
build过程把config弄出来了


传统工作模式:
- 创建SqlSessionFactoryBuilder对象,调用build(inputstream)方法读取并解析配置文件,返回SqlSessionFactory对象
- 由SqlSessionFactory创建SqlSession 对象,没有手动设置的话事务默认开启
- 调用SqlSession中的api,传入Statement Id和参数,内部进行复杂的处理,最后调用jdbc执行SQL语句,封装结果返回。
public static void main(String[] args) {
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession();
String name = "tom";
List<User> list = sqlSession.selectList("com.demo.mapper.UserMapper.getUserByName",params);
} 使用Mapper接口:
由于面向接口编程的趋势,MyBatis也实现了通过接口调用mapper配置文件中的SQL语句
public static void main(String[] args) {
//前三步都相同
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession();
//这里不再调用SqlSession 的api,而是获得了接口对象,调用接口中的方法。
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
List<User> list = mapper.getUserByName("tom");
}
原生MyBatis原理分析
初始化工作
解析配置文件Resources获取加载全局配置文件
实例化SqlSessionFactoryBuilder构造器
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
//这一行代码正是初始化工作的开始。
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);进入源码分析:SqlSessionFactory 的build方法解析和配置文件流XMLConfigBuilder
// 1.我们最初调用的build
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream) {
//调用了重载方法
return build(inputStream, null, null);
}
// 2.调用的重载方法
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
// XMLConfigBuilder是专门解析mybatis的配置文件的类
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
//这里又调用了一个重载方法。parser.parse()的返回值是Configuration对象
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} //省略部分代码
}下面进入对配置文件解析部分:
首先对Configuration对象进行介绍:
Configuration对象的结构和xml配置文件的对象几乎相同。
回顾一下xml中的配置标签有哪些:
properties(属性),settings(设置),typeAliases(类型别名),typeHandlers(类型处理器),objectFactory(对象工厂),mappers(映射器)等
Configuration也有对应的对象属性来封装它们:
(图片来自:https://blog.csdn.net/luanlouis/article/details/37744073)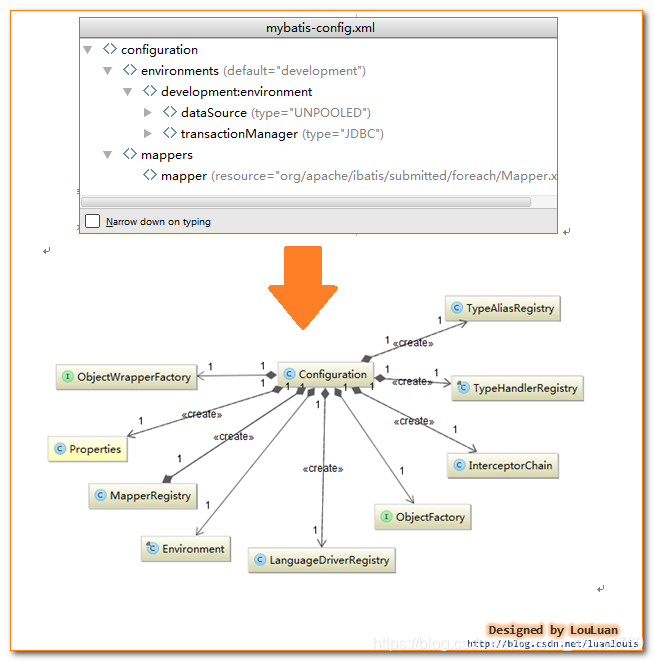
也就是说,初始化配置文件信息的本质就是创建Configuration对象,将解析的xml数据封装到Configuration内部的属性中。
Configuration所有的配置信息
//在创建XMLConfigBuilder时,它的构造方法中解析器XPathParser已经读取了配置文件
//3. 进入XMLConfigBuilder 中的 parse()方法。
public Configuration parse() {
if (parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
parsed = true;
//parser是XPathParser解析器对象,读取节点内数据,<configuration>是MyBatis配置文件中的顶层标签
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
//最后返回的是Configuration 对象
return configuration;
}
//4. 进入parseConfiguration方法
//此方法中读取了各个标签内容并封装到Configuration中的属性中。
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
//issue #117 read properties first
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));
loadCustomVfs(settings);
loadCustomLogImpl(settings);
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));
settingsElement(settings);
// read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
配置类方式
发散一下思路,既然解析xml是对Configuration中的属性进行复制,那么我们同样可以在一个类中创建Configuration对象,手动设置其中属性的值来达到配置的效果。
SqlSession实例化(相当于之前的connection)
transaction事务管理
执行SQL
先简单介绍SqlSession:
SqlSession是一个接口,它有两个实现类:DefaultSqlSession(默认)和SqlSessionManager(弃用,不做介绍)
SqlSession是MyBatis中用于和数据库交互的顶层类,通常将它与ThreadLocal绑定,一个会话使用一个SqlSession,并且在使用完毕后需要close。
SqlSession中的两个最重要的参数,configuration与初始化时的相同,Executor为执行器,
Executor:创建executor执行器


