Given a sorted array of integers, find the starting and ending position of a given target value.
Your algorithm's runtime complexity must be in the order ofO(logn).
If the target is not found in the array, return[-1, -1].
For example,
Given[5, 7, 7, 8, 8, 10]and target value 8,
return[3, 4].
二分查找的变形:
1、没有找到返回[-1, -1]
2、只存在1个返回[pos, pos]
3、存在多个,返回端点[leftPos, rightPos]
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <bitset>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> searchRange(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
vector<int>vec;
int leftPos = BinarySearchLeft(nums, target);
int rightPos = BinarySearchRight(nums, target);
if (nums[leftPos] != target)
{
vec.push_back(-1);
vec.push_back(-1);
}
else
{
vec.push_back(leftPos);
vec.push_back(rightPos);
}
return vec;
}
private:
int BinarySearchLeft(vector<int>& nums, int target)
{
int left = 0;
int right = nums.size() - 1;
while(left <= right)
{
int mid = left + ((right - left) >> 1);
if (nums[mid] >= target)
{
right = mid - 1;
}
else
{
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return left;
}
int BinarySearchRight(vector<int>& nums, int target)
{
int left = 0;
int right = nums.size() - 1;
while(left <= right)
{
int mid = left + ((right - left) >> 1);
if (nums[mid] > target)
{
right = mid - 1;
}
else
{
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return right;
}
};
int main()
{
Solution s;
vector<int>vec{0,0,0,1,2,3};
vector<int>v = s.searchRange(vec, 0);
for (auto it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << endl;
}
return 0;
}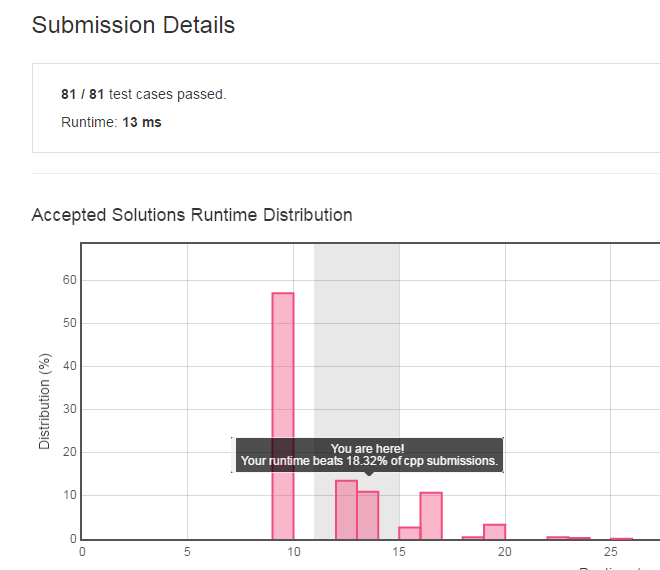
看,这个时间,估计得有更高效的算法了。























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








