CSS3新增
「1. CSS3属性选择器」
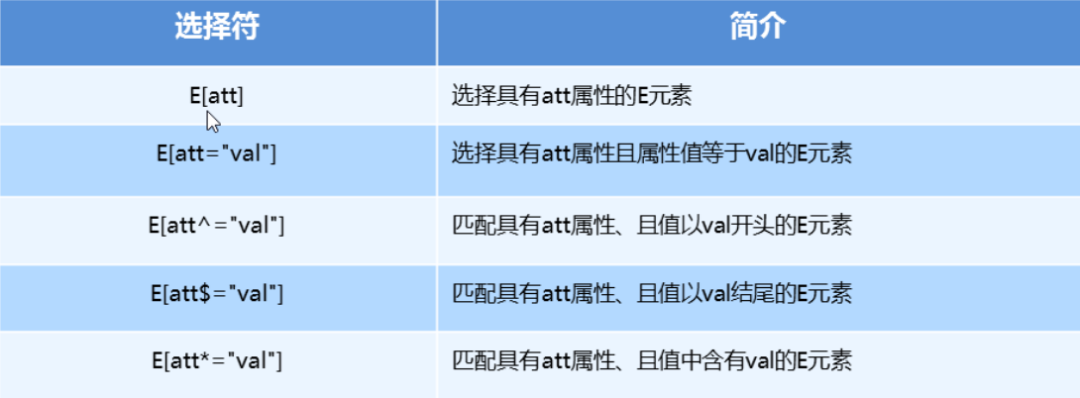
button {
cursor: pointer;
}
button[disabled] {
cursor: default;
}
input[type=search] {
color: skyblue;
}
span[class^=black] {
color: lightgreen;
}
span[class$=black] {
color: lightsalmon;
}
span[class*=black] {
color: lightseagreen;
}
「2. 结构伪类选择器」
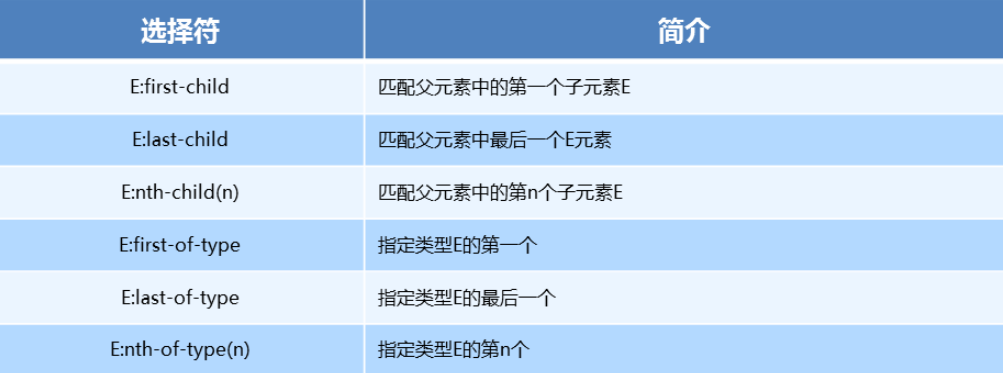
ul li:first-child {
background-color: lightseagreen;
}
ul li:last-child {
background-color: lightcoral;
}
ul li:nth-child(3) {
background-color: aqua;
}
-
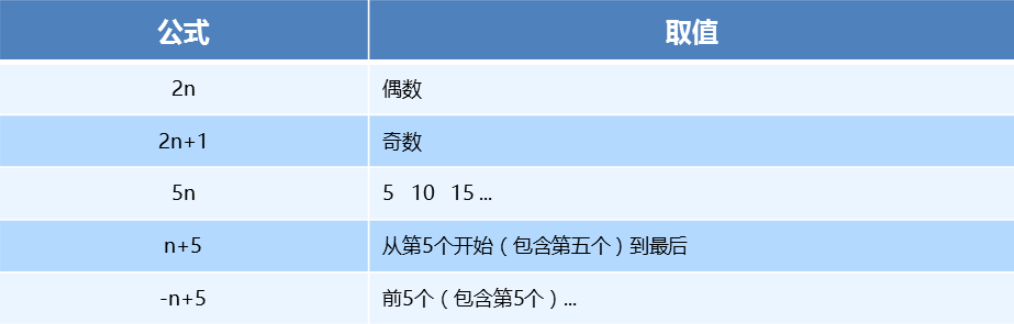
nth-child(n)参数n详解
-
注意:本质上就是选中第几个子元素
-
n 可以是数字、关键字、公式
-
n 如果是数字,就是选中第几个
-
常见的关键字有
even偶数、odd奇数 -
常见的公式如下(如果 n 是公式,则从 0 开始计算)
-
但是第 0 个元素或者超出了元素的个数会被忽略
-
<style>
/* 偶数 */
ul li:nth-child(even) {
background-color: aquamarine;
}
/* 奇数 */
ul li:nth-child(odd) {
background-color: blueviolet;
}
/*n 是公式,从 0 开始计算 */
ul li:nth-child(n) {
background-color: lightcoral;
}
/* 偶数 */
ul li:nth-child(2n) {
background-color: lightskyblue;
}
/* 奇数 */
ul li:nth-child(2n + 1) {
background-color: lightsalmon;
}
/* 选择第 0 5 10 15, 应该怎么选 */
ul li:nth-child(5n) {
background-color: orangered;
}
/* n + 5 就是从第5个开始往后选择 */
ul li:nth-child(n + 5) {
background-color: peru;
}
/* -n + 5 前五个 */
ul li:nth-child(-n + 5) {
background-color: tan;
}
</style>
-
nth-child与nth-of-type区别-
nth-child选择父元素里面的第几个子元素,不管是第几个类型 -
nth-of-type选择指定类型的元素
-
<style>
div :nth-child(1) {
background-color: lightblue;
}
div :nth-child(2) {
background-color: lightpink;
}
div span:nth-of-type(2) {
background-color: lightseagreen;
}
div span:nth-of-type(3) {
background-color: #fff;
}
</style>
「3. 伪元素选择器」

