Given an n-ary tree, return the level order traversal of its nodes’ values.
Nary-Tree input serialization is represented in their level order traversal, each group of children is separated by the null value (See examples).
Example 1:
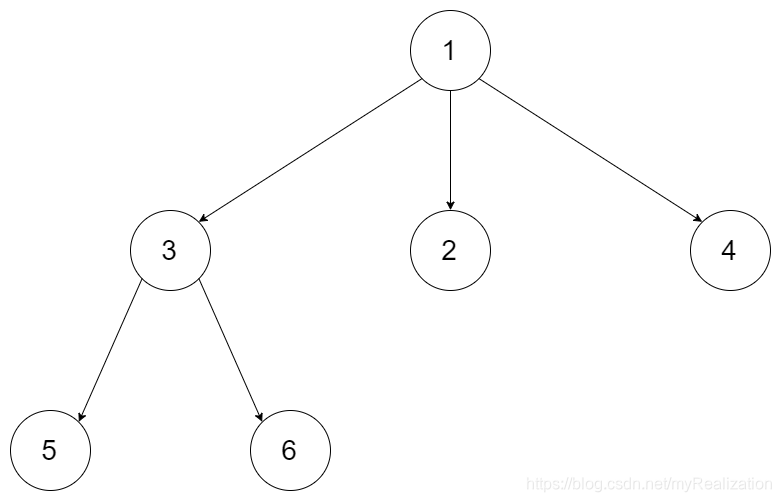
Input: root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6]
Output: [[1],[3,2,4],[5,6]]
Example 2:
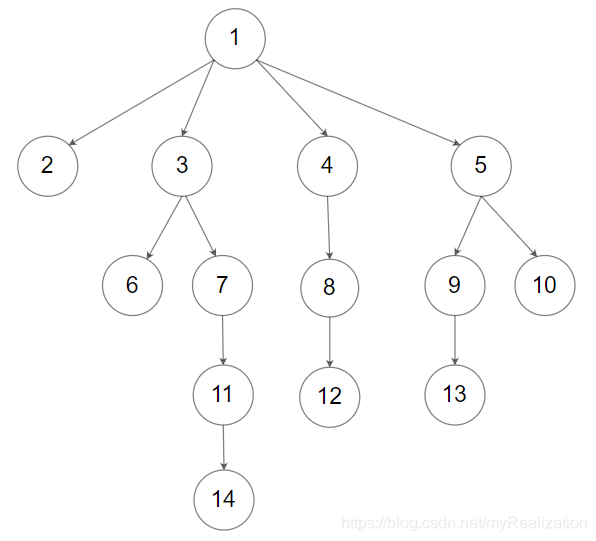
Input: root = [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14]
Output: [[1],[2,3,4,5],[6,7,8,9,10],[11,12,13],[14]]
Constraints:
- The height of the n-ary tree is less than or equal
to 1000 - The total number of nodes is between
[0, 10^4]
题意:N叉树的层次遍历。
思路1:N叉树层次遍历,并存储每层的结点值为一个 vector ,相当于按层打印。这是很基础的内容,按层次进行宽度遍历即可。
代码:
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(Node* root) {
vector<vector<int>> ans;
if (!root) return ans;
queue<Node*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
int size = q.size(); //保存每层结点数目
ans.emplace_back(vector<int>());
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
Node *t = q.front(); q.pop();
ans.back().push_back(t->val);
for (const auto p : t->children) q.push(p);
}
}
return ans;
}
};
思路2:如果使用简单的宽度优先遍历,需要进行一些改进:用两个 Node* 变量 last, nLast 来表示正在遍历的当前行的最右结点、下一行的最右结点:
- 每层进行从左到右的宽度优先遍历,如果发现遍历到的结点等于
last并且队列非空,说明该换下个vector或者说该换行了。 - 换行的做法是:令
last = nLast,继续下一行的遍历过程;直到所有结点值都打印完。 nLast则一直跟踪BFS队列中的最新加入的结点,因为,最新加入队列的结点一定是目前已经发现的下一行的最右结点。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(Node* root) {
vector<vector<int>> ans;
if (!root) return ans;
ans.emplace_back(vector<int>());
Node *last = root, *nlast = nullptr;
queue<Node*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
Node *t = q.front(); q.pop();
ans.back().push_back(t->val);
for (const auto p : t->children) {
q.push(p);
nlast = p; //一直跟踪最新加入队列的结点
}
if (t == last && !q.empty()) {
ans.emplace_back(vector<int>());
last = nlast;
}
}
return ans;
}
};
甚至于我们可以不用 nLast 这个变量,只需要在遍历到的结点等于 last 的时候,令 last = q.back() —— 更新 last 为最新加入队列的结点指针即可。代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(Node* root) {
vector<vector<int>> ans;
if (!root) return ans;
vector<int> v;
Node *last = root;
queue<Node*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
Node *t = q.front(); q.pop();
v.push_back(t->val);
for (const auto p : t->children) q.push(p);
if (t == last) {
if (!q.empty()) last = q.back();
ans.emplace_back(v);
v.clear();
}
}
return ans;
}
};
思路3:DFS,从第 0 层向下深度遍历,每次如果 depth >= ans.size() ,就要添加一个 vector 进入 ans 。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> ans;
void DFS(const Node *root, int depth) {
if (!root) return;
if (ans.size() <= depth) ans.emplace_back(vector<int>());
ans[depth].push_back(root->val);
for (const Node *p : root->children)
DFS(p, depth + 1);
}
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(Node* root) {
if (!root) return ans;
DFS(root, 0);
return ans;
}
};






















 218
218











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










