目录:
1.ArrayList集合(最常用)
-
长度可变
-
可以存放引用数据类型
-
不可以直接存基本数据类型,如果要存,只能存包装类
-
索引是从0开始
成员方法
//1.添加元素,返回布尔类型
list.add("aaa");
list.add("bbb");
list.add("ccc");
list.add("ddd");
list.add("eee");
//2.删除元素
//在根据具体元素删除时,会返回布尔类型
boolean re = list.remove("aaa");
System.out.println(re);
//在根据索引删除时,会直接返回被删除的元素
String res = list.remove(0);
System.out.println(res);
//3.修改元素
String ddd = list.set(0, "ddd");
System.out.println(ddd);//返回被修改的元素
//4.查询
String s = list.get(2);
System.out.println(s);
//5.获取长度
int size = list.size();
System.out.println(size);
//6.遍历
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(list.get(i));
}练习
练习一
遍历输出集合中的元素
import java.util.ArrayList;
//遍历输出集合中的元素
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("aaa");
list.add("bbb");
list.add("ccc");
System.out.print("[");
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
if (i == list.size()-1){
System.out.print(list.get(i));
}else {
System.out.print(list.get(i)+",");
}
}
System.out.println("]");
}
}练习二

import java.util.ArrayList;
//测试类
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student = new Student(18,"asd",101);
Student student1 = new Student(17,"aea",102);
ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(student);
list.add(student1);
boolean contains = contains(list, 103);
System.out.println(contains);
}
public static boolean contains(ArrayList<Student> list,int num){
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
Student s = list.get(i);
int sNum = s.getNum();
if (sNum==num){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}//学生类
public class Student {
private int age;
private String name;
private int num;
public Student() {
}
public Student(int age, String name, int num) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
this.num = num;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return age
*/
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param age
*/
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return name
*/
public String getName() {
return name;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param name
*/
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return num
*/
public int getNum() {
return num;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param num
*/
public void setNum(int num) {
this.num = num;
}
public String toString() {
return "Student{age = " + age + ", name = " + name + ", num = " + num + "}";
}
}
练习三

import java.util.ArrayList;
//测试类
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Phone> list = new ArrayList<>();
Phone p1 = new Phone(3000,"小米");
Phone p2 = new Phone(5000,"华为");
Phone p3 = new Phone(7000,"苹果");
list.add(p1);
list.add(p2);
list.add(p3);
ArrayList<Phone> contains = contains(list, 5000);
for (int i = 0; i < contains.size(); i++) {
Phone phone = contains.get(i);
int price = phone.getPrice();
String brand = phone.getBrand();
System.out.println("价格为:"+price+" "+"品牌为:"+brand);
}
}
public static ArrayList<Phone> contains(ArrayList<Phone> list,int price){
