Java常用类
文章目录
String StringBuffer StringBuilder的区别
一、String类
- java.lang.String类代表不可变的字符序列
- “xxxxxx”为该类的一个对象
- String类的常见构造方法,具体可查看api文档
- String类举例:
public class TestString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "Hello";
String s2 = "world";
String s3 = "Hello";
System.out.println(s1 == s3);//true
s1 = new String("hello");
s2 = new String("hello");
System.out.println(s1 == s2);//false
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));//true
char c[] = {'s','u','n',' ','j','a','v','a'};
String s4 = new String(c);
String s5 = new String(c,4,4);
System.out.println(s4);//sun java
System.out.println(s5);//java
}
}
二、String类小练习
编写算法输出一个字符串中的大写英文字母数,小写英文字母数以及非英文字符数
public class TestStringMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int lcount = 0,ucount = 0,ncount = 0;
String s = "aaabbecHKILaaa$%^&Ab289HIQETRC";
for(int i = 0;i < s.length();i++){
char c = s.charAt(i);
if(c >= 'a' && c <= 'z'){
lcount ++;
}else if(c >= 'A' && c <= 'Z'){
ucount++;
}else {
ncount++;
}
}
System.out.println("小写字母个数是 " + lcount + " 大写字母的个数是 " + ucount
+ " 非英文的字符数是 " + ncount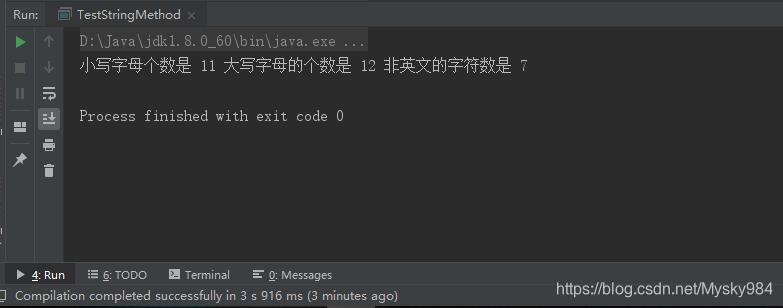);
}
}
输出结果如下:

三、编写一个方法,输出在一个字符串中,指定字符串出现的次数。请编写代码实现。
public class AppearStringCount {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "helloJavaGoodJavahahaJavaHiJava";
String sToFind = "Java";
int count = 0;
int index = -1;
while ((index = s.indexOf(sToFind)) != -1){
index = index + sToFind.length();
s = s.substring(index);
count++;
}
System.out.println(count);
}
}

四、基本数据类型包装类
- 包装类(如Integer,Double等)这些类封装了一个相应的基本数据类型数值,并为其提供了一系列操作,以java.lang.Integer类为例,构造方法:
Integer(int value)
Integer(String s)
常用方法还有:Integer.parseInt()-转换成int,基本数据类型转换成一个对象,Long number = new Long(5)即可,对象转换成一个基本数据类型,number.longValue()即可,其他的包装类也有类似的方法。
- 包装类常见方法。以下方法以java.lang.Integer为例
public static final int MAX_VALUE //最大的int型数(2的31次方-1)
public static final int MIN_VALUE //最小的int型数(-2的31次方)
public long longValue() //返回封装数据的long型值
public double doubleValue() //返回封装数据的double型值
public int intValue() //返回封装数据的int型值
public static int parseInt(String s) throws NumberFormatException //将字符串解析成int型数据,返回该数据
public static Integer valueOf(String s) throws NumberFormatException //返回Integer对象
五、小练习
编写一个方法返回一个double类型的二维数组,数组中的元素通过解析字符串参数获得。如字符串参数:“1,2;3,4,5;6,7,8”对应的数组为:d[0,0] = 1.0,d[0,1] = 2.0,d[1,0] = 3.0,d[1,1] = 4.0,d[1,2] = 5.0,d[2,0] = 6.0,d[2,1] = 7.0,d[2,2] = 8.0。
public class ArrarParser {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double[][] d;
String s = "1,2;3,4,5;6,7,8";
String[] sFirst = s.split(";");
d = new double[sFirst.length][];
for(int i = 0;i < sFirst.length;i++){
String [] sSecond = sFirst[i].split(",");
d[i] = new double[sSecond.length];
for(int j = 0;j < sSecond.length;j++){
d[i][j] = Double.parseDouble(sSecond[j]);
}
}
/**
* 输出二维数组
*/
for(int i = 0;i < d.length;i++){
for(int j = 0;j < d[i].length;j++){
System.out.print(d[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}

