一、背景介绍
提到微服务我们可能会想到许多热门的知识点,比如Spring Boot、docker、k8s、restful、持续交付、分布式事务,服务拆分等等,接下来我会给大家分享Spring Boot相关的系列知识,同时欢迎大家留言共同讨论,指出不足之处。
相信大部分学习Java的人都会这样的经历,在你第一次接触和学习spring框架的时候,在感叹它的强大同时也会其繁杂的配置拍桌而起,“我”明明配置和视频讲述的一样,为啥我的不能运行呢(然后一些人退却啦)?即使你熟悉了Spring,也会因为一堆反复黏贴xml配置而烦恼,然后有一批聪明人出现,Spring annotation出现极大简化了配置,简化了spring学习曲线,但是拦截器,监听器,事务,数据库连接等还是进行配置。然而,人类对于技术追求是无止境,如实就有人想到如果spring不存在xml配置多好?那么很高兴告诉你,它已经出现,它叫Spring Boot。
什么是Spring Boot呢?官网是这么说的“Spring Boot makes it easy to create stand-alone, production-gradeSpring based Applications that you can “just run”. ”,大致的意思是:Spring Boot使我们更容易去创建基于Spring的独立和产品级的可以”即时运行“的应用和服务。支持约定大于配置,目的是尽可能快地构建和运行Spring应用。Spring Boot的主要优点:
(1) 为所有Spring开发者更快的入门;
(2) 开箱即用,提供各种默认配置来简化项目配置;
(3) 提供一系列的非功能性的功能,是常见的大型类的项目(例如:内嵌式容器、安全、健康检查等)
(4) 没有冗余代码生成和XML配置的要求
二、快速入门实例
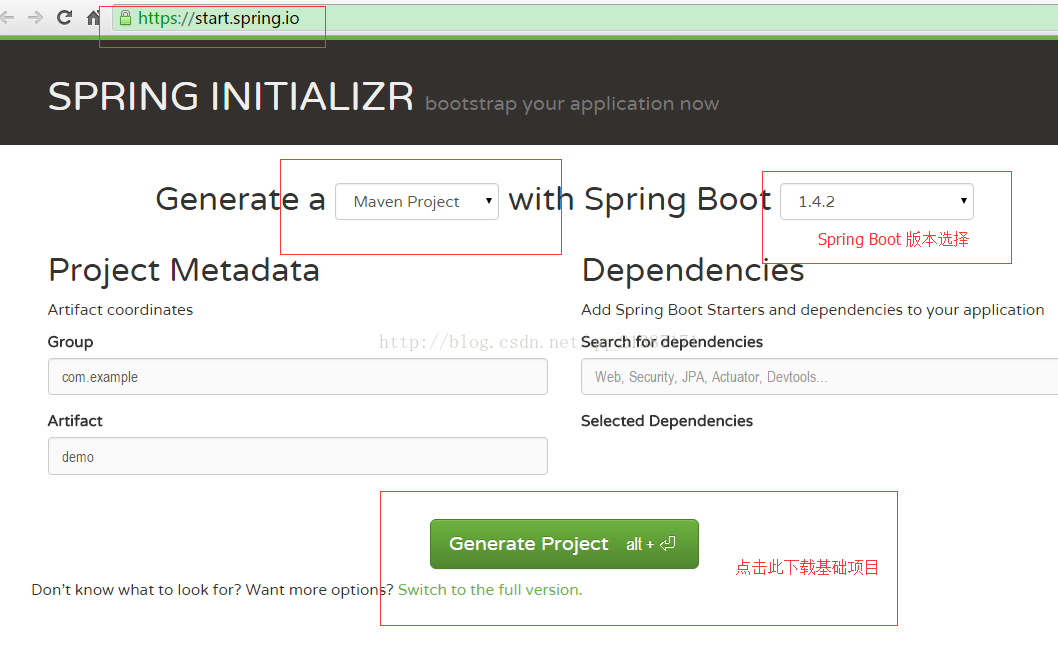
本实例是快速开发一个“Hello World”Web应用程序,通过这个例子对Spring Boot有一个初步的了解,并体验其结构简单、开发快速的特性。除了传统的使用IDEA或者Eclipse创建项目外,SpringBoot提供使用SPRINGINITIALIZR 工具(https://start.spring.io )产生基础项目(选择Spring Boot版本以及其他选项,然后下载即可),项目范例源代码下载地址为:https://github.com/dreamerkr/SpringBoot , 具体如下图所示:
(1) 项目结构简介
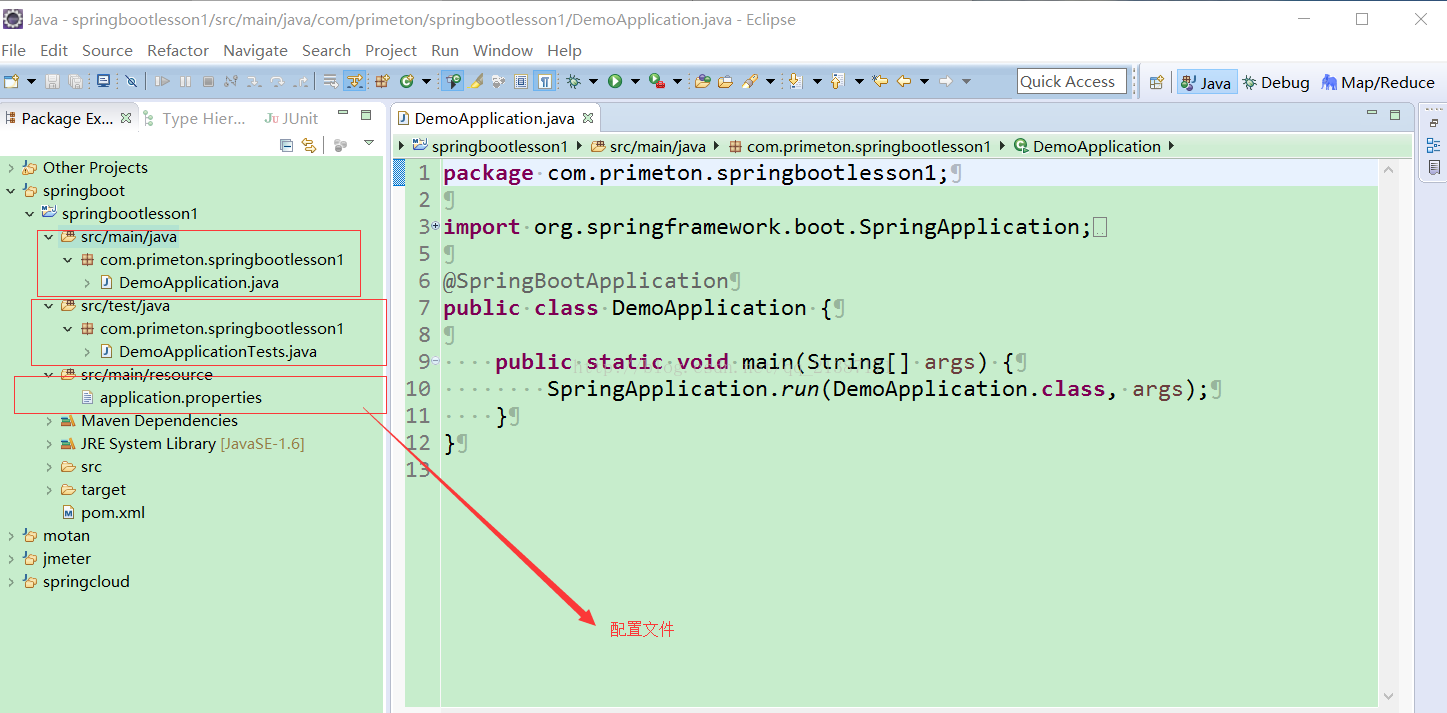
我这里是自己手动创建项目,不过和上面Spring提供的工具创建是一样的效果,创建好的项目结构如下所示:
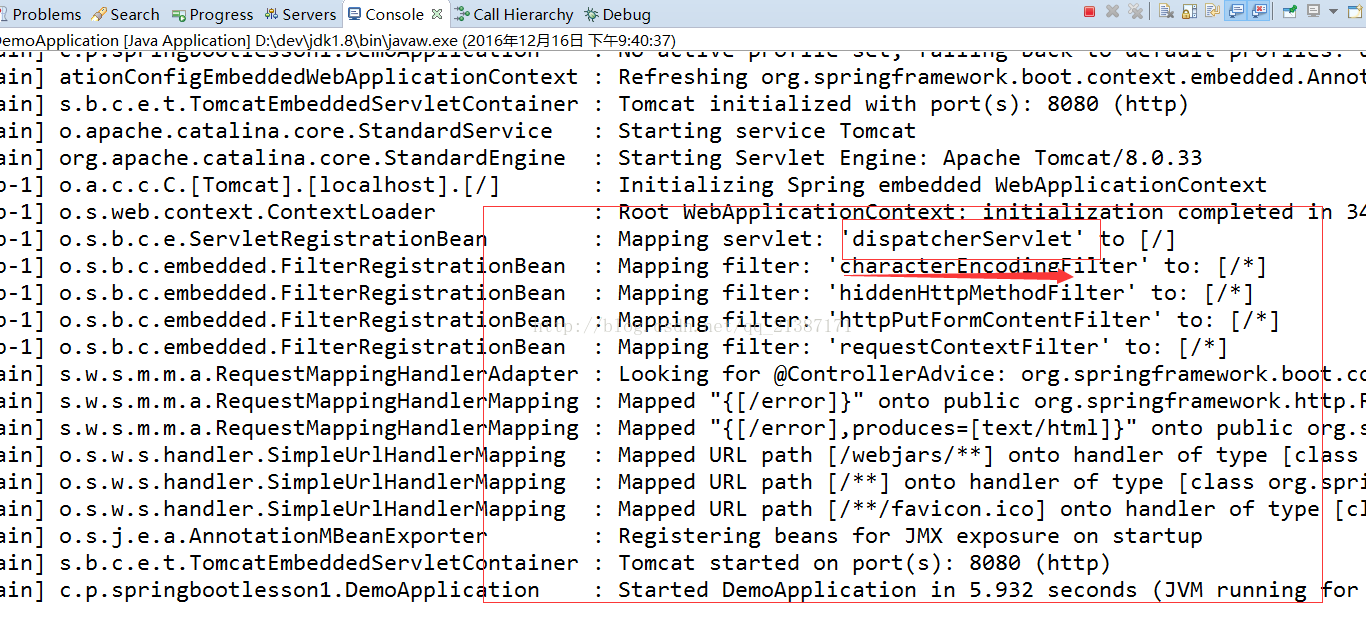
主要有java、resources、test三目录,分别是程序入口、配置文件和测试入口,使用DemoApplication和DemoApplicationTests类均可以启动项目,通过观察启动日志发现使用很多的默认设置,具体如下图所示:
