hello~ 很高兴见到大家! 这次带来的是C++中关于stack与queue容器迭代器这部分的一些知识点,如果对你有所帮助的话,可否留下你宝贵的三连呢?
个 人 主 页: 默|笙

文章目录
一、stack与queue
1. stack(栈)
粗浅的了解一下栈:
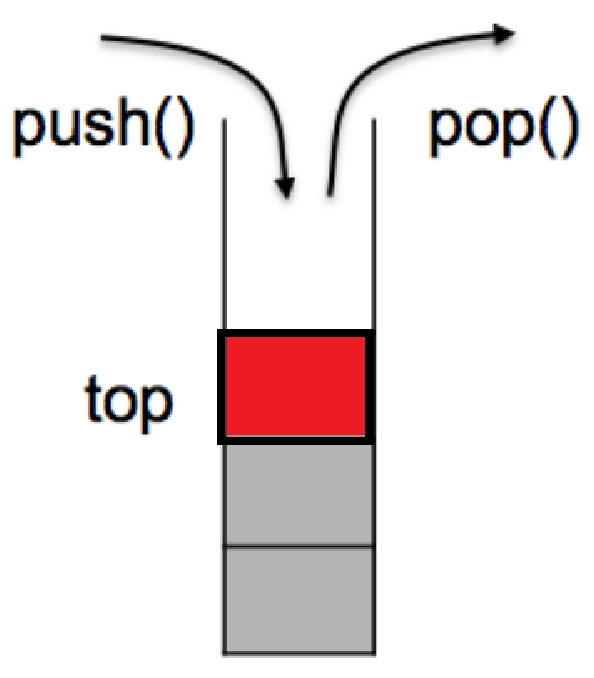
- 栈(Stack) 是一种遵循 后进先出原则的线性数据结构。它只有一端(称为栈顶)允许进行插入(入栈)和删除(出栈)操作。
- c++里面的stack是一种容器适配器,专门设计用于在后进先出(LIFO)环境中运行,其中元素仅从容器的一端插入和提取。
以下,是c++里stack容器适配器提供的一些接口:
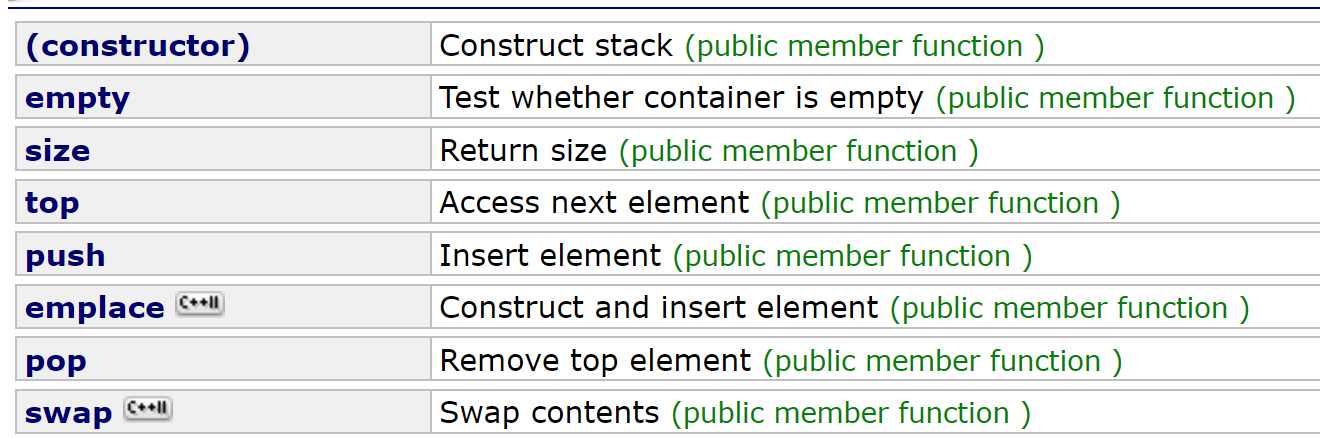
- 为了实现后进先出,它只提供了push()(压入)和pop()(弹出)接口,只能在栈顶进行存取数据,它也不支持迭代器(意味着允许任意位置访问数据)。
- 接口top()用来取栈顶数据。
- 接口pop()没有返回值,它只负责删除数据,获得堆顶数据只能用接口top()。
2. queue(队列)
了解队列:
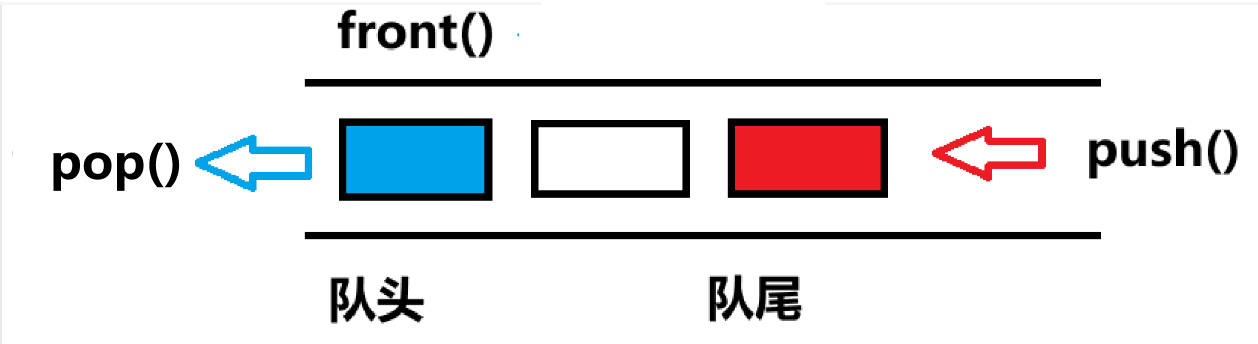
- 队列(queue)是一种先进先出的线性数据结构,元素从尾部加入,从头部移除。
- c++里面的queue也是一种容器适配器,专门设计用于在先进先出(FIFO) 的上下文中操作。在这种结构中,元素从容器的一端插入,从另一端提取。
以下,是c++里queue容器适配器提供的一些接口:
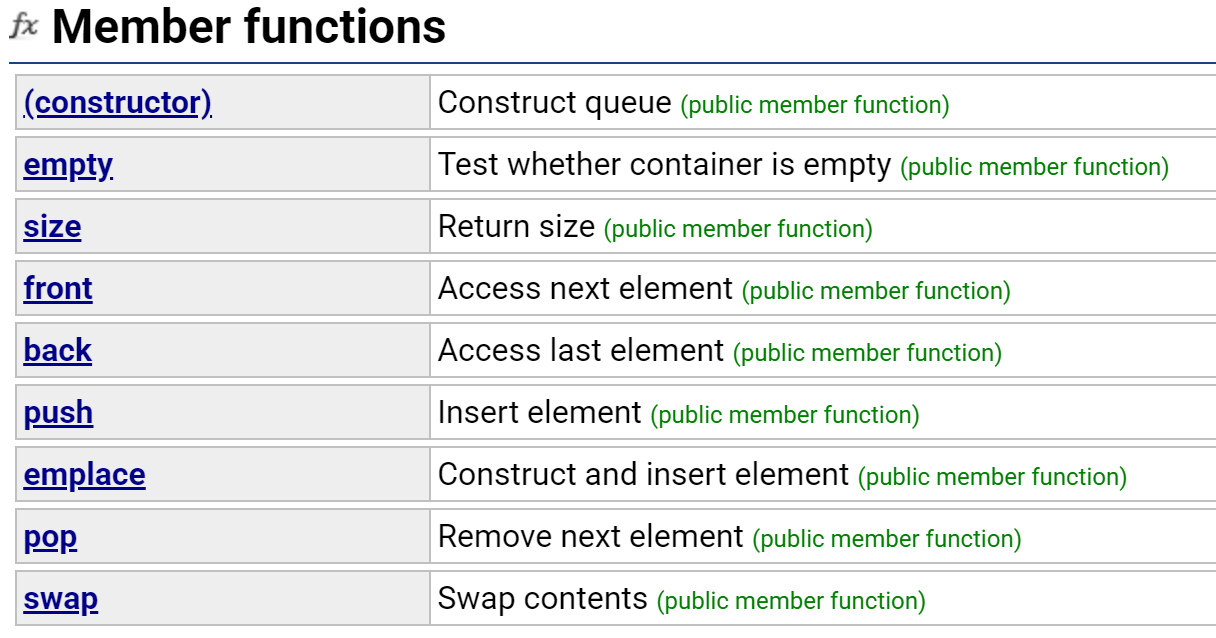
- push()在队尾压入数据,pop()在队头弹出数据,从而实现先进先出,同样,它也不支持迭代器。
- 接口front()用来取队头数据。
- 接口pop()同样没有返回值。
3. 底层实现以及容器适配器
- 在数据结构里,栈和队列的实现依赖于顺序表和链表。栈可以根据底层容器的不同分为顺序栈和链式栈,队列可以分为顺序队列和链式队列。
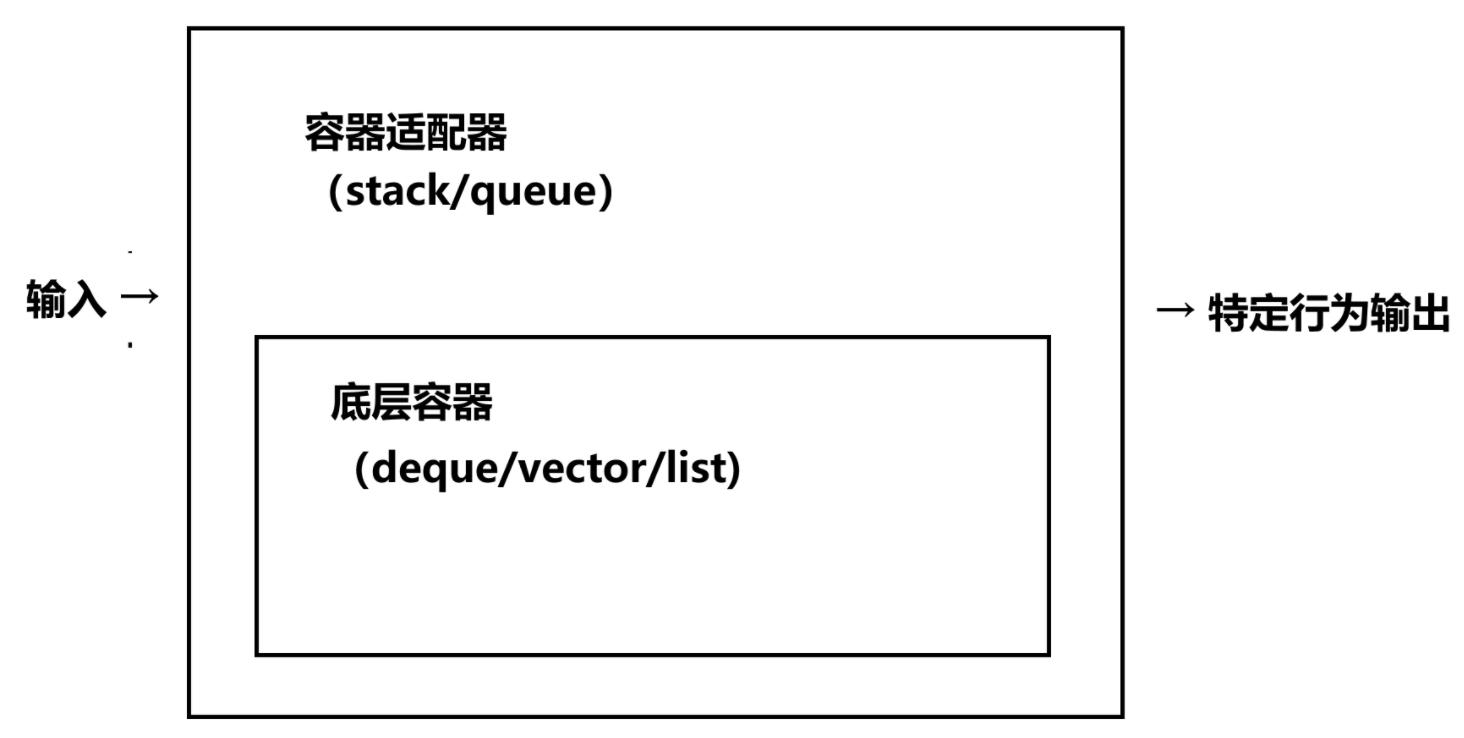
- 在c++里,我们需要把它们(底层的容器)糅合在一起,然后根据用户的需求来决定底层由什么容器来实现,而不是一开始就设计好它由什么底层容器实现。也就是容器适配器。
3.1 容器适配器
概念:容器适配器是一种类,它使用特定容器类的封装对象(deque/vector/list) 作为其底层容器,并提供一组特定的成员函数来访问其元素。它不是独立容器,而是行为控制器。
- 它跟交流电适配器有点类似,可以将一个接口(deque/vector/list)转变成用户希望的另一个接口(stack/queue),不同的交流电适配器就像是不同的转换过程。
3.2 stack和queue的底层实现
stack
- 栈是作为容器适配器实现的。元素从特定容器的“后端 (back)”推入 (push) 和弹出 (pop),该后端被称为栈顶 (top of the stack)。
- 底层容器可以是任何标准容器类模板,也可以是其他专门设计的容器类。该底层容器必须支持以下操作:
- empty (检查是否为空)
- size (获取大小)
- back (访问后端元素)
- push_back (向后端添加元素)
- pop_back (从后端移除元素)
- 标准容器类 vector、deque (双端队列) 和 list (链表) 满足这些要求。默认情况下,如果在实例化特定的栈类时未指定容器类,则使用标准容器 deque (双端队列)。

- 底层实现代码:
template<class T, class Container = deque<T>>
class stack
{
public:
void push(const T& x)
{
_con.push_back(x);
}
T& top()
{
return _con.back();
}
const T& top()const
{
return _con.back();
}
void pop()
{
