这是我们今天要讨论的话题,因为我觉得它非常的有趣。
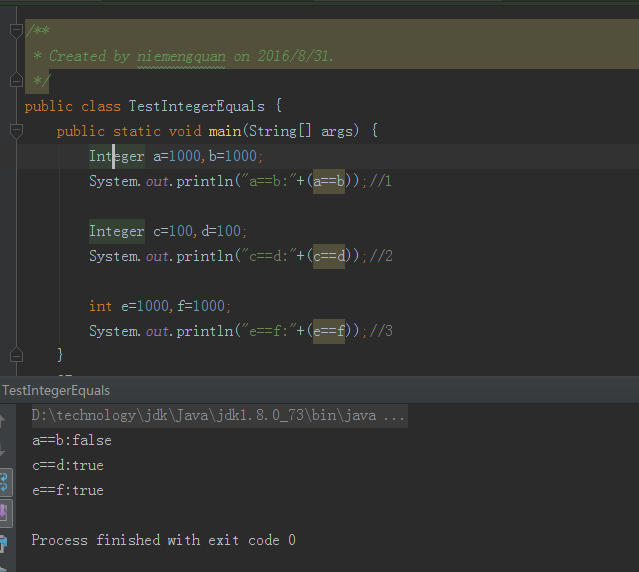
如果你运行如下代码:
Integer a = 1000, b = 1000;
System.out.println(a == b);//1
Integer c = 100, d = 100;
System.out.println(c == d);//2
你会得到以下运行结果:
false
true
我们知道,如果两个引用指向同一个对象,那么==就成立;反之,如果两个引用指向的不是同一个对象,那么==就不成立,即便两个引用的内容是一样的。因此,结果就会出现false。
这是非常有趣的地方。如果你查看Integer.java类,你会找到IntegerCache.java这个内部私有类,它为-128到127之间的所有整数对象提供缓存。
这个东西为那些数值比较小的整数提供内部缓存,当进行如此声明时:
Integer c = 100;
它的内部就是这样的:
Integer i = Integer.valueOf(100);
如果我们观察valueOf()类函数,我们可以看到
static final int low = -128;
static final int high;
static {
// high value may be configured by property
int h = 127;
String integerCacheHighPropValue =
sun.misc.VM.getSavedProperty("java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high");
if (integerCacheHighPropValue != null) {
try {
int i = parseInt(integerCacheHighPropValue);
i = Math.max(i, 127);
// Maximum array size is Integer.MAX_VALUE
h = Math.min(i, Integer.MAX_VALUE - (-low) -1);
} catch( NumberFormatException nfe) {
// If the property cannot be parsed into an int, ignore it.
}
}
high = h;
cache = new Integer[(high - low) + 1];
int j = low;
for(int k = 0; k < cache.length; k++)
cache[k] = new Integer(j++);
// range [-128, 127] must be interned (JLS7 5.1.7)
assert IntegerCache.high >= 127;
}
public static Integer valueOf(int i) {
if (i >= IntegerCache.low && ii <= IntegerCache.high)
return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)];
return new Integer(i);
}如果值在-128到127之间,它就会返回该缓存的实例。
因此。。。
Integer c = 100, d = 100;
两者指向同样的对象。
这就是为什么这段代码的结果为true了:
System.out.println(c == d);
现在你可能会问,为什么会为-128到127之间的所有整数设置缓存?
这是因为在这个范围内的小数值整数在日常生活中的使用频率要比其它的大得多,多次使用相同的底层对象这一特性可以通过该设置进行有效的内存优化。你可以使用reflection API任意使用这个功能。
运行下面的这段代码,你就会明白它的神奇所在了。
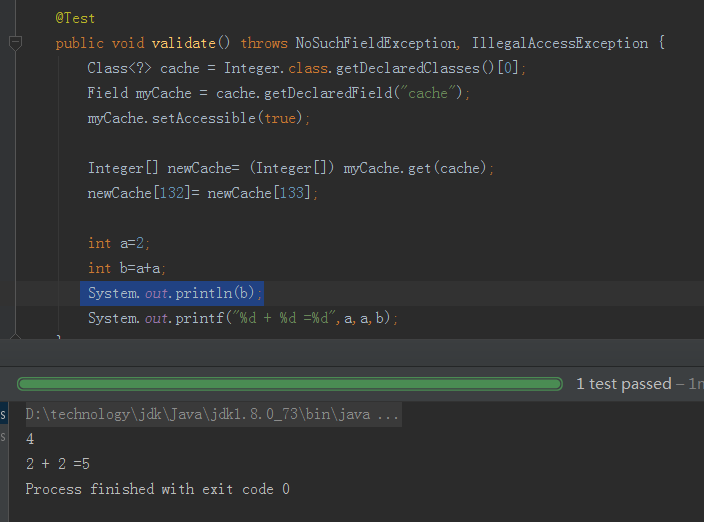
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
Class cache = Integer.class.getDeclaredClasses()[0]; //1
Field myCache = cache.getDeclaredField("cache"); //2
myCache.setAccessible(true);//3
Integer[] newCache = (Integer[]) myCache.get(cache); //4
newCache[132] = newCache[133]; //5:这里将缓存值的[132]替换为[133]
int a = 2;
int b = a + a;
System.out.println(b);
System.out.printf("%d + %d = %d", a, a, b); //
}运行结果:
本文翻译自 dzone.com ,由回忆和感动翻译,转载请注明文章来自慧都控件网。





















 468
468











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








