Rust Slint虚拟键盘源码分享
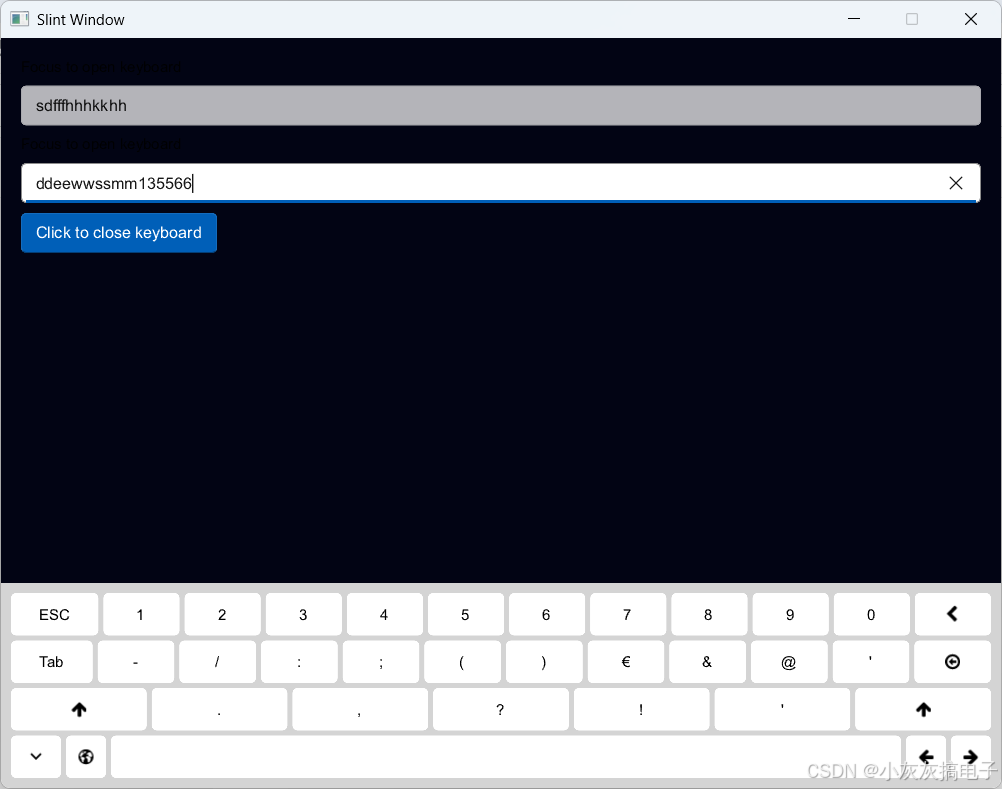
一、效果展示
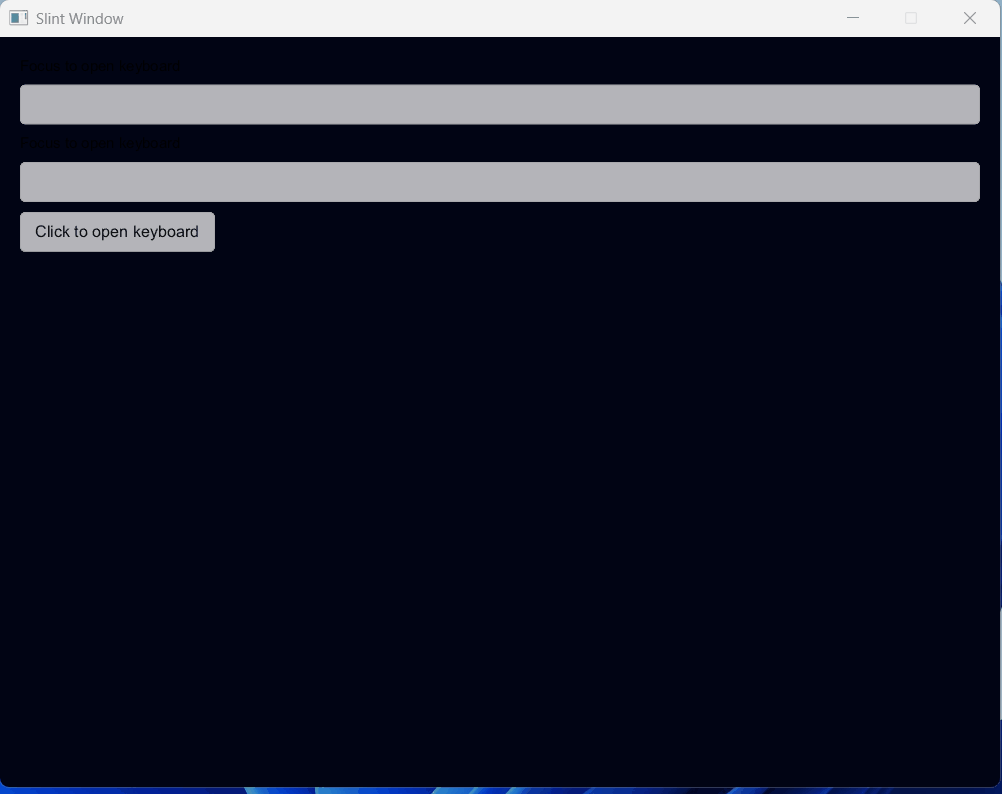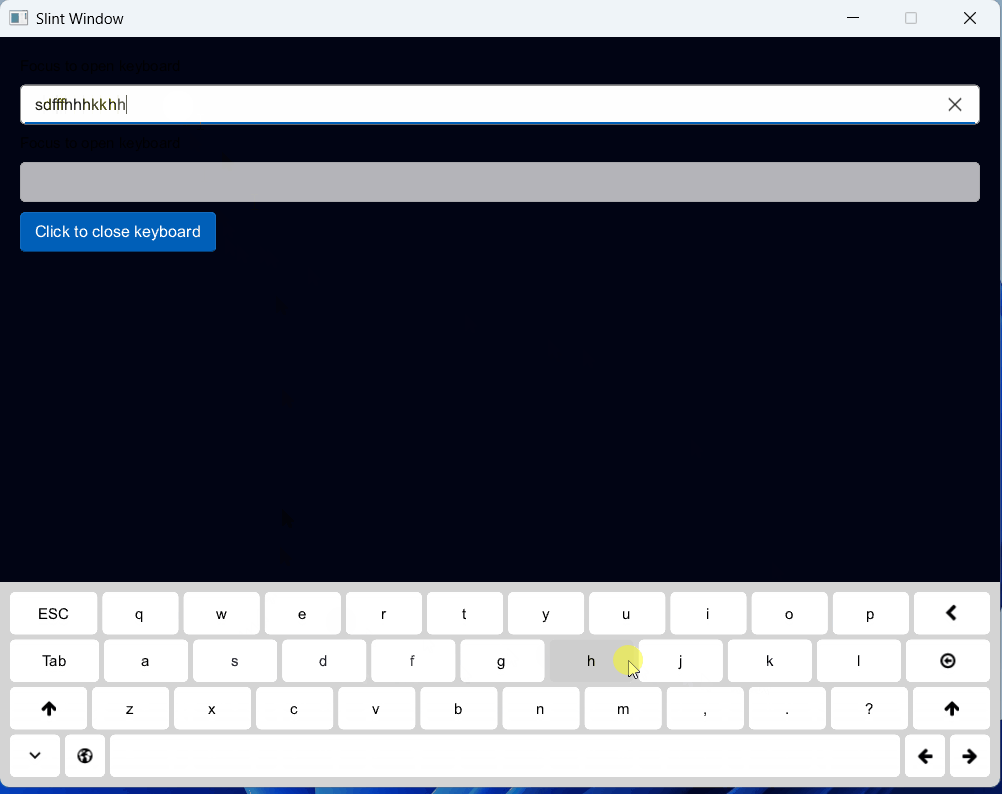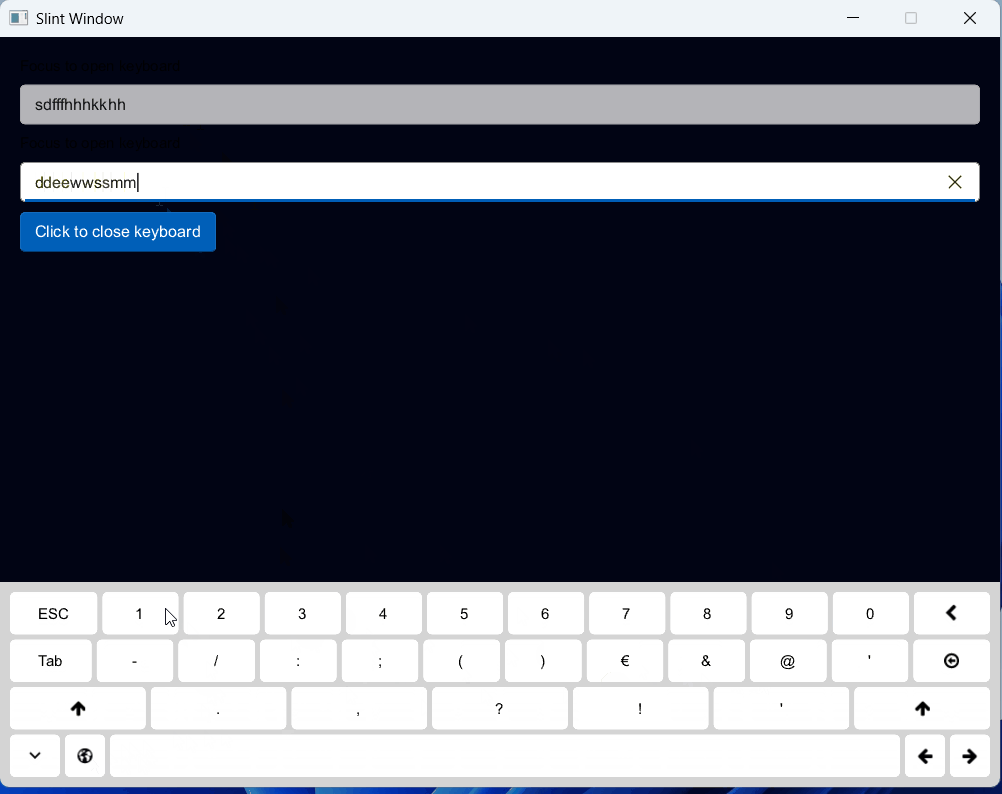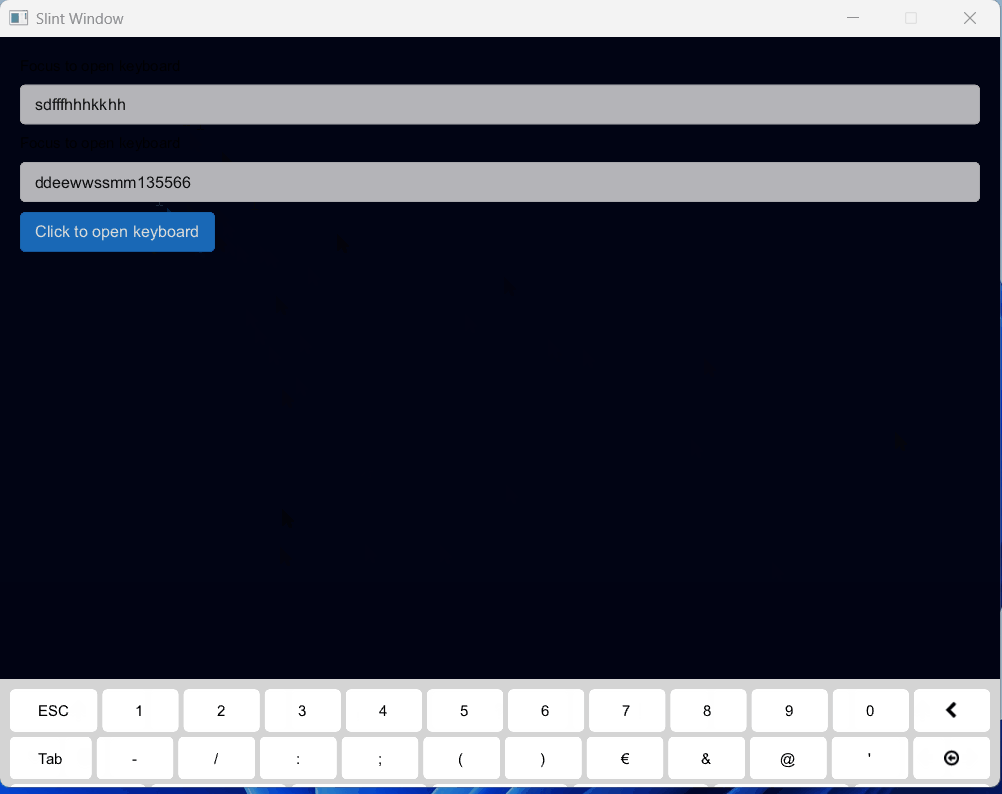
二、源码分享
1、main.rs
use std::any::Any;
use slint::{PlatformError};
slint::include_modules!();
fn main() ->Result<(), PlatformError>{
let app: MainWindow = MainWindow::new()?;
let weak: slint::Weak<MainWindow> = app.as_weak();
app.global::<DataAdapter>().on_btn_clicked({
let weak = weak.clone();
move |text|{
if let Some(strong) = weak.upgrade(){
let adapter = strong.global::<DataAdapter>();
println!("{}",text);
}
}
});
app.global::<VirtualKeyboardHandler>().on_key_pressed({
move |key| {
weak.unwrap()
.window()
.dispatch_event(slint::platform::WindowEvent::KeyPressed { text: key.clone() });
weak.unwrap()
.window()
.dispatch_event(slint::platform::WindowEvent::KeyReleased { text: key });
}
});
let _ = app.run();
Ok(())
}
2、icons.slint
// Copyright © SixtyFPS GmbH <info@slint.dev>
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
export global Icons {
out property <image> arrow-up: @image-url("image/arrow-up.svg");
out property <image> arrow-left: @image-url("image/arrow-left.svg");
out property <image> arrow-right: @image-url("image/arrow-right.svg");
out property <image> chevron-left: @image-url("image/chevron-left.svg");