_con.pop_back();
}
bool empty()const
{
return _con.empty();
}
size_t size()const
{
return _con.size();
}
private:
Container _con;
};
- 我们可以增添一个模板参数 Container 来达到根据需求来决定具体的底层容器。
queue
- 队列是作为容器适配器实现的。元素被推入 (push) 到特定容器的“后端 (back)”,并从其“前端 (front)”弹出 (pop)。
- 底层容器可以是标准容器类模板之一,也可以是其他专门设计的容器类。该底层容器必须至少支持以下操作:
- empty (检查是否为空)
- size (获取大小)
- **front (访问前端元素)
- back (访问后端元素)**
- push_back (向后端添加元素)
- pop_front (从前端移除元素)
-
标准容器类 deque (双端队列) 和 list (链表) 满足这些要求,vector这个容器从前端移除元素效率很低所以不支持 pop_back(),进而不支持vector。默认情况下,如果在实例化特定的队列类时未指定容器类,则使用标准容器 deque。
-
代码实现:
template<class T, class Container = deque<T>>
class queue
{
public:
void push(const T& x)
{
_con.push_back(x);
}
T& front()
{
return _con.front();
}
const T& front()const
{
return _con.front();
}
T& back()
{
return _con.back();
}
const T& back()const
{
return _con.back();
}
void pop()
{
_con.pop_front();
}
bool empty()const
{
return _con.empty();
}
size_t size()const
{
return _con.size();
}
private:
Container _con;
};
- 跟stack的实现差不了太多。
为什么默认容器类都是deque,首先我们需要了解一下这个容器类,再比较一下vector、list、deque的优劣势就能知道了。
二、了解deque
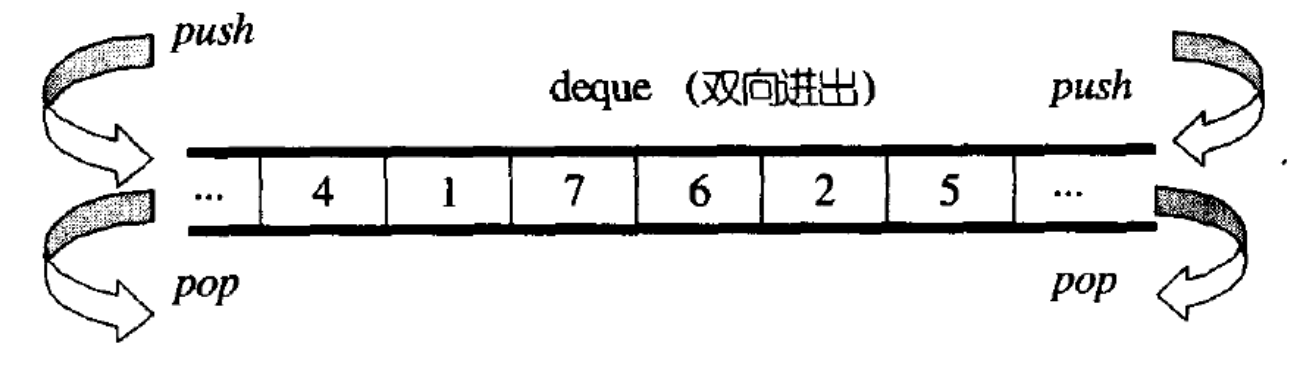
了解:双端队列(deque)是一种动态大小的序列容器,可在其前端(front)和后端(back) 进行扩展或收缩。
- 我们知道,数组和链表的优势各不相同,数组的随机访问效率特别高,链表任意位置O(1)的删除时间复杂度。那么我们能不能创造出一个新的容器,能够集两家之长呢?于是,deque诞生了。
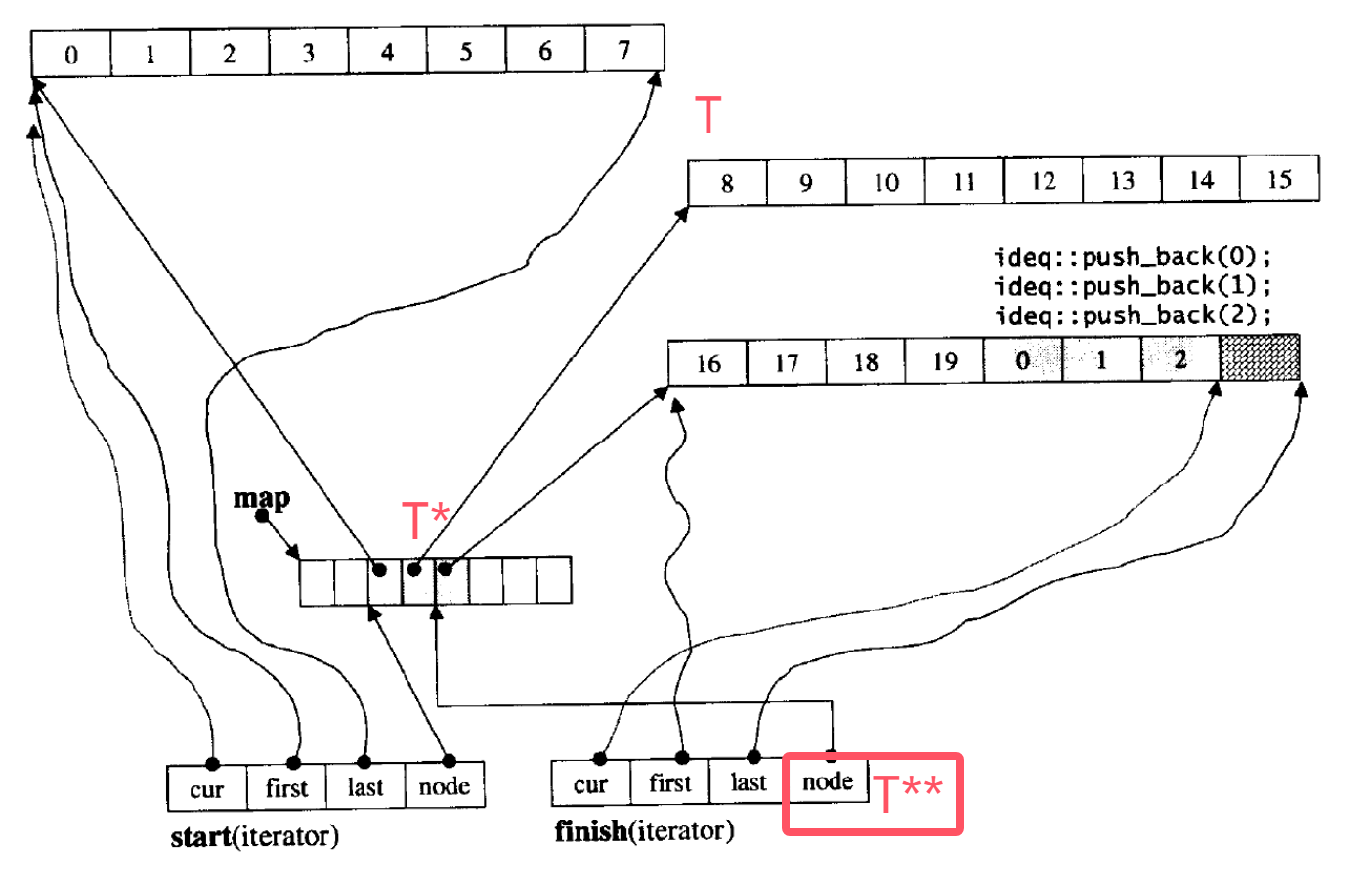
-
关于deque的结构:看上图,map(中央控制数组)是一个指针数组,里面存放着一个个指向数组(这里称每个数组为缓冲区buffer)的指针。每个buffer大小相等,deque的底层是有所有buffer组成的一块分段连续的空间。
-
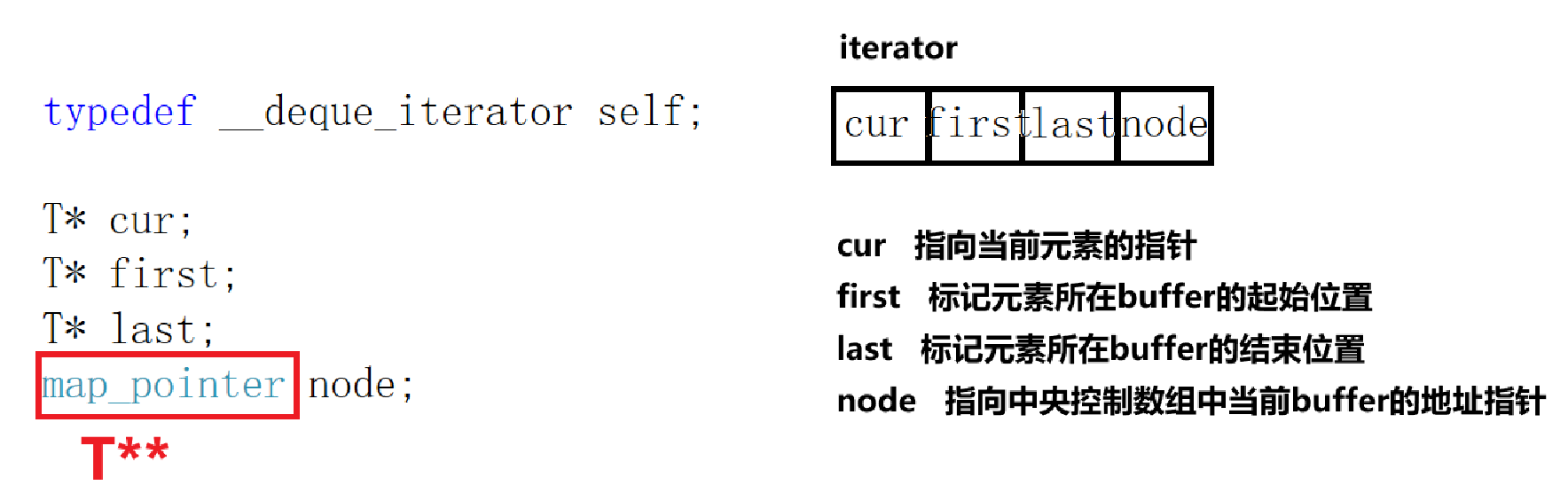
首先,是对迭代器的改造。就像list,底层空间不连续,需要通过重载运算符来达到预期目的。不过改造之后的deque迭代器包含四个成员,分别是cur(指向当前元素的指针)、first(标记元素所在buffer的起始位置)、last(标记元素所在buffer的结束位置)以及node(指向中央控制数组中当前buffer的地址指针)。而它自身有着两个迭代器,一个start迭代器,一个finish迭代器。值得注意的是start迭代器指向deque的起始buffer,finish迭代器指向deque的目前最后一个buffer。以下是linux系统某版本里里iterator的成员变量。
-
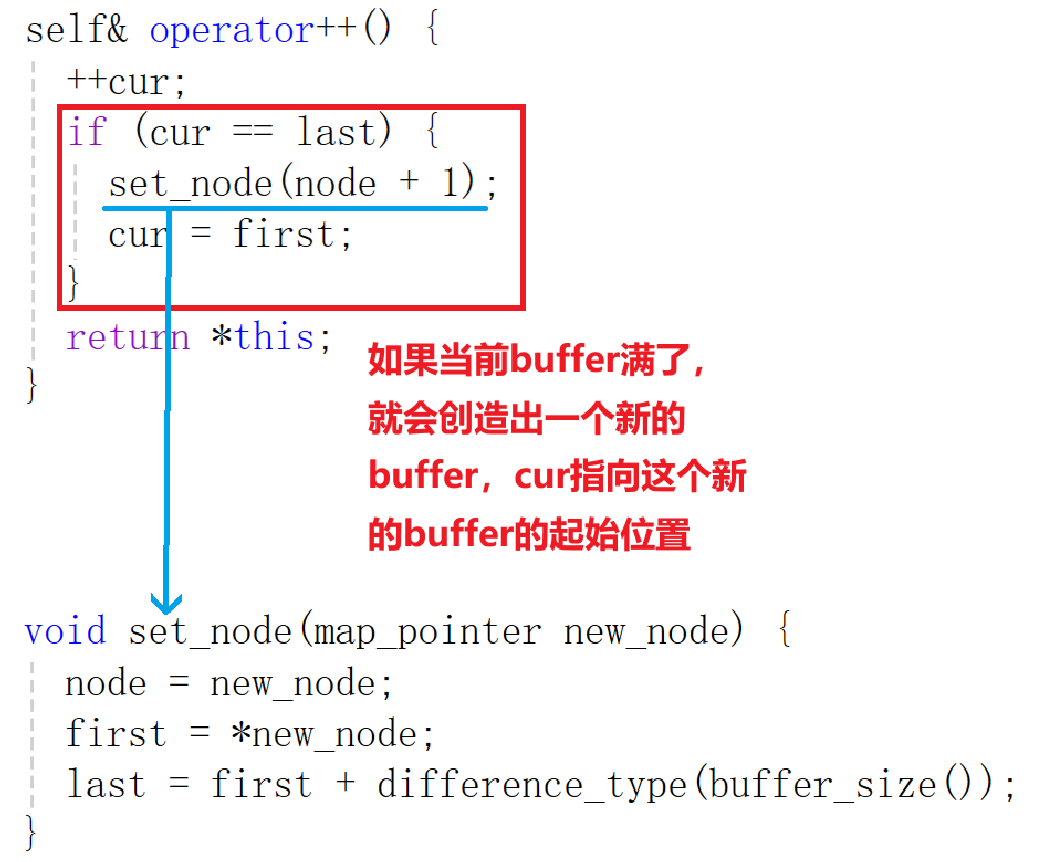