六、Math类
java.lang.Math提供了一系列静态方法用于科学计算,其方法的参数和返回值类型一般为double类型,常用的方法如下:
abs//绝对值
acos,asin,atan,cos,sin,tan//三角函数
sqrt//平方根
pow(double a,double b)a的b次幂
log//自然对数
exp//为底指数
max(double a,double b)//最大值
min(double a,double b)//最小值
random()//返回0.0到1.0之间的随机数
long round(double a)//double型的数据a转换为long型(四舍五入)
toDegrees(double angrad)//弧度转换为角度
toRadians(double angoleg)//角度转为弧度
七、File类介绍
- java.io.File类代表系统文件名(路径和文件名)
- File类的常见构造方法:
public File(String pathname)//以pathname为路径创建File对象,如果pathname是相对路径,则默认的当前路径在系统属性user.dir中存储
public File(String parent,String child)//以parent为父路径,child为子路径创建File对象
- File的静态属性String separator(分隔符)存储了当前系统的路径分隔符,此方法主要为跨平台的时候使用,其实路径使用正斜杠"/"能达到同样的效果。
- File类常用方法:
//1.通过File对象可以访问文件的属性
public boolean canRead()//是否可读
public boolean canWrite()//是否可写
public boolean exists()//文件是否存在
public boolean isDirectory()//是否是一个目录
public boolean isFile()//是否是一个文件
public boolean isHidden()//是不是隐藏的
public long lastModefied()//上次修改的时间
public long length()//文件内容长度
public String getName()//获得文件名字
public String getPath()/getAbsolutePath//获的文件路径/绝对路径
//2.通过file对象创建空文件或目录(在该对象所指的文件或目录不存在的情况下)
public boolean createNewFile() throws IOException//创建文件
public boolean delete()//删除文件
public boolean mkdir()//创建一个路径(目录)
public boolean mkdirs()//创建在路径中的一系列目录
八、编写一个程序,在命令行中以树状结构展现特定的文件夹及其子文件和子文件夹
import java.io.File;
public class FileList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File f = new File("D:/A");
System.out.println(f.getName());
tree(f,1);
}
/**
* 递归方式实现
* @param f 文件
* @param level 添加目录层次
*/
private static void tree(File f,int level){
String preStr = " ";
for(int i = 0;i < level;i++){
preStr += " ";
}
File[] childs = f.listFiles();
for(int i = 0;i<childs.length;i++){
System.out.println(preStr + childs[i].getName());
if(childs[i].isDirectory()){
tree(childs[i],level + 1);
}
}
}
}
输出结果:

九、java.lang.Enum枚举类型
- 只能够取特定值中的一个
- 使用enum关键字
- 是java.lang.Enum类型
- 使用枚举类型目的就是限制某些值,使其能够在编译过程中就能够限制,而免去了在运行时的判断,能够精简代码,防止错误的发生。
- 小例子如下:
public class TestEnum {
/**
* 定义一个enum类型
*/
public enum MyCloor {
red,
green,
blue
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyCloor m = MyCloor.red;
switch (m) {
case red:
System.out.println("red");
break;
case green:
System.out.println("green");
break;
case blue:
System.out.println("blue");
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}






















 1820
1820

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