out property <image> arrow-circle-o-left: @image-url("image/arrow-circle-o-left.svg");
out property <image> globe: @image-url("image/globe.svg");
out property <image> expand-more: @image-url("image/expand-more.svg");
}
3、main.slint
import { AboutSlint, VerticalBox, LineEdit, HorizontalBox, Button, GroupBox, GridBox,
ComboBox, Spinner, Slider, ListView, Palette, ProgressIndicator, CheckBox, Switch } from "std-widgets.slint";
import { DataAdapter} from "models.slint";
export { DataAdapter}
import { VirtualKeyboardHandler, VirtualKeyboard, KeyModel } from "virtual_keyboard.slint";
export { VirtualKeyboardHandler, KeyModel }
export component MainWindow inherits Window {
width: 800px;
height: 600px;
background: #020414;
Rectangle {
VerticalLayout {
alignment: start;
padding: 16px;
spacing: 8px;
Text {
text: "Focus to open keyboard";
horizontal-alignment: left;
}
LineEdit {}
Text {
text: "Focus to open keyboard";
horizontal-alignment: left;
}
LineEdit {}
HorizontalLayout {
alignment: start;
Button {
text: self.checked ? "Click to close keyboard" : "Click to open keyboard";
checked: TextInputInterface.text-input-focused;
clicked => {
TextInputInterface.text-input-focused = !TextInputInterface.text-input-focused;
}
}
}
}
keyboard := VirtualKeyboard {
y: TextInputInterface.text-input-focused ? parent.height - self.height : parent.height;
}
}
}
4、virtual_keyboard.slint
// Copyright © SixtyFPS GmbH <info@slint.dev>
