关于FFmpeg解码请看第一篇教程:FFmpeg解码
下载转码库libyuv
一般我们用surfaceview播放视频都是才用RGBA格式等播放的,但我们解码之后的视频可能是h.264等等 所以我们这里不管解码的是什么格式直接转化为RGBA即可.
所以我们这里用ffmeg解码再用libyuv转码(谷歌推出的一个转码库)
转码库:libyuv是谷歌推出一个转码库
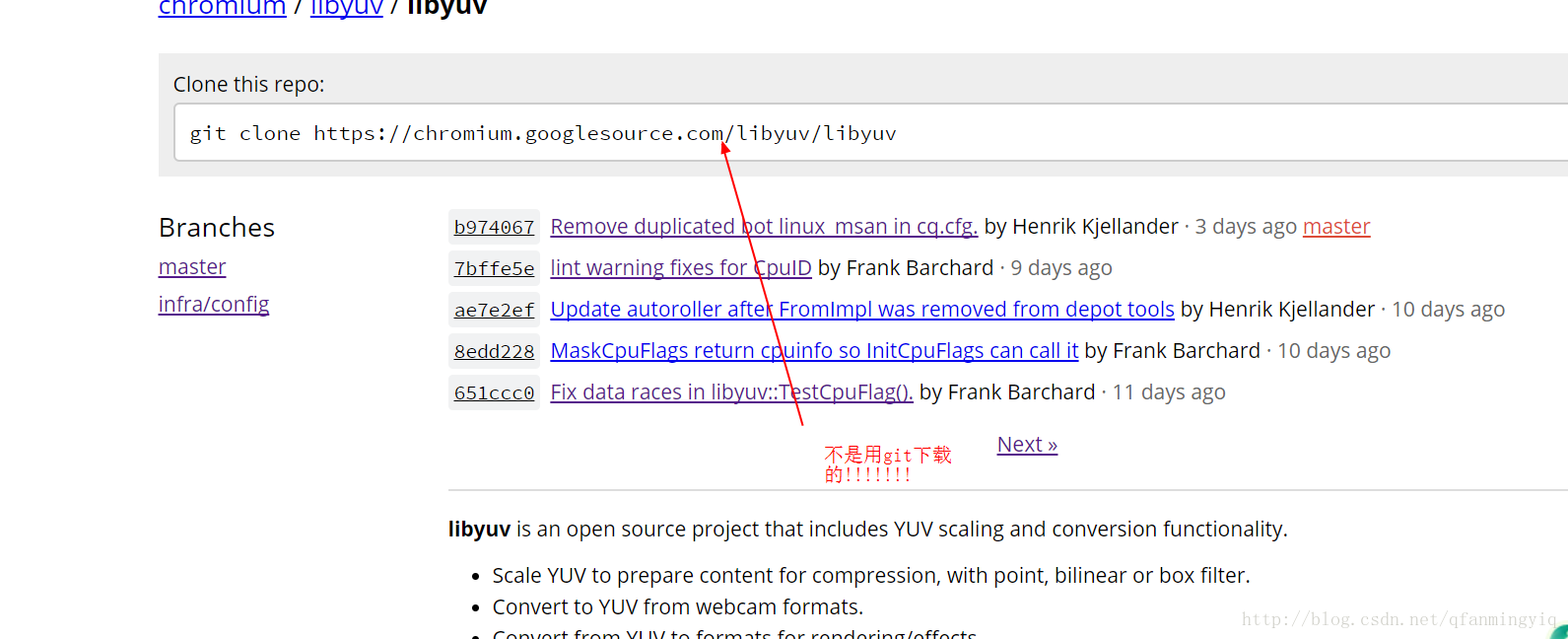
libyuv官网地址(请科学上网)
我用的版本是我现在看到最新的:星期六01 17:57:45 2017
我用的版本地址
注意:官网有个git XXXX 的地址 不使用git来下载的
下载方式:
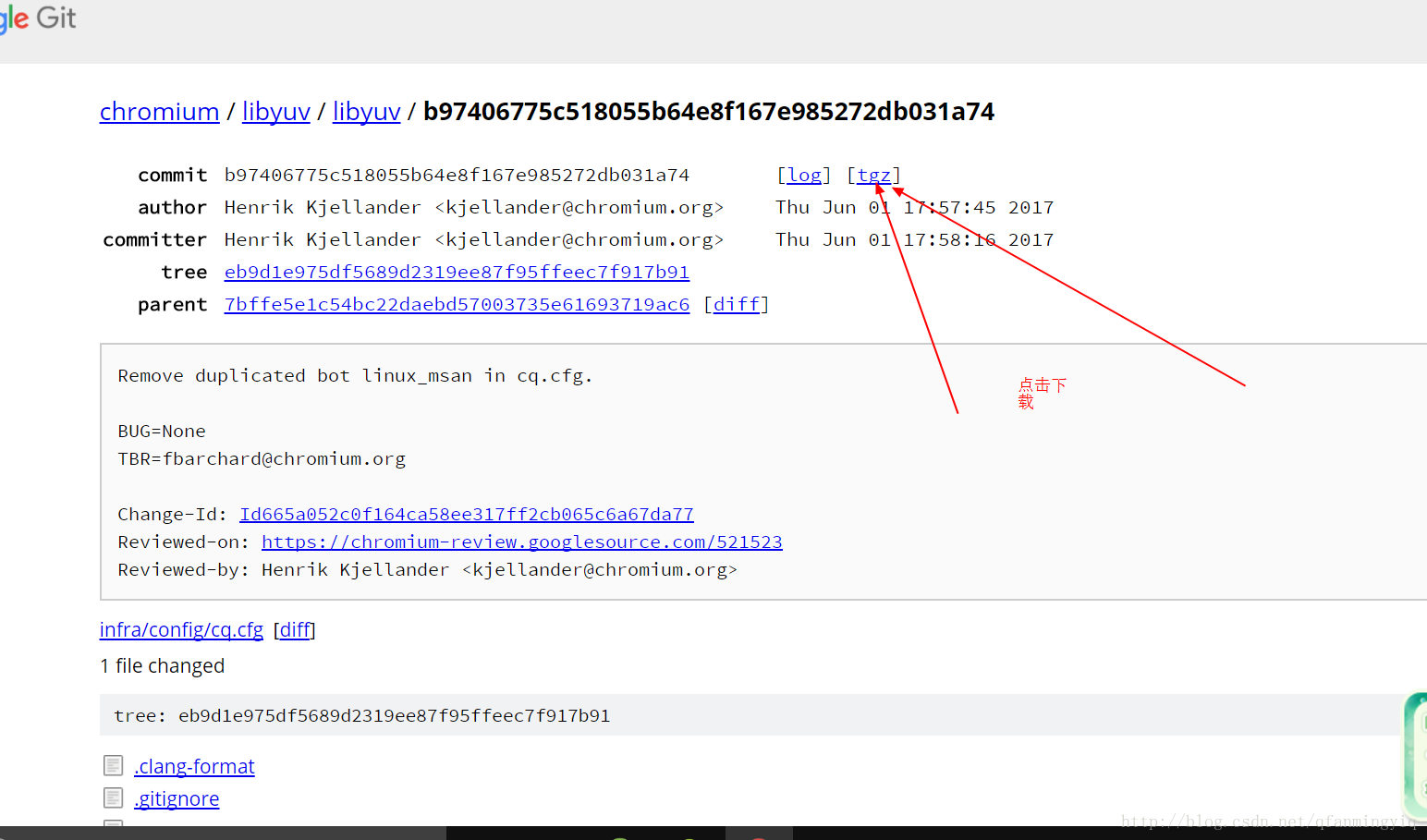
点击你想要的版本后 会跳转到二级页面 ,在二级界面点击tgz即可下载压缩包.