关于deque的push_back(尾插)实现:跟 vector 容器一样,离不开++运算符。不过它的++需要重载。
-
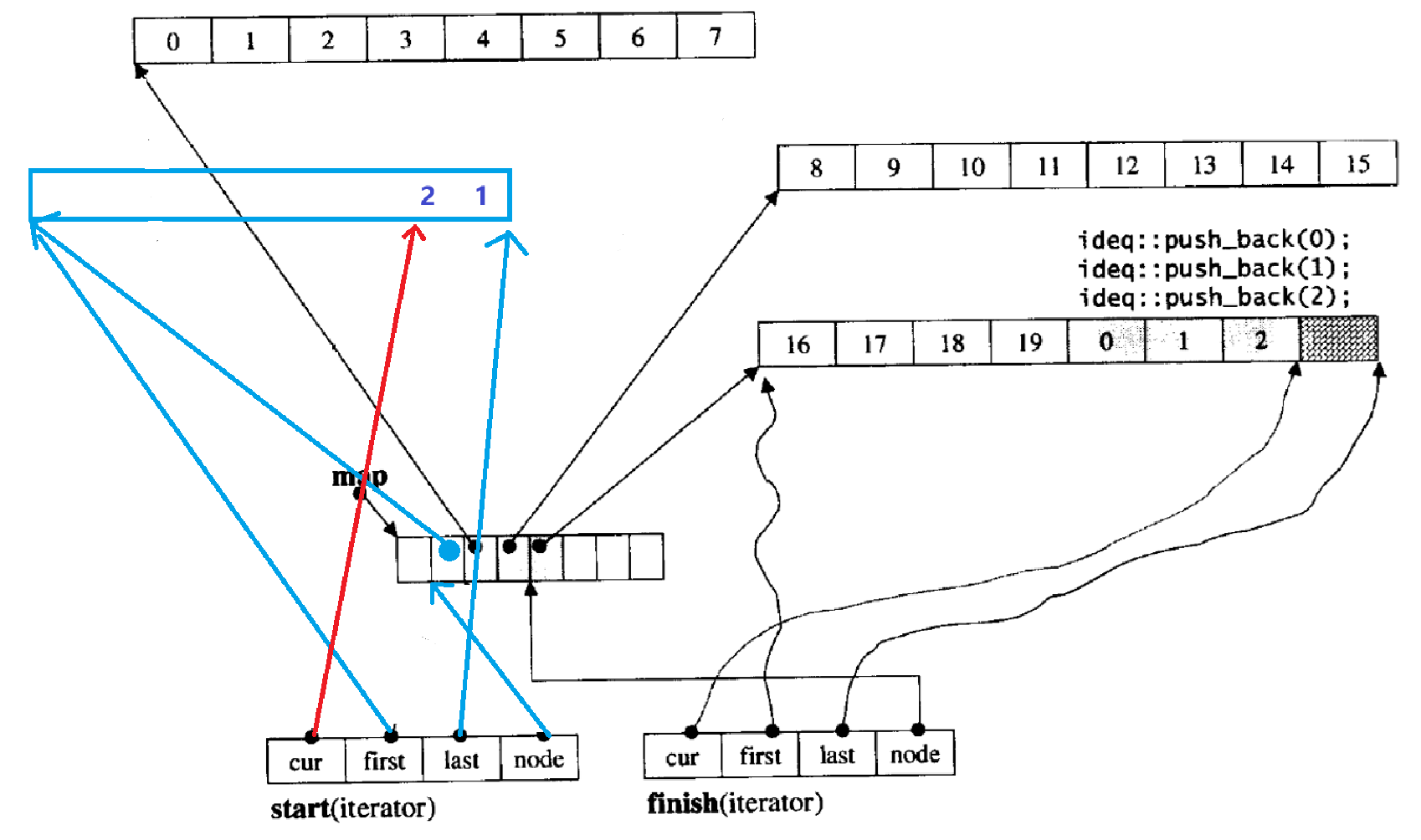
关于deque的push_front(头插)的实现:在 3 中有提到deque内部拥有两个迭代器start和finish,这代表着deque不仅可以在中央控制数组末尾添加buffer,也可以在起始buffer之前添加新的buffer来方便我们的头插操作。为了让数据连续,数据会插入在新的buffer的末尾,就像下图(先1后2):
- 关于deque随机访问的实现:是[ ] 的重载。就是要弄清楚需要访问的元素在第几个buffer,在buffer的哪一个位置。它可以通过 / 与 % 来很好的实现,毕竟每个buffer的大小是固定的。

- 对于deque有一定的了解就够了,想深入了解可以参考下面的源代码。
三、三者比较
1. vector:
优点:
- 下标随机访问快。
- 尾插尾删效率高。
- cpu高速缓存命中率高。
缺点:
- 头部或中间插入删除效率低下。
- 插入空间不够要进行扩容,扩容有一定性能消耗,倍数级扩容很容易存在空间浪费。
2. list:
优点:
- 任意位置插入删除时间复杂度O(1)。
- 按需申请内存,基本不存在空间浪费。
缺点:
- 不支持下标随机访问。
- cpu高速缓存命中率低,还存在缓存污染。
可以看到,vector和list的优势都很极致且互补。
3. deque:
优点:
- deque非常适合头尾插入删除,效率很高。
- 下标随机访问速率也很不错,但是与vector相比,在处理大量数据(100w级以上)时会略逊一筹。
- cpu高速缓存命中率高。
- 按需申请内存。
缺点:中间插入删除效率低下,vector所拥有的弊端未能得到全部改善。
- 关于vector与deque下标访问速率问题,用sort(需要频繁访问数据)再合适不过,可以通过以下代码进行检测(一个vector与deque排序版本,一个将deque数据先拷贝到vector排完序再拷贝回deque与deque排序版本):
void test_op1()
{
srand(time(0));
const int N = 1000000;
deque<int> dq;
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
auto e = rand() + i;
v.push_back(e);
dq.push_back(e);
}
int begin1 = clock();
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
int end1 = clock();
int begin2 = clock();
sort(dq.begin(), dq.end());
int end2 = clock();
printf("vector:%d\n", end1 - begin1);
printf("deque:%d\n", end2 - begin2);
}
void test_op2()
{
srand(time(0));
const int N = 1000000;
deque<int> dq1;
deque<int> dq2;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
auto e = rand() + i;
dq1.push_back(e);
dq2.push_back(e);
}
int begin1 = clock();
sort(dq1.begin(), dq1.end(), less<int>());
int end1 = clock();
int begin2 = clock();
// vector
vector<int> v(dq2.begin(), dq2.end());
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
dq2.assign(v.begin(), v.end());