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
import { Button, Palette } from "std-widgets.slint";
import { Icons } from "icons.slint";
component VirtualKeyboardButton {
in property <string> key;
in property <image> icon;
callback key-pressed(/* key */ string);
min-width: 32px;
min-height: 32px;
horizontal-stretch: 0;
states [
pressed when i-touch-area.pressed : {
i-state-area.opacity: 0.5;
}
]
i-container := Rectangle {
border-radius: 4px;
background: Palette.color-scheme == ColorScheme.dark ? #373737 : #ffffff;
HorizontalLayout {
padding: 8px;
if (root.key != "") : Text {
text: root.key;
color: Palette.color-scheme == ColorScheme.dark ? #ffffff : #000000;
font-size: 12px;
vertical-alignment: center;
horizontal-alignment: center;
}
if (root.key == "") : Image {
y: (parent.height - self.height) / 2;
source: root.icon;
height: 18px;
colorize: Palette.color-scheme == ColorScheme.dark ? #ffffff : #000000;
}
}
}
i-state-area := Rectangle {
border-radius: i-container.border-radius;
opacity: 0;
background: #000000;
animate opacity { duration: 150ms; }
}
i-touch-area := TouchArea {
pointer-event(event) => {
if(event.kind == PointerEventKind.down) {
root.key-pressed(key);
}
}
}
}
export struct KeyModel {
key: string,
shift-key: string,
}
export global VirtualKeyboardHandler {
in property <[[[KeyModel]]]> default-key-sets: [
[
[
{ key: "q", shift-key: "Q" },