编译libyuv
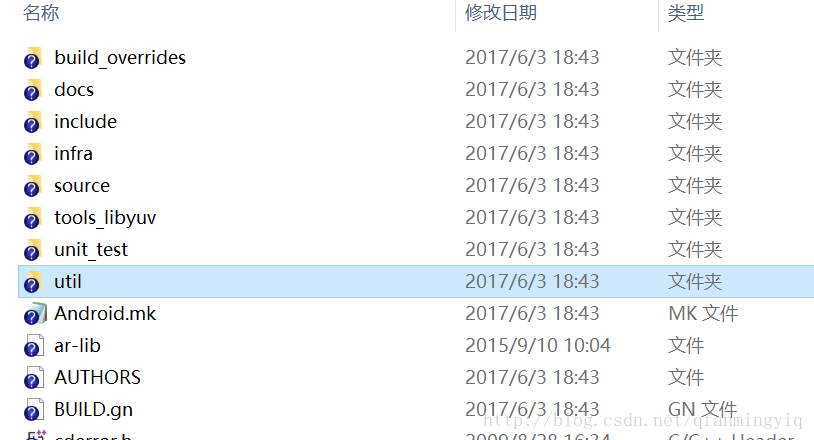
我下载后打开解压查看目录:
其实里面很多文件都是多余的.
我们现在来精简下.
1 创建一个文件夹名字为jni(一定要这个 后面解释)
2 将解压目录的Android.mk 和include文件夹和source文件夹放入
如图:
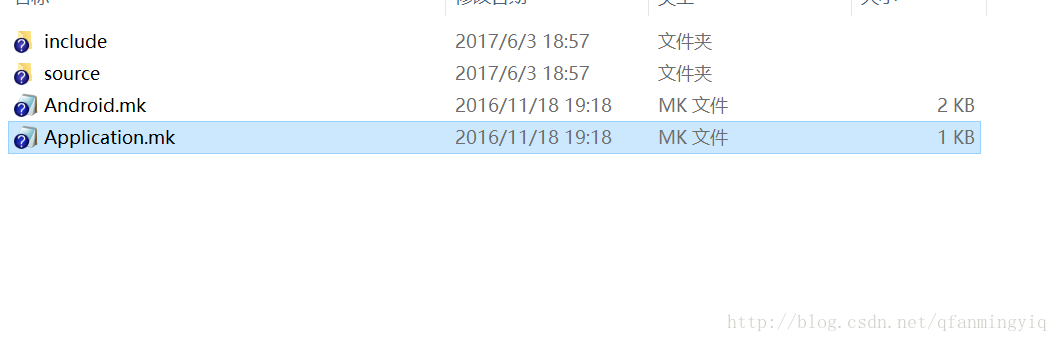
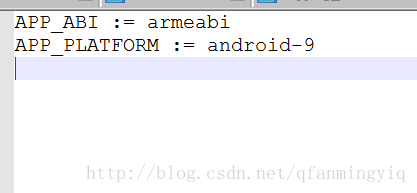
注:上面的Application.mk是我自己创建的.是用来控制编译生成不同架构的共享库,当然这个文件也可以不要默认生成arm架构
下面是这个文件内容
3 修改Android.mk内容
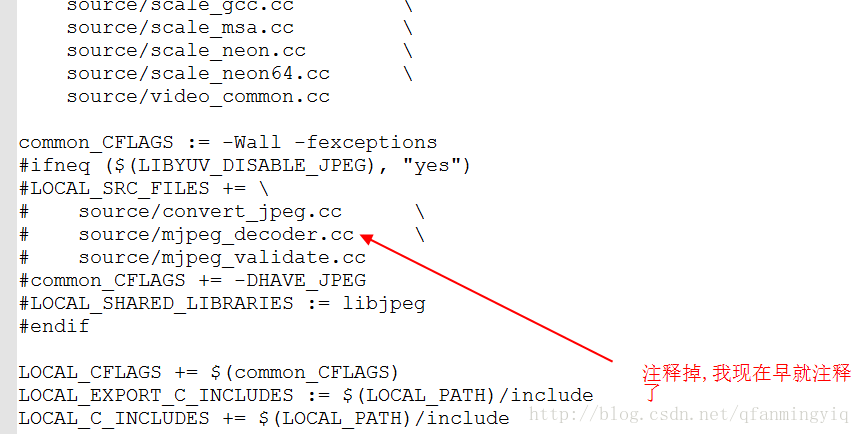