-
伪元素选择器注意事项
-
before和after必须有content属性 -
before在内容前面,after 在内容后面 -
before和after创建的是一个元素,但是属于行内元素 -
创建出来的元素在
Dom中查找不到,所以称为伪元素 -
伪元素和标签选择器一样,权重为 1
-
<style>
div {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid lightcoral;
}
div::after,
div::before {
width: 20px;
height: 50px;
text-align: center;
display: inline-block;
}
div::after {
content: '德';
background-color: lightskyblue;
}
div::before {
content: '道';
background-color: mediumaquamarine;
}
</style>
伪元素字体图标
p {
position: relative;
width: 220px;
height: 22px;
border: 1px solid lightseagreen;
margin: 60px;
}
p::after {
content: '\ea50';
font-family: 'icomoon';
position: absolute;
top: -1px;
right: 10px;
}
「4. 2D 转换之translate」
-
2D转换
-
2D转换是改变标签在二维平面上的位置和形状
-
移动:translate
-
旋转:rotate
-
缩放:scale
-
-
translate语法
-
x就是X轴上水平移动
-
y就是y轴上水平移动
-
transform: translate(x, y)
transform: translateX(n)
transfrom: translateY(n)
-
重点知识点
-
2D的移动主要是指水平、垂直方向上的移动
-
translate最大的优点就是不影响其他元素的位置
-
translate中的100%单位,是相对于本身的宽度和高度来进行计算的
-
行内标签没有效果
-




 本文详细介绍了CSS3中的新特性,包括属性选择器、结构伪类选择器和伪元素选择器。通过实例展示了如何使用CSS3选择器进行元素定位,以及如何利用伪类和伪元素实现页面元素的动态效果和内容插入。同时,解释了`nth-child()`和`nth-of-type()`的区别,并探讨了2D转换中的`translate`方法及其在布局中的应用。
本文详细介绍了CSS3中的新特性,包括属性选择器、结构伪类选择器和伪元素选择器。通过实例展示了如何使用CSS3选择器进行元素定位,以及如何利用伪类和伪元素实现页面元素的动态效果和内容插入。同时,解释了`nth-child()`和`nth-of-type()`的区别,并探讨了2D转换中的`translate`方法及其在布局中的应用。



















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