{ key: "w", shift-key: "W" },
{ key: "e", shift-key: "E" },
{ key: "r", shift-key: "R" },
{ key: "t", shift-key: "T" },
{ key: "y", shift-key: "Y" },
{ key: "u", shift-key: "U" },
{ key: "i", shift-key: "I" },
{ key: "o", shift-key: "O" },
{ key: "p", shift-key: "P" }
],
[
{ key: "a", shift-key: "A" },
{ key: "s", shift-key: "S" },
{ key: "d", shift-key: "D" },
{ key: "f", shift-key: "F" },
{ key: "g", shift-key: "G" },
{ key: "h", shift-key: "H" },
{ key: "j", shift-key: "J" },
{ key: "k", shift-key: "K" },
{ key: "l", shift-key: "L" }
],
[
{ key: "z", shift-key: "Z" },
{ key: "x", shift-key: "X" },
{ key: "c", shift-key: "C" },
{ key: "v", shift-key: "V" },
{ key: "b", shift-key: "B" },
{ key: "n", shift-key: "N" },
{ key: "m", shift-key: "M" },
{ key: ",", shift-key: ";" },
{ key: ".", shift-key: ":" },
{ key: "?", shift-key: "?" }
],
],
[
[
{ key: "1", shift-key: "[" },
{ key: "2", shift-key: "]" },
{ key: "3", shift-key: "{" },
{ key: "4", shift-key: "}" },
{ key: "5", shift-key: "#" },
{ key: "6", shift-key: "%" },
{ key: "7", shift-key: "^" },
{ key: "8", shift-key: "*" },
{ key: "9", shift-key: "+" },
{ key: "0", shift-key: "=" }
],
[
{ key: "-", shift-key: "_" },
{ key: "/", shift-key: "\\" },
{ key: ":", shift-key: "|" },
{ key: ";", shift-key: "~" },
{ key: "(", shift-key: "<" },
{ key: ")", shift-key: ">" },
{ key: "€", shift-key: "$" },