解释下为什么要修改:上面是配置libjpeg库的一些内容,这里暂时不需要,如果你需要的话,需要上面下载libjpeg库放入和修改
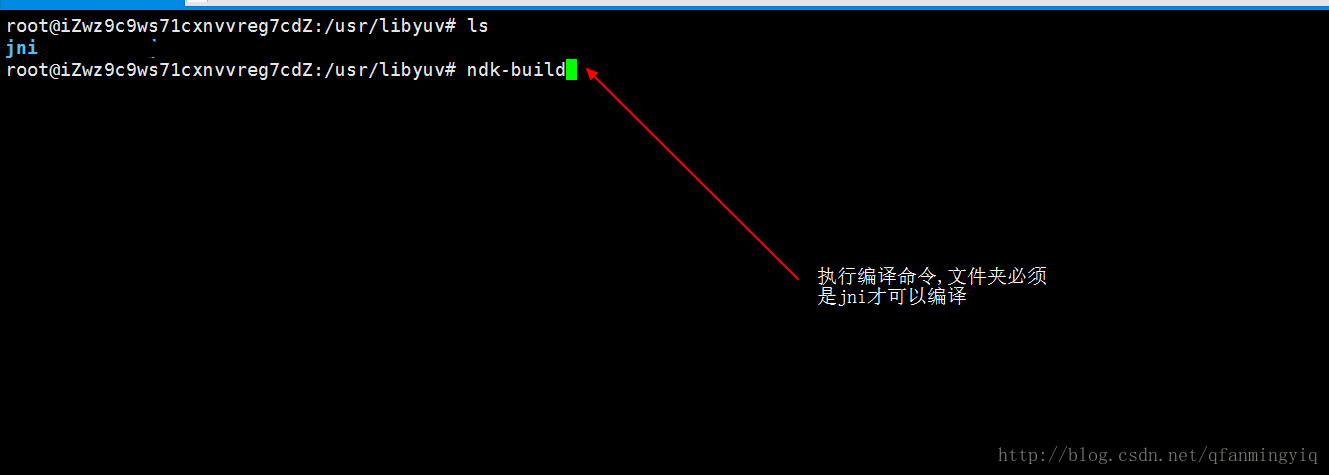
4 把jni放入linux系统下使用ndk-build进行编译
关于ndk-build编译:大家在网上自行下载bdk文件到linux下然后解压配置环境变量.
NDK下载地址
5 在linux系统下的jni目录使用ndk-build编译(刚刚第四部上传的)
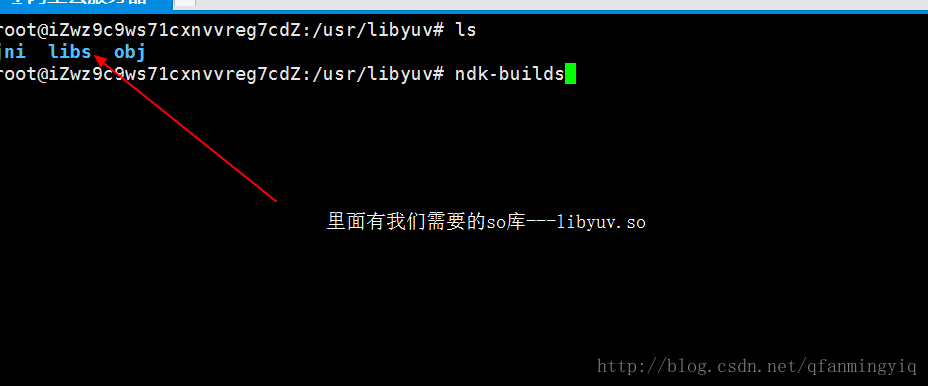
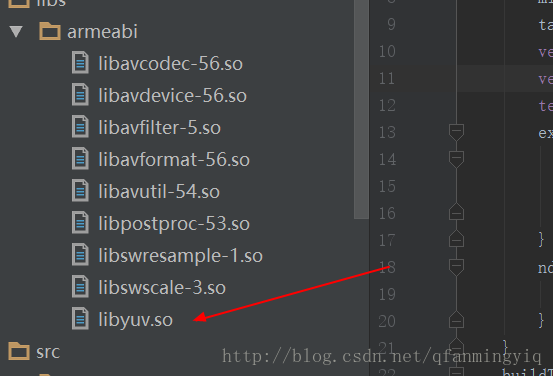
编译完成之后会在jni 目录下生成libs和obj文件夹,我们拷贝libs下的so文件到本地即可
eclipse
关于FFmpeg解码请看第一篇教程:FFmpeg解码
接续用上一篇文章的代码修改使用.
