Spring的Java配置方式是通过 @Configuration 和 @Bean 这两个注解实现的:
1、@Configuration 作用于类上,相当于一个xml配置文件;
2、@Bean 作用于方法上,相当于xml配置中的<bean>;
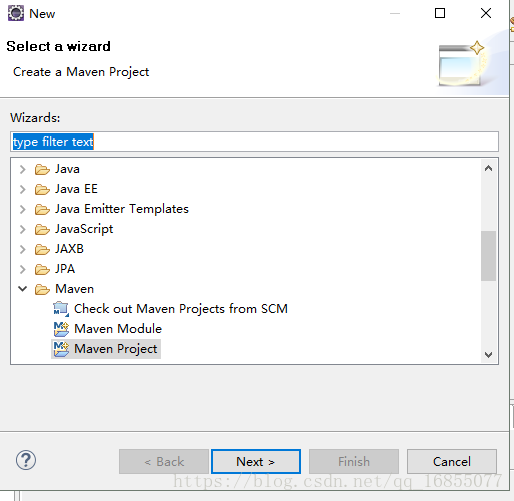
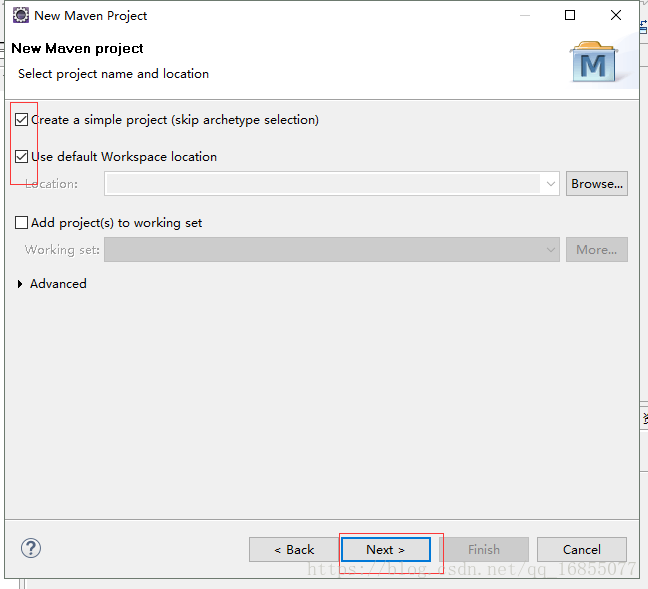
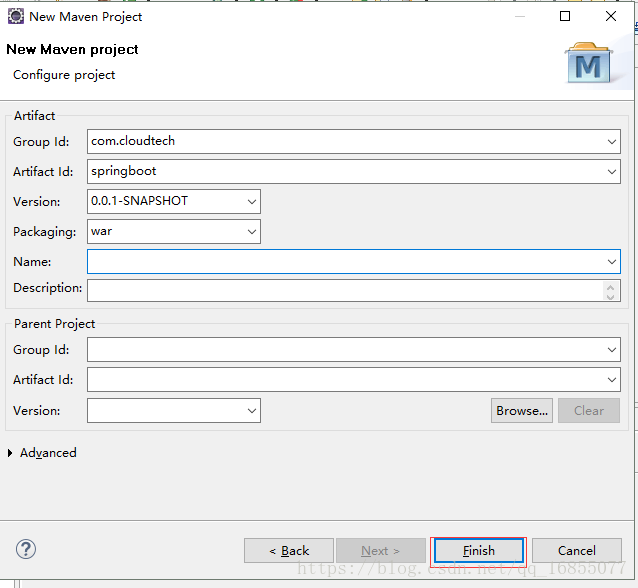
1.新建一个maven项目
2.pom.xml设置
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.cloudtech</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>4.3.7.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 连接池 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.jolbox</groupId>
<artifactId>bonecp-spring</artifactId>
<version>0.8.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<finalName>${project.artifactId}</finalName>
<plugins>
<!-- 资源文件拷贝插件 -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-resources-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<encoding>UTF-8</encoding>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<!-- java编译插件 -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<source>1.7</source>
<target>1.7</target>
<encoding>UTF-8</encoding>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
<pluginManagement>
<plugins>
<!-- 配置Tomcat插件 -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat7-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.2</version>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</pluginManagement>
</build>
</project>
package com.cloudtech.dao;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import com.cloudtech.entity.User;
public class UserDAO {
public List<User> queryUserList(){
List<User> result = new ArrayList<User>();
// 模拟数据库的查询
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("username_" + i);
user.setPassword("password_" + i);
user.setAge(i + 1);
result.add(user);
}
return result;
}
}
package com.cloudtech.entity;
public class User {
private String username;
private String password;
private Integer age;
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
package com.cloudtech.javaconfig;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import com.cloudtech.entity.User;
import com.cloudtech.service.UserService;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 通过Java配置来实例化Spring容器
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
// 在Spring容器中获取Bean对象
UserService userService = context.getBean(UserService.class);
// 调用对象中的方法
List<User> list = userService.queryUserList();
for (User user : list) {
System.out.println(user.getUsername() + ", " + user.getPassword() + ", " + user.getPassword());
}
// 销毁该容器
context.destroy();
}
}
package com.cloudtech.javaconfig;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import com.cloudtech.dao.UserDAO;
@Configuration //通过该注解来表明该类是一个Spring的配置,相当于一个xml文件
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.cloudtech") //配置扫描包
public class SpringConfig {
@Bean // 通过该注解来表明是一个Bean对象,相当于xml中的<bean>
public UserDAO getUserDAO(){
return new UserDAO(); // 直接new对象做演示
}
}
package com.cloudtech.service;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.cloudtech.dao.UserDAO;
import com.cloudtech.entity.User;
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired // 注入Spring容器中的bean对象
private UserDAO userDAO;
public List<User> queryUserList() {
// 调用userDAO中的方法进行查询
return this.userDAO.queryUserList();
}
}
启动main方法效果如下
八月 07, 2018 12:05:17 上午 org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext prepareRefresh
信息: Refreshing org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext@4d405ef7: startup date [Tue Aug 07 00:05:17 CST 2018]; root of context hierarchy
username_0, password_0, password_0
username_1, password_1, password_1
username_2, password_2, password_2
username_3, password_3, password_3
username_4, password_4, password_4
username_5, password_5, password_5
username_6, password_6, password_6
username_7, password_7, password_7
username_8, password_8, password_8
username_9, password_9, password_9
八月 07, 2018 12:05:17 上午 org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext doClose
信息: Closing org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext@4d405ef7: startup date [Tue Aug 07 00:05:17 CST 2018]; root of context hierarchy
从以上的示例中可以看出,使用Java代码就完美的替代xml配置文件,并且结构更加的清晰。





















 64
64











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








