Given a binary tree, return the vertical order traversal of its nodes values.
For each node at position (X, Y), its left and right children respectively will be at positions (X-1, Y-1) and (X+1, Y-1).
Running a vertical line from X = -infinity to X = +infinity, whenever the vertical line touches some nodes, we report the values of the nodes in order from top to bottom (decreasing Y coordinates).
If two nodes have the same position, then the value of the node that is reported first is the value that is smaller.
Return an list of non-empty reports in order of X coordinate. Every report will have a list of values of nodes.
Example 1:
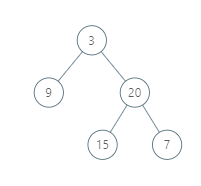
Input: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: [[9],[3,15],[20],[7]]
Explanation:
Without loss of generality, we can assume the root node is at position (0, 0):
Then, the node with value 9 occurs at position (-1, -1);
The nodes with values 3 and 15 occur at positions (0, 0) and (0, -2);
The node with value 20 occurs at position (1, -1);
The node with value 7 occurs at position (2, -2).
Example 2:

Input: [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
Output: [[4],[2],[1,5,6],[3],[7]]
Explanation:
The node with value 5 and the node with value 6 have the same position according to the given scheme.
However, in the report "[1,5,6]", the node value of 5 comes first since 5 is smaller than 6.
Note:
- The tree will have between 1 and
1000nodes. - Each node's value will be between
0and1000.
题目理解:
给定一棵二叉树,如图,二叉树的每一个节点都有行坐标和列坐标,输出每一个列中的节点的值,按照行坐标递增顺序排列,如果有两个值的行列坐标都相同,那么按照值的大小排序
解题思路:
用字典表示二维数组,第一维表示列,第二维表示行,每一个元素都是一个链表,使用递归的方式遍历二叉树中的每一个节点,遍历的时候就附带上行列坐标,将每一个值都存储在对应的链表中,遍历完成之后按照要求组织答案即可
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
TreeMap<Integer, TreeMap<Integer, List<Integer>>> map;
public void helper(TreeNode root, int row, int col){
if(root == null)
return;
if(!map.containsKey(col))
map.put(col, new TreeMap<Integer, List<Integer>>());
TreeMap<Integer, List<Integer>> it = map.get(col);
if(!it.containsKey(row))
it.put(row, new ArrayList<Integer>());
it.get(row).add(root.val);
helper(root.left, row + 1, col - 1);
helper(root.right, row + 1, col + 1);
}
public List<List<Integer>> verticalTraversal(TreeNode root) {
map = new TreeMap<>();
helper(root, 0, 0);
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
for(int col : map.keySet()){
TreeMap<Integer, List<Integer>> it = map.get(col);
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(int row : it.keySet()){
List<Integer> cur = it.get(row);
Collections.sort(cur);
list.addAll(cur);
}
res.add(list);
}
return res;
}
}






















 187
187

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








