】
1、我们通过相同的产品类型来进行分组,然后查询相同产品类型卖出最多的订单详情 ,相当于SQL: select max(quantity) as quantity from items group by pnumber
- > db.items.aggregate([{$group:{_id:"$pnumber",max:{$max:"$quantity"}}}])
- { "_id" : "p001", "max" : 10 }
- { "_id" : "p002", "max" : 5 }
- { "_id" : "p003", "max" : 10 }
2、我们通过相同的产品类型来进行分组,然后查询相同产品类型卖出最多的订单详情 ,相当于SQL:select min(quantity) as quantity from items group by pnumber
- > db.items.aggregate([{$group:{_id:"$pnumber",min:{$min:"$quantity"}}}])
- { "_id" : "p001", "min" : 2 }
- { "_id" : "p002", "min" : 1 }
- { "_id" : "p003", "min" : 2 }
3、我们通过相同的产品类型来进行分组,统计各个产品数量,然后获取最大的数量,相当于SQL: select max(t.total) from (select sum(quantity) as total from items group by pnumber) t
- > db.items.aggregate([{$group:{_id:"$pnumber",total:{$sum:"$quantity"}}}])
- { "_id" : "p001", "total" : 12 }
- { "_id" : "p002", "total" : 8 }
- { "_id" : "p003", "total" : 16 }
- > db.items.aggregate([{$group:{_id:"$pnumber",total:{$sum:"$quantity"}}},{$group:{_id:null,max:{$max:"$total"}}}])
- { "_id" : null, "max" : 16 }
【$avg】
先根据$group,在计算平均值,只会针对数字的进行计算,会对字符串忽略
1、我们通过相同的产品类型来进行分组,然后查询每个订单详情相同产品类型卖出的平均价格,相当于SQL:select avg(price) as price from items group by pnumber
-
- > db.items.aggregate([{$group:{_id:"$pnumber",price:{$avg:"$price"}}}])
- { "_id" : "p001", "price" : 12 }
- { "_id" : "p002", "price" : 7.333333333333333 }
- { "_id" : "p003", "price" : 11.666666666666666 }
【$push】
将指定的表达式的值添加到一个数组中,这个值不要超过16M,不然会出现错误
1、我们通过相同的产品类型来进行分组,然后查询每个相同产品卖出的数量放在数组里面
- > db.items.aggregate([{$group:{_id:"$pnumber",quantitys:{$push:"$quantity"}}}])
- { "_id" : "p001", "quantitys" : [ 2, 10 ] }
- { "_id" : "p002", "quantitys" : [ 2, 1, 5 ] }
- { "_id" : "p003", "quantitys" : [ 2, 4, 10 ] }
- > db.items.aggregate([{$group:{_id:"$pnumber",quantitys:{$push:{quantity:"$quantity",price:"$price"}}}}])
- { "_id" : "p001", "quantitys" : [ { "quantity" : 2, "price" : 4 }, { "quantity": 10, "price" : 20 } ] }
- { "_id" : "p002", "quantitys" : [ { "quantity" : 2, "price" : 8 }, { "quantity": 1, "price" : 4 }, { "quantity" : 5, "price" : 10 } ] }
- { "_id" : "p003", "quantitys" : [ { "quantity" : 2, "price" : 5 }, { "quantity": 4, "price" : 10 }, { "quantity" : 10, "price" : 20 } ] }
【 $addToSet】
将表达式的值添加到一个数组中(无重复值),这个值不要超过16M,不然会出现错误
- > db.items.aggregate([{$group:{_id:"$pnumber",quantitys:{$addToSet:"$quantity"}}}])
- { "_id" : "p001", "quantitys" : [ 10, 2 ] }
- { "_id" : "p002", "quantitys" : [ 5, 1, 2 ] }
- { "_id" : "p003", "quantitys" : [ 10, 4, 2 ] }
【 $first、 $last】
$first:返回每组第一个文档,如果有排序,按照排序,如果没有按照默认的存储的顺序的第一个文档。
$last:返回每组最后一个文档,如果有排序,按照排序,如果没有按照默认的存储的顺序的最后个文档。
- > db.items.aggregate([{$group:{_id:"$pnumber",quantityFrist:{$first:"$quantity"}}}])
- { "_id" : "p001", "quantityFrist" : 2 }
- { "_id" : "p002", "quantityFrist" : 2 }
- { "_id" : "p003", "quantityFrist" : 2 }
我们这篇主要介绍了aggregate pipeline的$group 基础操作,后续介绍了 pipeline其他参数和options使用























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








