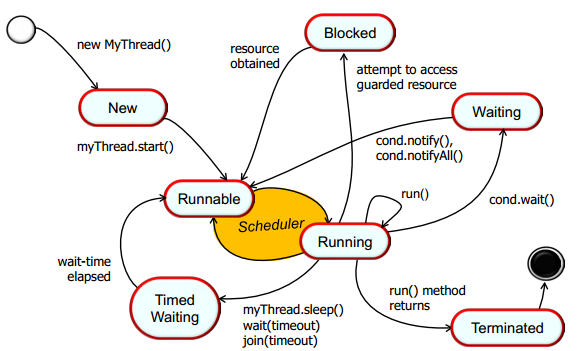
The state machine for Java threads
Starting Java Threads
- key thing to remember: starting a thread consumes a non-trivial amount of resources. Consider threads for fairly long running computations that make it worthwhile to start the threads.
Stoping Java Threads
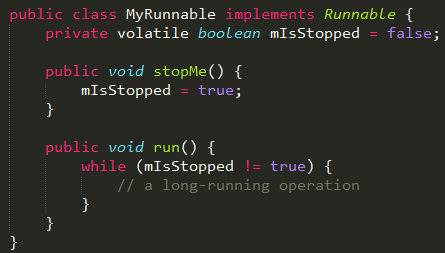
One way is to use a “stop” volatile flag.
- This solution is lightweight, but isn’t integrated into the JVM. Any blocking operations, like blocking reads, writes, waits, joins, sleeps. All those other things won’t be awakened by this solution, which could impede the shutdown processing in the applications for a very long period of time.
Another way is to use Interrupt Request.
- Interrupts are implemented via an internal interrupt status flag. Invoking Thread.interrupt() sets this flag.
- run() method has to check periodically to see if Thread’s been stopped.
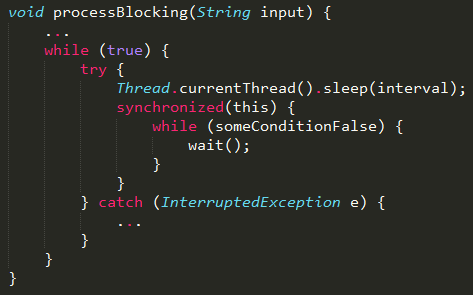
For threads that block in various library calls and system calls.
Certain blocking operations will return automatically, like wait(), join(), sleep() & blocking I/O calls. Need to use try() catch() block to handle in run()
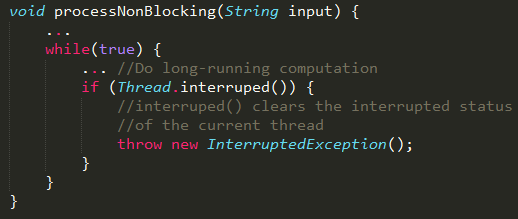
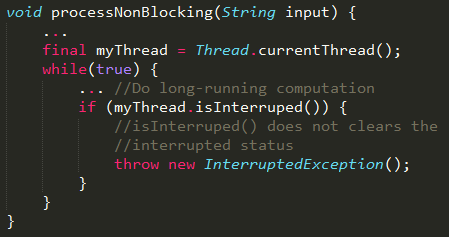
For non-blocking operations, we need to periodically check to see if interrupt() has been called.
- call interrupted()
- call isInterrupted()
Java Thread interrupts don’t behave like traditional hardware
or operating system interrupts. They are delivered synchronously
& non-preemptively. The thread has to be prepared to handle them.
Patterns for dealing with Java InterruptedException:
(next)






















 410
410











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