int end2 = clock();
printf("deque sort:%d\n", end1 - begin1);
printf("deque copy vector sort, copy back deque:%d\n", end2 - begin2);
}
release版本下:
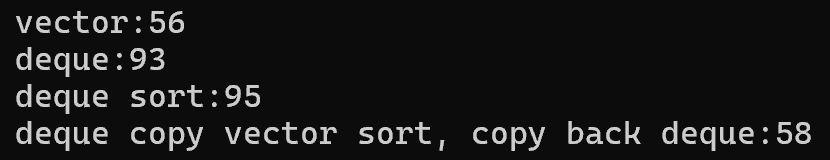
总结:虽然deque最开始的目的是集vector和list之长,但是最终实现出来的效果并没有达到预期目标,它取代不了它们两个。下标访问没有vector快,中间插入删除效率低下不如list,它的优点都不够极致,平常用的少,但是作为stack与queue(要求双端存取效率高)的默认底层容器就再合适不过了。
四、反向迭代器实现
反向迭代器其实是对普通迭代器的封装从而实现复用。不使用萃取的话需要三个模板参数。
#pragma once
template<class Iterator, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct ReverseIterator
{
typedef ReverseIterator<Iterator, Ref, Ptr> Self;
ReverseIterator(Iterator it)
:_it(it)
{}
Ref operator*()const
{
Iterator tmp = _it;
tmp--;
return *tmp;
}
Ptr operator->()const
{
Iterator tmp = _it;
--tmp;
return &(*tmp);
}
Self& operator++()
{
return --_it;
}
Self operator++(int)
{
Self tmp = _it;
--_it;
return tmp;
}
Self& operator--()
{
return ++_it;
}
Self operator--(int)
{
Self tmp = _it;
++_it;
return tmp;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& tmp)const
{
return _it != tmp._it;
}
bool operator== (const Self& tmp)const
{
return _it == tmp._it;
}
public:
Iterator _it;
};

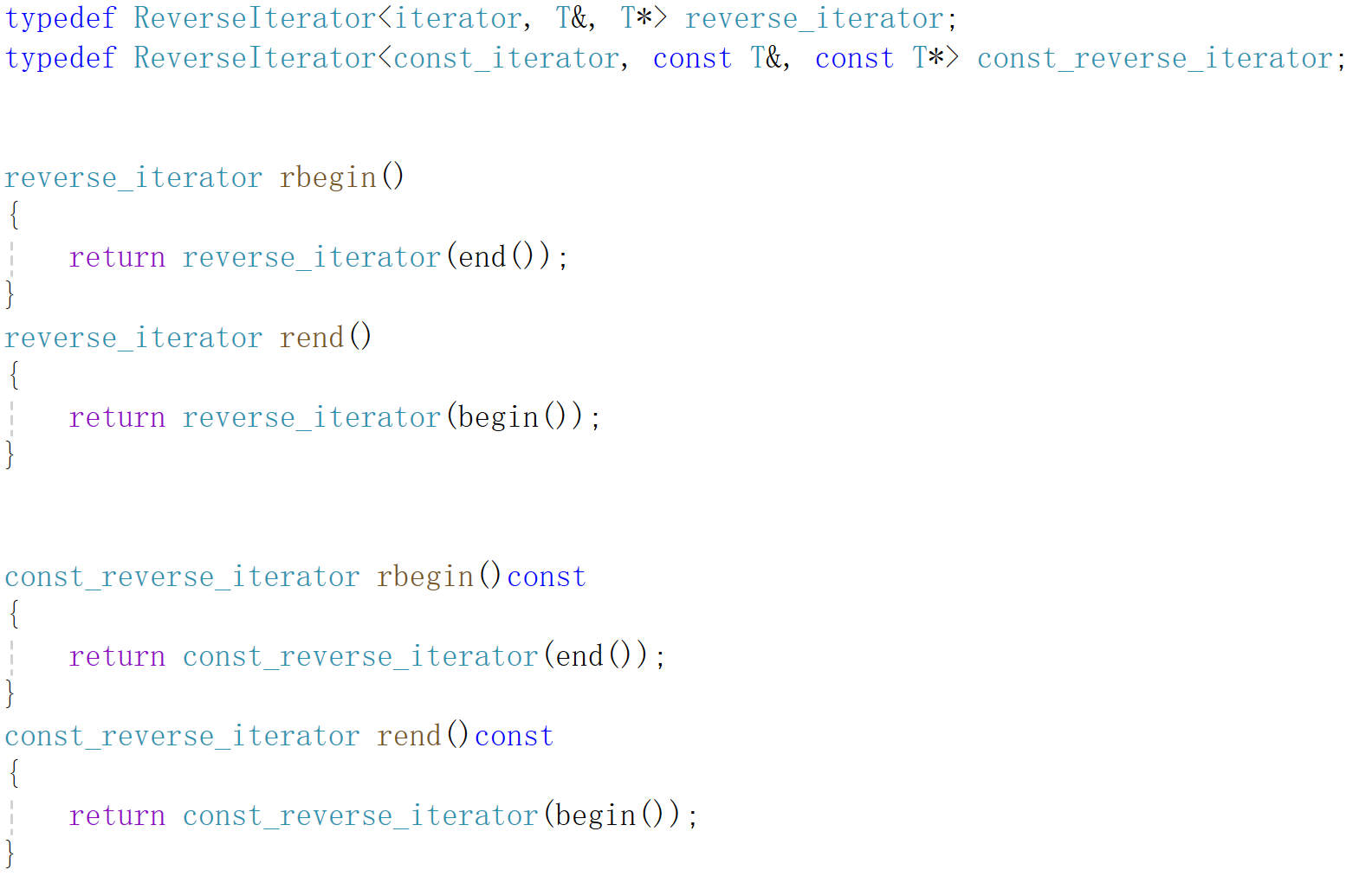
反向迭代器的实现只要清楚大概思路,按照自己的思路走就可以,这里的*与->的实现是参考了Linux里iterator里的源码。主要是为了让之后的 rbegin() 与 rend()的实现变得工整。
五、deque源代码(Linux)
/*
*
* Copyright (c) 1994
* Hewlett-Packard Company
*
* Permission to use, copy, modify, distribute and sell this software
* and its documentation for any purpose is hereby granted without fee,
* provided that the above copyright notice appear in all copies and
* that both that copyright notice and this permission notice appear
* in supporting documentation. Hewlett-Packard Company makes no
* representations about the suitability of this software for any
* purpose. It is provided "as is" without express or implied warranty.
