文件状态
返利 https://m.cpa5.cn/你工作目录下的每一个文件只有两种状态:tracked 或 untracked
tracked
- 已跟踪 tracked 的文件是指那些被纳入了版本控制的文件
- 在上一次快照中有它们的记录,在工作一段时间后, 它们的状态可能是未修改unmodified、已修改modified 或已放入暂存区staged
- 简单来说,已跟踪 tracked 的文件就是 Git 知道的文件
untracked
- 工作目录中除 tracked 文件外的其它所有文件都属于 untracked 文件
- 它们既不存在于上次快照的记录中,也没有被放入暂存区
- 初次 clone 某个仓库的时候,工作目录中的所有文件都属于 tracked 文件,并处于 unmodified
- 编辑文件后,Git 将它们标记为 modified 文件。 在工作时,你可以选择性地将这些修改过的文件放入暂存区,然后提交所有已暂存的修改
文件的状态变化周期
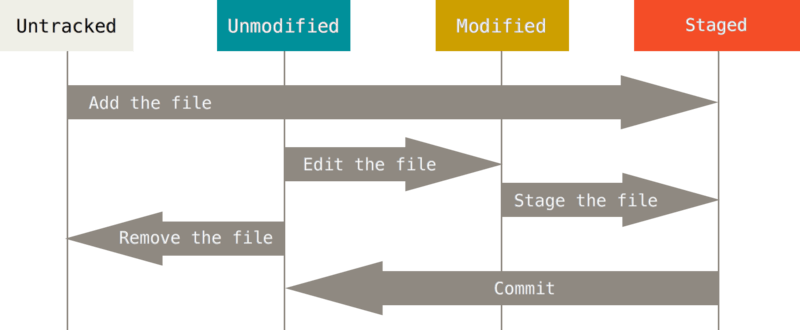
检查当前文件状态
可以用 git status 命令查看哪些文件处于什么状态。 如果在克隆仓库后立即使用此命令,会看到类似这样的输出:
git status On branch master Your branch is up-to-date with 'origin/master'. nothing to commit, working directory clean
可以获取到的内容
- 所有 tracked 件在上次提交后都未被更改过
- 当前目录下没有出现任何 untracked 的新文件,否则 Git 会在这里列出来
- 还显示了当前所在分支,并告诉你这个分支同远程服务器上对应的分支没有偏离,现在,分支名是“master”,这是默认的分支名
在项目下创建一个新的 README 文件,使用 git status 命令,将看到一个新的 untracked 文件
echo 'My Project' > README $ git status On branch master Your branch is up-to-date with 'origin/master'. Untracked files: (use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed) README nothing added to commit but untracked files present (use "git add" to track)
可以获取到的内容
-
README文件出现在Untracked files下面 - untracked 的文件意味着 Git 在之前的快照(提交)中没有这些文件
如何跟踪
git add 文件名
# 更新目录下所有文件
git add .
后面会再详细讲这个命令
跟踪新文件
使用命令 git add 开始跟踪一个文件。 所以,要跟踪 README 文件,运行:
git add README
此时再运行 git status 命令,会看到 README 文件已被跟踪,并处于 staged
git status On branch master Your branch is up-to-date with 'origin/master'. Changes to be committed: (use "git restore --staged <file>..." to unstage) new file: README
可以获取到的内容
- 只要在
Changes to be committed这行下面的,就说明是 staged 状态 - 如果此时提交,那么该文件在你运行
git add时的版本将被留存在后续的历史记录中
暂存已修改的文件
如果修改了一个名为 CONTRIBUTING.md 的已被 tracked 的文件,然后运行 git status 命令,会看到下面内容
git status On branch master Your branch is up-to-date with 'origin/master'. Changes to be committed: (use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage) new file: README Changes not staged for commit: (use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed) (use "git checkout -- <file>..." to discard changes in working directory) modified: CONTRIBUTING.md
可以获取到的内容
CONTRIBUTING.md出现在Changes not staged for commit这行下面,说明已跟踪文件的内容发生了变化,但还没有放到暂存区- 要暂存这次更新,需要运行
git add命令
再次运行 git add 命令
运行 git add 将“CONTRIBUTING.md”放到暂存区,然后再看看 git status 的输出:
$ git add CONTRIBUTING.md $ git status On branch master Your branch is up-to-date with 'origin/master'. Changes to be committed: (use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage) new file: README modified: CONTRIBUTING.md
再次修改文件内容
编辑 CONTRIBUTING.md,再运行 git status 看看
$ vim CONTRIBUTING.md $ git status On branch master Your branch is up-to-date with 'origin/master'. Changes to be committed: (use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage) new file: README modified: CONTRIBUTING.md Changes not staged for commit: (use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed) (use "git checkout -- <file>..." to discard changes in working directory) modified: CONTRIBUTING.md
可以获取到的内容
CONTRIBUTING.md文件同时出现在暂存区和非暂存区- 实际上 Git 只不过暂存了运行
git add命令时的版本 - 如果你现在提交代码,
CONTRIBUTING.md的版本是你最后一次运行git add命令时的那个版本,而不是当前版本 - 所以,运行了
git add之后又编辑了文件,需要再次git add把最新版本暂存
$ git add CONTRIBUTING.md $ git status On branch master Your branch is up-to-date with 'origin/master'. Changes to be committed: (use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage) new file: README modified: CONTRIBUTING.md
真实的实际操作栗子

