Given two strings a = a0a1...ap and b = b0b1...bq, where each ai and each bj is in some ordered set of characters, we say that string a is lexicographically less than string b if either
-
there exists an integer j, where 0 ≤ j ≤ min(p, q), such that ai = bi for all i = 0, 1, ..., j - 1 and aj < bj, or
-
p < q and ai = bi for all i = 0, 1, ..., p.
For example, if a and b are bit strings, then 10100 < 10110 by rule 1 (letting j = 3) and 10100 < 101000 by rule 2. This is similar to the ordering used in English-language dictionaries.
The radix tree data structure shown in Figure 12.5 stores the bit strings 1011, 10, 011, 100, and 0. When searching for a key a = a0a1...ap, we go left at a node of depth i if ai = 0 and right if ai = 1. Let S be a set of distinct binary strings whose lengths sum to n. Show how to use a radix tree to sort S lexicographically in Θ(n) time. For the example in Figure 12.5, the output of the sort should be the sequence 0, 011, 10, 100, 1011.
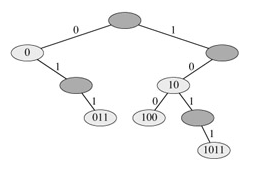
Figure 12.5: A radix tree storing the bit strings 1011, 10, 011, 100, and 0. Each node's key can be determined by traversing the path from the root to that node. There is no need, therefore, to store the keys in the nodes; the keys are shown here for illustrative purposes only. Nodes are heavily shaded if the keys corresponding to them are not in the tree; such nodes are present only to establish a path to other nodes.
解:
利用中序遍历的方法,关键字在数中以白点显示,通常是一个link到一组信息上,为加入基数树的节点用黑点表示,通常link到一个NULL.
则有在中序遍历过程中,只要访问到白点就输出,这样恰好是字典序,由BST性质保证。另外中序遍历的时间复杂度为O(lgn).
证明:令T(n)为对一个n个结点的树执行一次中序遍历的代价,对空树T(0)=C,C为某个正常数。利用substitution方法,假设T(n)=(c+d)n + c
- T(n)=T(K) + T(n - k - 1) + d //左树K个结点,右树n - k - 1个结点
- T(n)=((c + d)k + c) + ((c + d)(n - k - 1) + c) + d // 归纳假设
- T(n)=(c + d)n + c




 本文介绍了一种使用基数树进行字典序排序的方法。通过构造特定的基数树,并采用中序遍历的方式,可以有效地实现字符串集合的排序。该方法适用于二进制字符串,并能在Θ(n)时间内完成排序。
本文介绍了一种使用基数树进行字典序排序的方法。通过构造特定的基数树,并采用中序遍历的方式,可以有效地实现字符串集合的排序。该方法适用于二进制字符串,并能在Θ(n)时间内完成排序。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