*
*
* Copyright (c) 1997
* Silicon Graphics Computer Systems, Inc.
*
* Permission to use, copy, modify, distribute and sell this software
* and its documentation for any purpose is hereby granted without fee,
* provided that the above copyright notice appear in all copies and
* that both that copyright notice and this permission notice appear
* in supporting documentation. Silicon Graphics makes no
* representations about the suitability of this software for any
* purpose. It is provided "as is" without express or implied warranty.
*/
/* NOTE: This is an internal header file, included by other STL headers.
* You should not attempt to use it directly.
*/
#ifndef __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_DEQUE_H
#define __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_DEQUE_H
/* Class invariants:
* For any nonsingular iterator i:
* i.node is the address of an element in the map array. The
* contents of i.node is a pointer to the beginning of a node.
* i.first == *(i.node)
* i.last == i.first + node_size
* i.cur is a pointer in the range [i.first, i.last). NOTE:
* the implication of this is that i.cur is always a dereferenceable
* pointer, even if i is a past-the-end iterator.
* Start and Finish are always nonsingular iterators. NOTE: this means
* that an empty deque must have one node, and that a deque
* with N elements, where N is the buffer size, must have two nodes.
* For every node other than start.node and finish.node, every element
* in the node is an initialized object. If start.node == finish.node,
* then [start.cur, finish.cur) are initialized objects, and
* the elements outside that range are uninitialized storage. Otherwise,
* [start.cur, start.last) and [finish.first, finish.cur) are initialized
* objects, and [start.first, start.cur) and [finish.cur, finish.last)
* are uninitialized storage.
* [map, map + map_size) is a valid, non-empty range.
* [start.node, finish.node] is a valid range contained within
* [map, map + map_size).
* A pointer in the range [map, map + map_size) points to an allocated
* node if and only if the pointer is in the range [start.node, finish.node].
*/
/*
* In previous versions of deque, node_size was fixed by the
* implementation. In this version, however, users can select
* the node size. Deque has three template parameters; the third,
* a number of type size_t, is the number of elements per node.
* If the third template parameter is 0 (which is the default),
* then deque will use a default node size.
*
* The only reason for using an alternate node size is if your application
* requires a different performance tradeoff than the default. If,
* for example, your program contains many deques each of which contains
* only a few elements, then you might want to save memory (possibly
* by sacrificing some speed) by using smaller nodes.
*
* Unfortunately, some compilers have trouble with non-type template
* parameters; stl_config.h defines __STL_NON_TYPE_TMPL_PARAM_BUG if
* that is the case. If your compiler is one of them, then you will
* not be able to use alternate node sizes; you will have to use the
* default value.
*/
__STL_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
#if defined(__sgi) && !defined(__GNUC__) && (_MIPS_SIM != _MIPS_SIM_ABI32)
#pragma set woff 1174
#endif
// Note: this function is simply a kludge to work around several compilers'
// bugs in handling constant expressions.
inline size_t __deque_buf_size(size_t n, size_t sz)
{
return n != 0 ? n : (sz < 512 ? size_t(512 / sz) : size_t(1));
}
#ifndef __STL_NON_TYPE_TMPL_PARAM_BUG
template <class T, class Ref, class Ptr, size_t BufSiz>
struct __deque_iterator {
typedef __deque_iterator<T, T&, T*, BufSiz> iterator;
typedef __deque_iterator<T, const T&, const T*, BufSiz> const_iterator;
static size_t buffer_size() {return __deque_buf_size(BufSiz, sizeof(T)); }
#else /* __STL_NON_TYPE_TMPL_PARAM_BUG */
template <class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct __deque_iterator {
typedef __deque_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef __deque_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
static size_t buffer_size() {return __deque_buf_size(0, sizeof(T)); }
#endif
typedef random_access_iterator_tag iterator_category;
typedef T value_type;
typedef Ptr pointer;
typedef Ref reference;
typedef size_t size_type;
typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;
typedef T** map_pointer;
typedef __deque_iterator self;
T* cur;
T* first;
T* last;
map_pointer node;
__deque_iterator(T* x, map_pointer y)
: cur(x), first(*y), last(*y + buffer_size()), node(y) {}
__deque_iterator() : cur(0), first(0), last(0), node(0) {}
__deque_iterator(const iterator& x)
: cur(x.cur), first(x.first), last(x.last), node(x.node) {}
reference operator*() const { return *cur; }
#ifndef __SGI_STL_NO_ARROW_OPERATOR
pointer operator->() const { return &(operator*()); }
#endif /* __SGI_STL_NO_ARROW_OPERATOR */
difference_type operator-(const self& x) const {
return difference_type(buffer_size()) * (node - x.node - 1) +
(cur - first) + (x.last - x.cur);
}
self& operator++() {
++cur;
if (cur == last) {
set_node(node + 1);
cur = first;
}
return *this;
}
self operator++(int) {
self tmp = *this;
++*this;
return tmp;
}
self& operator--() {
if (cur == first) {
set_node(node - 1);
cur = last;
}
--cur;
return *this;
}
self operator--(int) {
self tmp = *this;
--*this;
return tmp;
}
self& operator+=(difference_type n) {
difference_type offset = n + (cur - first);
if (offset >= 0 && offset < difference_type(buffer_size()))
cur += n;
else {
difference_type node_offset =
offset > 0 ? offset / difference_type(buffer_size())
: -difference_type((-offset - 1) / buffer_size()) - 1;
set_node(node + node_offset);
cur = first + (offset - node_offset * difference_type(buffer_size()));
}
return *this;
}
self operator+(difference_type n) const {
self tmp = *this;
return tmp += n;
}
self& operator-=(difference_type n) { return *this += -n; }
self operator-(difference_type n) const {
self tmp = *this;
return tmp -= n;
}
reference operator[](difference_type n) const { return *(*this + n); }
bool operator==(const self& x) const { return cur == x.cur; }
bool operator!=(const self& x) const { return !(*this == x); }
bool operator<(const self& x) const {
return (node == x.node) ? (cur < x.cur) : (node < x.node);
}
void set_node(map_pointer new_node) {
node = new_node;
first = *new_node;
last = first + difference_type(buffer_size());
}
};
#ifndef __STL_CLASS_PARTIAL_SPECIALIZATION
#ifndef __STL_NON_TYPE_TMPL_PARAM_BUG
template <class T, class Ref, class Ptr, size_t BufSiz>
inline random_access_iterator_tag
iterator_category(const __deque_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr, BufSiz>&) {
return random_access_iterator_tag();
}
template <class T, class Ref, class Ptr, size_t BufSiz>
inline T* value_type(const __deque_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr, BufSiz>&) {
return 0;
}
template <class T, class Ref, class Ptr, size_t BufSiz>
inline ptrdiff_t* distance_type(const __deque_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr, BufSiz>&) {
return 0;
}
#else /* __STL_NON_TYPE_TMPL_PARAM_BUG */
template <class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
inline random_access_iterator_tag
iterator_category(const __deque_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr>&) {
return random_access_iterator_tag();
}
template <class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
inline T* value_type(const __deque_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr>&) { return 0; }
template <class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
inline ptrdiff_t* distance_type(const __deque_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr>&) {
return 0;
}
#endif /* __STL_NON_TYPE_TMPL_PARAM_BUG */
#endif /* __STL_CLASS_PARTIAL_SPECIALIZATION */
// See __deque_buf_size(). The only reason that the default value is 0
// is as a workaround for bugs in the way that some compilers handle
// constant expressions.
template <class T, class Alloc = alloc, size_t BufSiz = 0>
class deque {
public: // Basic types
typedef T value_type;
typedef value_type* pointer;
typedef const value_type* const_pointer;
typedef value_type& reference;
typedef const value_type& const_reference;
typedef size_t size_type;
typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;
public: // Iterators
#ifndef __STL_NON_TYPE_TMPL_PARAM_BUG
typedef __deque_iterator<T, T&, T*, BufSiz> iterator;
typedef __deque_iterator<T, const T&, const T&, BufSiz> const_iterator;
#else /* __STL_NON_TYPE_TMPL_PARAM_BUG */
typedef __deque_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef __deque_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
#endif /* __STL_NON_TYPE_TMPL_PARAM_BUG */
#ifdef __STL_CLASS_PARTIAL_SPECIALIZATION
typedef reverse_iterator<const_iterator> const_reverse_iterator;
typedef reverse_iterator<iterator> reverse_iterator;
#else /* __STL_CLASS_PARTIAL_SPECIALIZATION */
typedef reverse_iterator<const_iterator, value_type, const_reference,
difference_type>
const_reverse_iterator;
typedef reverse_iterator<iterator, value_type, reference, difference_type>
reverse_iterator;
#endif /* __STL_CLASS_PARTIAL_SPECIALIZATION */
protected: // Internal typedefs
typedef pointer* map_pointer;
typedef simple_alloc<value_type, Alloc> data_allocator;
typedef simple_alloc<pointer, Alloc> map_allocator;
static size_type buffer_size() {
return __deque_buf_size(BufSiz, sizeof(value_type));
}
static size_type initial_map_size() { return 8; }
protected: // Data members
iterator start;
iterator finish;
map_pointer map;
size_type map_size;
public: // Basic accessors
iterator begin() { return start; }
iterator end() { return finish; }
const_iterator begin() const { return start; }
const_iterator end() const { return finish; }
reverse_iterator rbegin() { return reverse_iterator(finish); }
reverse_iterator rend() { return reverse_iterator(start); }
const_reverse_iterator rbegin() const {
return const_reverse_iterator(finish);
}
const_reverse_iterator rend() const {
return const_reverse_iterator(start);
}
reference operator[](size_type n) { return start[difference_type(n)]; }
const_reference operator[](size_type n) const {
return start[difference_type(n)];
}
reference front() { return *start; }
reference back() {
iterator tmp = finish;
--tmp;
return *tmp;
}
const_reference front() const { return *start; }
const_reference back() const {
const_iterator tmp = finish;
--tmp;
return *tmp;
}
size_type size() const { return finish - start;; }
size_type max_size() const { return size_type(-1); }
bool empty() const { return finish == start; }
public: // Constructor, destructor.