状态简述
git status命令的输出十分详细,但其用语有些繁琐git status -s或git status --short,输出结果更加简洁
git status -s
M markers.py
M test.py
D test_func01.py
D test_login.py
?? text.txt
忽略文件
https://www.cnblogs.com/poloyy/p/12342073.html
查看已暂存和未暂存的修改
修改 README 文件后暂存,然后编辑 CONTRIBUTING.md 文件后先不暂存, 运行 status 命令将会看到:
$ git status On branch master Your branch is up-to-date with 'origin/master'. Changes to be committed: (use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage) modified: README Changes not staged for commit: (use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed) (use "git checkout -- <file>..." to discard changes in working directory) modified: CONTRIBUTING.md
初次使用 git diff
要查看尚未暂存的文件更新了哪些部分,不加参数直接输入 git diff:
$ git diff diff --git a/CONTRIBUTING.md b/CONTRIBUTING.md index 8ebb991..643e24f 100644 --- a/CONTRIBUTING.md +++ b/CONTRIBUTING.md @@ -65,7 +65,8 @@ branch directly, things can get messy. Please include a nice description of your changes when you submit your PR; if we have to read the whole diff to figure out why you're contributing in the first place, you're less likely to get feedback and have your change -merged in. +merged in. Also, split your changes into comprehensive chunks if your patch is +longer than a dozen lines. If you are starting to work on a particular area, feel free to submit a PR that highlights your work in progress (and note in the PR title that it's
实际栗子

git diff 的作用
- 比较的是当前文件和暂存区快照之间的差异,也就是修改之后还没有暂存起来的变化内容
- 若要查看已暂存且要添加到下次提交里的内容,可以用
git diff --staged命令 - 会比较已暂存文件与最后一次提交的文件差异
$ git diff --staged diff --git a/README b/README new file mode 100644 index 0000000..03902a1 --- /dev/null +++ b/README @@ -0,0 +1 @@ +My Project
git diff
git diff 本身只显示尚未暂存的改动,而不是自上次提交以来所做的所有改动,所以有时候一下子暂存了所有更新过的文件,运行 git diff 后却什么也没有
像之前说的,暂存 CONTRIBUTING.md 后再编辑,可以使用 git status 查看已被暂存的修改或未被暂存的修改。 如果我们的环境(终端输出)看起来如下:
$ git add CONTRIBUTING.md $ echo '# test line' >> CONTRIBUTING.md $ git status On branch master Your branch is up-to-date with 'origin/master'. Changes to be committed: (use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage) modified: CONTRIBUTING.md Changes not staged for commit: (use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed) (use "git checkout -- <file>..." to discard changes in working directory) modified: CONTRIBUTING.md
现在运行 git diff 看暂存前后的变化:
$ git diff diff --git a/CONTRIBUTING.md b/CONTRIBUTING.md index 643e24f..87f08c8 100644 --- a/CONTRIBUTING.md +++ b/CONTRIBUTING.md @@ -119,3 +119,4 @@ at the ## Starter Projects See our [projects list](https://github.com/libgit2/libgit2/blob/development/PROJECTS.md). +# test line
然后用 git diff --cached 查看已经暂存起来的变化( --staged 和 --cached 是同义词):
$ git diff --cached diff --git a/CONTRIBUTING.md b/CONTRIBUTING.md index 8ebb991..643e24f 100644 --- a/CONTRIBUTING.md +++ b/CONTRIBUTING.md @@ -65,7 +65,8 @@ branch directly, things can get messy. Please include a nice description of your changes when you submit your PR; if we have to read the whole diff to figure out why you're contributing in the first place, you're less likely to get feedback and have your change -merged in. +merged in. Also, split your changes into comprehensive chunks if your patch is +longer than a dozen lines. If you are starting to work on a particular area, feel free to submit a PR that highlights your work in progress (and note in the PR title that it's
实际栗子

提交更新
- 现在的暂存区已经准备就绪,可以提交了
- 在此之前,请务必确认还有什么已修改或新建的文件还没有
git add过, 否则提交的时候不会记录这些尚未暂存的变化 - 这些已修改但未暂存的文件只会保留在本地磁盘
- 所以,每次准备提交前,先用
git status看下,你所需要的文件是不是都已暂存起来了, 然后再运行提交命令git commit:
git commit -m "test"

可以获取到的内容
- commit 之后 git status 可以看到本地是干净的
- 提交后会显示当前是在哪个分支(
master)提交的 - 本次提交的完整 SHA-1 校验和是什么(
9a8c6b3) - 以及在本次提交中,有多少文件修订过,多少行添加和删改过
重点
- 提交时(git commit)记录的是放在暂存区域的快照
- 每一次运行提交操作,都是对项目作一次快照,以后可以回到指定快照版本,或者进行比较
跳过使用暂存区域
- Git 提供了一个跳过使用暂存区域的方式
git commit加上-a选项,Git 就会自动把所有已经跟踪过的文件暂存起来一并提交,从而跳过git add步骤

-a 选项使本次提交包含了所有修改过的文件,但是要小心,有时这个选项会将不需要的文件添加到提交中
移除文件
两种情况
- 直接删除文件(从本地删除):-f 参数
- 只是将文件从 Git 的暂存区移除,并不会删除本地文件:--cached
直接看栗子

已跟踪的文件(出现在暂存区)的文件被执行 git rm --cached 命令后,它会被移出暂存区,重新变成一个未跟踪的文件
移动文件
在 Git 中对文件改名
$ git mv file_from file_to
查看状态信息,也会看到关于重命名操作的说明

文件会自动提交到暂存区,且不需要手动执行 git add
其实,运行 git mv 就相当于运行了下面三条命令
$ mv README.md README $ git rm README.md $ git add README























 248
248

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