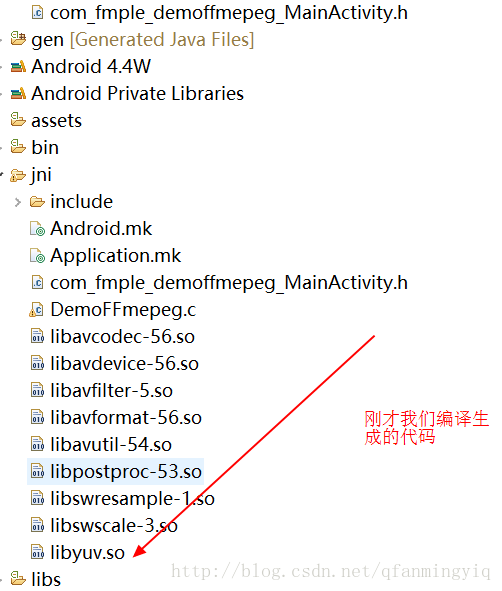
把刚才编译生成的so文件放入jni下
把linyuv的include(我们前面编译jni文件里面)头文件放入 jni/include下
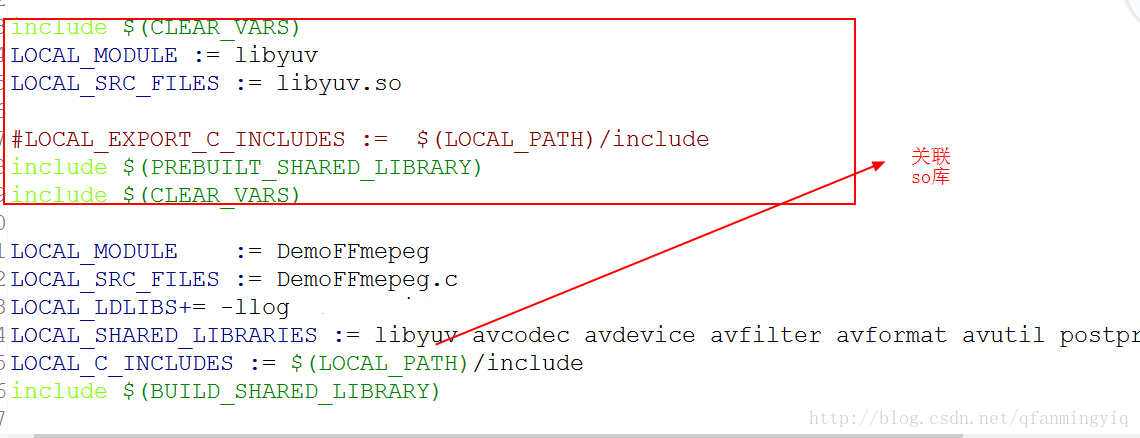
最后修改Android.mk文件关联下so库
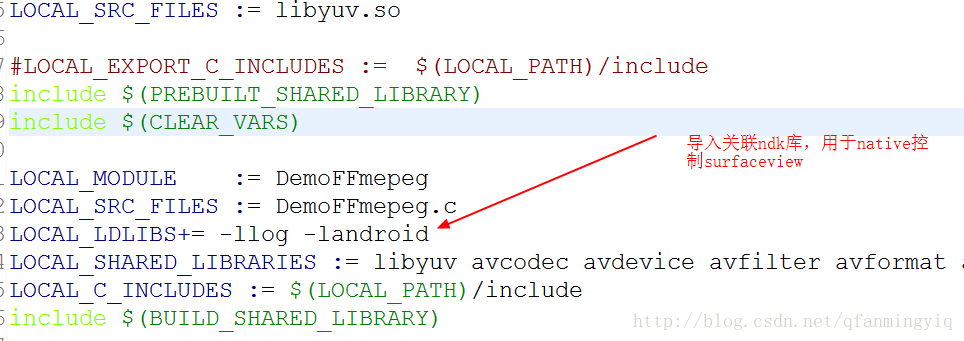
这篇标题说了用surfaceview进行播放,那么surfaceview肯定要传入jni代码内控制。而在c代码控制(专业点就是native控制)需要带入ndk自带的库
配置完成,接下来看下其代码(需要看过上篇文章)
1 创建一个继承SurfaceView的控件VideoView.之所以继承是方便初始化的.这个控件用于解码把视频显示在界面上
//VideoView.java文件
package com.fmple.demoffmepeg;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.PixelFormat;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.SurfaceHolder;
import android.view.SurfaceView;
public class VideoView extends SurfaceView{
public VideoView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
init();
}
public VideoView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs,0);
}
public VideoView(Context context) {
super(context,null);
}
//初始化进行输出设置格式
public void init(){
SurfaceHolder holder = getHolder();
holder.setFormat(PixelFormat.RGB_888);
}
}
接着我们看布局文件:
<!--activity_main.xml-->
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context="com.fmple.demoffmepeg.MainActivity" >
<com.fmple.demoffmepeg.VideoView
android:id="@+id/vv"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
最后看看java层代码
//MainActivity.java
package com.fmple.demoffmepeg;
import java.io.File;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Environment;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.MenuItem;
import android.view.Surface;
import android.view.SurfaceView;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private VideoView videoView;
static{
System.loadLibrary("DemoFFmepeg");
}
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
videoView = (VideoView) findViewById(R.id.vv);
final File inputFile = new File(Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory(),"a.mov");
//由于是耗时操作 所以开了个线程
new Thread(){
public void run() {
ffmpeg(inputFile.getAbsolutePath(),videoView.getHolder().getSurface() );
};
}.start();
}
/**
*
* @param input 视频文件的输入路径
* @param out 把视频文件解码成yuv格式输出路径
*/
public native void ffmpeg(String input,Surface surface);
}
在看c代码之前先补充知识
Native控制surfaceview方法步骤:
1 ANativeWindow_fromSurface函数关联java层的suraceview:
API介绍:
/**
*返回 ANativeWindow 相关联的java层的surfaceview对象,以它作为媒介和c交互
* 使用后一定要调用ANativeWindow_release(),不然会内存泄露
*/
2 ANativeWindow_Buffer 是一个结构体,surfaceview读取它的内容然后绘制到界面上
typedef struct ANativeWindow_Buffer {
// The number of pixels that are show horizontally.
int32_t width;
// The number of pixels that are shown vertically.
int32_t height;
// The number of *pixels* that a line in the buffer takes in
// memory. This may be >= width.
int32_t stride;
// The format of the buffer. One of WINDOW_FORMAT_*
int32_t format;
// The actual bits.
void* bits;
// Do not touch.
