Fail-Fast(快速失败)
Fail-Fast是一种机制,当在遍历集合的过程中检测到集合被修改(例如添加和删除),会立即抛出ConcurrentModificationException异常,而不是继续执行。
实现原理:
Fail-Fast集合(如ArrayList、HashMap)内部维护一个修改计数器(moudCount)该计数器用来记录集合的修改次数,迭代期间通过对比预期修改次数与实际修改次数expectedMoshdCount和modCount是否一致来判断是否存在并发操作,从而实现快速失败。
/*
* Private remove method that skips bounds checking and does not
* return the value removed.
*/
private void fastRemove(int index) {
//执行操作之后,操作数+1
modCount++;
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
}
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> consumer) {
Objects.requireNonNull(consumer);
final int size = ArrayList.this.size;
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size) {
return;
}
final Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
while (i != size && modCount == expectedModCount) {
consumer.accept((E) elementData[i++]);
}
// update once at end of iteration to reduce heap write traffic
cursor = i;
lastRet = i - 1;
//比较实际操作数与预期操作数是否相等
checkForComodification();
}
final void checkForComodification() {
//如果不匹配快速失败
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
代码实现:
{
{
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
// 添加元素
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
list.add(i);
}
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
// 迭代元素 (注意:Integer 是不可变的,这里的 i++ 不会修改 list 中的值)
for (Integer i : list) {
i++; // 这行代码实际上没有修改list中的元素
try {
countDownLatch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("删除元素1");
list.remove(Integer.valueOf(1)); // 使用 Integer.valueOf(1) 删除指定值的对象
countDownLatch.countDown();
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
countDownLatch.await();
}
}
最终会抛出异常:
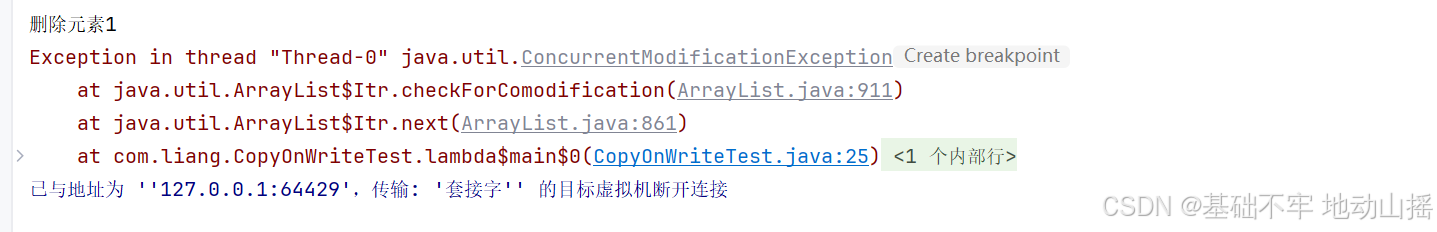
Fail-Safe(安全失败)
Fail-Safe 是一种机制,当在遍历集合的过程中集合被修改,不会抛出异常,而是继续使用原来的集合副本进行遍历。
实现原理:
Fail-Safe 集合(如 CopyOnWriteArrayList、ConcurrentHashMap)在遍历时使用集合的 副本 或 快照。
private boolean remove(Object o, Object[] snapshot, int index) {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
Object[] current = getArray();
int len = current.length;
if (snapshot != current) findIndex: {
int prefix = Math.min(index, len);
for (int i = 0; i < prefix; i++) {
if (current[i] != snapshot[i] && eq(o, current[i])) {
index = i;
break findIndex;
}
}
if (index >= len)
return false;
if (current[index] == o)
break findIndex;
index = indexOf(o, current, index, len);
if (index < 0)
return false;
}
Object[] newElements = new Object[len - 1];
//复制新的数组,避免老的数组迭代过程中失败
System.arraycopy(current, 0, newElements, 0, index);
System.arraycopy(current, index + 1,
newElements, index,
len - index - 1);
setArray(newElements);
return true;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
代码实现:
{
// 使用线程安全的 CopyOnWriteArrayList 避免 ConcurrentModificationException
List<Integer> list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
// List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
// 添加元素
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
list.add(i);
}
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
// 迭代元素 (注意:Integer 是不可变的,这里的 i++ 不会修改 list 中的值)
for (Integer i : list) {
i++; // 这行代码实际上没有修改list中的元素
try {
countDownLatch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("删除元素1");
list.remove(Integer.valueOf(1)); // 使用 Integer.valueOf(1) 删除指定值的对象
countDownLatch.countDown();
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
// countDownLatch.await();
}




















 635
635

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