{ key: "&", shift-key: "€" },
{ key: "@", shift-key: "°" },
{ key: "'", shift-key: "#" },
],
[
{ key: ".", shift-key: "." },
{ key: ",", shift-key: "," },
{ key: "?", shift-key: "?" },
{ key: "!", shift-key: "!" },
{ key: "'", shift-key: "'" },
],
]
];
out property <int> current-key-set;
out property <[[KeyModel]]> keys: default-key-sets[self.current-key-set];
in-out property <bool> open;
callback key_pressed(/* key */ string);
public function switch-keyboard() {
if (self.current-key-set < self.default-key-sets.length - 1) {
self.current-key-set += 1;
} else {
self.current-key-set -= 1;
}
self.current-key-set = min(self.default-key-sets.length - 1, max(0, self.current-key-set))
}
}
export component VirtualKeyboard {
private property <bool> shift;
callback close();
preferred-width: 100%;
TouchArea {}
Rectangle {
background: Palette.color-scheme == ColorScheme.dark ? #1c1c1c : #d4d4d4;
height: 100%;
}
i-layout := VerticalLayout {
padding: 8px;
spacing: 4px;
for row[index] in VirtualKeyboardHandler.keys : HorizontalLayout {
spacing: 4px;
if (index == 0) : VirtualKeyboardButton {
key: "ESC";
key-pressed => {
VirtualKeyboardHandler.key-pressed(Key.Escape);
}
}
if (index == 1) : VirtualKeyboardButton {
key: "Tab";
key-pressed => {
VirtualKeyboardHandler.key-pressed(Key.Tab);
}
}
// shift
if (index == 2) : VirtualKeyboardButton {
icon: Icons.arrow-up;
key-pressed => {