uint32_t reserved[6];
} ANativeWindow_Buffer;
3 ANativeWindow_lock
锁定窗口(window)的下一个画面就行写入
int32_t ANativeWindow_lock(ANativeWindow* window, ANativeWindow_Buffer* outBuffer,
ARect* inOutDirtyBounds);第一个参数:和java层suraceview相关联的ANativeWindow对象,就是我们介绍的第一个函数所返回值
第二个参数: 缓存对象.我们介绍的第二个对象
第三个参数:输出的矩形位置.如果不指定那么全部绘制
4 ANativeWindow_setBuffersGeometry
int32_t ANativeWindow_setBuffersGeometry(ANativeWindow* window, int32_t width, int32_t height, int32_t format);
API介绍:
改变窗口缓存区的格式和大小
宽度和高度控制缓存区的像素数量,而不是窗口屏幕的宽高
如果尺寸和窗口的物理尺寸不同,则缓存区将进行缩放后合成到屏幕
对于所有参数,如果返回0则窗口的所有基本数值将会强制回滚设置缓冲区的一些格式
第一个参数:和java层相关联的ANativeWindow
第二个参数: 宽 像素宽(不是播放的宽和高)
第三个参数:高 像素高
第四个参数:缓存区格式 一般和我们的surfaceview初始化的格式一致
5 ANativeWindow_unlockAndPost
解锁先前锁定的窗口 ,将新的缓存区内容显示在界面上
6 ANativeWindow_release
释放和java层关联的对象
那么大致的流程图:
最后看先代码吧
#include <jni.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<android/log.h>
//编码
#include "libavcodec/avcodec.h"
//封装格式处理
#include "libavformat/avformat.h"
//像素处理
#include "libswscale/swscale.h"
#include <android/native_window_jni.h>
#include <android/native_window.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include "libyuv.h"
#define LOGI(FORMAT,...) __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_INFO," FMY",FORMAT,##__VA_ARGS__);
#define LOGE(FORMAT,...) __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_ERROR,"FMY",FORMAT,##__VA_ARGS__);
char * output_cstr;
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_com_fmple_demoffmepeg_MainActivity_ffmpeg
(JNIEnv * env, jobject jobj, jstring input, jobject surface){
char * input_char = (*env)->GetStringUTFChars(env,input,NULL);
//头文件libavformat/avformat.h
//注册所有组件
/**
* 初始化libavformat和注册所有的 muxers, demuxers 和协议,如果你不想使用次函数,
* 则可以手动选择你想要的支持格式
* 详情你可以选择下面的函数查询
* @see av_register_input_format()
* @see av_register_output_format()
*
* muxer是合并将视频文件、音频文件和字幕文件合并为某一个视频格式。如,可将a.avi, a.mp3, a.srt用muxer合并为mkv格式的视频文件。
* demuxer是拆分这些文件的。
*/
av_register_all();
// 封装格式上下文结构体,也是统领全局的结构体,保存了视频文件封装格式相关信息。
AVFormatContext * pFormatCtx = avformat_alloc_context();
/**
* 打开输入流并且读取头信息。但解码器没有打开
* 这个输入流必须使用avformat_close_input()关闭
* @param ps(第一个参数的形参名称) 指向 你由你提供AVFormatContext(AVFormatContext是由avformat_alloc_context函数分配的)。
* 有可能ps指向空,在这种情况下,AVFormatContext由此函数分配并写入ps。
* 注意: 你提供的AVFormatContext在函数执行失败的时候将会被释放
* @param url 你要打开视频文件路径.
* @param fmt 如果不为空,那么这个参数将强制作为输入格式,否则自动检索
* @param options 一个关于AVFormatContext and demuxer-private 选项的字典.
* 返回时,此参数将被销毁,并替换为包含未找到的选项的dict。有可能是空的
*
* @return 返回0表示成功, 一个负数常量AVERROR是失败的.
*
* @note 如果你想自定义IO,你需要预分配格式内容并且设置pd属性
*/
if(avformat_open_input(&pFormatCtx,input_char,NULL,NULL)!=0){
LOGE("NDK>>>%s","avformat_open_input打开失败");
return;
}
//上面打开输入流后会将视频封装格式信息写入AVFormatContext中那么我们下一步就可以得到一些展示信息
/**
*
* 读取媒体文件中的数据包以获取流信息,这个对于对于文件格式没有头信息的很有帮助,比如说mpeg
* 这个函数还可以计算在MPEG-2重复帧模式的真实帧速率。
* 逻辑文件位置不会被这个函数改变
* 检索过的数据包或许会缓存以供后续处理
* @param ic 第一个参数 封装格式上下文
* @param options
* 如果不为空, 一个长度为 ic.nb_streams (封装格式所有流,字幕 视频 音频等) 的字典。
* 字典中第i个成员 包含一个对应ic第i个流中对的编码器。
* 在返回时,每个字典将会填充没有找到的选项
* @return 如果返回>=0 代表成功, AVERROR_xxx 表示失败
*
* @note 这个函数 不保证能打开所有编码器,所以返回一个非空的选项是一个完全正常的行为
*
*
* @todo
* 下个版本目标无视即可
* Let the user decide somehow what information is needed so that
* we do not waste time getting stuff the user does not need.
*/
if( avformat_find_stream_info(pFormatCtx,NULL)<0){
LOGE("NDK>>>%s","avformat_find_stream_info失败");
return ;
}
LOGE("NDK>>>%s","成功");
// //输出视频信息
// LOGI("视频的文件格式:%s",pFormatCtx->iformat->name);
// LOGI("视频时长:%d", (pFormatCtx->duration)/1000000);
//获取视频流的索引位置
//遍历所有类型的流(音频流、视频流、字幕流),找到视频流
int v_stream_idx = -1;
int i = 0;
//遍历封装格式中所有流
for (; i < pFormatCtx->nb_streams; ++i) {
//获取视频流pFormatCtx->streams[i]
//pFormatCtx->streams[i]->codec获取编码器
//codec_type获取编码器类型
//当前流等于视频 记录下标
if (pFormatCtx->streams[i]->codec->codec_type ==AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO) {
v_stream_idx = i;
break;
}
}
if (v_stream_idx==-1) {
LOGE("没有找视频流")
}else{
LOGE("找到视频流")
}
//编码器上下文结构体,保存了视频(音频)编解码相关信息
//得到视频流编码器
AVCodecContext *pCodecCtx = pFormatCtx->streams[v_stream_idx]->codec;
// 每种视频(音频)编解码器(例如H.264解码器)对应一个该结构体。
AVCodec *pCodec =avcodec_find_decoder(pCodecCtx->codec_id);
//(迅雷看看,找不到解码器,临时下载一个解码器)
if (pCodec == NULL)
{
LOGE("%s","找不到解码器\n");
return;
}else{
LOGE("%s","找到解码器\n");
}
//打开解码器
/**
* 初始化 指定AVCodecContext去使用 给定的AVCodec
* 在使用之前函数必须使用avcodec_alloc_context3()分配上下文。
*
* 以下函数 avcodec_find_decoder_by_name(), avcodec_find_encoder_by_name(),
* avcodec_find_decoder() and avcodec_find_encoder() 提供了一个简便的得到一个解码器的方法
*
* @warning 这个函数线程不是安全的
*
* @note 在使用解码程序之前,始终调用此函数 (如 @ref avcodec_decode_video2()).