ArrayList<Phone> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
Phone phone = list.get(i);
int pr = phone.getPrice();
if (pr>=price){
list1.add(phone);
}
}
return list1;
}
}package ArrayList.Test3;
//手机类
public class Phone {
private int price;
private String brand;
public Phone() {
}
public Phone(int price, String brand) {
this.price = price;
this.brand = brand;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return price
*/
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param price
*/
public void setPrice(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return brand
*/
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param brand
*/
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public String toString() {
return "Phone{price = " + price + ", brand = " + brand + "}";
}
}
2.LinkedList
-
LinkedList采用的是链表的形式存储
-
用于插入和删除时,拥有跟好的性能
public class NewsMgr {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NewTitle title1 = new NewTitle(1, "北京热门景点1", "author");
NewTitle title2 = new NewTitle(1, "北京热门景点2", "author");
NewTitle title3 = new NewTitle(1, "北京热门景点3", "author");
NewTitle title4 = new NewTitle(1, "北京热门景点4", "author");
NewTitle title5 = new NewTitle(1, "北京热门景点5", "author");
//创建集合对象,将新闻标题添加到集合中
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.add(title1);
list.add(title2);
list.add(title3);
list.add(title4);
list.add(1,title5);
//在列表首部添加元素
NewTitle title6 = new NewTitle(6, "北京热门景点5", "author");
list.addFirst(title6);
System.out.println("新闻标题一共有"+list.size()+"条");
System.out.println("***************************");
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
NewTitle title = (NewTitle) list.get(i);//list.get()得到的是object类型,需要强转成NewTitle类型
System.out.println(title.getTitle()+"-"+title.getAuthor());
}
System.out.println("***************************");
for (Object obj:list) {
NewTitle title = (NewTitle) obj;
System.out.println(title.getTitle()+"-"+title.getAuthor());
}
System.out.println("***************************");
//获取头条信息和末条信息
NewTitle titleFirst = (NewTitle)list.getFirst();
System.out.println("头条新闻信息:"+titleFirst.getTitle()+"-"+titleFirst.getAuthor());
NewTitle titleLast = (NewTitle)list.getLast();
System.out.println("末条新闻信息:"+titleLast.getTitle()+"-"+titleLast.getAuthor());
}
}3.Set
-
Set接口存储一组唯一,无序的对象
-
HashSet是Set接口常用的实现类
-
Set存放对象的引用
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set set = new HashSet();
String s1 = new String("java");
String s2 = s1;
String s3 = new String("JAVA");
String s4 = new String("JAVA_home");
set.add(s1);
set.add(s1);
set.add(s2);
set.add(s3);
set.add(s4);
//由于set是无序的,所以不能通过下标的方式使用add方法
//set.add(1,s1);
//使用增强for输出
for (Object obj: set) {
System.out.println(obj);//由于无序,获得的结果不会按照添加的顺序输出
}
//使用迭代器Iterator输出
Iterator iterator = set.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
Object next = iterator.next();
System.out.println(next);
}
System.out.println(set.size());//3
