简介
顺序访问聚集中的对象
实现
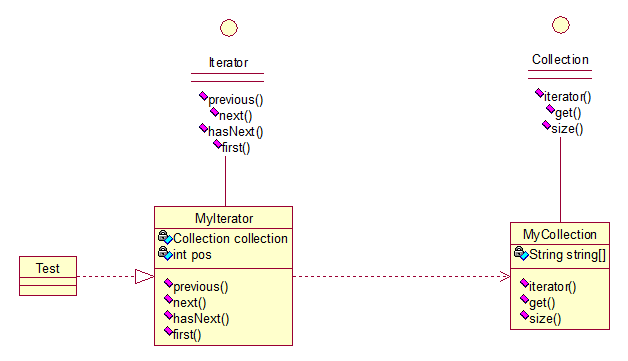
两个接口
public interface Collection {
public Iterator iterator();
/*取得集合元素*/
public Object get(int i);
/*取得集合大小*/
public int size();
} public interface Iterator {
//前移
public Object previous();
//后移
public Object next();
public boolean hasNext();
//取得第一个元素
public Object first();
} 两个实现:
public class MyCollection implements Collection {
public String string[] = {"A","B","C","D","E"};
@Override
public Iterator iterator() {
return new MyIterator(this);
}
@Override
public Object get(int i) {
return string[i];
}
@Override
public int size() {
return string.length;
}
} public class MyIterator implements Iterator {
private Collection collection;
private int pos = -1;
public MyIterator(Collection collection){
this.collection = collection;
}
@Override
public Object previous() {
if(pos > 0){
pos--;
}
return collection.get(pos);
}
@Override
public Object next() {
if(pos<collection.size()-1){
pos++;
}
return collection.get(pos);
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
if(pos<collection.size()-1){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
@Override
public Object first() {
pos = 0;
return collection.get(pos);
}
} 测试类:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection collection = new MyCollection();
Iterator it = collection.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
} 其他设计模式http://blog.csdn.net/qq_23370223/article/category/7193147






















 513
513

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