* 下面是示例代码
* @code
* avcodec_register_all();
* av_dict_set(&opts, "b", "2.5M", 0);
* codec = avcodec_find_decoder(AV_CODEC_ID_H264);
* if (!codec)
* exit(1);
*
* context = avcodec_alloc_context3(codec);
*
* if (avcodec_open2(context, codec, opts) < 0)
* exit(1);
* @endcode
*
*
* @param avctx 要初始化的编码器
* @param codec 用这个codec去打开给定的上下文编码器.如果 codec 不为空 那么必须
* 事先用avcodec_alloc_context3和avcodec_get_context_defaults3传递给这个context,那么这个codec
* 要么为NULL要么就是上面调用函数所使用的codec
*
* @param
*
* 选项填充AVCodecContext和编解码器私有选项的字典。返回时,此对象将填充未找到的选项。
*
* @return 返回0表示成功, 负数失败
* @see avcodec_alloc_context3(), avcodec_find_decoder(), avcodec_find_encoder(),
* av_dict_set(), av_opt_find().
*/
if(avcodec_open2(pCodecCtx,pCodec,NULL)==0){
LOGE("%s","打开编码器成功\n");
}else{
LOGE("%s","打开编码器失败\n");
return;
}
//输出视频信息
LOGE("视频的文件格式:%s",pFormatCtx->iformat->name);
//得到视频播放时长
if(pFormatCtx->duration != AV_NOPTS_VALUE){
int hours, mins, secs, us;
int64_t duration = pFormatCtx->duration + 5000;
secs = duration / AV_TIME_BASE;
us = duration % AV_TIME_BASE;
mins = secs / 60;
secs %= 60;
hours = mins/ 60;
mins %= 60;
LOGE("%02d:%02d:%02d.%02d\n", hours, mins, secs, (100 * us) / AV_TIME_BASE);
}
LOGE("视频的宽高:%d,%d",pCodecCtx->width,pCodecCtx->height);
LOGE("解码器的名称:%s",pCodec->name);
//
// //存储一帧压缩编码数据。
AVPacket *packet =av_malloc(sizeof(AVPacket));
//
// //输出转码文件地址
// FILE *fp_yuv = fopen(output_cstr,"wb+");
//
// //AVFrame用于存储解码后的像素数据(YUV)
// //内存分配
AVFrame *pFrame = av_frame_alloc();
//
// //YUV420转码用
// AVFrame *pFrameYUV = av_frame_alloc();
// //avpicture_get_size()函数介绍:
// //
// /**
// * 如果给定存储图片的格式,那么计算给定的宽高所占用的大小
// *
// * @param pix_fmt 图片像素格式
// * @param width 图片宽
// * @param height 图片高
// * @return 返回计算的图片缓存大小或者错误情况下的负数错误代码
// *
// *
// * 这里计算缓存区的大小,但是没有分配,这里是用来后面转码使用
// */
// uint8_t *out_buffer = av_malloc(avpicture_get_size(AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P,pCodecCtx->width,pCodecCtx->height));
//
// //初始化缓冲区
// /**
// * 基于指定的图片参数和提供的图片缓存区去设置图片字段
// *
// * 使用ptr所指向的图片数据缓存 填充图片属性
// *
// * 如果 ptr是空,这个函数仅填充图片行大小(linesize)的数组并且返回图片缓存请求的大小
// *
// * 要分配图片缓存并且再一次填充图片数据请使用 avpicture_alloc().
// * @param picture 要填充的图片
// * @param ptr 存储图片的数据的缓存区, or NULL
// * @param pix_fmt 图片像素格式
// * @param width 图片宽
// * @param height 图片高
// * @return 返回请求的字节大小,在错误的情况下返回负数
// *
// * @see av_image_fill_arrays()
// */
// avpicture_fill((AVPicture *)pFrameYUV, out_buffer, AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P, pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height);
// //用于转码(缩放)的参数,转之前的宽高,转之后的宽高,格式等
// /**
// *分配和返回 SwsContext. You need it to perform
// * scaling/conversion operations using sws_scale().
// *
// * @param srcW 原始图宽
// * @param srcH 原始图高
// * @param srcFormat 原始图格式
// * @param dstW 目标图宽
// * @param dstH 不解释
// * @param dstFormat 不解释
// * @param flags 指定一个标志用于重新调整算法和选项
// * 具体参考:http://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020/article/details/12029505
// * @return 一个指定分配内容的指针, 错误情况返回空
// * @note this function is to be removed after a saner alternative is
// * written
// */
// struct SwsContext *sws_ctx =sws_getContext(pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height,pCodecCtx->pix_fmt,
// pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height,AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P,
// SWS_BICUBIC, NULL, NULL, NULL);
//
//
// //标志位
int got_picture, ret;
//
// //返回和java surface关联的ANativeWindow通过本地本地方法交互
ANativeWindow * nativeWindow =ANativeWindow_fromSurface(env,surface);
//缓存
ANativeWindow_Buffer outBuffer;
//设置缓存的几何信息
AVFrame *rgb_frame = av_frame_alloc();
uint8_t *out_buffer = av_malloc(avpicture_get_size(AV_PIX_FMT_RGBA,pCodecCtx->width,pCodecCtx->height));
//
//
//读取每一帧
/**
*返回下一帧的流
* 此函数返回存储在文件中的内容,并且不会验证解码器有什么有效帧。
* 函数将存储在文件中的帧进行分割 并且返回给每一个调用者。
*
* 函数不会删除在有效帧之间的无效数据 以便在可能解码过程中提供解码器最大的信息帮助
* 如果 pkt->buf 是空的,那么这个对应数据包是有效的直到下一次调用av_read_frame()
* 或者直到使用avformat_close_input().否则包无期限有效
* 在这两种情况下 这个数据包当你不在需要的时候,你必须使用使用av_free_packet释放它
* 对于视屏,数据包刚好只包含一帧.对于音频,如果它每一帧是一个已知固定大小的,那么他包含整数帧(如. PCM or ADPCM data)
* 如果音频帧具有可变大小(如. MPEG audio),那么他只包含一帧
* pkt->pts, pkt->dts and pkt->duration 始终在AVStream.time_base 单位设置正确的数值
*(如果这个格式无法提供.那么进行猜测)
* 如果视频格式有B帧那么pkt->pts可以是 AV_NOPTS_VALUE.如果你没有解压他的有效部分那么最好依靠pkt->dts
*
* @return 0表示成功, < 0 错误或者文结束
*/
while(av_read_frame(pFormatCtx,packet)>=0){
//一个包里有很多种类型如音频视频等 所以判断 这个包对应的流的在封装格式的下表
//如果这个包是视频频包那么得到压缩的视频包
if (packet->stream_index==v_stream_idx) {
LOGE("测试");
/**
* 解码视频帧 从avpkt->data读取数据并且解码avpkt->size的大小后转化为图片.