//当set存数据时,会先将存入的数据与存在的数据进行equals()比较,如果为ture,则不添加
}
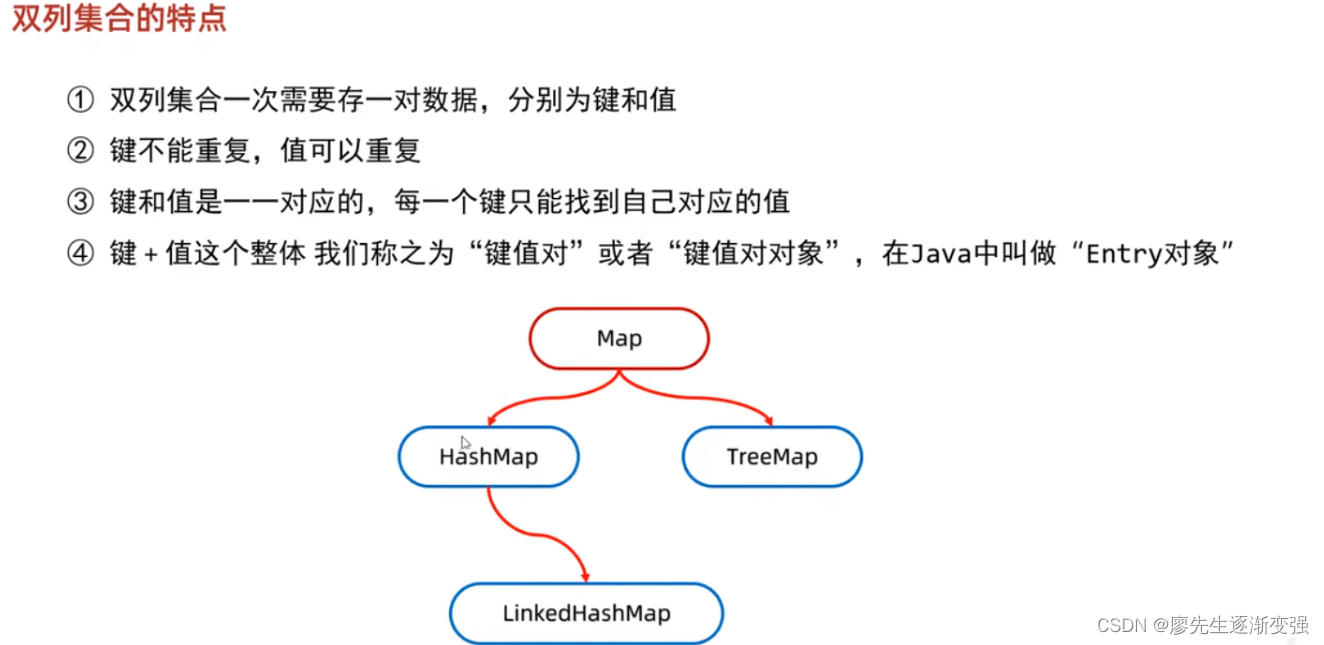
}4.Map
Map 是一种键-值对(key-value)集合,Map 集合中的每一个元素都包含一个键对象和一个值对象。其中,键对象不允许重复,而值对象可以重复,并且值对象还可以是 Map 类型的,就像数组中的元素还可以是数组一样。
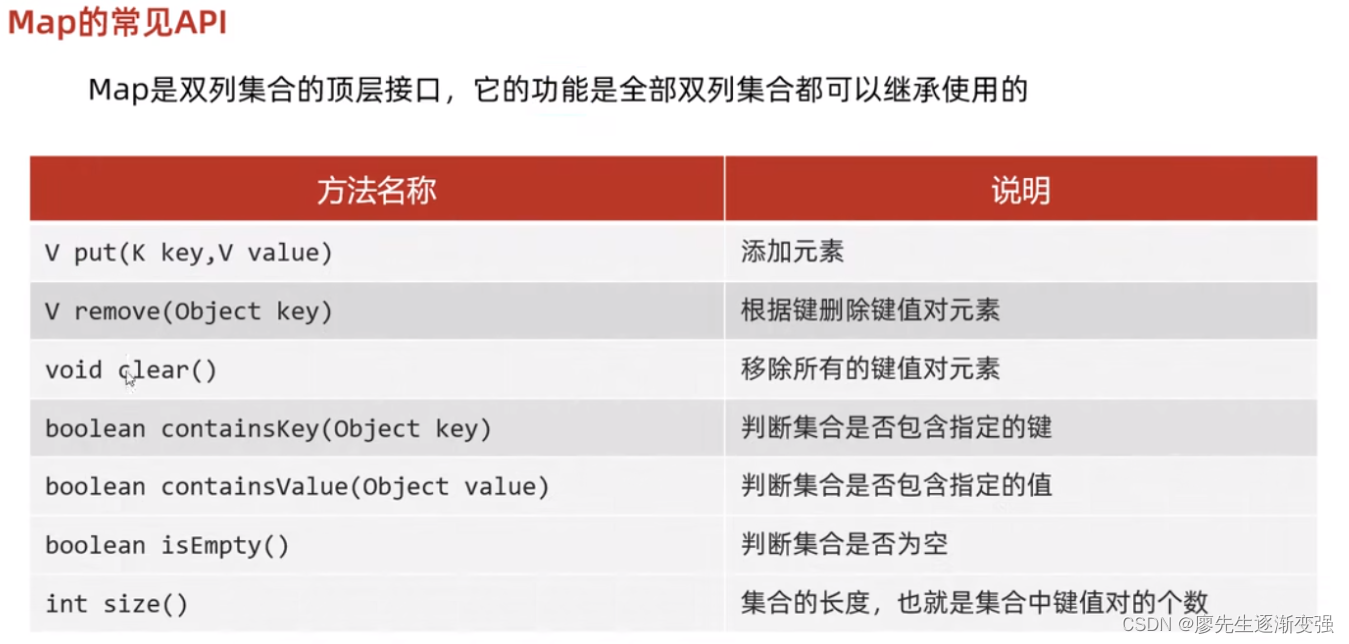
Map 的API实现:
public class demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* put(key,value) 添加元素
* remove(object key) 根据键删除键值对元素
* clear() 移除所有的键值对元素
* containsKey(Object key) 判断集合是否包含指定的键
* containsValue(Object value) 判断集合是否包含指定的值
* isEmpty()判断集合是否为空
* size() 集合的长度
*/
//1.创建Map集合的对象
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
String put = map.put("温迪", "酒蒙子");
map.put("钟离", "街溜子");
map.put("影", "土妹子");
map.put("纳西妲", "小孩子");
System.out.println("map:"+map);//{影=土妹子, 纳西妲=小孩子, 温迪=酒蒙子, 钟离=街溜子}
System.out.println("put:"+put);//null
//remove
String s = map.remove("温迪");//酒蒙子
System.out.println("s:"+s);
//isEmpty()
boolean empty = map.isEmpty();
System.out.println("empty:"+empty);
//containsKey()
boolean key = map.containsKey("钟离");
System.out.println("key:"+key);
//containsValue()
boolean value = map.containsValue("椰奶");
System.out.println("value:"+value);
//size()
int size = map.size();
System.out.println("size:"+size);
//clear
map.clear();
System.out.println("put:"+put);//null
}
}
Map的遍历
public class demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//map集合的三种遍历方式
//1.创建Map集合的对象
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
//2.添加元素
map.put("温迪", "酒蒙子");
map.put("钟离", "街溜子");
map.put("影", "土妹子");
map.put("纳西妲", "小孩子");
//3.1通过键找值
//获取所有的键,把这些键放到一个单列集合中
System.out.println("========键找值========");
Set<String> keySet = map.keySet();
//遍历单例集合,得到每一个键
for (String key: keySet) {
//利用map集合中的键获取对应的值 get
String value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key+"="+value);
}
//3.2通过键值对对象进行遍历
System.out.println("=======键值对==========");
Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> entries = map.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String,String> entry:entries) {
String key = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key+"="+value);
}
//3.3通过lambda表达式进行遍历
map.forEach(new BiConsumer<String, String>() {
@Override
public void accept(String key, String value) {
System.out.println(key+"="+value);
}
});
System.out.println("------------------------");
//简化版
map.forEach((String key, String value)-> {
System.out.println(key+"="+value);
}
);
//精简版
map.forEach((key,value)-> System.out.println(key+"="+value));
}
}
5.HashMap
HashMap 是一个散列表,它存储的内容是键值对(key-value)映射。
HashMap 实现了 Map 接口,根据键的 HashCode 值存储数据,具有很快的访问速度,最多允许一条记录的键为 null,不支持线程同步。
HashMap 是无序的,即不会记录插入的顺序。
HashMap 继承于AbstractMap,实现了 Map、Cloneable、java.io.Serializable 接口。
- HashMap是Map里面的一个实现类
- 无序、不重复、无索引
- HashMap和HashSet底层一样,都是哈希表
public class demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 某个班级80名学生,现在需要组成秋游活动
* 班长提供了四个景点A B C D
* 每个学生只能选择一个景点,请统计出最终那个景点想去的人数最多
*/
//定义一个数组存储四个景点
String []arr = {"A","B","C","D"};