deque()
: start(), finish(), map(0), map_size(0)
{
create_map_and_nodes(0);
}
deque(const deque& x)
: start(), finish(), map(0), map_size(0)
{
create_map_and_nodes(x.size());
__STL_TRY {
uninitialized_copy(x.begin(), x.end(), start);
}
__STL_UNWIND(destroy_map_and_nodes());
}
deque(size_type n, const value_type& value)
: start(), finish(), map(0), map_size(0)
{
fill_initialize(n, value);
}
deque(int n, const value_type& value)
: start(), finish(), map(0), map_size(0)
{
fill_initialize(n, value);
}
deque(long n, const value_type& value)
: start(), finish(), map(0), map_size(0)
{
fill_initialize(n, value);
}
explicit deque(size_type n)
: start(), finish(), map(0), map_size(0)
{
fill_initialize(n, value_type());
}
#ifdef __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES
template <class InputIterator>
deque(InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
: start(), finish(), map(0), map_size(0)
{
range_initialize(first, last, iterator_category(first));
}
#else /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */
deque(const value_type* first, const value_type* last)
: start(), finish(), map(0), map_size(0)
{
create_map_and_nodes(last - first);
__STL_TRY {
uninitialized_copy(first, last, start);
}
__STL_UNWIND(destroy_map_and_nodes());
}
deque(const_iterator first, const_iterator last)
: start(), finish(), map(0), map_size(0)
{
create_map_and_nodes(last - first);
__STL_TRY {
uninitialized_copy(first, last, start);
}
__STL_UNWIND(destroy_map_and_nodes());
}
#endif /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */
~deque() {
destroy(start, finish);
destroy_map_and_nodes();
}
deque& operator= (const deque& x) {
const size_type len = size();
if (&x != this) {
if (len >= x.size())
erase(copy(x.begin(), x.end(), start), finish);
else {
const_iterator mid = x.begin() + difference_type(len);
copy(x.begin(), mid, start);
insert(finish, mid, x.end());
}
}
return *this;
}
void swap(deque& x) {
__STD::swap(start, x.start);
__STD::swap(finish, x.finish);
__STD::swap(map, x.map);
__STD::swap(map_size, x.map_size);
}
public: // push_* and pop_*
void push_back(const value_type& t) {
if (finish.cur != finish.last - 1) {
construct(finish.cur, t);
++finish.cur;
}
else
push_back_aux(t);
}
void push_front(const value_type& t) {
if (start.cur != start.first) {
construct(start.cur - 1, t);
--start.cur;
}
else
push_front_aux(t);
}
void pop_back() {
if (finish.cur != finish.first) {
--finish.cur;
destroy(finish.cur);
}
else
pop_back_aux();
}
void pop_front() {
if (start.cur != start.last - 1) {
destroy(start.cur);
++start.cur;
}
else
pop_front_aux();
}
public: // Insert
iterator insert(iterator position, const value_type& x) {
if (position.cur == start.cur) {
push_front(x);
return start;
}
else if (position.cur == finish.cur) {
push_back(x);
iterator tmp = finish;
--tmp;
return tmp;
}
else {
return insert_aux(position, x);
}
}
iterator insert(iterator position) { return insert(position, value_type()); }
void insert(iterator pos, size_type n, const value_type& x);
void insert(iterator pos, int n, const value_type& x) {
insert(pos, (size_type) n, x);
}
void insert(iterator pos, long n, const value_type& x) {
insert(pos, (size_type) n, x);
}
#ifdef __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES
template <class InputIterator>
void insert(iterator pos, InputIterator first, InputIterator last) {
insert(pos, first, last, iterator_category(first));
}
#else /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */
void insert(iterator pos, const value_type* first, const value_type* last);
void insert(iterator pos, const_iterator first, const_iterator last);
#endif /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */
void resize(size_type new_size, const value_type& x) {
const size_type len = size();
if (new_size < len)
erase(start + new_size, finish);
else
insert(finish, new_size - len, x);
}
void resize(size_type new_size) { resize(new_size, value_type()); }
public: // Erase
iterator erase(iterator pos) {
iterator next = pos;
++next;
difference_type index = pos - start;
if (index < (size() >> 1)) {
copy_backward(start, pos, next);
pop_front();
}
else {
copy(next, finish, pos);
pop_back();
}
return start + index;
}
iterator erase(iterator first, iterator last);
void clear();
protected: // Internal construction/destruction
void create_map_and_nodes(size_type num_elements);
void destroy_map_and_nodes();
void fill_initialize(size_type n, const value_type& value);
#ifdef __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES
template <class InputIterator>
void range_initialize(InputIterator first, InputIterator last,
input_iterator_tag);
template <class ForwardIterator>
void range_initialize(ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last,
forward_iterator_tag);
#endif /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */
protected: // Internal push_* and pop_*
void push_back_aux(const value_type& t);
void push_front_aux(const value_type& t);
void pop_back_aux();
void pop_front_aux();
protected: // Internal insert functions
#ifdef __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES
template <class InputIterator>
void insert(iterator pos, InputIterator first, InputIterator last,
input_iterator_tag);
template <class ForwardIterator>
void insert(iterator pos, ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last,
forward_iterator_tag);
#endif /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */
iterator insert_aux(iterator pos, const value_type& x);
void insert_aux(iterator pos, size_type n, const value_type& x);
#ifdef __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES
template <class ForwardIterator>
void insert_aux(iterator pos, ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last,
size_type n);
#else /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */
void insert_aux(iterator pos,
const value_type* first, const value_type* last,
size_type n);
void insert_aux(iterator pos, const_iterator first, const_iterator last,
size_type n);
#endif /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */
iterator reserve_elements_at_front(size_type n) {
size_type vacancies = start.cur - start.first;
if (n > vacancies)
new_elements_at_front(n - vacancies);
return start - difference_type(n);
}
iterator reserve_elements_at_back(size_type n) {
size_type vacancies = (finish.last - finish.cur) - 1;
if (n > vacancies)
new_elements_at_back(n - vacancies);
return finish + difference_type(n);
}
void new_elements_at_front(size_type new_elements);
void new_elements_at_back(size_type new_elements);
void destroy_nodes_at_front(iterator before_start);
void destroy_nodes_at_back(iterator after_finish);
protected: // Allocation of map and nodes
// Makes sure the map has space for new nodes. Does not actually
// add the nodes. Can invalidate map pointers. (And consequently,
// deque iterators.)