* 一些解码器可以支持在一个ACpacket中存在多帧的情况,像这样的解码器将只解码第一帧
*
* @warning 输入缓存区必须 实际读取的字节流小于 FF_INPUT_BUFFER_PADDING_SIZE,
* 一些优化过的比特流 读取32位或者64字节 的时候可以一次性读取完
*
* @warning 在缓冲器的buf结尾设置0以确保被破坏的MPEG流不会发生超线程
*
* @note 有 CODEC_CAP_DELAY 才能设置一个在输入和输出之间的延迟,这些需要使用avpkt->data=NULL,
* 在结束返回剩余帧数的时候avpkt->size=0
*
* @note 这个AVCodecContext 在数据包传入解码器之前必须调用avcodec_open2
*
*
* @param avctx 解码器上下文
*
* @param[out] 解码的视频帧图片将会被存储在AVFrame.
* 使用av_frame_alloc 得到一个AVFrame,
* 编码器将会分配 使用 AVCodecContext.get_buffer2() 回调
* 的实际图片的内存.
* 当AVCodecContext.refcounted_frames 设置为1,这帧(frame)是引用计数,并且返回
* 的引用计数是属于调用者的.
* frame在长实际不使用的时候调用者必须调用av_frame_unref()就行释放
* 如果av_frame_is_writable()返回1那么调用者可以安全的写入到这个frame中。
* 当AVCodecContext.refcounted_frames设置为0,返回的引用属于解码器,
* 只有下次使用这个函数或者关闭或者刷新这个编码器之前有效。调用者不会写入它
*
*@param[in,out] got_picture_ptr 如果为0表示不能解压, 否者它不是0.
*
* @param[in] avpkt 这个输入的avpkt包含输入缓存区
* 你能使用av_init_packet()创建像这样的packet然后设置数据和大小,
* 一些解码器还可以添加一些其他字段 比如 flags&AV_PKT_FLAG_KEY flags&AV_PKT_FLAG_KEY
* 所有解码器都设计为尽可能少地使用
*
* @return 再错误时返回一个负数 , 否则返回使用字节数或者或者0(没有帧被解压返回0)otherwise the number of bytes
*
*/
ret=avcodec_decode_video2(pCodecCtx,pFrame,&got_picture,packet);
if(ret>=0){
LOGE("解压成功");
//AVFrame转为像素格式YUV420,宽高
//2 6输入、输出数据
//3 7输入、输出画面一行的数据的大小 AVFrame 转换是一行一行转换的
//4 输入数据第一列要转码的位置 从0开始
//5 输入画面的高度
// sws_scale(sws_ctx,pFrame->data,pFrame->linesize,0,pCodecCtx->height,pFrameYUV->data,pFrameYUV->linesize);
//输出到YUV文件
//AVFrame像素帧写入文件
//data解码后的图像像素数据(音频采样数据)
//Y 亮度 UV 色度(压缩了) 人对亮度更加敏感
//U V 个数是Y的1/4
// int y_size = pCodecCtx->width * pCodecCtx->height;
ANativeWindow_lock(nativeWindow,&outBuffer,NULL);
//
ANativeWindow_setBuffersGeometry(nativeWindow,pCodecCtx->width,pCodecCtx->height,WINDOW_FORMAT_RGBA_8888);
avpicture_fill((AVPicture *)rgb_frame,out_buffer, AV_PIX_FMT_RGBA, pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height);
//
//
I420ToARGB(pFrame->data[0],pFrame->linesize[0],
pFrame->data[2],pFrame->linesize[2],
pFrame->data[1],pFrame->linesize[1],
rgb_frame->data[0], rgb_frame->linesize[0],
pCodecCtx->width,pCodecCtx->height);
int h = 0;
for (h = 0; h < pCodecCtx->height; h++) {
memcpy(outBuffer.bits + h * outBuffer.stride*4, out_buffer + h * rgb_frame->linesize[0], rgb_frame->linesize[0]);
// memcpy(outBuffer.bits,out_buffer,pCodecCtx->width*pCodecCtx->height*4);
}
LOGE("锁定成功");
ANativeWindow_unlockAndPost(nativeWindow);
// //获取帧率tbr fbs
//float fram_rate =pFormatCtx->streams[v_stream_idx]->avg_frame_rate.num/pFormatCtx->streams[v_stream_idx]->avg_frame_rate.den;
// 如果奔溃请开启下面的线程休眠
// usleep(1000);
}
}
av_free_packet(packet);
}
(*env)->ReleaseStringUTFChars(env,input,input_char);
//关闭文件
// fclose(fp_yuv);
ANativeWindow_release(nativeWindow);
// //关闭资源
av_frame_free(&pFrame);
// // av_frame_free(&pFrameYUV);
// av_frame_free(&rgb_frame);
// //关闭编码器上下文
avcodec_close(pCodecCtx);
// //关闭输入流
avformat_close_input(&pFormatCtx);
// //关闭封装格式
avformat_free_context(pFormatCtx);
}
Studio版本
都差不多 只不过才用Cmake方式.这里和上一篇差不多 所以在上一篇基础添加修改方法而已
导入所有so库到
关于FFmpeg解码请看第一篇教程:FFmpeg解码
关于有人说找不到so库的,请在build.gradle里面添加如下代码
//对应子项目的build下android标签下,不是工程的build
sourceSets{
main{
jniLibs.srcDirs =['libs']
}
}1 添加yuvso.so到libs中
2 修改cmake文件
# For more information about using CMake with Android Studio, read the
# documentation: https://d.android.com/studio/projects/add-native-code.html
# Sets the minimum version of CMake required to build the native library.
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.4.1)
# Creates and names a library, sets it as either STATIC
# or SHARED, and provides the relative paths to its source code.
# You can define multiple libraries, and CMake builds them for you.
# Gradle automatically packages shared libraries with your APK.
add_library( # Sets the name of the library.