(2) pom.xml文件简介
此文件引入了三个模块分别是starter(核心模块,包括自动配置支持、日志和YAML)、starter-test(测试模块,包括JUnit、Hamcrest、Mockito)、starter-web(Web模块,包括SpringMVC、Tomcat),具体代码如下所示:
< span style = "font-size:14px;" > < parent > < groupId > org.springframework.boot </ groupId > < artifactId > spring-boot-starter-parent </ artifactId > < version > 1.3.5.RELEASE </ version > </ parent > < dependencies > < dependency > < groupId > org.springframework.boot </ groupId > < artifactId > spring-boot-starter </ artifactId > </ dependency > < dependency > < groupId > org.springframework.boot </ groupId > < artifactId > spring-boot-starter-web </ artifactId > </ dependency > < dependency > < groupId > org.springframework.boot </ groupId > < artifactId > spring-boot-starter-test </ artifactId > < scope > test </ scope > </ dependency > </ dependencies > </ span >
(3) 编写HelloController类
HelloController类的内容如下:
package com.primeton.springbootlesson1; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController public class HelloController { @RequestMapping ( "/hello" ) public String sayHello(){ return "Hello World" ; } }
(4) 编写单元测试用例
DemoApplicationTests类代码如下所示:
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.equalTo; import staticorg.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.content; import staticorg.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.status; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.boot.test.SpringApplicationConfiguration; import org.springframework.http.MediaType; import org.springframework.mock.web.MockServletContext; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; import org.springframework.test.context.web.WebAppConfiguration; import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc; import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders; import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.setup.MockMvcBuilders; @RunWith (SpringJUnit4ClassRunner. class ) @SpringApplicationConfiguration (classes = MockServletContext. class ) @WebAppConfiguration public class DemoApplicationTests { private MockMvc mockMvc; @Before public void setUp(){ mockMvc = MockMvcBuilders.standaloneSetup(new HelloController()).build(); } @Test public void getHello() throws Exception { mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/hello" ).accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)) .andExpect(status().isOk()) .andExpect(content().string(equalTo("Hello World" ))); } }
(5) 启动运行范例
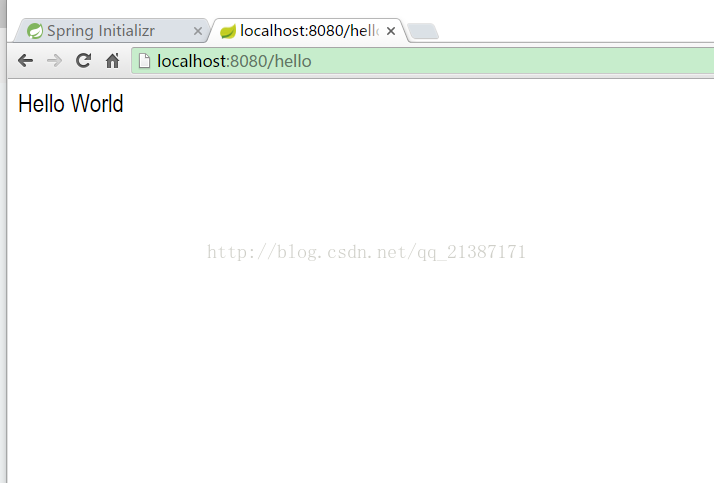
运行DemoApplication主程序,然后打开浏览器访问http://localhost:8080/hello ,页面显示如下图所示:






















 4868
4868

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