root.shift = !root.shift;
}
}
for km in row : VirtualKeyboardButton {
key: root.shift ? km.shift-key : km.key;
key-pressed(key) => {
VirtualKeyboardHandler.key-pressed(key);
root.shift = false;
}
}
if (index == 0) : VirtualKeyboardButton {
icon: Icons.chevron-left;
key-pressed => {
VirtualKeyboardHandler.key-pressed(Key.Backspace);
}
}
if (index == 1) : VirtualKeyboardButton {
icon: Icons.arrow-circle-o-left;
key-pressed => {
VirtualKeyboardHandler.key-pressed(Key.Return);
}
}
// shift
if (index == 2) : VirtualKeyboardButton {
icon: Icons.arrow-up;
key-pressed => {
root.shift = !root.shift;
}
}
}
HorizontalLayout {
spacing: 4px;
VirtualKeyboardButton {
icon: Icons.expand-more;
key-pressed(key) => {
root.close();
}
}
VirtualKeyboardButton {
icon: Icons.globe;
key-pressed(key) => {
VirtualKeyboardHandler.switch-keyboard();
}
}
VirtualKeyboardButton {
horizontal-stretch: 1;
key: " ";
key-pressed(key) => {
root.shift = false;
VirtualKeyboardHandler.key-pressed(key);
}
}
VirtualKeyboardButton {
icon: Icons.arrow-left;
key-pressed(key) => {
VirtualKeyboardHandler.key-pressed(Key.LeftArrow);
}
}
VirtualKeyboardButton {
icon: Icons.arrow-right;
key-pressed(key) => {
VirtualKeyboardHandler.key-pressed(Key.RightArrow);
}
}
}
}
animate y { duration: 500ms; easing: cubic-bezier(0.05, 0.7, 0.1, 1.0); }
}
5、资源文件
文章顶部下载
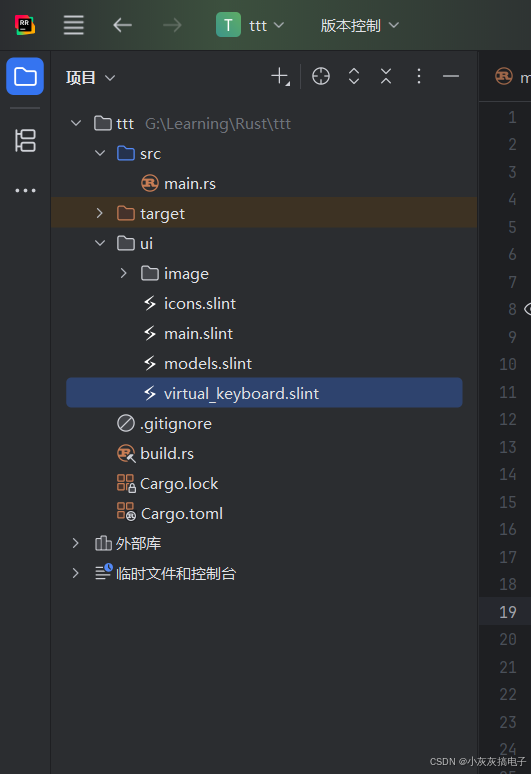
6、工程结构
三、Slint介绍
1、 Slint 是什么?