Executor也是一个接口,他有三个常用的实现类BatchExecutor(重用语句并执行批量更新),ReuseExecutor(重用预处理语句prepared statements),SimpleExecutor(普通的执行器,默认)。
SqlSession API方式
继续分析,初始化完毕后,我们就要执行SQL了:
获得sqlSession
//6. 进入openSession方法。
public SqlSession openSession() {
//getDefaultExecutorType()传递的是SimpleExecutor
return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false);
}
//7. 进入openSessionFromDataSource。
//ExecutorType 为Executor的类型,TransactionIsolationLevel为事务隔离级别,autoCommit是否开启事务
//openSession的多个重载方法可以指定获得的SeqSession的Executor类型和事务的处理
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
//根据参数创建指定类型的Executor
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
//返回的是DefaultSqlSession
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}执行sqlsession中的api创建sqlSession
//8.进入selectList方法,多个重载方法。
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement) {
return this.selectList(statement, null);
}
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter) {
return this.selectList(statement, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT);
}
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
//根据传入的全限定名+方法名从映射的Map中取出MappedStatement对象
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
//调用Executor中的方法处理
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}介绍一下MappedStatement :

- 作用: MappedStatement与Mapper配置文件中的一个select/update/insert/delete节点相对应。mapper中配置的标签都被封装到了此对象中,主要用途是描述一条SQL语句。
- **初始化过程:**回顾刚开始介绍的加载配置文件的过程中,会对mybatis-config.xml中的各个标签都进行解析,其中有 mappers标签用来引入
mapper.xml文件或者配置mapper接口的目录。 -
<select id="getUser" resultType="user" > select * from user where id=#{id} </select>这样的一个select标签会在
初始化配置文件时被解析封装成一个MappedStatement对象,然后存储在Configuration对象的mappedStatements属性中,mappedStatements 是一个HashMap,存储时key = 全限定类名 + 方法名,value = 对应的MappedStatement对象。 - 在configuration中对应的属性为
Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements = new StrictMap<MappedStatement>("Mapped Statements collection") - 在XMLConfigBuilder中的处理:
-
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) { try { // 省略其他标签的处理 mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers")); } catch (Exception e) { throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e); } }
继续源码中的步骤,进入 executor.query()
//此方法在SimpleExecutor的父类BaseExecutor中实现 public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException { //根据传入的参数动态获得SQL语句,最后返回用BoundSql对象表示 BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter); //为本次查询创建缓存的Key CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql); return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); } //进入query的重载方法中 public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId()); if (closed) { throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed."); } if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) { clearLocalCache(); } List<E> list; try { queryStack++; list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null; if (list != null) { handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql); } else { // 如果缓存中没有本次查找的值,那么从数据库中查询 list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); } } finally { queryStack--; } if (queryStack == 0) { for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) { deferredLoad.load(); } // issue #601 deferredLoads.clear(); if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) { // issue #482 clearLocalCache(); } } return list; } //从数据库查询 private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { List<E> list; localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER); try { // 查询的方法 list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); } finally { localCache.removeObject(key); } // 将查询结果放入缓存 localCache.putObject(key, list); if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) { localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter); } return list; } // SimpleExecutor中实现父类的doQuery抽象方法 public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { Statement stmt = null; try { Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); // 传入参数创建StatementHanlder对象来执行查询 StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); // 创建jdbc中的statement对象 stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog()); // StatementHandler进行处理 return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler); } finally { closeStatement(stmt); } } // 创建Statement的方法 private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException { Statement stmt; //条代码中的getConnection方法经过重重调用最后会调用openConnection方法,从连接池中获得连接。 Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog); stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout()); handler.parameterize(stmt); return stmt; } //从连接池获得连接的方法 protected void openConnection() throws SQLException { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Opening JDBC Connection"); } //从连接池获得连接 connection = dataSource.getConnection(); if (level != null) { connection.setTransactionIsolation(level.getLevel()); } setDesiredAutoCommit(autoCommit); } //进入StatementHandler进行处理的query,StatementHandler中默认的是PreparedStatementHandler public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException { PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement; //原生jdbc的执行 ps.execute(); //处理结果返回。 return resultSetHandler.handleResultSets(ps); }接口方式
回顾一下写法:
-
public static void main(String[] args) { //前三步都相同 InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml"); SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession(); //这里不再调用SqlSession 的api,而是获得了接口对象,调用接口中的方法。 UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class); List<User> list = mapper.getUserByName("tom"); }思考一个问题,通常的Mapper接口我们都没有实现的方法却可以使用,是为什么呢?答案很简单
