1.用递归算法,删除带结点的单链表L中所有值为x的结点。
由于是带头结点的,所以并且查找值为x的结点时,从L->next的值开始判断,
如果L->next的data等于x,那么就要将L->next的值删除并且将L的后继结点换成L->next的后继结点,并且将它删除。
LNode *P = L->next ;
L->next=L->next->next;
free(P)
递归模型:
终止条件:
L->next == NULL
递归主体:
如果L->next->data= = x:
删除L->next结点,并执行L->next=L->next->next操作,继续执行下一个结点值判断。
如果L->next != x:
直接判断下一个结点。
LNode* delectList(LNode*L, int x)
{
if (L->next== NULL)
return L;
else
{
if (L->next->data==x)
{
LNode *P = L->next;
L ->next= L->next->next;
free(P);
delectList(L, x);
}
else
{
delectList(L->next, x);
}
}
}
2.在头结点的单链表,编写算法实现从尾到头反向输出每个结点的值。
第一种:
反向输出,可以头结点的后继结点开始,直到L->next=NULL,用头插法的方式将后面的结点插在头结点后面,然后在依次打印。
第二种:
栈是一种后进先出的结构,递归就是用栈的思想实现的。
void R_Print(LNode *L){
if (L->next != NULL)
{
R_Print(L->next);//递归
}
cout << L->data << endl;
}3.将带头结点的链表就地逆置(就地要求辅助空间复杂度为O(1))。
其实这几道题的思想都差不多,这道题就是将头结点取下然后将后续结点用头插法的方式插入,直到最后一个结点。
LNode* Reverse_L(LNode *L)
{
LNode *move = L->next;//移动指针,头结点后的一个结点开始
L->next = NULL;
LNode *r;
while (move != NULL)
{
r = move->next;//存放带插入的结点
move->next = L->next;//头插法的方式
L->next = move;
move = r;//移动工作结点
}
return L;
}4.将带头结点的链表删除最小值结点的高效算法(最小结点唯一)
思路:
第一步寻找最小值
第二步将最小值删除
在寻找最小值时用需要从头到尾一次比较,将最小值的前驱用指针保存。
删除时只需要将前驱的后继结点指向改变即可。
空间复杂度为O(1),时间复杂度为O(n)
LNode* deletemin(LNode *L)
{
LNode *move = L->next;//移动的工作结点
LNode *min = L;//保存最小值前驱的结点
while (move->next != NULL)
{
if (min->next->data > move->next->data)
{
min = move;
}
move = move->next;
}
LNode *s = min->next;//要删除的结点
min->next = min->next->next;//前驱结点的后继结点改变
free(s);
return L;
}
全部代码:
/*
Instruction:Linklist insertion
author:huangpingyi
date:2017/02/23
*/
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct LNode
{
int data;
LNode *next;
};
//尾插法
LNode* CreateListT(LNode *L, int x, int array[])
{
L->next = NULL;
LNode *q = L;
LNode *s;//插入的结点
int i = 0;
while (i < x)
{
s = new LNode;
s->data = array[i];
//以下三步是尾插法和头插法的区别
L->next = s;
s->next = NULL;
L = s;
i++;
}
return q;
}
//递归删除值为x的结点
LNode* delectList(LNode*L, int x)
{
if (L->next== NULL)
return L;
else
{
if (L->next->data==x)
{
LNode *P = L->next;
L ->next= L->next->next;
free(P);
delectList(L, x);
}
else
{
delectList(L->next, x);
}
}
}
//从头到尾反向输出结点
void R_Print(LNode *L){
if (L->next != NULL)
{
R_Print(L->next);//递归
}
cout << L->data << endl;
}
//就地逆置链表
LNode* Reverse_L(LNode *L)
{
LNode *move = L->next;//移动指针,头结点后的一个结点开始
L->next = NULL;
LNode *r;
while (move != NULL)
{
r = move->next;//存放带插入的结点
move->next = L->next;//头插法的方式
L->next = move;
move = r;//移动工作结点
}
return L;
}
//删除链表中最小值结点
LNode* deletemin(LNode *L)
{
LNode *move = L->next;//移动的工作结点
LNode *min = L;//保存最小值前驱的结点
while (move->next != NULL)
{
if (min->next->data > move->next->data)
{
min = move;
}
move = move->next;
}
LNode *s = min->next;//要删除的结点
min->next = min->next->next;//前驱结点的后继结点改变
free(s);
return L;
}
//打印结果
void Print(LNode *L)
{
L = L->next;//第一个是头结点
while (L != NULL)
{
cout << L->data << endl;
L = L->next;
}
}
int main(){
int x, array[10];
cout << "请输入插入个数:" << endl;
cin >> x;
cout << "输入需要插入的数据:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < x; i++)
{
cin >> array[i];
}
LNode* L = new LNode;
CreateListT(L, x, array);//d调用后为啥L不变
cout << "用尾插法创建链表的结果:" << endl;
Print(L);
int delect;
cout << "请输入需要删除的数" << endl;
cin >> delect;
delectList(L, delect);
cout << "用递归法删除x后结果" << endl;
Print(L);
cout << "从头到尾反向输出结果" << endl;
R_Print(L->next);
cout << "此时链表的顺序" << endl;
Print(L);
Reverse_L(L);
cout << "就地逆置后的结果:" << endl;
Print(L);
cout << "删除结点的最小值结果" << endl;
deletemin(L);
Print(L);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
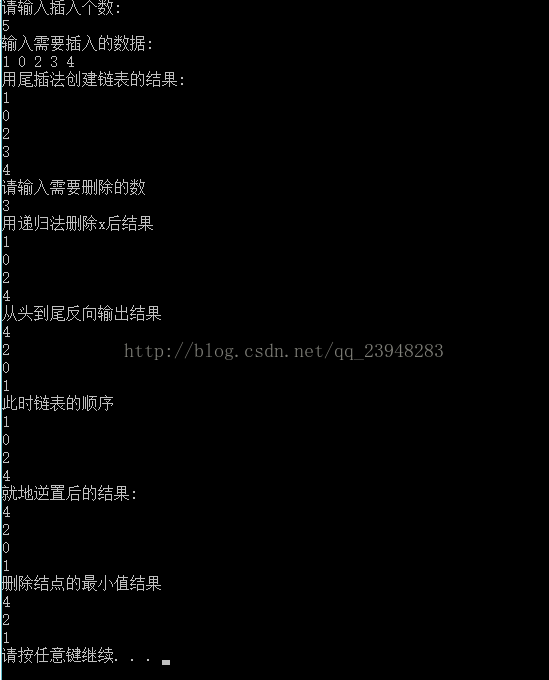
运行效果:





















 6665
6665











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