Slint 是一个用于构建原生用户界面的工具包,特别适用于嵌入式设备和桌面应用程序。它最初是用 Rust 编写的,并且为 Rust 开发者提供了优秀的支持。其核心目标是提供一种高效、安全且现代化的方式来创建流畅、响应式的 UI。
2、核心特点
- 声明式 UI:Slint 使用一种名为
.slint的声明式语言(受 QML 和 HTML 启发)来描述用户界面。开发者专注于定义 UI 的结构和状态,而不是编写大量的命令式代码来控制每个像素。 - 高效渲染:它使用轻量级的渲染引擎,针对性能进行了优化,特别适合资源受限的环境(如微控制器)。
- 数据绑定:UI 元素可以轻松绑定到 Rust 代码中的数据模型或属性。当底层数据发生变化时,UI 会自动更新(响应式)。
- 内存安全:得益于 Rust 的所有权和借用规则,Slint 能够帮助开发者避免常见的内存错误和安全漏洞。
- 跨平台:支持 Linux、Windows、macOS 以及各种嵌入式平台(如通过 LVGL 集成)。
3、 Slint 的核心组成部分
.slint文件:这是定义 UI 布局、组件、属性、状态和交互逻辑的主要文件。它使用类似 QML 的语法。- Slint 编译器 (
slint-compiler):将.slint文件编译成高效的 Rust 代码(或 C++ 代码)。 - Slint 运行时库 (
slintcrate):提供在运行时渲染 UI、处理事件、管理状态和执行数据绑定所需的库功能。
4、 基本用法示例 (Rust)
假设我们有一个简单的 UI,包含一个按钮和一个标签。点击按钮时,标签显示点击次数。
Step 1: 定义 UI (example.slint)
import { Button, VerticalBox } from "std-widgets.slint";
export component ExampleWindow {
callback button-clicked;
in-out property <int> count: 0;
VerticalBox {
Text {
text: "Count: " + count;
}
Button {
text: "Click Me!";
clicked => {
button-clicked();
}
}
}
}
Step 2: Rust 代码集成
// 引入 slint 宏和类型
slint::slint! {
// 编译器会自动处理 example.slint 并生成 Rust 代码
include!("example.slint");
}
use slint::ComponentHandle; // 用于访问窗口实例的方法
fn main() {
// 创建 UI 窗口实例
let ui = ExampleWindow::new().unwrap();
// 获取对 count 属性的弱引用 (Weak<> 避免循环引用)
let ui_weak = ui.as_weak();
// 连接按钮点击信号到 Rust 闭包
ui.on_button_clicked(move || {
let ui = ui_weak.unwrap();
// 更新 count 属性 (会自动触发 UI 更新)
let current_count = ui.get_count();
ui.set_count(current_count + 1);
});
// 运行 UI 主循环
ui.run().unwrap();
}
关键点解释
slint::slint!宏:它将.slint文件编译并集成到 Rust 代码中,生成ExampleWindow结构体和相关方法。- 属性 (
property <int> count):在.slint文件中定义了一个可读写的整数属性count。在 Rust 中,可以通过get_count()和set_count()方法访问和修改它。 - 信号 (
callback button-clicked):定义了一个信号button-clicked。在 Rust 中,使用on_button_clicked方法注册一个闭包来处理这个信号。 - 数据绑定:在
.slint文件中,Text的text属性绑定到表达式"Count: " + count。当 Rust 代码调用set_count改变count的值时,这个文本会自动更新。 ComponentHandle:提供访问窗口实例的方法,如as_weak用于获取弱引用。run():启动 UI 的事件循环。
5、 优势
- 开发效率:声明式语法和数据绑定简化了 UI 开发。
- 性能:轻量级渲染引擎和优化的 Rust 代码带来流畅体验。
- 安全:Rust 的内存安全特性贯穿整个 UI 开发过程。
- 跨平台:一套代码可部署到多种设备。
- 现代性:响应式设计理念。
6、适用场景
- 嵌入式设备仪表盘
- 桌面应用 GUI (替代部分 Electron 场景)
- 工业控制界面
- 需要高性能和低资源占用的 UI
7、与其他 Rust GUI 库的比较
| 特性 | Slint | Druid | Iced | egui |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 范式 | 声明式 (.slint) | 命令式/响应式 | 响应式/Elm-like | 即时模式 (Immediate) |
| 学习曲线 | 中等 (需学新语言) | 中等 | 中等 | 较低 |
| 性能 | 非常高 | 高 | 高 | 中等 |
| 跨平台 | 广泛 (含嵌入式) | 桌面 | 桌面/Web | 桌面/Web/WASM |
| 成熟度 | 快速发展 | 较成熟 | 较成熟 | 较成熟 |
| 强项 | 嵌入式、性能、安全性 | 数据驱动、灵活性 | 纯 Rust、Elm 架构 | 简单、快速原型 |
8、总结
Slint 为 Rust 开发者提供了一个强大且现代的解决方案,用于构建高性能、安全且美观的用户界面,尤其是在嵌入式系统和资源受限的桌面环境中表现出色。其声明式的 .slint 语言结合 Rust 的强大功能,使得开发响应式 UI 变得更加高效和安全。如果你正在寻找一个高效、跨平台且安全的 Rust GUI 框架,Slint 绝对值得一试。

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