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 80; i++) {
int index = random.nextInt(arr.length);
list.add(arr[index]);
}
HashMap<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (String name:list) {
if (map.containsKey(name)){
Integer integer = map.get(name);
map.put(name,integer+1);
}else{
map.put(name,1);
}
}
Set<String> keySet = map.keySet();
//遍历单例集合,得到每一个键
for (String key: keySet) {
//利用map集合中的键获取对应的值 get
Integer ke = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key+"="+ke);
}
//求最大值
int max = 0;
int count=0;
Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> entries = map.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> ma:entries) {
count = ma.getValue();
if (count>max){
max = count;
}
}
Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> entrie = map.entrySet();
String key="";
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> ma:entrie) {
Integer value = ma.getValue();
if (value==max){
key = ma.getKey();
}
}
System.out.println("经过投票,"+key+"的票数最多,为"+max+"票");
}
}6.TreeMap
是一个有序的key-value集合,它是通过红黑树实现的。该映射根据其键的自然顺序进行排序,或者根据创建映射时提供的 Comparator 进行排序,具体取决于使用的构造方法。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 字符串aababcabcdabcde
* 请统计字符串中每一个字符出现的次数,并按照一下格式输出
* a(5) b(4) c(3) d(2) e(1)
*/
TreeMap<Character,Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
String st = "aababcabcdabcde";
for (int i = 0; i < st.length(); i++) {
char c = st.charAt(i);
if (map.containsKey(c)){
Integer integer = map.get(c);
map.put(c,integer+1);
}else {
map.put(c,1);
}
}
Set<Character> strings = map.keySet();
for (Character key:strings) {
Integer value = map.get(key);
System.out.print(key+"("+value+")"+" ");
}
System.out.println();
Set<Map.Entry<Character, Integer>> entries = map.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Character, Integer> entry:entries){
Character key = entry.getKey();
Integer value = entry.getValue();
System.out.print(key+"("+value+")"+" ");
}
System.out.println();
map.forEach((key,value)-> System.out.print(key+"("+value+")"+" "));
}
}练习
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//随机抽
//百分之30女生,百分之70男生
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list,1,1,1,1,1,1,1);
Collections.addAll(list,0,0,0);
Collections.shuffle(list);
Random random = new Random();
int index = random.nextInt(list.size());
Integer integer = list.get(index);
System.out.println(integer);
ArrayList<String> boyList = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<String> girlList = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(boyList,"子轩","子俊","俊豪","家杰","家聪","智辉","浩然");
Collections.addAll(girlList,"品如","玉儿","倩雪");
if (integer==1){
int boyIndex = random.nextInt(boyList.size());
String name = boyList.get(boyIndex);
System.out.println(name);
}else {
int girlIndex = random.nextInt(girlList.size());
String name = girlList.get(girlIndex);
System.out.println(name);
}
}
}





















 1022
1022

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