动态代理
开始之前介绍一下MyBatis初始化时对接口的处理:MapperRegistry是Configuration中的一个属性,它内部维护一个HashMap用于存放mapper接口的
工厂类,每个接口对应一个工厂类。mappers中可以配置接口的包路径,或者某个具体的接口类。 -
<!-- 将包内的映射器接口实现全部注册为映射器 --> <mappers> <mapper class="com.demo.mapper.UserMapper"/> <package name="com.demo.mapper"/> </mappers> - 当解析mappers标签时,它会判断解析到的是mapper配置文件时,会再将对应配置文件中的增删改查标签一 一封装成MappedStatement对象,存入mappedStatements中。(上文介绍了)
- 当判断解析到接口时,会创建此接口对应的MapperProxyFactory对象,存入HashMap中,key = 接口的字节码对象,value = 此接口对应的MapperProxyFactory对象。
//MapperRegistry类 public class MapperRegistry { private final Configuration config; //这个类中维护一个HashMap存放MapperProxyFactory private final Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> knownMappers = new HashMap<>(); //解析到接口时添加接口工厂类的方法 public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) { if (type.isInterface()) { if (hasMapper(type)) { throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry."); } boolean loadCompleted = false; try { //重点在这行,以接口类的class对象为key,value为其对应的工厂对象,构造方法中指定了接口对象 knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type)); // It's important that the type is added before the parser is run // otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the // mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try. MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type); parser.parse(); loadCompleted = true; } finally { if (!loadCompleted) { knownMappers.remove(type); } } } } }正文:
进入sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class)中//DefaultSqlSession中的getMapper public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) { return configuration.<T>getMapper(type, this); } //configuration中的给getMapper public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) { return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession); } //MapperRegistry中的getMapper public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) { //从MapperRegistry中的HashMap中拿MapperProxyFactory final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type); if (mapperProxyFactory == null) { throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry."); } try { // 通过动态代理工厂生成示例。 return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession); } catch (Exception e) { throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e); } } //MapperProxyFactory类中的newInstance方法 public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) { // 创建了JDK动态代理的Handler类 final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache); // 调用了重载方法 return newInstance(mapperProxy); } //MapperProxy类,实现了InvocationHandler接口 public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable { //省略部分源码 private final SqlSession sqlSession; private final Class<T> mapperInterface; private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache; // 构造,传入了SqlSession,说明每个session中的代理对象的不同的! public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class<T> mapperInterface, Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache) { this.sqlSession = sqlSession; this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface; this.methodCache = methodCache; } //省略部分源码 } //重载的方法,由动态代理创建新示例返回。 protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) { return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy); }在动态代理返回了示例后,我们就可以直接调用mapper类中的方法了,说明在MapperProxy中的invoke方法中已经为
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { try { //判断调用是是不是Object中定义的方法,toString,hashCode这类非。是的话直接放行。 if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) { return method.invoke(this, args); } else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) { return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args); } } catch (Throwable t) { throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t); } final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method); // 重点在这:MapperMethod最终调用了执行的方法 return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args); } public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) { Object result; //判断mapper中的方法类型,最终调用的还是SqlSession中的方法 switch (command.getType()) { case INSERT: { Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param)); break; } case UPDATE: { Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param)); break; } case DELETE: { Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param)); break; } case SELECT: if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) { executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args); result = null; } else if (method.returnsMany()) { result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args); } else if (method.returnsMap()) { result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args); } else if (method.returnsCursor()) { result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args); } else { Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param); if (method.returnsOptional() && (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) { result = Optional.ofNullable(result); } } break; case FLUSH: result = sqlSession.flushStatements(); break; default: throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName()); } if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) { throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName() + " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ")."); } return result; }我们实现了方法。
























 529
529











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