native-lib
# Sets the library as a shared library.
SHARED
# Provides a relative path to your source file(s).
src/main/cpp/native-lib.c)
##################################################################################################
##################################################################################################
set(distribution_DIR ${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/libs/)
#libavcodec-56.so
add_library(libavcodec-56-lib SHARED IMPORTED)
set_target_properties(libavcodec-56-lib PROPERTIES IMPORTED_LOCATION
${distribution_DIR}/${ANDROID_ABI}/libavcodec-56.so)
#libavdevice-56.so
add_library(libavdevice-56-lib SHARED IMPORTED)
set_target_properties(libavdevice-56-lib PROPERTIES IMPORTED_LOCATION
${distribution_DIR}/${ANDROID_ABI}/libavdevice-56.so)
#libavfilter-5.so
add_library(libavfilter-5-lib SHARED IMPORTED)
set_target_properties(libavfilter-5-lib PROPERTIES IMPORTED_LOCATION
${distribution_DIR}/${ANDROID_ABI}/libavfilter-5.so)
#libavformat-56.so
add_library(libavformat-56-lib SHARED IMPORTED)
set_target_properties(libavformat-56-lib PROPERTIES IMPORTED_LOCATION
${distribution_DIR}/${ANDROID_ABI}/libavformat-56.so)
#libavutil-54.so
add_library(libavutil-54-lib SHARED IMPORTED)
set_target_properties(libavutil-54-lib PROPERTIES IMPORTED_LOCATION
${distribution_DIR}/${ANDROID_ABI}/libavutil-54.so)
#libpostproc-53.so
add_library(libpostproc-53-lib SHARED IMPORTED)
set_target_properties(libpostproc-53-lib PROPERTIES IMPORTED_LOCATION
${distribution_DIR}/${ANDROID_ABI}/libpostproc-53.so)
#libswresample-1.so
add_library(libswresample-1-lib SHARED IMPORTED)
set_target_properties(libswresample-1-lib PROPERTIES IMPORTED_LOCATION
${distribution_DIR}/${ANDROID_ABI}/libswresample-1.so)
#libswscale-3.so
add_library(libswscale-3-lib SHARED IMPORTED)
set_target_properties(libswscale-3-lib PROPERTIES IMPORTED_LOCATION
${distribution_DIR}/${ANDROID_ABI}/libswscale-3.so)
#libyuv.so
add_library(libyuv-lib SHARED IMPORTED)
set_target_properties(libyuv-lib PROPERTIES IMPORTED_LOCATION ${distribution_DIR}/${ANDROID_ABI}/libyuv.so)
##################################################################################################
##################################################################################################
# Searches for a specified prebuilt library and stores the path as a
# variable. Because CMake includes system libraries in the search path by
# default, you only need to specify the name of the public NDK library
# you want to add. CMake verifies that the library exists before
# completing its build.
find_library( # Sets the name of the path variable.
log-lib
# Specifies the name of the NDK library that
# you want CMake to locate.
log )
#这个库是用于surface在c代码中交互而添加的
find_library( # Sets the name of the path variable.
lnative_window_jni-lib
# Specifies the name of the NDK library that
# you want CMake to locate.
android )
# Specifies libraries CMake should link to your target library. You
# can link multiple libraries, such as libraries you define in this
# build script, prebuilt third-party libraries, or system libraries.
include_directories(src/main/cpp/include/)
target_link_libraries( # Specifies the target library.
native-lib
# Links the target library to the log library
# included in the NDK.
${log-lib}
${lnative_window_jni-lib}
libavcodec-56-lib
libavdevice-56-lib
libavfilter-5-lib
libavformat-56-lib
libavutil-54-lib
libpostproc-53-lib
libswresample-1-lib
libswscale-3-lib
libyuv-lib
)最后看看界面
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="com.example.demoffmpeg.MainActivity">
<SurfaceView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:id="@+id/sv"
android:layout_height="0dp"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/sample_text"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:onClick="onClick"
android:textColor="#fff"
android:text="播放视频!"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>
最后看java代码吧
package com.example.demoffmpeg;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Environment;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.view.Surface;
import android.view.SurfaceView;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.TextView;
import java.io.File;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
// Used to load the 'native-lib' library on application startup.
static {
System.loadLibrary("native-lib");
}
private SurfaceView sv;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
// Example of a call to a native method
TextView tv = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.sample_text);
sv = (SurfaceView) findViewById(R.id.sv);
}
/**
* A native method that is implemented by the 'native-lib' native library,
* which is packaged with this application.
*/
public native void plays(String videoPath, Surface surface);
//点击播放视频
public void onClick(View view) {
final File inputFile = new File(Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory(),"a.mp4");
//由于是耗时操作 所以开了个线程
new Thread(){
public void run() {
plays(inputFile.getAbsolutePath(),sv.getHolder().getSurface() );
};
}.start();
}
}
附上build.gradle
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
android {
compileSdkVersion 25
buildToolsVersion "25.0.3"
defaultConfig {
applicationId "com.example.demoffmpeg"
minSdkVersion 21
targetSdkVersion 25
versionCode 1
versionName "1.0"
testInstrumentationRunner "android.support.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"
externalNativeBuild {
cmake {
cppFlags "-frtti -fexceptions"
}
}
ndk{
abiFilters 'armeabi'
}
}
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled false
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
}
externalNativeBuild {
cmake {
path "CMakeLists.txt"
}
}
sourceSets{
main{
jniLibs.srcDirs =['libs']
}
}
}
dependencies {
compile fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar'])
androidTestCompile('com.android.support.test.espresso:espresso-core:2.2.2', {
exclude group: 'com.android.support', module: 'support-annotations'
})
compile 'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:25.3.1'
compile 'com.android.support.constraint:constraint-layout:1.0.2'
testCompile 'junit:junit:4.12'
}























 3万+
3万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








