在要排序的一组数中,对当前还未排好序的范围内的全部数,自上而下对相邻的两个数依次进行比较和调整,让较大的数往下沉,较小的往上冒。即:每当两相邻的数比较后发现它们的排序与排序要求相反时,就将它们互换。
冒泡排序代码:
package BubbleSort;
/**
* Created by root on 3/8/16.
*/
public class BubbleSort<T extends Comparable<T>> {
private T sort[];
public BubbleSort(T...sort){
this.sort = sort;
}
/**
*对输入的所有的参数进行排序。冒泡排序法。把较大的数往下沉,较小数网上冒泡。
*
*/
public void sort(){
if(sort.length == 0){
throw new RuntimeException("您没有输入参数。。。。。。");
}else {
T temp;
for(int i=0;i<sort.length-1;i++){
for(int j=0;j<sort.length-i-1;j++){
int result = sort[j].compareTo(sort[j+1]);
if(result > 0){
temp = sort[j];
sort[j] = sort[j+1];
sort[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
}
/**
* 还有一种解决方案:定义两个数,low = 0 ; high = sort.length - 1;
* 依次把小的数往上冒,大的数往下沉,排序效率比上一种(sort方法)高效一点。
*/
public void sortOther(){
if(sort.length == 0){
throw new RuntimeException("您没有输入参数。。。。。。");
}else {
int low = 0,high = sort.length-1;
T temp;
while(low < high){
for(int i=low;i<high;i++){
if(sort[i].compareTo(sort[i+1]) > 0){
temp = sort[i];
sort[i] = sort[i+1];
sort[i+1] = temp;
}
}
high --;
for(int j =high;j>low;j--){
if(sort[j].compareTo(sort[j-1]) < 0){
temp = sort[j];
sort[j] = sort[j-1];
sort[j-1] = temp;
}
}
low ++;
}
}
}
/**
* 输出当前的所有的参数
*/
public void display(){
if(sort.length == 0){
throw new RuntimeException("您没有输入参数。。。。。。");
}else {
for(int i=0;i < sort.length;i++){
System.out.print(sort[i]+"\t");
}
}
}
}
上面提供了两种冒泡排序方法。
测试类:
package BubbleSort;
/**
* Created by root on 3/8/16.
*/
public class TestBubbleSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BubbleSort<Integer> bubbleSort = new BubbleSort<Integer>(2,43,23,1,34,54,12,5);
System.out.println("排序前:");
bubbleSort.display();
bubbleSort.sort();
// bubbleSort.sortOther();
System.out.println("\n排序后:");
bubbleSort.display();
}
}
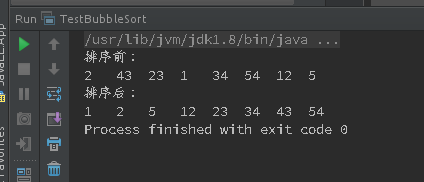
程序运行结果:
























 38万+
38万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