void reserve_map_at_back (size_type nodes_to_add = 1) {
if (nodes_to_add + 1 > map_size - (finish.node - map))
reallocate_map(nodes_to_add, false);
}
void reserve_map_at_front (size_type nodes_to_add = 1) {
if (nodes_to_add > start.node - map)
reallocate_map(nodes_to_add, true);
}
void reallocate_map(size_type nodes_to_add, bool add_at_front);
pointer allocate_node() { return data_allocator::allocate(buffer_size()); }
void deallocate_node(pointer n) {
data_allocator::deallocate(n, buffer_size());
}
#ifdef __STL_NON_TYPE_TMPL_PARAM_BUG
public:
bool operator==(const deque<T, Alloc, 0>& x) const {
return size() == x.size() && equal(begin(), end(), x.begin());
}
bool operator!=(const deque<T, Alloc, 0>& x) const {
return size() != x.size() || !equal(begin(), end(), x.begin());
}
bool operator<(const deque<T, Alloc, 0>& x) const {
return lexicographical_compare(begin(), end(), x.begin(), x.end());
}
#endif /* __STL_NON_TYPE_TMPL_PARAM_BUG */
};
// Non-inline member functions
template <class T, class Alloc, size_t BufSize>
void deque<T, Alloc, BufSize>::insert(iterator pos,
size_type n, const value_type& x) {
if (pos.cur == start.cur) {
iterator new_start = reserve_elements_at_front(n);
uninitialized_fill(new_start, start, x);
start = new_start;
}
else if (pos.cur == finish.cur) {
iterator new_finish = reserve_elements_at_back(n);
uninitialized_fill(finish, new_finish, x);
finish = new_finish;
}
else
insert_aux(pos, n, x);
}
#ifndef __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES
template <class T, class Alloc, size_t BufSize>
void deque<T, Alloc, BufSize>::insert(iterator pos,
const value_type* first,
const value_type* last) {
size_type n = last - first;
if (pos.cur == start.cur) {
iterator new_start = reserve_elements_at_front(n);
__STL_TRY {
uninitialized_copy(first, last, new_start);
start = new_start;
}
__STL_UNWIND(destroy_nodes_at_front(new_start));
}
else if (pos.cur == finish.cur) {
iterator new_finish = reserve_elements_at_back(n);
__STL_TRY {
uninitialized_copy(first, last, finish);
finish = new_finish;
}
__STL_UNWIND(destroy_nodes_at_back(new_finish));
}
else
insert_aux(pos, first, last, n);
}
template <class T, class Alloc, size_t BufSize>
void deque<T, Alloc, BufSize>::insert(iterator pos,
const_iterator first,
const_iterator last)
{
size_type n = last - first;
if (pos.cur == start.cur) {
iterator new_start = reserve_elements_at_front(n);
__STL_TRY {
uninitialized_copy(first, last, new_start);
start = new_start;
}
__STL_UNWIND(destroy_nodes_at_front(new_start));
}
else if (pos.cur == finish.cur) {
iterator new_finish = reserve_elements_at_back(n);
__STL_TRY {
uninitialized_copy(first, last, finish);
finish = new_finish;
}
__STL_UNWIND(destroy_nodes_at_back(new_finish));
}
else
insert_aux(pos, first, last, n);
}
#endif /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */
template <class T, class Alloc, size_t BufSize>
deque<T, Alloc, BufSize>::iterator
deque<T, Alloc, BufSize>::erase(iterator first, iterator last) {
if (first == start && last == finish) {
clear();
return finish;
}
else {
difference_type n = last - first;
difference_type elems_before = first - start;
if (elems_before < (size() - n) / 2) {
copy_backward(start, first, last);
iterator new_start = start + n;
destroy(start, new_start);
for (map_pointer cur = start.node; cur < new_start.node; ++cur)
data_allocator::deallocate(*cur, buffer_size());
start = new_start;
}
else {
copy(last, finish, first);
iterator new_finish = finish - n;
destroy(new_finish, finish);
for (map_pointer cur = new_finish.node + 1; cur <= finish.node; ++cur)
data_allocator::deallocate(*cur, buffer_size());
finish = new_finish;
}
return start + elems_before;
}
}
template <class T, class Alloc, size_t BufSize>
void deque<T, Alloc, BufSize>::clear() {
for (map_pointer node = start.node + 1; node < finish.node; ++node) {
destroy(*node, *node + buffer_size());
data_allocator::deallocate(*node, buffer_size());
}
if (start.node != finish.node) {
destroy(start.cur, start.last);
destroy(finish.first, finish.cur);
data_allocator::deallocate(finish.first, buffer_size());
}
else
destroy(start.cur, finish.cur);
finish = start;
}
template <class T, class Alloc, size_t BufSize>
void deque<T, Alloc, BufSize>::create_map_and_nodes(size_type num_elements) {
size_type num_nodes = num_elements / buffer_size() + 1;
map_size = max(initial_map_size(), num_nodes + 2);
map = map_allocator::allocate(map_size);
map_pointer nstart = map + (map_size - num_nodes) / 2;
map_pointer nfinish = nstart + num_nodes - 1;
map_pointer cur;
__STL_TRY {
for (cur = nstart; cur <= nfinish; ++cur)
*cur = allocate_node();
}
# ifdef __STL_USE_EXCEPTIONS
catch(...) {
for (map_pointer n = nstart; n < cur; ++n)
deallocate_node(*n);
map_allocator::deallocate(map, map_size);
throw;
}
# endif /* __STL_USE_EXCEPTIONS */
start.set_node(nstart);
finish.set_node(nfinish);
start.cur = start.first;
finish.cur = finish.first + num_elements % buffer_size();
}
// This is only used as a cleanup function in catch clauses.
template <class T, class Alloc, size_t BufSize>
void deque<T, Alloc, BufSize>::destroy_map_and_nodes() {
for (map_pointer cur = start.node; cur <= finish.node; ++cur)
deallocate_node(*cur);
map_allocator::deallocate(map, map_size);
}
template <class T, class Alloc, size_t BufSize>
void deque<T, Alloc, BufSize>::fill_initialize(size_type n,
const value_type& value) {
create_map_and_nodes(n);
map_pointer cur;
__STL_TRY {
for (cur = start.node; cur < finish.node; ++cur)
uninitialized_fill(*cur, *cur + buffer_size(), value);
uninitialized_fill(finish.first, finish.cur, value);
}
# ifdef __STL_USE_EXCEPTIONS
catch(...) {
for (map_pointer n = start.node; n < cur; ++n)
destroy(*n, *n + buffer_size());
destroy_map_and_nodes();
throw;
}
# endif /* __STL_USE_EXCEPTIONS */
}
#ifdef __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES
template <class T, class Alloc, size_t BufSize>
template <class InputIterator>
void deque<T, Alloc, BufSize>::range_initialize(InputIterator first,
InputIterator last,
input_iterator_tag) {
create_map_and_nodes(0);
for ( ; first != last; ++first)
push_back(*first);
}
template <class T, class Alloc, size_t BufSize>
template <class ForwardIterator>
void deque<T, Alloc, BufSize>::range_initialize(ForwardIterator first,
ForwardIterator last,
forward_iterator_tag) {
size_type n = 0;
distance(first, last, n);
create_map_and_nodes(n);
__STL_TRY {
uninitialized_copy(first, last, start);
}
__STL_UNWIND(destroy_map_and_nodes());
}
#endif /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */
// Called only if finish.cur == finish.last - 1.
template <class T, class Alloc, size_t BufSize>
void deque<T, Alloc, BufSize>::push_back_aux(const value_type& t) {
value_type t_copy = t;
reserve_map_at_back();
*(finish.node + 1) = allocate_node();
__STL_TRY {
construct(finish.cur, t_copy);
finish.set_node(finish.node + 1);
finish.cur = finish.first;
}
__STL_UNWIND(deallocate_node(*(finish.node + 1)));
}
// Called only if start.cur == start.first.
template <class T, class Alloc, size_t BufSize>
void deque<T, Alloc, BufSize>::push_front_aux(const value_type& t) {
value_type t_copy = t;
reserve_map_at_front();
*(start.node - 1) = allocate_node();
__STL_TRY {
start.set_node(start.node - 1);
start.cur = start.last - 1;
construct(start.cur, t_copy);
}
# ifdef __STL_USE_EXCEPTIONS
catch(...) {
start.set_node(start.node + 1);
start.cur = start.first;
deallocate_node(*(start.node - 1));
throw;
}
# endif /* __STL_USE_EXCEPTIONS */
}
// Called only if finish.cur == finish.first.
template <class T, class Alloc, size_t BufSize>
void deque<T, Alloc, BufSize>:: pop_back_aux() {
deallocate_node(finish.first);
finish.set_node(finish.node - 1);
finish.cur = finish.last - 1;
destroy(finish.cur);
}
// Called only if start.cur == start.last - 1. Note that if the deque
// has at least one element (a necessary precondition for this member
// function), and if start.cur == start.last, then the deque must have
// at least two nodes.
template <class T, class Alloc, size_t BufSize>
void deque<T, Alloc, BufSize>::pop_front_aux() {
destroy(start.cur);
deallocate_node(start.first);
start.set_node(start.node + 1);
start.cur = start.first;
}
#ifdef __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES
template <class T, class Alloc, size_t BufSize>
template <class InputIterator>
void deque<T, Alloc, BufSize>::insert(iterator pos,
InputIterator first, InputIterator last,
input_iterator_tag) {
copy(first, last, inserter(*this, pos));
}
template <class T, class Alloc, size_t BufSize>
template <class ForwardIterator>
void deque<T, Alloc, BufSize>::insert(iterator pos,
ForwardIterator first,
ForwardIterator last,
forward_iterator_tag) {
size_type n = 0;
distance(first, last, n);
if (pos.cur == start.cur) {
iterator new_start = reserve_elements_at_front(n);
__STL_TRY {
uninitialized_copy(first, last, new_start);
start = new_start;
}
__STL_UNWIND(destroy_nodes_at_front(new_start));
}
else if (pos.cur == finish.cur) {
iterator new_finish = reserve_elements_at_back(n);
__STL_TRY {
uninitialized_copy(first, last, finish);
finish = new_finish;
}
__STL_UNWIND(destroy_nodes_at_back(new_finish));
}
else
insert_aux(pos, first, last, n);
}
#endif /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */
template <class T, class Alloc, size_t BufSize>
typename deque<T, Alloc, BufSize>::iterator
deque<T, Alloc, BufSize>::insert_aux(iterator pos, const value_type& x) {
difference_type index = pos - start;
value_type x_copy = x;
if (index < size() / 2) {
push_front(front());
iterator front1 = start;
++front1;
iterator front2 = front1;
++front2;
pos = start + index;
iterator pos1 = pos;
++pos1;
copy(front2, pos1, front1);
}
else {
push_back(back());
iterator back1 = finish;
--back1;
iterator back2 = back1;
--back2;
pos = start + index;
copy_backward(pos, back2, back1);
}
*pos = x_copy;
return pos;
}
template <class T, class Alloc, size_t BufSize>
void deque<T, Alloc, BufSize>::insert_aux(iterator pos,
size_type n, const value_type& x) {
const difference_type elems_before = pos - start;
size_type length = size();
value_type x_copy = x;
if (elems_before < length / 2) {
iterator new_start = reserve_elements_at_front(n);
iterator old_start = start;
pos = start + elems_before;
__STL_TRY {
if (elems_before >= difference_type(n)) {
iterator start_n = start + difference_type(n);
uninitialized_copy(start, start_n, new_start);
start = new_start;
copy(start_n, pos, old_start);
fill(pos - difference_type(n), pos, x_copy);
}
else {
__uninitialized_copy_fill(start, pos, new_start, start, x_copy);
start = new_start;
fill(old_start, pos, x_copy);
}
}
__STL_UNWIND(destroy_nodes_at_front(new_start));
}
else {
iterator new_finish = reserve_elements_at_back(n);
iterator old_finish = finish;
const difference_type elems_after = difference_type(length) - elems_before;
pos = finish - elems_after;
__STL_TRY {
if (elems_after > difference_type(n)) {
iterator finish_n = finish - difference_type(n);
uninitialized_copy(finish_n, finish, finish);
finish = new_finish;
copy_backward(pos, finish_n, old_finish);
fill(pos, pos + difference_type(n), x_copy);
}
else {
__uninitialized_fill_copy(finish, pos + difference_type(n),
x_copy,
pos, finish);
finish = new_finish;
fill(pos, old_finish, x_copy);
}
}
__STL_UNWIND(destroy_nodes_at_back(new_finish));
}
}
#ifdef __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES
template <class T, class Alloc, size_t BufSize>
template <class ForwardIterator>
void deque<T, Alloc, BufSize>::insert_aux(iterator pos,
ForwardIterator first,
ForwardIterator last,
size_type n)
{
const difference_type elems_before = pos - start;
size_type length = size();
if (elems_before < length / 2) {
iterator new_start = reserve_elements_at_front(n);
iterator old_start = start;
pos = start + elems_before;
__STL_TRY {
if (elems_before >= difference_type(n)) {
iterator start_n = start + difference_type(n);
uninitialized_copy(start, start_n, new_start);
start = new_start;
copy(start_n, pos, old_start);
copy(first, last, pos - difference_type(n));
}
else {
ForwardIterator mid = first;
advance(mid, difference_type(n) - elems_before);
__uninitialized_copy_copy(start, pos, first, mid, new_start);
start = new_start;
copy(mid, last, old_start);
}
}
__STL_UNWIND(destroy_nodes_at_front(new_start));
}
else {
iterator new_finish = reserve_elements_at_back(n);
iterator old_finish = finish;
const difference_type elems_after = difference_type(length) - elems_before;
pos = finish - elems_after;
__STL_TRY {
if (elems_after > difference_type(n)) {
iterator finish_n = finish - difference_type(n);
uninitialized_copy(finish_n, finish, finish);
finish = new_finish;
copy_backward(pos, finish_n, old_finish);
copy(first, last, pos);
}
else {
ForwardIterator mid = first;
advance(mid, elems_after);
__uninitialized_copy_copy(mid, last, pos, finish, finish);
finish = new_finish;
copy(first, mid, pos);
}
}
__STL_UNWIND(destroy_nodes_at_back(new_finish));
}
}
#else /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */
template <class T, class Alloc, size_t BufSize>
void deque<T, Alloc, BufSize>::insert_aux(iterator pos,
const value_type* first,
const value_type* last,
size_type n)
{
const difference_type elems_before = pos - start;
size_type length = size();
if (elems_before < length / 2) {
iterator new_start = reserve_elements_at_front(n);
iterator old_start = start;
pos = start + elems_before;
__STL_TRY {
if (elems_before >= difference_type(n)) {
iterator start_n = start + difference_type(n);
uninitialized_copy(start, start_n, new_start);
start = new_start;
copy(start_n, pos, old_start);
copy(first, last, pos - difference_type(n));
}
else {
const value_type* mid = first + (difference_type(n) - elems_before);
__uninitialized_copy_copy(start, pos, first, mid, new_start);
start = new_start;
copy(mid, last, old_start);
}
}
__STL_UNWIND(destroy_nodes_at_front(new_start));
}
else {
iterator new_finish = reserve_elements_at_back(n);
iterator old_finish = finish;
const difference_type elems_after = difference_type(length) - elems_before;
pos = finish - elems_after;
__STL_TRY {
if (elems_after > difference_type(n)) {
iterator finish_n = finish - difference_type(n);
uninitialized_copy(finish_n, finish, finish);
finish = new_finish;
copy_backward(pos, finish_n, old_finish);
copy(first, last, pos);
}
else {
const value_type* mid = first + elems_after;
__uninitialized_copy_copy(mid, last, pos, finish, finish);
finish = new_finish;
copy(first, mid, pos);
}
}
__STL_UNWIND(destroy_nodes_at_back(new_finish));
}
}
template <class T, class Alloc, size_t BufSize>
void deque<T, Alloc, BufSize>::insert_aux(iterator pos,
const_iterator first,
const_iterator last,
size_type n)
{
const difference_type elems_before = pos - start;
size_type length = size();
if (elems_before < length / 2) {
iterator new_start = reserve_elements_at_front(n);
iterator old_start = start;
pos = start + elems_before;
__STL_TRY {
if (elems_before >= n) {
iterator start_n = start + n;
uninitialized_copy(start, start_n, new_start);
start = new_start;
copy(start_n, pos, old_start);
copy(first, last, pos - difference_type(n));
}
else {
const_iterator mid = first + (n - elems_before);
__uninitialized_copy_copy(start, pos, first, mid, new_start);
start = new_start;
copy(mid, last, old_start);
}
}
__STL_UNWIND(destroy_nodes_at_front(new_start));
}
else {
iterator new_finish = reserve_elements_at_back(n);
iterator old_finish = finish;
const difference_type elems_after = length - elems_before;
pos = finish - elems_after;
__STL_TRY {
if (elems_after > n) {
iterator finish_n = finish - difference_type(n);
uninitialized_copy(finish_n, finish, finish);
finish = new_finish;
copy_backward(pos, finish_n, old_finish);
copy(first, last, pos);
}
else {
const_iterator mid = first + elems_after;
__uninitialized_copy_copy(mid, last, pos, finish, finish);
finish = new_finish;
copy(first, mid, pos);
}
}
__STL_UNWIND(destroy_nodes_at_back(new_finish));
}
}
#endif /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */
template <class T, class Alloc, size_t BufSize>
void deque<T, Alloc, BufSize>::new_elements_at_front(size_type new_elements) {
size_type new_nodes = (new_elements + buffer_size() - 1) / buffer_size();
reserve_map_at_front(new_nodes);
size_type i;
__STL_TRY {
for (i = 1; i <= new_nodes; ++i)
*(start.node - i) = allocate_node();
}
# ifdef __STL_USE_EXCEPTIONS
catch(...) {
for (size_type j = 1; j < i; ++j)
deallocate_node(*(start.node - j));
throw;
}
# endif /* __STL_USE_EXCEPTIONS */
}
template <class T, class Alloc, size_t BufSize>
void deque<T, Alloc, BufSize>::new_elements_at_back(size_type new_elements) {
size_type new_nodes = (new_elements + buffer_size() - 1) / buffer_size();
reserve_map_at_back(new_nodes);
size_type i;
__STL_TRY {
for (i = 1; i <= new_nodes; ++i)
*(finish.node + i) = allocate_node();
}
# ifdef __STL_USE_EXCEPTIONS
catch(...) {
for (size_type j = 1; j < i; ++j)
deallocate_node(*(finish.node + j));
throw;
}
# endif /* __STL_USE_EXCEPTIONS */
}
template <class T, class Alloc, size_t BufSize>
void deque<T, Alloc, BufSize>::destroy_nodes_at_front(iterator before_start) {
for (map_pointer n = before_start.node; n < start.node; ++n)
deallocate_node(*n);
}
template <class T, class Alloc, size_t BufSize>
void deque<T, Alloc, BufSize>::destroy_nodes_at_back(iterator after_finish) {
for (map_pointer n = after_finish.node; n > finish.node; --n)
deallocate_node(*n);
}
template <class T, class Alloc, size_t BufSize>
void deque<T, Alloc, BufSize>::reallocate_map(size_type nodes_to_add,
bool add_at_front) {
size_type old_num_nodes = finish.node - start.node + 1;
size_type new_num_nodes = old_num_nodes + nodes_to_add;
map_pointer new_nstart;
if (map_size > 2 * new_num_nodes) {
new_nstart = map + (map_size - new_num_nodes) / 2
+ (add_at_front ? nodes_to_add : 0);
if (new_nstart < start.node)
copy(start.node, finish.node + 1, new_nstart);
else
copy_backward(start.node, finish.node + 1, new_nstart + old_num_nodes);
}
else {
size_type new_map_size = map_size + max(map_size, nodes_to_add) + 2;
map_pointer new_map = map_allocator::allocate(new_map_size);
new_nstart = new_map + (new_map_size - new_num_nodes) / 2
+ (add_at_front ? nodes_to_add : 0);
copy(start.node, finish.node + 1, new_nstart);
map_allocator::deallocate(map, map_size);
map = new_map;
map_size = new_map_size;
}
start.set_node(new_nstart);
finish.set_node(new_nstart + old_num_nodes - 1);
}
// Nonmember functions.
#ifndef __STL_NON_TYPE_TMPL_PARAM_BUG
template <class T, class Alloc, size_t BufSiz>
bool operator==(const deque<T, Alloc, BufSiz>& x,
const deque<T, Alloc, BufSiz>& y) {
return x.size() == y.size() && equal(x.begin(), x.end(), y.begin());
}
template <class T, class Alloc, size_t BufSiz>
bool operator<(const deque<T, Alloc, BufSiz>& x,
const deque<T, Alloc, BufSiz>& y) {
return lexicographical_compare(x.begin(), x.end(), y.begin(), y.end());
}
#endif /* __STL_NON_TYPE_TMPL_PARAM_BUG */
#if defined(__STL_FUNCTION_TMPL_PARTIAL_ORDER) && \
!defined(__STL_NON_TYPE_TMPL_PARAM_BUG)
template <class T, class Alloc, size_t BufSiz>
inline void swap(deque<T, Alloc, BufSiz>& x, deque<T, Alloc, BufSiz>& y) {
x.swap(y);
}
#endif
#if defined(__sgi) && !defined(__GNUC__) && (_MIPS_SIM != _MIPS_SIM_ABI32)
#pragma reset woff 1174
#endif
__STL_END_NAMESPACE
#endif /* __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_DEQUE_H */
// Local Variables:
// mode:C++
// End:
今天的分享就到此结束啦,如果对读者朋友们有所帮助的话,可否留下宝贵的三连呢~~
如果可以, 那就让我们共同努力, 一起走下去!





















 575
575

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








